Geothermal power

| Part of a series on |
| Sustainable energy |
|---|
 |
|
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 26 countries,[1][2] while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries.[3]
As of 2019, worldwide geothermal power capacity amounts to 15.4 gigawatts (GW), of which 23.86 percent or 3.68 GW are installed in the United States.[4] International markets grew at an average annual rate of 5 percent over the three years to 2015, and global geothermal power capacity is expected to reach 14.5–17.6 GW by 2020.[5] Based on current geologic knowledge and technology the GEA publicly discloses, the Geothermal Energy Association (GEA) estimates that only 6.9 percent of total global potential has been tapped so far, while the IPCC reported geothermal power potential to be in the range of 35 GW to 2 TW.[3] Countries generating more than 15 percent of their electricity from geothermal sources include El Salvador, Kenya, the Philippines, Iceland, New Zealand,[6] and Costa Rica.
Geothermal power is considered to be a sustainable, renewable source of energy because the heat extraction is small compared with the Earth's heat content.[7] The greenhouse gas emissions of geothermal electric stations are on average 45 grams of carbon dioxide per kilowatt-hour of electricity, or less than 5 percent of that of conventional coal-fired plants.[8]
As a source of renewable energy for both power and heating, geothermal has the potential to meet 3-5% of global demand by 2050. With economic incentives, it is estimated that by 2100 it will be possible to meet 10% of global demand.[6]
History and development[]
In the 20th century, demand for electricity led to the consideration of geothermal power as a generating source. Prince Piero Ginori Conti tested the first geothermal power generator on 4 July 1904 in Larderello, Italy. It successfully lit four light bulbs.[9] Later, in 1911, the world's first commercial geothermal power station was built there. Experimental generators were built in Beppu, Japan and the Geysers, California, in the 1920s, but Italy was the world's only industrial producer of geothermal electricity until 1958.

In 1958, New Zealand became the second major industrial producer of geothermal electricity when its Wairakei station was commissioned. Wairakei was the first station to use flash steam technology.[11] Over the past 60 years, net fluid production has been in excess of 2.5 km3. Subsidence at Wairakei-Tauhara has been an issue in a number of formal hearings related to environmental consents for expanded development of the system as a source of renewable energy.[6]
In 1960, Pacific Gas and Electric began operation of the first successful geothermal electric power station in the United States at The Geysers in California.[12] The original turbine lasted for more than 30 years and produced 11 MW net power.[13]
The binary cycle power station was first demonstrated in 1967 in the Soviet Union and later introduced to the United States in 1981,[12] following the 1970s energy crisis and significant changes in regulatory policies. This technology allows the use of much lower temperature resources than were previously recoverable. In 2006, a binary cycle station in Chena Hot Springs, Alaska, came on-line, producing electricity from a record low fluid temperature of 57 °C (135 °F).[14]
Geothermal electric stations have until recently been built exclusively where high-temperature geothermal resources are available near the surface. The development of binary cycle power plants and improvements in drilling and extraction technology may enable enhanced geothermal systems over a much greater geographical range.[15] Demonstration projects are operational in Landau-Pfalz, Germany, and Soultz-sous-Forêts, France, while an earlier effort in Basel, Switzerland was shut down after it triggered earthquakes. Other demonstration projects are under construction in Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America.[16]
The thermal efficiency of geothermal electric stations is low, around 7–10%,[17] because geothermal fluids are at a low temperature compared with steam from boilers. By the laws of thermodynamics this low temperature limits the efficiency of heat engines in extracting useful energy during the generation of electricity. Exhaust heat is wasted, unless it can be used directly and locally, for example in greenhouses, timber mills, and district heating. The efficiency of the system does not affect operational costs as it would for a coal or other fossil fuel plant, but it does factor into the viability of the station. In order to produce more energy than the pumps consume, electricity generation requires high-temperature geothermal fields and specialized heat cycles.[citation needed] Because geothermal power does not rely on variable sources of energy, unlike, for example, wind or solar, its capacity factor can be quite large – up to 96% has been demonstrated.[18] However the global average capacity factor was 74.5% in 2008, according to the IPCC.[19]
Resources[]

The Earth's heat content is about 1×1019 TJ (2.8×1015 TWh).[3] This heat naturally flows to the surface by conduction at a rate of 44.2 TW[20] and is replenished by radioactive decay at a rate of 30 TW.[7] These power rates are more than double humanity's current energy consumption from primary sources, but most of this power is too diffuse (approximately 0.1 W/m2 on average) to be recoverable. The Earth's crust effectively acts as a thick insulating blanket which must be pierced by fluid conduits (of magma, water or other) to release the heat underneath.
