FasTrak


FasTrak is the electronic toll collection (ETC) system used in the state of California in the United States. The system is used statewide on all of the toll roads, toll bridges, and high-occupancy toll lanes along the California Freeway and Expressway System.
As with other ETC systems, FasTrak is designed to eliminate the need for cars to stop to pay at toll booths, thus decreasing the traffic congestion traditionally associated with toll roads. Its use of technology to improve transit is in line with the U.S. Department of Transportation's Intelligent Transportation Systems initiative.
Under California's government structure, the state's toll facilities are operated by various agencies and special-purpose districts. Concerned that they would each introduce different, incompatible ETC systems, the California State Legislature passed Senate Bill 1523 in 1990, requiring the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) to develop a statewide specification that all these toll agencies were required to meet.[1] Three years later, Transportation Corridor Agencies opened the Foothill Toll Road in Orange County, implementing the statewide ETC system for the first time, and naming it FasTrak. The state continues to delegate the responsibility of selling and maintaining FasTrak accounts to the different toll agencies.
Operations and functionality[]
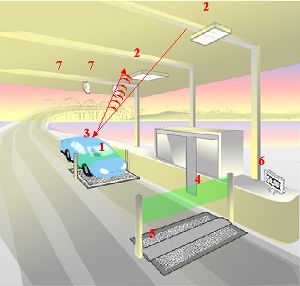
Under California law, the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) was given the mandate to develop and maintain an open, statewide ETC specification. This specification is known in the transportation industry as "Title 21" after it was added to Title 21 of the California Code of Regulations. FasTrak uses RFID technology near 915 MHz to read data from a transponder placed in a vehicle (usually mounted by Velcro strips to the windshield) moving at speeds that may exceed 70 mph (112 km/h). The RFID transponder in each vehicle is associated with a prepaid debit account; each time the vehicle passes underneath a toll collection site, the account is debited to pay the toll.
Currently, FasTrak transponders are not compatible with E-ZPass and other ETC systems used in other states because they use a different specification than Title 21. If a vehicle does not have a transponder, or if a transponder is not detected at the toll plaza, a violation enforcement system triggers cameras that capture photos of the vehicle and its license plate for processing. If the license plate is registered as belonging to a FasTrak user, the account is debited only the toll charge, and no penalty is charged. This is a backup in case a transponder fails to read. Otherwise, a toll violation notice is sent to the registered owner of the vehicle.[2] In the case of drivers whose vehicles are company owned or leased, as long as the vehicle license plates are properly listed, the violations will be sent to the registered owner and not the employee driver. It is for this reason that the License Agreement mandates that customers list all vehicles, including motorcycles, motor homes, and trailers of all types on their accounts so that when transponders fail to read the toll can be debited based upon the vehicle's license plate. A license plate may be listed only on one account.
A toll collected based on a license plate is called an Image Toll and can be identified on the customer statement by noticing the license plate number listed instead of the transponder number. If one fails to correctly list license plates on their account, the FasTrak customer will receive toll violation notices as if they were another driver. If a FasTrak customer receives a toll violation notice under these circumstances, they only refer to the reverse side of the Toll Violation notice and complete the section at the bottom of the notice that will add the new vehicle to their account. Conversely, a license plate should be removed from an account after a change in ownership, otherwise resulting in paying for another driver's tolls via the Image Toll process.
Service center operations[]
Each toll agency in Southern California has their own billing and customer service center. For convenience, all toll facilities in the San Francisco Bay Area instead share the same billing and customer service center. Although anybody with a FasTrak transponder can use it to pay tolls on any California toll facility using the system, people are encouraged to open their accounts with the local agency in charge of the one that they use the most. Each center establishes its own fee and discount structures, and people may be charged a fee if the majority of their FasTrak use occurs elsewhere.
