Human overpopulation
This article duplicates the scope of other articles, specifically Resource depletion and Human impact on the environment. (July 2021) |
An editor has expressed concern that this article may have a number of irrelevant citations. (July 2021) |

Human overpopulation (or human population overshoot) is the concept of a human population becoming too large to be sustained by its environment in the long term. The idea is usually discussed in the context of world population, though it may also concern regions. Human population growth has increased in recent centuries due to medical advancements and improved agricultural productivity. Those concerned by this trend argue that it results in a level of resource consumption which exceeds the environment's carrying capacity, leading to population overshoot. The concept is often discussed in relation to other population concerns such as demographic push and depopulation, as well as in relation to resource depletion and the human impact on the environment.
Discussion of overpopulation follow a similar line of inquiry as Malthusianism and its Malthusian catastrophe,[1][2] a hypothetical event where population exceeds agricultural capacity, causing famine or war over resources, resulting in poverty and depopulation.
Recent discussion of overpopulation was popularized by Paul Ehrlich in his 1968 book The Population Bomb. Ehrlich described overpopulation as a function of overconsumption,[3] arguing that overpopulation should be defined by a population being unable to sustain itself without depleting non-renewable resources.[4][5][6] Modern proponents of the concept have suggested a link between overpopulation and human-caused environmental issues such as global warming and biodiversity loss. To mitigate this, population planning strategies have been advocated to establish what proponents consider a sustainable population.
The concept of overpopulation is controversial. A 2015 article in Nature listed overpopulation as a pervasive science myth.[7] Demographic projections suggest that population growth will stabilise in the 21st century, and many experts believe that global resources can meet this increased demand, suggesting a global overpopulation scenario is unlikely.[8][9] Critics highlight how attempts to blame environmental issues on overpopulation tend to oversimplify complex social or economic systems, or place blame on developing countries and poor populations—reinscribing colonial or racist assumptions.[2][10][11] For these reasons, critics of overpopulation suggest overconsumption be treated as an issue separate from population growth.[12]
History of concept[]
This section needs expansion. You can help by . (March 2021) |
Concerns about population size or density have a long history: Tertullian, a resident of the city of Carthage in the second century CE, criticized population at the time saying "Our numbers are burdensome to the world, which can hardly support us.. In very deed, pestilence, and famine, and wars, and earthquakes have to be regarded as a remedy for nations, as the means of pruning the luxuriance of the human race."[citation needed] Despite these concerns, scholars have not found historic societies which have collapsed because of overpopulation or overconsumption.[13] This could be because, prior to modern medicine, infectious diseases prevented populations from growing too large.[citation needed]
By the beginning of the 19th century, intellectuals such as Thomas Malthus predicted that humankind would outgrow its available resources because a finite amount of land would be incapable of supporting a population with limitless potential for increase.[14] During the 19th century, Malthus' work, particularly An Essay on the Principle of Population, was often interpreted in a way that blamed the poor alone for their condition and helping them was said to worsen conditions in the long run.[15] This resulted, for example, in the English poor laws of 1834[15] and a hesitating response to the Irish Great Famine of 1845–52.[16]
Paul R. Ehrlich's book The Population Bomb became a bestseller upon its release in 1968, creating renewed interest in overpopulation. The book predicted population growth would lead to famine, societal collapse, and other social, environmental and economic strife in the coming decades, and advocated for policies to curb it.[4][11][17] The idea of overpopulation was also a topic of some works of English-language science fiction and dystopian fiction during the latter part of the 1960s.[17] Human population and family planning policies were adopted by some nations in the late 20th century in an effort to curb population growth, including in China and India.[18] Albert Allen Bartlett gave more than 1,742 lectures on the threat of exponential population growth starting in 1969.[7]
As the profile of environmental issues facing humanity increased during the end of the 20th century, some have looked to population growth as a root cause. In 2017, more than one-third of 50 Nobel prize-winning scientists surveyed by the Times Higher Education at the Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings said that human overpopulation and environmental degradation are the two greatest threats facing mankind.[19] In November that same year, a statement by 15,364 scientists from 184 countries indicated that rapid human population growth is "a primary driver behind many ecological and even societal threats."[20] In 2019, a warning on climate change signed by 11,000 scientists from 153 nations said that human population growth adds 80 million humans annually, and "the world population must be stabilized—and, ideally, gradually reduced—within a framework that ensures social integrity" to reduce the impact of "population growth on GHG emissions and biodiversity loss."[21][22]
Advocacy organizations[]
More recently, overpopulation organizations have promoted the conversation in academic and policy circles. Organizations focused on population stabilization and population concern often focus on the policy of particular governments, or particular solutions to overpopulation. Some of these organizations are popular or visible because of their association with major public figures, such as Population Matters' connection with David Attenborough, while others are more closely associated with particular academic interpretations or solutions.