Electricity generation requires high-temperature resources that can only come from deep underground. The heat must be carried to the surface by fluid circulation, either through magma conduits, hot springs, hydrothermal circulation, oil wells, drilled water wells, or a combination of these. This circulation sometimes exists naturally where the crust is thin: magma conduits bring heat close to the surface, and hot springs bring the heat to the surface. If no hot spring is available, a well must be drilled into a hot aquifer. Away from tectonic plate boundaries the geothermal gradient is 25–30 °C per kilometre (km) of depth in most of the world, so wells would have to be several kilometres deep to permit electricity generation.[3] The quantity and quality of recoverable resources improves with drilling depth and proximity to tectonic plate boundaries.
In ground that is hot but dry, or where water pressure is inadequate, injected fluid can stimulate production. Developers bore two holes into a candidate site, and fracture the rock between them with explosives or high-pressure water. Then they pump water or liquefied carbon dioxide down one borehole, and it comes up the other borehole as a gas.[15] This approach is called hot dry rock geothermal energy in Europe, or enhanced geothermal systems in North America. Much greater potential may be available from this approach than from conventional tapping of natural aquifers.[15]
Estimates of the electricity generating potential of geothermal energy vary from 35 to 2000 GW depending on the scale of investments.[3] This does not include non-electric heat recovered by co-generation, geothermal heat pumps and other direct use. A 2006 report by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) that included the potential of enhanced geothermal systems estimated that investing US$1 billion in research and development over 15 years would allow the creation of 100 GW of electrical generating capacity by 2050 in the United States alone.[15] The MIT report estimated that over 200×109 TJ (200 ZJ; 5.6×107 TWh) would be extractable, with the potential to increase this to over 2,000 ZJ with technology improvements – sufficient to provide all the world's present energy needs for several millennia.[15]
At present, geothermal wells are rarely more than 3 km (1.9 mi) deep.[3] Upper estimates of geothermal resources assume wells as deep as 10 km (6.2 mi). Drilling near this depth is now possible in the petroleum industry, although it is an expensive process. The deepest research well in the world, the Kola Superdeep Borehole (KSDB-3), is 12.261 km (7.619 mi) deep.[21] This record has recently been imitated by commercial oil wells, such as Exxon's Z-12 well in the Chayvo field, Sakhalin.[22] Wells drilled to depths greater than 4 km (2.5 mi) generally incur drilling costs in the tens of millions of dollars.[23] The technological challenges are to drill wide bores at low cost and to break larger volumes of rock.
Geothermal power is considered to be sustainable because the heat extraction is small compared to the Earth's heat content, but extraction must still be monitored to avoid local depletion.[7] Although geothermal sites are capable of providing heat for many decades, individual wells may cool down or run out of water. The three oldest sites, at Larderello, Wairakei, and the Geysers have all reduced production from their peaks. It is not clear whether these stations extracted energy faster than it was replenished from greater depths, or whether the aquifers supplying them are being depleted. If production is reduced, and water is reinjected, these wells could theoretically recover their full potential. Such mitigation strategies have already been implemented at some sites. The long-term sustainability of geothermal energy has been demonstrated at the Lardarello field in Italy since 1913, at the Wairakei field in New Zealand since 1958,[24] and at the Geysers field in California since 1960.[25]
Power station types[]
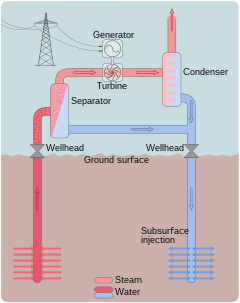
Geothermal power stations are similar to other steam turbine thermal power stations in that heat from a fuel source (in geothermal's case, the Earth's core) is used to heat water or another working fluid. The working fluid is then used to turn a turbine of a generator, thereby producing electricity. The fluid is then cooled and returned to the heat source.