Fees[]
Each FasTrak account agency has its own monthly minimums / monthly fees (from lowest to highest)
| Agency | Area | Fee(s) |
|---|---|---|
| San Francisco Bay Area | None[3] | |
| The Toll Roads of Orange County | Orange County | None[4] |
| Metro ExpressLanes | Los Angeles County | $1 monthly account maintenance fee.[5] |
| Interstate 15 Express Lanes | San Diego County | $3.50 minimum monthly toll, plus $1 per transponder.[6] |
| South Bay Expressway | San Diego County | $3.50 minimum monthly toll, plus $1 per transponder.[7] |
| 91 Express Lanes | Orange and Riverside Counties | Account dependent, with plans ranging from a $75 one-time fee with no monthly fees, to a $7 minimum monthly toll.[8] |
| Riverside Express | Riverside County | $40.00 initial prepaid toll deposit, plus $2 monthly account maintenance fee.[9] |
Security[]

A teardown analysis of the transponder and analysis of its security issues was published at Black Hat 2008.[10] They are updated remotely, and do not use encryption.[11] Furthermore, FasTrak's basic functionality and specifications are listed under Title 21, Division 2, Chapter 16 of the California Code of Regulations, and are thus freely accessible to the general public.[12]
FasTrak units are used to generate 5-1-1 traffic data, using sensors and antennae placed across various freeways.[11]
History[]
As the first ETC system in North America was installed on the Dallas North Tollway in 1989, many California toll facilities started to express interest in the technology. Because the state's toll roads and bridges are run by different government agencies, there was the possibility that a number of different incompatible ETC systems would be instituted throughout California. Therefore, the California State Legislature passed Senate Bill 1523 in 1990, requiring Caltrans, the state's Department of Transportation, to develop a statewide technical specification which all systems would be required to meet.[1] As a result, California was the first in the nation to require all of its toll bridges and roads to use the same ETC system.[13] This technical specification was later codified in Title 21, Division 2, Chapter 16 of the California Code of Regulations.[12]
When the Foothill Toll Road in Orange County opened in 1993, it became the first California toll facility to use an ETC system. Transportation Corridor Agencies (TCA), the local agency in charge of the toll road, named the system "FasTrak".[14] To this day, TCA still holds the trademark to the "FasTrak" name and logo.[15]
When TCA first introduced the FasTrak system, the electronic transponders consisted of a gadget about the size of a Walkman in which a smart card was inserted.[16] However, the smart cards were unpopular with both tollway officials and users because they cost more, offered little advantage, and customers were charged with a $10 annual fee (which has since been discontinued).[17] By the time the 91 Express Lanes opened in 1995, the FasTrak transponders were redesigned to be the size of a coaster that could be mounted by Velcro strips to the windshield.[18]

TCA later deployed the FasTrak system to the two other toll roads they administer as soon as they opened: the San Joaquin Hills Toll Road in 1996 and the Eastern Toll Road in 1998. Also in 1998, the system was then deployed on the high-occupancy toll (HOT) lanes along Interstate 15 in San Diego.

However, the system had to be modified so that it could be used on California's toll bridges. After a test run on the Carquinez Bridge in 1996, it had accuracy problems in dealing with the 18 different toll classifications for different kinds of trucks.[19] After the changes were made and another test run, the Carquinez Bridge became the first California toll bridge to use FasTrak in 1997. However, bureaucratic inaction, technical difficulties, and financial mismanagement delayed the deployment of the system to the other six state-run toll bridges in the San Francisco Bay Area until October 2000.[20] Meanwhile, the Golden Gate Bridge, run by the independent Golden Gate Bridge, Highway and Transportation District, installed their system a few months earlier in July of that year. The FasTrak system was also briefly used on the state-owned San Diego-Coronado Bridge until tolls were discontinued on that structure in 2002. The Bay Area FasTrak Customer Center then opened in 2005, merging the service center for the state's Bay Area bridges with the one that was being operated separately by the Golden Gate Bridge District.[21]
Since then, several other new toll facilities around California have either opened, are under construction, or are in the planning stages. They are all required to accept FasTrak as per the aforementioned state law.
