Guanosine diphosphate
| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
IUPHAR/BPS
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
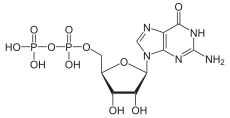
| C10H15N5O11P2 | |
| Molar mass | 443.200522 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine.[1]
GDP is the product of GTP dephosphorylation by GTPases, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction.
GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate.
See also[]
- DNA
- Guanosine triphosphate
- Nucleoside
- Nucleotide
- Oligonucleotide
- RNA
References[]
- ^ Crane, Laura J; Miller, David Lee (1974). "Guanosine triphosphate and guanosine diphosphate as conformation-determining molecules. Differential interaction of a fluorescent probe with the guanosine nucleotide complexes of bacterial elongation factor Tu". Biochemistry. 13 (5): 933–939. doi:10.1021/bi00702a017. PMID 4591619.
Categories:
- Biochemistry stubs
- Nucleotides
- Phosphate esters
- Purines
- Pyrophosphates