Dry steam power stations[]
Dry steam stations are the simplest and oldest design. This type of power station is not found very often, because it requires a resource that produces dry steam, but is the most efficient, with the simplest facilities.[26] In these sites, there may be liquid water present in the reservoir, but no water is produced to the surface, only steam.[26] Dry Steam Power directly uses geothermal steam of 150 °C or greater to turn turbines.[3] As the turbine rotates it powers a generator which then produces electricity and adds to the power field.[27] Then, the steam is emitted to a condenser. Here the steam turns back into a liquid which then cools the water.[28] After the water is cooled it flows down a pipe that conducts the condensate back into deep wells, where it can be reheated and produced again. At The Geysers in California, after the first 30 years of power production, the steam supply had depleted and generation was substantially reduced. To restore some of the former capacity, supplemental water injection was developed during the 1990s and 2000s, including utilization of effluent from nearby municipal sewage treatment facilities.[29]
Flash steam power stations[]
Flash steam stations pull deep, high-pressure hot water into lower-pressure tanks and use the resulting flashed steam to drive turbines. They require fluid temperatures of at least 180 °C, usually more. This is the most common type of station in operation today. Flash steam plants use geothermal reservoirs of water with temperatures greater than 360 °F (182 °C). The hot water flows up through wells in the ground under its own pressure. As it flows upward, the pressure decreases and some of the hot water is transformed into steam. The steam is then separated from the water and used to power a turbine/generator. Any leftover water and condensed steam may be injected back into the reservoir, making this a potentially sustainable resource.[30] [31]
Binary cycle power stations[]
Binary cycle power stations are the most recent development, and can accept fluid temperatures as low as 57 °C.[14] The moderately hot geothermal water is passed by a secondary fluid with a much lower boiling point than water. This causes the secondary fluid to flash vaporize, which then drives the turbines. This is the most common type of geothermal electricity station being constructed today.[32] Both Organic Rankine and Kalina cycles are used. The thermal efficiency of this type of station is typically about 10–13%.[citation needed]

Worldwide production[]

This section needs to be updated. (February 2021) |
The International Geothermal Association (IGA) has reported that 10,715 megawatts (MW) of geothermal power in 24 countries is online, which is expected to generate 67,246 GWh of electricity in 2010.[1][2] This represents a 20% increase in geothermal power online capacity since 2005. IGA projected this would grow to 18,500 MW by 2015, due to the large number of projects that were under consideration, often in areas previously assumed to have little exploitable resource.[1]
In 2010, the United States led the world in geothermal electricity production with 3,086 MW of installed capacity from 77 power stations;[33] the largest group of geothermal power plants in the world is located at The Geysers, a geothermal field in California.[34] The Philippines follows the US as the second highest producer of geothermal power in the world, with 1,904 MW of capacity online; geothermal power makes up approximately 27% of the country's electricity generation.[33]
Al Gore said in The Climate Project Asia Pacific Summit that Indonesia could become a super power country in electricity production from geothermal energy.[35] India has announced a plan to develop the country's first geothermal power facility in Chhattisgarh.[36]
Canada is the only major country on the Pacific Ring of Fire which has not yet developed geothermal power. The region of greatest potential is the Canadian Cordillera, stretching from British Columbia to the Yukon, where estimates of generating output have ranged from 1,550 MW to 5,000 MW.[37]
Utility-grade stations[]

The largest group of geothermal power plants in the world is located at The Geysers, a geothermal field in California, United States.[38] As of 2004, five countries (El Salvador, Kenya, the Philippines, Iceland, and Costa Rica) generate more than 15% of their electricity from geothermal sources.[3]
Geothermal electricity is generated in the 24 countries listed in the table below. During 2005, contracts were placed for an additional 500 MW of electrical capacity in the United States, while there were also stations under construction in 11 other countries.[15] Enhanced geothermal systems that are several kilometres in depth are operational in France and Germany and are being developed or evaluated in at least four other countries.