In 2009, San Francisco International Airport began accepting FasTrak in all of its parking garages, including long-term parking.[22] Currently only FasTrak accounts opened from either the Bay Area FasTrak Customer Center or from Transportation Corridor Agencies can be used at the airport.[23]

When the Metro ExpressLanes opened in Los Angeles in late 2012, it introduced FasTrak transponders with a special switch that indicates the number of occupants (1, 2, or 3 or more) in the vehicle. This enables the open road tolling system to automatically compute the carpool or solo driver toll,[24] as well as allow the California Highway Patrol to visually check to see if there are more or fewer people in the car than indicated on the transponder.[25] For the convenience of their FasTrak customers in the Greater Los Angeles urban area who may also use the Metro ExpressLanes, TCA began offering switchable transponders in 2013,[26] and the 91 Express Lanes followed suit by 2015.[27] With the switchable transponders, the violation rate on the Metro ExpressLanes fell to 10 percent from the 20 to 25 percent cheating rate in toll lanes that do not require transponders for carpoolers, prompting Alameda County officials to include the system on the then-planned I-580 Express Lanes.[28] The Bay Area FasTrak Customer Center then started to offer switchable transponders, under the name "FasTrak Flex", in summer 2015.[29] In other HOT lane facilities, drivers "declare" that they are a carpool (and thus do not have to pay a toll) by covering their FasTrak transponder in a mylar bag.[29]
There has been a push to strictly use open road tolling, accepting only payments via a FasTrak transponder, a toll-by-plate account, or one-time payments via online or by phone instead of cash. All of California's HOT lanes only use open road tolling. The Golden Gate Bridge began requiring electronic payments for all tolls in March 2013,[30] and all the Orange County toll roads run by TCA likewise did the same in May 2014.[31] A plan to also eliminate toll takers on all seven of the state-owned bridges was approved in 2019.[32] On March 20, 2020, at midnight, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, all-electronic tolling was temporarily placed in effect for those seven state-owned toll bridges, and as of December 10, 2020, all of them are now permanently cashless.[33] The only toll facility that still accepts cash is the South Bay Expressway in San Diego County, but it uses unstaffed toll booths with cash machines that require exact change.[34]
Under MAP-21, passed by the Federal government in 2012, all ETC facilities in the United States must reach some form of interoperability by October 1, 2016. In response, the California State Legislature passed Assembly Bill 493 in 2013, authorizing Caltrans and the state's various toll agencies to help develop compatible systems.[35] However, the deadline, which had neither penalty nor funding attached, was not met. California regulators later approved a phase-in of transponder technology using the ISO/IEC 18000-63 (6C) standard, released in 2004, which began in 2018 and is expected to end in 2024. This would allow compatibility with systems used in nearby states of Washington, Colorado, and Utah; and also Kentucky, Indiana, Georgia, North Carolina, and Louisiana, plus NationalPass.[36]
In 2019, TCA introduced a sticker transponder to replace the former plastic transponder.[37][38][39] The sticker transponder is similar to the eGo Plus toll sticker introduced by TxTag in 2005, SunPass Mini toll sticker introduced by SunPass in 2008, and the sticker tag introduced by MnPASS in 2015.
Toll facilities using FasTrak[]
Current[]
HOV 2+ indicates that carpools require two or more persons.
HOV 3+ indicates that carpools require three or more persons.
† indicates that two-person carpools are tolled differently than those with three or more.
Planned or proposed facilities[]
The following is a partial list of toll facilities that are either in the planning or proposal stages:
| Name | Highway(s) | Location | From | To | Direction tolled | Scheduled to open |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-5 Express Lanes (North County Corridor Project) |
San Diego County | La Jolla Village Drive in San Diego | Harbor Drive in Oceanside | Both directions | 2021-2035[59] | |
| US 101 Express Lanes (Silicon Valley Express Lanes Project & San Mateo County Express Lanes Project) |
Santa Clara and San Mateo Counties | Dunne Avenue in Morgan Hill | 2022 (north of SR 237)[60][61] 2024-2035 (south of SR 237) | |||
| SR 85 Express Lanes (Silicon Valley Express Lanes Project) |
Santa Clara County | 2022 (north of SR 82/SR 237)[60] | ||||
| I-405 Express Lanes (San Diego Freeway Improvement Project) |
Orange County | Both directions | 2023[62] | |||
| I-80 Express Lanes | Solano County | Red Top Road in Fairfield | 2021-2026[63] | |||
| I-10 Express Lanes Phase 1 (San Bernardino Express Lanes Project) |
San Bernardino County | 2023[64] | ||||
| I-105 Express Lanes | Los Angeles County | Studebaker Rd in Norwalk | 2025[65] | |||
| I-405 Express Lanes (Sepulveda Pass Express Lanes Project) |
Los Angeles County | 2028[66] | ||||
| East Otay Mesa Port of Entry Freeway | San Diego County | Otay Mesa East Port of Entry | Unknown, pending at least the completion of the proposed Otay Mesa East Port of Entry.[67] | |||
| Foothill-South | Orange and San Diego counties | Oso Parkway near Rancho Santa Margarita | Unknown. The project has been opposed by conservationists and environmental groups.[68] |
References[]
- ^ a b Halloran, James V., III (September 1992). "Standardizing Electronic Toll Collection". Reason Foundation. Archived from the original on May 27, 2006. Retrieved April 27, 2006.