Global population dynamics, their history and factors[]

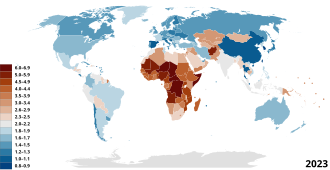

World population has been rising continuously since the end of the Black Death, around the year 1350.[23] The fastest doubling of the world population happened between 1950 and 1986: a doubling from 2.5 to 5 billion people in just 37 years, [24] mainly due to medical advancements and increases in agricultural productivity.[25][26] Due to its dramatic impact on the human ability to grow food, the Haber process enabling the global population to increase from 1.6 billion in 1900 to 7.7 billion by November 2018.[27]
Some researchers analyze this growth in population like other animal populations, human populations predictably grow and shrink according to their available food supply (see Lotka–Volterra equations), including agronomist and insect ecologist David Pimentel,[28] behavioral scientist Russell Hopfenberg,[29] and anthropologist Virginia Abernethy.[30]
History of world population[]
| Population[31] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Billion | ||
| 1804 | 1 | ||
| 1927 | 2 | ||
| 1959 | 3 | ||
| 1974 | 4 | ||
| 1987 | 5 | ||
| 1999 | 6 | ||
| 2011 | 7 | ||
| 2021 | 7.8[32] | ||
World population has gone through a number of periods of growth since the dawn of civilization in the Holocene period, around 10,000 BCE. The beginning of civilization roughly coincides with the receding of glacial ice following the end of the last glacial period.[33]Farming allowed for the growth of populations in many parts of the world, including Europe, the Americas and China through the 1600s, occasionally disrupted by plagues or other crisis.[34][35] For example, the Black Death is thought to have reduced the world's population, then at an estimated 450 million, to between 350 and 375 million by 1400.[36]
After the start of the Industrial Revolution, during the 18th century, the rate of population growth began to increase. By the end of the century, the world's population was estimated at just under 1 billion.[37] At the turn of the 20th century, the world's population was roughly 1.6 billion.[37] Dramatic growth beginning in 1950 (above 1.8% per year) coincided with greatly increased food production as a result of the industrialization of agriculture brought about by the Green Revolution.[38] The rate of human population growth peaked in 1964, at about 2.1% per year.[39] By 1940, this figure had increased to 2.3 billion.[40] Each subsequent addition of a billion humans took less and less time: 33 years to reach three billion in 1960, 14 years for four billion in 1974, 13 years for five billion in 1987, and 12 years for six billion in 1999.[41]
On 14 May 2018 , the United States Census Bureau calculates 7,472,985,269 for that same date[42] and the United Nations estimated over 7 billion.[43][44][45] In 2017, the United Nations increased the medium variant projections[46] to 9.8 billion for 2050 and 11.2 billion for 2100.[47] The UN population forecast of 2017 was predicting "near end of high fertility" globally and anticipating that by 2030 over ⅔ of the world population will be living in countries with fertility below the replacement level[48] and for total world population to stabilize between 10 and 12 billion people by the year 2100.[49]
Proposed impacts[]
Biologists and sociologists have discussed overpopulation as a threat to the quality of human life.[50][51] Some environmentalists, such as Pentti Linkola, have argued human overpopulation represents a threat to Earth's biosphere.[52]
Paul R. Ehrlich argued in 2017:
Rich western countries are now siphoning up the planet's resources and destroying its ecosystems at an unprecedented rate. We want to build highways across the Serengeti to get more rare earth minerals for our cellphones. We grab all the fish from the sea, wreck the coral reefs and put carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. We have triggered a major extinction event ... If everyone consumed resources at the US level—which is what the world aspires to—you will need another four or five Earths. We are wrecking our planet's life support systems.[53]
However, Ehrlich's earlier predictions were controversial. In 1968 book The Population Bomb, he stated that "[i]n the 1970s hundreds of millions of people will starve to death in spite of any crash programs embarked upon now,"[54] with later editions changing to instead be "in the 1980s".[1]
Poverty, and infant and child mortality[]
Although proponents of human overpopulation have expressed concern that growing population will lead to an increase in global poverty and infant mortality, both indicators have declined over the last 200 years of population growth.[8][55]
Environmental impacts[]