| Country | Capacity (MW) 2007[10] |
Capacity (MW) 2010[39] |
Capacity (MW) 2013[40] |
Capacity (MW) 2015[41] |
Capacity (MW)
2018[42] |
Capacity (MW)
2019[4] |
Share of national generation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 2687 | 3086 | 3389 | 3450 | 3591 | 3676 | 0.3 |
| Indonesia | 992 | 1197 | 1333 | 1340 | 1948 | 2133 | 3.7 |
| Philippines | 1969.7 | 1904 | 1894 | 1870 | 1868 | 1918 | 27.0 |
| Turkey | 38 | 82 | 163 | 397 | 1200 | 1526 | 0.3 |
| New Zealand | 471.6 | 628 | 895 | 1005 | 1005 | 1005 | 14.5[43] |
| Mexico | 953 | 958 | 980 | 1017 | 951 | 962.7 | 3.0 |
| Italy | 810.5 | 843 | 901 | 916 | 944 | 944 | 1.5 |
| Kenya | 128.8 | 167 | 215 | 594 | 676 | 861 | 38[44] |
| Iceland | 421.2 | 575 | 664 | 665 | 755 | 755 | 30.0 |
| Japan | 535.2 | 536 | 537 | 519 | 542 | 601 | 0.1 |
| Costa Rica | 162.5 | 166 | 208 | 207 | 14.0 | ||
| El Salvador | 204.4 | 204 | 204 | 204 | 25.0[45][46] | ||
| Nicaragua | 79 | 82 | 97 | 82 | 9.9 | ||
| Russia | 79 | 79 | 82 | 82 | |||
| 53 | 52 | 42 | 52 | ||||
| 56 | 56 | 56 | 50 | ||||
| Portugal | 23 | 29 | 28 | 29 | |||
| China | 27.8 | 24 | 27 | 27 | |||
| Germany | 8.4 | 6.6 | 13 | 27 | |||
| 14.7 | 16 | 15 | 16 | ||||
| Ethiopia | 7.3 | 7.3 | 8 | 7.3 | |||
| 1.1 | 1.4 | 1 | 1.2 | ||||
| Australia | 0.2 | 1.1 | 1 | 1.1 | |||
| 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||||
| Total | 9,731.9 | 10,709.7 | 11,765 | 12,635.9 | 14,369 | 15,406 | – |
Environmental impact[]

Fluids drawn from the deep earth carry a mixture of gases, notably carbon dioxide (CO
2), hydrogen sulfide (H
2S), methane (CH
4), ammonia (NH
3), and radon (Rn). If released, these pollutants contribute to global warming, acid rain, radiation, and noxious smells.[failed verification]
Existing geothermal electric stations, that fall within the 50th percentile of all total life cycle emissions studies reviewed by the IPCC, produce on average 45 kg of CO
2 equivalent emissions per megawatt-hour of generated electricity (kg CO
2eq/MW·h). For comparison, a coal-fired power plant emits 1,001 kg of CO
2 equivalent per megawatt-hour when not coupled with carbon capture and storage (CCS).[8]
Stations that experience high levels of acids and volatile chemicals are usually equipped with emission-control systems to reduce the exhaust. Geothermal stations can also inject these gases back into the earth as a form of carbon capture and storage, such as in the CarbFix project in Iceland.
Other stations like the Kızıldere geothermal power plant, exhibit the capability to utilize geothermal fluids to process carbon dioxide gas into dry ice at two nearby plants resulting in very little environmental impact.[47]
In addition to dissolved gases, hot water from geothermal sources may hold in solution trace amounts of toxic chemicals, such as mercury, arsenic, boron, antimony, and salt.[48] These chemicals come out of solution as the water cools, and can cause environmental damage if released. The modern practice of injecting geothermal fluids back into the Earth to stimulate production has the side benefit of reducing this environmental risk.
Station construction can adversely affect land stability. Subsidence has occurred in the Wairakei field in New Zealand.[49] Enhanced geothermal systems can trigger earthquakes due to water injection. The project in Basel, Switzerland was suspended because more than 10,000 seismic events measuring up to 3.4 on the Richter Scale occurred over the first 6 days of water injection.[50] The risk of geothermal drilling leading to uplift has been experienced in Staufen im Breisgau.
Geothermal has minimal land and freshwater requirements. Geothermal stations use 404 square meters per GW·h versus 3,632 and 1,335 square meters for coal facilities and wind farms respectively.[49] They use 20 litres of freshwater per MW·h versus over 1000 litres per MW·h for nuclear, coal, or oil.[49]
Geothermal power stations can also disrupt the natural cycles of geysers. For example, the Beowawe, Nevada geysers, which were uncapped geothermal wells, stopped erupting due to the development of the dual-flash station.
