1988 United States presidential election in West Virginia
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 County Results
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in West Virginia |
|---|
 |
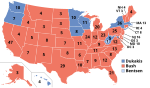
The 1988 United States presidential election in West Virginia took place on November 8, 1988. All 50 states and the District of Columbia were part of the 1988 United States presidential election. West Virginia voters chose six electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.
West Virginia was won by Massachusetts Governor Michael Dukakis who was running against incumbent United States Vice President George H. W. Bush of Texas. Dukakis ran with Texas Senator Lloyd Bentsen as Vice President, and Bush ran with Indiana Senator Dan Quayle.
West Virginia weighed in for this election as 13% more Democratic than the national average. To date this is also the last time the state voted for a losing Democratic presidential candidate.
The 1988 election cycle is also the last time that West Virginia did not vote for the same presidential candidate as neighboring Kentucky.
As of 2021, this is the last time West Virginia voted to the left of several modern day Democratic strongholds, namely Illinois, Maryland, New York, and Vermont.
Partisan background[]
The presidential election of 1988 was a very partisan election for West Virginia, with over 99% of the electorate voting for either the Republican or Democratic parties, and only three candidates appearing on the ballot.[1]
Republican national victory[]
Dukakis won the election in West Virginia with a 5-point margin. The relatively narrow election results in West Virginia are reflective of a nationwide reconsolidation of base for the Republican Party, which took place through the 1980s. Through the passage of some very controversial economic programs, spearheaded by then President Ronald Reagan (called, collectively, "Reaganomics"), the mid-to-late 1980s saw a period of economic growth and stability. The hallmark for Reaganomics was, in part, the wide-scale deregulation of corporate interests, and tax cuts for the wealthy.[2]
Dukakis ran his campaign on a socially liberal platform, and advocated for higher economic regulation and environmental protection. Bush, alternatively, ran on a campaign of continuing the social and economic policies of former President Reagan - which gained him much support with social conservatives and people living in rural areas. Additionally, while the economic programs passed under Reagan, and furthered under Bush, may have boosted the economy for a brief period, they are criticized by many analysts as "setting the stage" for economic troubles in the United States after 2007, such as the Great Recession.[3]
Faithless elector[]
A rare event in any United States presidential election, West Virginia was home to a faithless elector in the election of 1988. During the assembly of the electoral college, one elector from West Virginia, Margarette Leach, cast her vote for Democratic vice presidential nominee Lloyd Bentsen as president, and Dukakis as the vice president. She did this in order to draw attention to the lack of accountability for electors under the Electoral College system.[4]
Results[]
Statewide results[]
| 1988 United States presidential election in West Virginia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
| Democratic | Michael Dukakis | 341,016 | 52.20% | 5 | |
| Republican | George H. W. Bush | 310,065 | 47.46% | 0 | |
| New Alliance Party | Lenora Fulani | 2,230 | 0.34% | 0 | |
| Democratic | Lloyd Bentsen | 0 | 0.00% | 1 | |
| Totals | 653,311 | 100.00% | 6 | ||
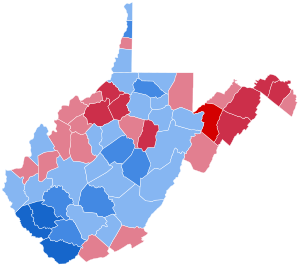
By county[]
| Michael Stanley Dukakis
Democratic |
George Herbert Walker Bush
Republican |
Various candidates
Other parties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County | % | # | % | # | % | # |