- ^ FasTrak. "Popular FAQs". FasTrak.
- ^ "FAQ: General Information". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved February 26, 2019.
- ^ "Are there any monthly fees associated with having a FasTrak account?". thetollroads.com. Transportation Corridor Agencies. Retrieved July 1, 2019.
- ^ "FAQ". Metro ExpressLanes. Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved February 26, 2019.
- ^ "Get FasTrak". 511sd.com. San Diego Association of Governments. Retrieved February 26, 2019.
- ^ "FAQ". South Bay Expressway. Retrieved February 26, 2019.
- ^ "Getting Started". The 91 Express Lanes. Retrieved February 26, 2019.
- ^ a b "Information". Riverside Express. Retrieved April 15, 2021.
- ^ Lawson, Nate (August 6, 2008). "Highway to Hell: Hacking Toll Systems" (PDF). BlackHat USA. Root Labs.
- ^ a b Lawson, Nate (August 7, 2008). "FasTrak Talk Summary and Slides". Root Labs Rdist.
- ^ a b California Department of Transportation Division of Traffic Operations (2013). "Title 21 Support". California Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on December 30, 2013. Retrieved December 29, 2013.
- ^ Hallissy, Erin (February 20, 1996). "Bay Area Bridges to Offer Electronic Tolls". San Francisco Chronicle. p. A1. Retrieved April 27, 2006.
- ^ Downey, Cheryl (October 4, 1993). "Tollway Officials Must Sell the Public on New Product". Orange County Register. p. A4.
- ^ Transportation Corridor Agencies (April 13, 2006). "Pilot Program Puts TCA FasTrak on Costco Shelves" (Press release). Transportation Corridor Agencies. Archived from the original on May 10, 2006. Retrieved April 27, 2006.
- ^ Downey, Cheryl (August 13, 1993). "Toll Tech: 4 Ways to Pay: Transportation: Video Enforcement Will Capture License Plates When Drivers Don't Pay on Foothill Toll Road". Orange County Register. p. B4.
- ^ Downey, Cheryl (July 29, 1994). "County Tollway Officials Are Having Second Thoughts About Expensive Toll-Paying 'Smart Cards'". Orange County Register. p. C4.
- ^ Pund, Ernest E. (December 24, 1995). "Highway 91 About to Take Its First Toll". The Press-Enterprise. Riverside, CA. p. A1.
- ^ Nolte, Carl (September 23, 1996). "Automatic Tollbooth Technology Not Yet Ready for Prime Time". San Francisco Chronicle. p. A15. Retrieved April 27, 2006.
- ^ Cabanatuan, Michael (October 5, 2000). "All Bay Toll Spans Finally Going FasTrak". San Francisco Chronicle. p. A1. Retrieved April 27, 2006.
- ^ Golden Gate Bridge, Highway and Transportation District (June 7, 2005). "June 7th Marks Grand Opening of New Regional FasTrak Customer Service Center in San Francisco" (Press release). Golden Gate Bridge, Highway and Transportation District. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ McCarron, Michael C. (May 15, 2009). "Easy Payment System Will Save Time and Help Reduce Emissions" (Press release). San Francisco International Airport. Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved July 4, 2009.
- ^ Bay Area FasTrak Customer Service Center. "FasTrak FAQs". Bay Area FasTrak Customer Service Center. Archived from the original on April 14, 2014. Retrieved April 23, 2014.
Bay Area FasTrak customers and The Toll Roads customers are both eligible to use FasTrak at SFO ... Customers of Orange County's 91 Express Lanes, and San Diego's I-15 and South Bay Expressway, currently are not eligible to pay for parking at SFO.
- ^ Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. "Metro ExpressLanes FAQ". Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved July 6, 2012.
- ^ Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (July 24, 2012). Metro ExpressLanes: Rules of the Road (Video). Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. 2 minutes in – via YouTube.