Local climate cooling is possible as a result of the work of the geothermal circulation systems. However, according to an estimation given by Leningrad Mining Institute in 1980s, possible cool-down will be negligible compared to natural climate fluctuations.[51]
Economics[]
Geothermal power requires no fuel; it is therefore immune to fuel cost fluctuations. However, capital costs tend to be high. Drilling accounts for over half the costs, and exploration of deep resources entails significant risks. A typical well doublet in Nevada can support 4.5 megawatts (MW) of electricity generation and costs about $10 million to drill, with a 20% failure rate.[23] In total, electrical station construction and well drilling costs about 2–5 million € per MW of electrical capacity, while the levelised energy cost is 0.04–0.10 € per kW·h.[10] Enhanced geothermal systems tend to be on the high side of these ranges, with capital costs above $4 million per MW and levelized costs above $0.054 per kW·h in 2007.[52]
Geothermal power is highly scalable: a small power station can supply a rural village, though initial capital costs can be high.[53]
The most developed geothermal field is the Geysers in California. In 2008, this field supported 15 stations, all owned by Calpine, with a total generating capacity of 725 MW.[38]
See also[]
- Enhanced geothermal system
- Geothermal heating
- Hot dry rock geothermal energy
- Iceland Deep Drilling Project
- List of renewable energy topics by country
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Geothermal Energy Association. Geothermal Energy: International Market Update May 2010, p. 4-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bassam, Nasir El; Maegaard, Preben; Schlichting, Marcia (2013). Distributed Renewable Energies for Off-Grid Communities: Strategies and Technologies Toward Achieving Sustainability in Energy Generation and Supply. Newnes. p. 187. ISBN 978-0-12-397178-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Fridleifsson, Ingvar B.; Bertani, Ruggero; Huenges, Ernst; Lund, John W.; Ragnarsson, Arni; Rybach, Ladislaus (11 February 2008). O. Hohmeyer and T. Trittin (ed.). The possible role and contribution of geothermal energy to the mitigation of climate change (PDF). IPCC Scoping Meeting on Renewable Energy Sources. Luebeck, Germany. pp. 59–80. Retrieved 6 April 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Richter, Alexander (27 January 2020). "The Top 10 Geothermal Countries 2019 – based on installed generation capacity (MWe)". Think GeoEnergy - Geothermal Energy News. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ "The International Geothermal Market At a Glance – May 2015" (PDF). GEA—Geothermal Energy Association. May 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Craig, William; Gavin, Kenneth (2018). Geothermal Energy, Heat Exchange Systems and Energy Piles. London: ICE Publishing. pp. 41–42. ISBN 9780727763983.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Rybach, Ladislaus (September 2007), "Geothermal Sustainability" (PDF), Geo-Heat Centre Quarterly Bulletin, Klamath Falls, Oregon: Oregon Institute of Technology, 28 (3), pp. 2–7, ISSN 0276-1084, retrieved 9 May 2009
- ^ Jump up to: a b Moomaw, W., P. Burgherr, G. Heath, M. Lenzen, J. Nyboer, A. Verbruggen, 2011: Annex II: Methodology. In IPCC: Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation (ref. page 10)
- ^ Tiwari, G. N.; Ghosal, M. K. Renewable Energy Resources: Basic Principles and Applications. Alpha Science Int'l Ltd., 2005 ISBN 1-84265-125-0
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Bertani, Ruggero (September 2007), "World Geothermal Generation in 2007" (PDF), Geo-Heat Centre Quarterly Bulletin, Klamath Falls, Oregon: Oregon Institute of Technology, 28 (3), pp. 8–19, ISSN 0276-1084, retrieved 12 April 2009
- ^ IPENZ Engineering Heritage Archived 22 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Ipenz.org.nz. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lund, J. (September 2004), "100 Years of Geothermal Power Production" (PDF), Geo-Heat Centre Quarterly Bulletin, Klamath Falls, Oregon: Oregon Institute of Technology, 25 (3), pp. 11–19, ISSN 0276-1084, retrieved 13 April 2009
- ^ McLarty, Lynn; Reed, Marshall J. (October 1992), "The U.S. Geothermal Industry: Three Decades of Growth" (PDF), Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, London: Taylor & Francis, 14 (4): 443–455, doi:10.1080/00908319208908739, archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2016, retrieved 29 July 2013
- ^ Jump up to: a b Erkan, K.; Holdmann, G.; Benoit, W.; Blackwell, D. (2008), "Understanding the Chena Hot Springs, Alaska, geothermal system using temperature and pressure data", Geothermics, 37 (6): 565–585, doi:10.1016/j.geothermics.2008.09.001, ISSN 0375-6505
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Tester, Jefferson W. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology); et al., The Future of Geothermal Energy (PDF), Impact, of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (Egs) on the United States in the 21st Century: An Assessment, Idaho Falls: Idaho National Laboratory, ISBN 0-615-13438-6, archived from the original (PDF) on 10 March 2011, retrieved 7 February 2007
- ^ Bertani, Ruggero (2009). "Geothermal Energy: An Overview on Resources and Potential" (PDF). Proceedings of the International Conference on National Development of Geothermal Energy Use. Slovakia.
