Department of Space
| Antarikṣ Vibhāg | |
 Emblem of India | |
| Department overview | |
|---|---|
| Jurisdiction | Government of India |
| Headquarters | Antariksh Bhavan, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India |
| Annual budget | ₹13,949 crore (US$2.0 billion) (2021–22 est.)[1] |
| Ministers responsible |
|
| Department executive |
|
| Child agencies |
|
| Website | www |
The Department of Space (DoS) (ISO 15919: Antarikṣ Vibhāg or Antrikṣ Vibhāg) is an Indian government department responsible for administration of the Indian space program. It manages several agencies and institutes related to space exploration and space technologies. The Indian space program under the DoS aims to promote the development and application of space science and technology for the socio-economic benefit of the country. It includes two major satellite systems, INSAT for communication, television broadcasting and meteorological services, and Indian Remote Sensing Satellites (IRS) system for resources monitoring and management. It has also developed two satellite launch vehicles Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) to place IRS and INSAT class satellites in orbit.
History[]
In 1961, the Government of India and Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru entrusted the responsibility for space research and for the peaceful use of outer space to the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), then under the leadership of Dr. Homi J. Bhabha. In 1962, the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) set up Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR), with Dr. Vikram Sarabhai as chairman, to organise a national space programme.
In 1969, INCOSPAR was reconstituted as an advisory body under the India National Science Academy (INSA) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) was established. The Government of India constituted the Space Commission and established the Department of Space (DoS) in 1972 and brought ISRO under DoS management on 1 June 1972.
Kailasavadivoo Sivan is the current Secretary (Space) and ex-officio chairman of Indian Space Research Organisation and Space Commission. Vanditha Sharma is the additional secretary of the department.[3]
Agencies and institutes[]
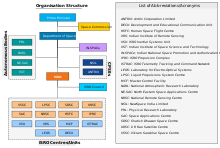

The Department of Space manages the following agencies and institutes:[4]
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) – The primary research and development arm of the DoS.
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram.
- Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), Thiruvananthapuram.
- Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC-SHAR), Sriharikota.
- ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC), Bangalore.
- Space Applications Centre (SAC), Ahmedabad.
- National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), Hyderabad.
- ISRO Inertial Systems Unit (IISU), Thiruvananthapuram.
- Development and Educational Communication Unit (DECU), Ahmedabad.
- Master Control Facility (MCF), Hassan.
- ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bangalore.
- Laboratory for Electro-Optics Systems (LEOS), Bangalore.
- Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS), Dehradun.
- Antrix Corporation – The marketing arm of ISRO.
- Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad.
- National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL), Gadanki.
- North-Eastern Space Applications Centre[5] (NE-SAC), Umiam.
- Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL), Mohali.
- Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), Thiruvananthapuram – India's space university.
- New Space India Limited (NSIL), Bangalore.
- Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN–SPACe)[6][7]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Union Budget 2021: Dept of Space allocated Rs 13,949 cr in budget, Rs 4,449 cr more than last fiscal". The Financial Express. 1 February 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ "Chairman ISRO, Secretary DOS". Department of Space, Government of India. Retrieved 23 January 2018.
- ^ "Space Commission". Department of Space.
- ^ "DoS structure". Department of Space, Government of India. Archived from the original on 27 September 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ^ "NEC – North Eastern Council". Necouncil.nic.in. Archived from the original on 25 February 2012. Retrieved 8 February 2013.
- ^ "Historic space reforms by DoS, ISRO set in motion to empower private space sector, academia- Technology News, Firstpost". Tech2. 25 June 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ "In a first, Centre approves setting up a new space board". Livemint. 24 June 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
External links[]
- Ministry of Science and Technology (India)
- Space programme of India
- 1972 establishments in Delhi
- Government agencies established in 1972