It has been suggested[by whom?] that overpopulation has substantially adversely impacted the environment of Earth starting at least as early as the 20th century.[51][verification needed] There are also economic consequences of environmental degradation caused by excess waste production and overconsumption in the form of ecosystem services attrition.[56] Some scientists suggest that the overall human impact on the environment during the Great Acceleration, particularly due to human population size and growth, economic growth, overconsumption, pollution, and proliferation of technology, has pushed the planet into a new geological epoch known as the Anthropocene.[57][58]
However, even in countries which have both large population growth and major ecological problems, it is not necessarily true that curbing the population growth will make a major contribution towards resolving all environmental problems.[59]
Some studies and commentary link population growth with climate change.[21][62][63][64] However, critics have pointed out population growth may have less influence on climate change than other factors.[65] The global consumption of meat is projected to rise by as much as 76% by 2050 as the global population increases, with this projected to have further environmental impacts such as biodiversity loss and increased greenhouse gas emissions.[66][67]
Continued population growth and overconsumption have been posited as key drivers of biodiversity loss and the 6th (and ongoing) mass extinction,[68][69][70] with some researchers and environmentalists specifically suggesting this indicates a human overpopulation scenario.[71][72] Some prominent scientists and environmentalists, including Jared Diamond, E. O. Wilson, Jane Goodall[73] and David Attenborough[74] contend that population growth is devastating to biodiversity. Wilson for example, has expressed concern when Homo sapiens reached a population of six billion their biomass exceeded that of any other large land dwelling animal species that had ever existed by over 100 times.[75]
Resource depletion[]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2021) |
This section possibly contains original research. (January 2021) |
Some commentary has attributed depletion of non-renewable resources, such as land, food and water, to overpopulation[76] and suggested it could lead to a diminished quality of human life.[51] Ecologist David Pimentel was one such proponent, saying "with the imbalance growing between population numbers and vital life sustaining resources, humans must actively conserve cropland, freshwater, energy, and biological resources. There is a need to develop renewable energy resources. Humans everywhere must understand that rapid population growth damages the Earth's resources and diminishes human well-being."[77][78]
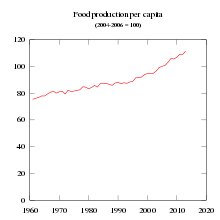
Although food shortages have been warned as a consequence of overpopulation, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization, global food production exceeds increasing demand from global population growth.[7] Food insecurity in some regions is attributable to the globally unequal distribution of food supplies.[7] Some proponents of overpopulation[who?] warn expansion of agricultural production to meet population growth is likely to have a substantial impact on the environment, and have expressed concern at usable land area becoming limited.[79][80][81]
The notion that space is limited has been decried by skeptics, who point out that the Earth's population of roughly 6.8 billion people could comfortably be housed an area comparable in size to the state of Texas, in the United States (about 269,000 square miles or 696,706.80 square kilometres).[80] Critics suggest changes to policies relating to land use or agriculture would be more likely to resolve land shortage issues.[65]
Water scarcity, on which agriculture depends, represents a global issue that some have linked to population growth.[82][83][84] Although water is not scarce on a global scale, water issues persist in many developing countries.[7][85]


Other[]
- Low life expectancy in countries with fastest growing populations.[86][failed verification] Overall life expectancy has increased globally despite of population growth, including countries with fast-growing populations.[55]
- Less personal freedom and more restrictive laws. It was speculated by Aldous Huxley in 1958 that democracy is threatened by overpopulation, and could give rise to totalitarian style governments.[87] Physics professor Albert Allen Bartlett at the University of Colorado Boulder warned in 2000 that overpopulation and the development of technology are the two major causes of the diminution of democracy.[88] However, over the last 200 years of population growth, the actual level of personal freedom has increased rather than declined.[55]
Future dynamics[]
Projections of population growth[]
| Continent | Projected 2050 population
by UN in 2017[89] |
|---|---|
| Africa | 2.5 billion |
| Asia | 5.5 billion |
| Europe | 716 million |
| Latin America and Caribbean | 780 million |
| North America | 435 million |