- ^ Schavemaker, Pieter; van der Sluis, Lou (2008). Electrical Power Systems Essentials. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ISBN 978-0470-51027-8.
- ^ Lund, John W. (2003), "The USA Geothermal Country Update", Geothermics, European Geothermal Conference 2003, Elsevier Science Ltd., 32 (4–6): 409–418, doi:10.1016/S0375-6505(03)00053-1
- ^ Goldstein, B., G. Hiriart, R. Bertani, C. Bromley, L. Gutiérrez-Negrín, E. Huenges, H. Muraoka, A. Ragnarsson, J. Tester, V. Zui (2011) "Geothermal Energy". In IPCC Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Geothermal Energy. p. 404.
- ^ Pollack, H.N.; S. J. Hurter, and J. R. Johnson; Johnson, Jeffrey R. (1993), "Heat Flow from the Earth's Interior: Analysis of the Global Data Set", Rev. Geophys., 30 (3), pp. 267–280, Bibcode:1993RvGeo..31..267P, doi:10.1029/93RG01249
- ^ "Kola". www.icdp-online.org. ICDP. Retrieved 27 May 2018.
- ^ Watkins, Eric (11 February 2008), "ExxonMobil drills record extended-reach well at Sakhalin-1", Oil & Gas Journal, archived from the original on 5 March 2010, retrieved 31 October 2009
- ^ Jump up to: a b Geothermal Economics 101, Economics of a 35 MW Binary Cycle Geothermal Plant (PDF), New York: Glacier Partners, October 2009, archived from the original (PDF) on 21 May 2013, retrieved 17 October 2009
- ^ Thain, Ian A. (September 1998), "A Brief History of the Wairakei Geothermal Power Project" (PDF), Geo-Heat Centre Quarterly Bulletin, Klamath Falls, Oregon: Oregon Institute of Technology, 19 (3), pp. 1–4, ISSN 0276-1084, retrieved 2 June 2009
- ^ Axelsson, Gudni; Stefánsson, Valgardur; Björnsson, Grímur; Liu, Jiurong (April 2005), "Sustainable Management of Geothermal Resources and Utilization for 100 – 300 Years" (PDF), Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005, International Geothermal Association, retrieved 2 June 2009[permanent dead link]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tabak, John (2009). Solar and Geothermal Energy. New York: Facts On File, Inc. pp. 97–183. ISBN 978-0-8160-7086-2.
- ^ "Geothermal Energy". National Geographic. National Geographic Society. 20 November 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Gawell, Karl (June 2014). "Economic Costs and Benefits of Geothermal Power" (PDF). Geothermal Energy Association. Retrieved 9 March 2018.
- ^ Scientific American Editors (8 April 2013). The Future of Energy: Earth, Wind and Fire. Scientific American. pp. 160–. ISBN 978-1-4668-3386-9.
- ^ US DOE EERE Hydrothermal Power Systems. eere.energy.gov (22 February 2012). Retrieved 2013-12-13.
- ^ Geothermal Energy. National Geographic.
- ^ "Geothermal Basics Overview". Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. Archived from the original on 4 October 2008. Retrieved 1 October 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Geothermal Energy Association. Geothermal Energy: International Market Update May 2010, p. 7.