| Barbour | 51.4% | 3,221 | 48.2% | 3,023 | 0.2% | 17 |
| Berkeley | 36.8% | 6,313 | 62.8% | 10,761 | 0.4% | 61 |
| Boone | 70.0% | 6,539 | 29.8% | 2,786 | 0.2% | 20 |
| Braxton | 62.2% | 3,377 | 37.3% | 2,024 | 0.4% | 22 |
| Brooke | 60.7% | 6,258 | 38.8% | 4,006 | 0.4% | 42 |
| Cabell | 47.1% | 15,368 | 52.7% | 17,197 | 0.3% | 97 |
| Calhoun | 53.8% | 1,644 | 45.6% | 1,395 | 0.6% | 18 |
| Clay | 59.4% | 2,263 | 40.3% | 1,536 | 0.3% | 12 |
| Doddridge | 33.5% | 955 | 66.0% | 1,880 | 0.4% | 12 |
| Fayette | 67.9% | 11,009 | 31.7% | 5,143 | 0.3% | 53 |
| Gilmer | 54.2% | 1,661 | 45.2% | 1,387 | 0.5% | 16 |
| Grant | 21.6% | 893 | 77.9% | 3,215 | 0.5% | 22 |
| Greenbrier | 52.9% | 6,091 | 46.8% | 5,395 | 0.3% | 35 |
| Hampshire | 38.9% | 2,085 | 60.7% | 3,253 | 0.5% | 25 |
| Hancock | 58.3% | 8,338 | 41.1% | 5,882 | 0.4% | 60 |
| Hardy | 39.4% | 1,689 | 60.2% | 2,581 | 0.4% | 18 |
| Harrison | 55.9% | 17,005 | 43.9% | 13,364 | 0.1% | 49 |
| Jackson | 44.4% | 4,573 | 55.4% | 5,696 | 0.2% | 22 |
| Jefferson | 44.6% | 4,334 | 55.0% | 5,349 | 0.4% | 43 |
| Kanawha | 51.7% | 41,144 | 48.0% | 38,140 | 0.3% | 258 |
| Lewis | 47.3% | 3,272 | 52.1% | 3,602 | 0.4% | 34 |
| Lincoln | 59.2% | 5,049 | 40.5% | 3,457 | 0.3% | 23 |
| Logan | 72.5% | 11,317 | 27.2% | 4,244 | 0.3% | 47 |
| Marion | 60.8% | 14,441 | 38.8% | 9,229 | 0.3% | 72 |
| Marshall | 53.4% | 7,903 | 45.9% | 6,793 | 0.5% | 83 |
| Mason | 50.5% | 5,468 | 49.3% | 5,332 | 0.2% | 25 |
| McDowell | 74.2% | 7,204 | 25.4% | 2,463 | 0.5% | 47 |
| Mercer | 49.7% | 10,152 | 50.0% | 10,221 | 0.3% | 57 |
| Mineral | 40.1% | 4,059 | 59.5% | 6,015 | 0.4% | 37 |
| Mingo | 71.8% | 7,429 | 28.0% | 2,896 | 0.2% | 25 |
| Monongalia | 53.8% | 14,178 | 45.9% | 12,091 | 0.2% | 69 |
| Monroe | 47.0% | 2,427 | 52.6% | 2,719 | 0.4% | 22 |
| Morgan | 33.9% | 1,545 | 65.8% | 3,002 | 0.4% | 17 |
| Nicholas | 57.9% | 5,173 | 41.8% | 3,731 | 0.4% | 32 |
| Ohio | 49.1% | 10,121 | 50.2% | 10,341 | 0.5% | 116 |
| Pendleton | 45.5% | 1,595 | 54.3% | 1,901 | 0.2% | 7 |
| Pleasants | 44.6% | 1,421 | 55.3% | 1,761 | 0.2% | 5 |
| Pocahontas | 50.8% | 1,958 | 48.7% | 1,876 | 0.5% | 18 |
| Preston | 42.7% | 4,357 | 56.9% | 5,804 | 0.3% | 35 |
| Putnam | 44.7% | 6,640 | 55.0% | 8,163 | 0.3% | 38 |
| Raleigh | 57.7% | 14,302 | 42.0% | 10,395 | 0.3% | 85 |
| Randolph | 52.2% | 5,233 | 47.3% | 4,746 | 0.3% | 38 |
| Ritchie | 33.3% | 1,446 | 66.2% | 2,874 | 0.4% | 18 |
| Roane | 45.9% | 2,447 | 53.7% | 2,861 | 0.5% | 24 |
| Summers | 57.8% | 3,072 | 42.0% | 2,231 | 0.2% | 11 |
| Taylor | 50.0% | 2,852 | 49.4% | 2,816 | 0.4% | 26 |
| Tucker | 52.2% | 1,869 | 47.5% | 1,699 | 0.2% | 9 |
| Tyler | 38.8% | 1,501 | 61.1% | 2,365 | 0.2% | 8 |
| Upshur | 38.8% | 3,065 | 60.9% | 4,813 | 0.2% | 16 |
| Wayne | 54.7% | 8,621 | 45.2% | 7,123 | 0.2% | 31 |
| Webster | 67.9% | 2,185 | 31.5% | 1,016 | 0.2% | 16 |
| Wetzel | 53.4% | 3,928 | 46.0% | 3,381 | 0.5% | 41 |
| Wirt | 45.0% | 929 | 54.5% | 1,125 | 0.6% | 12 |
| Wood | 39.8% | 12,959 | 59.7% | 19,450 | 0.5% | 154 |
| Wyoming | 63.4% | 6,138 | 36.3% | 3,516 | 0.3% | 30 |
See also[]
- Presidency of George H. W. Bush
Notes[]
- ^ A faithless Democratic elector voted for Bentsen for president and Dukakis for vice president
References[]
- ^ "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2013-07-21.
- ^ "Since 1980s, the Kindest of Tax Cuts for the Rich". The New York Times. 2012-01-18. Retrieved 2013-07-21.
- ^ Jerry Lanson (2008-11-06). "A historic victory. A changed nation. Now, can Obama deliver?". Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2013-07-21.
- ^ "James A. Michener, Near-Faithless Elector". Slate. 2000-11-09. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
- 1988 United States presidential election by state
- United States presidential elections in West Virginia
- 1988 West Virginia elections