Population projections are attempts to show how the human population living today will change in the future.[90] These projections are an important input to forecasts of the population's impact on this planet and humanity's future well-being.[91] Models of population growth take trends in human development, and apply projections into the future.[92] These models use trend-based-assumptions about how populations will respond to economic, social and technological forces to understand how they will affect fertility and mortality, and thus population growth.[92]
The 2019 forecast from the United Nation's Population Division (made before the COVID-19 pandemic) shows that world population growth peaked at 2.1% per year in 1968, has since dropped to 1.1%, and could drop even further to 0.1% by 2100, a growth rate not seen since pre-industrial revolution days.[93] Based on this, the UN Population Division expects the world population, which is at 7.8 billion as of 2020, to level out around 2100 at 10.9 billion (the median line),[94][95] assuming a continuing decrease in the global average fertility rate from 2.5 births per woman during the 2015–2020 period to 1.9 in 2095–2100, according to the medium-variant projection.[96]
However, estimates outside of the United Nations have put forward alternative models based on additional downward pressure on fertility (such as successful implementation of education and family planning goals in the Sustainable Development Goals) which could result in peak population during the 2060-2070 period rather than later.[92][97]
According to the UN, about two thirds of the predicted growth in population between 2020 and 2050 will take place in Africa.[98] It is projected that 50% of births in the 5-year period 2095-2100 will be in Africa.[99]Other organizations project lower levels of population growth in Africa based particularly on improvement in women’s education and met needs for family planning.[100]
By 2100, the UN projects the population in Sub-Saharan Africa will reach 3.8 billion, IHME projects 3.1 billion, and IIASA is the lowest at 2.6 billion. In contrast to the UN projections, the models of fertility developed by IHME and IIASA incorporate women’s educational attainment, and in the case of IHME, also consider met need for family planning.[101]

Overconsumption[]
Some groups (for example, the World Wide Fund for Nature[102][103] and Global Footprint Network) have stated that the yearly biocapacity of Earth is being exceeded as measured using the ecological footprint. In 2006, WWF's "Living Planet Report" stated that in order for all humans to live with the current consumption patterns of Europeans, we would be spending three times more than what the planet can renew.[104] Humanity as a whole was using, by 2006, 40 percent more than what Earth can regenerate.[105] However, Roger Martin of Population Matters states the view: "the poor want to get rich, and I want them to get rich," with a later addition, "of course we have to change consumption habits,... but we've also got to stabilise our numbers".[106] Another study by the World Wildlife Fund in 2014 found that it would take the equivalent of 1.5 Earths of biocapacity to meet humanity's current levels of consumption.[107]
But critics question the simplifications and statistical methods used in calculating ecological footprints. Therefore, Global Footprint Network and its partner organizations have engaged with national governments and international agencies to test the results—reviews have been produced by France, Germany, the European Commission, Switzerland, Luxembourg, Japan and the United Arab Emirates.[108] Some point out that a more refined method of assessing Ecological Footprint is to designate sustainable versus non-sustainable categories of consumption.[109][110]
Carrying capacity[]
Many attempts have been made to estimate the world's carrying capacity for humans; the maximum population the world can host.[111] A 2004 meta-analysis of 69 such studies from 1694 until 2001 found the average predicted maximum number of people the Earth would ever have was 7.7 billion people, with lower and upper meta-bounds at 0.65 and 98 billion people, respectively. They conclude: "recent predictions of stabilized world population levels for 2050 exceed several of our meta-estimates of a world population limit".[112]
A 2012 United Nations report summarized 65 different estimated maximum sustainable population sizes and the most common estimate was 8 billion.[113] Advocates of reduced population often put forward much lower numbers. Paul R. Ehrlich stated in 2018 that the optimum population is between 1.5 and 2 billion.[114] Geographer Chris Tucker estimates that 3 billion is a sustainable number.[115]
Critics of overpopulation criticize the basic assumptions associated with these estimates. For example, Jade Sasser believes that calculating a maximum of number of humanity is unethical while only some, mostly privileged European former colonial powers, are mostly responsible for unsustainably using up Earth's resources.[116]
Proposed solutions and mitigation measures[]
Several strategies have been proposed to mitigate overpopulation.