- ^ Khan, M. Ali (2007), The Geysers Geothermal Field, an Injection Success Story (PDF), Annual Forum of the Groundwater Protection Council, archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2011, retrieved 25 January 2010
- ^ Indonesia can be super power on geothermal energy: Al Gore. ANTARA News (9 January 2011). Retrieved 2013-12-13.
- ^ India's 1st geothermal power plant to come up in Chhattisgarh – Economic Times. The Economic Times. (17 February 2013). Retrieved 2013-12-13.
- ^ Morphet, Suzanne (March–April 2012), "Exploring BC's Geothermal Potential", Innovation Magazine (Journal of the Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of BC): 22, archived from the original on 27 July 2012, retrieved 5 April 2012
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Calpine Corporation (CPN) (NYSE Arca) Profile". Reuters (Press release). Archived from the original on 14 November 2012. Retrieved 14 October 2009.
- ^ Holm, Alison (May 2010), Geothermal Energy:International Market Update (PDF), Geothermal Energy Association, p. 7, retrieved 24 May 2010
- ^ Matek, Benjamin (June 2014). "2013 Geothermal Power: International Market Overview" (PDF). Geothermal Energy Association. pp. 10–11. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ Bertani, Ruggero (April 2015) Geothermal Power Generation in the World 2010–2014 Update Report. Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 April 2015. pp. 2, 3
- ^ Richter, Alexander (28 September 2018). "Global geothermal capacity reaches 14,369 MW – Top 10 Geothermal Countries, Oct 2018". Think GeoEnergy - Geothermal Energy News. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ^ "Energy in New Zealand 2014". New Zealand Ministry of Economic Development. September 2014. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^ Kushner, Jacob (5 March 2021). "How Kenya is harnessing the immense heat from the Earth". Future Planet. BBC.
- ^ "Generacion Electricidad El Salvador", IGA, archived from the original on 27 March 2012, retrieved 30 August 2011
- ^ "CENTROAMÉRICA: MERCADOS MAYORISTAS DE ELECTRICIDAD Y TRANSACCIONES EN EL MERCADO ELÉCTRICO REGIONAL, 2010" (PDF), CEPAL, retrieved 30 August 2011
- ^ Dipippo, Ronald (2012). Ph.D. Massachusetts; Dartmouth: Elsevier Ltd. pp. 437–438. ISBN 9780080982069.
- ^ Bargagli1, R.; Cateni, D.; Nelli, L.; Olmastroni, S.; Zagarese, B. (August 1997), "Environmental Impact of Trace Element Emissions from Geothermal Power Plants", Environmental Contamination Toxicology, New York, 33 (2): 172–181, doi:10.1007/s002449900239, PMID 9294245, S2CID 30238608
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Lund, John W. (June 2007), "Characteristics, Development and utilization of geothermal resources" (PDF), Geo-Heat Centre Quarterly Bulletin, Klamath Falls, Oregon: Oregon Institute of Technology, 28 (2), pp. 1–9, ISSN 0276-1084, retrieved 16 April 2009
- ^ Deichmann, N.; Mai, M.; Bethmann, F.; Ernst, J.; Evans, K.; Fäh, D.; Giardini, D.; Häring, M.; Husen, S.; Kästli, P.; Bachmann, C.; Ripperger, J.; Schanz, U.; Wiemer, S. (2007), "Seismicity Induced by Water Injection for Geothermal Reservoir Stimulation 5 km Below the City of Basel, Switzerland", American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting, 53: V53F–08, Bibcode:2007AGUFM.V53F..08D
- ^ Дядькин, Ю. Д. (2001). "Извлечение и использование тепла земли". Горный информационно-аналитический бюллетень (научно-технический журнал).
- ^ Sanyal, Subir K.; Morrow, James W.; Butler, Steven J.; Robertson-Tait, Ann (22 January 2007). "Cost of Electricity from Enhanced Geothermal Systems" (PDF). Proc. Thirty-Second Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering. Stanford, California.
- ^ Lund, John W.; Boyd, Tonya (June 1999), "Small Geothermal Power Project Examples" (PDF), Geo-Heat Centre Quarterly Bulletin, Klamath Falls, Oregon: Oregon Institute of Technology, 20 (2), pp. 9–26, ISSN 0276-1084, retrieved 2 June 2009
External links[]
- Geothermal energy
- Sustainable energy
- Power station technology