Hephaestus Fossae
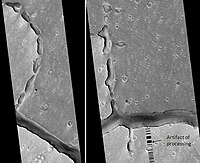 Two views of the Hephaestus Fossae, as seen by HiRISE. Picture on right lies to the top (north) of other picture. Fossae often form by material moving into an underground void. | |
| Coordinates | 21°06′N 237°30′W / 21.1°N 237.5°WCoordinates: 21°06′N 237°30′W / 21.1°N 237.5°W |
|---|---|
| Naming | a classical albedo feature name |
The Hephaestus Fossae are a system of troughs and channels in the Amenthes quadrangle of Mars, with a location centered at 21.1 N and 237.5 W. They are 604 km long and were named after a classical albedo feature name.[1] The fossae have been tentatively identified as outflow channels, but their origin and evolution remain ambiguous.[2] It has been proposed that water may have been released into the troughs as a catastrophic flood due to subsurface ice melting following a large bolide impact.[3]
References[]
- ^ http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov
- ^ Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of Mars. Cambridge Planetary Science Series, Cambridge University Press.
- ^ "Craters and channels in Hephaestus Fossae".
See also[]
- Fossa (geology)
- Geology of Mars
- HiRISE
Categories:
- Amenthes quadrangle
- Valleys and canyons on Mars
- Mars stubs