- ^ Transportation Corridor Agencies (September 23, 2013). "TCA Switchable Transponders Now Available". The Toll Roads Blog. Transportation Corridor Agencies. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Orange County Transportation Authority (Spring 2015). "A Tale of Two Transponders: Standard and Switchable" (PDF). 91 Express Lanes Newsletter. Orange County Transportation Authority. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Richards, Gary (July 11, 2014). "Bay Area Carpoolers Must Use FasTrak in Express Lanes Under New Law". San Jose Mercury News. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ a b Richards, Gary (February 18, 2015). "Roadshow: Who Needs the New FasTrak Device (and a Mylar Bag)". San Jose Mercury News. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- ^ Golden Gate Bridge, Highway and Transportation District. "All Electronic Tolling at the Golden Gate Bridge". Golden Gate Bridge, Highway and Transportation District. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- ^ Transportation Corridor Agencies. "All Electronic Tolling (AET)". Transportation Corridor Agencies. Archived from the original on October 16, 2012. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- ^ Smith, Darrell (September 7, 2019). "Do you drive to the Bay Area? A big change is coming to toll booths at the bridges". The Sacramento Bee. Retrieved April 12, 2020.
- ^ "Cash Toll Collection Suspended at Bay Area Bridges". Metropolitan Transportation Commission. March 20, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
- ^ San Diego Association of Governments. "Cash or Credit Payment". South Bay Expressway. San Diego Association of Governments. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- ^ California Legislature (August 12, 2013). "An Act to Amend Section 27565 of the Streets and Highways Code, Relating to Transportation". California Legislative Information. Retrieved December 29, 2013.
- ^ California approves 6C electronic toll collection protocol
- ^ "Sticker". Transportation Corridor Agencies. Retrieved July 1, 2019.
- ^ "FasTrak Replaces Hard-Case Transponders With Free Stickers For OC Drivers, Eliminates Fee". CBS Los Angeles. June 28, 2019.
- ^ Park, Jeong (June 7, 2019). "70¢ FasTrak stickers will replace $20 transponders, and TCA is mailing 15,000 of them daily". Orange County Register.
- ^ "Antioch Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Benicia–Martinez Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Carquinez Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Dumbarton Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Golden Gate Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Richmond–San Rafael Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "San Mateo–Hayward Bridge Bridge". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Map and Rates". thetollroads.com. Transportation Corridor Agencies. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "South Bay Expressway Toll Schedule" (PDF). South Bay Expressway. June 12, 2012. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "FAQ". The 91 Express Lanes. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Toll Schedules". The 91 Express Lanes. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Accessing the I-15 Express Lanes". 511sd.com. San Diego Association of Governments. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "I-580 Express Lanes". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "I-880 Express Lanes". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "I-680 Sunol Express Lanes". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "I-680 Contra Costa Express Lanes". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ "SR 237 Express Lanes". Bay Area FasTrak. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "Using Metro ExpressLanes". Metro ExpressLanes. Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ "I-5 Express Lanes Project". TransNet (San Diego Association of Governments). Retrieved February 26, 2019.
Later phases (2020-2035) will upgrade the carpool lanes to Express Lanes
- ^ a b Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. "State Route 85 and US 101 Express Lanes Projects". Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. Retrieved June 17, 2015.
- ^ Caltrans. "SM 101 Express Lanes Project". Caltrans. Retrieved August 8, 2019.
- ^ Orange County Transportation Authority. "San Diego Freeway (I-405) Improvement Project". Orange County Transportation Authority. Retrieved June 17, 2015.
- ^ "I-80 Solano County". Metropolitan Transportation Commission. May 13, 2016. Retrieved October 5, 2020.
- ^ "SBCTA Website".
- ^ "I-105 ExpressLanes Project" (PDF). California Transportation Commission. October 9, 2019. Retrieved May 29, 2020.
- ^ "I-405 Sepulveda Pass ExpressLanes Project". Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "State Route 11 Transport Concept Summary" (PDF). Caltrans District 11. Retrieved February 26, 2019.
- ^ Osborne, Thomas J. (2017). Coastal Sage: Peter Douglas and the Fight to Save California's Shore. University of California Press. pp. 135–138. ISBN 9780520283084.
External links[]
FasTrak account agencies
- Bay Area FasTrak Customer Service Center—handles accounts for all toll facilities in the San Francisco Bay Area
- SANDAG: Interstate 15 Express Lanes
- 91 Express Lanes
- Transportation Corridor Agencies—administers the Orange County toll roads
- South Bay Expressway
- Metro ExpressLanes
- Riverside Express—administers the Riverside County Transportation Commission's Express Lanes
Other links
- Golden Gate Bridge official web site
- Alameda County Express Lanes—information on the I-680 and I-580 HOT lanes in Alameda County
- Silicon Valley Express Lanes—information on the HOT projects in the Silicon Valley
- Electronic toll collection
- Road transportation in California