Population planning[]
Several scientists (including e.g. Paul and Anne Ehrlich and Gretchen Daily) proposed that humanity should work at stabilizing its absolute numbers, as a starting point towards beginning the process of reducing the total numbers. They suggested the following solutions and policies: following a small-family-size socio-cultural-behavioral norm worldwide (especially one-child-per-family ethos), and providing contraception to all along with proper education on its use and benefits (while providing access to safe, legal abortion as a backup to contraception), combined with a significantly more equitable distribution of resources globally.[117][118] Australian scientist Tim Flannery has advocated for population planning,[64] including in Australia, after suggesting the country's environment could not support its growing population.[119][120]
Population planning that is intended to reduce population size or growth rate may promote or enforce one or more of the following practices, although there are other methods as well:
- Greater and better access to contraception
- Reducing infant mortality so that parents do not need to have many children to ensure at least some survive to adulthood.[121]
- Improving the status of women in order to facilitate a departure from traditional sexual division of labour.
- Family planning[122]
- Creating small family "role models"[122]
Education and empowerment[]

Education and empowerment of women and giving access to family planning and contraception have demonstrated positive impacts on reducing birthrates.[123] Many studies conclude that educating girls reduces the number of children they have.[123] One option according to some activists is to focus on education about family planning and birth control methods, and to make birth-control devices like condoms, contraceptive pills and intrauterine devices easily available. Worldwide, nearly 40% of pregnancies are unintended (some 80 million unintended pregnancies each year).[124] An estimated 350 million women in the poorest countries of the world either did not want their last child, do not want another child or want to space their pregnancies, but they lack access to information, affordable means and services to determine the size and spacing of their families. In the developing world, some 514,000 women die annually of complications from pregnancy and abortion,[125] with 86% of these deaths occurring in the sub-Saharan Africa region and South Asia.[126] Additionally, 8 million infants die, many because of malnutrition or preventable diseases, especially from lack of access to clean drinking water.[127]
Women's rights and their reproductive rights in particular are issues regarded to have vital importance in the debate.[128] This incentive, however, has been questioned by Rosalind Pollack Petchesky. Citing his attendance of the 1994 Cairo conference, he reported that overpopulation and birth control were being diverted by feminists into women's rights issues, mostly downplaying the overpopulation issue as only one minor matter of many others; most of these focusing on women's rights. Upon his observation, he argued this was forging many faults and distractions on the main problem of human overpopulation and how to solve it.[129]
Coercive population control policies[]

Some nations, like China, have used strict or coercive measures such as the one-child policy to reduce birth rates.[130] Compulsory sterilization has also been implemented in many countries as a form of population control.[131][18]
Another choice-based approach is financial compensation or other benefits (free goods and/or services) by the state (or state-owned companies) offered to people who voluntarily undergo sterilization. Such compensation has been offered in the past by the government of India.[132][133]
Extraterrestrial settlement[]
An argument for space colonization is to mitigate proposed impacts of overpopulation of Earth, such as resource depletion.[134] If the resources of space were opened to use and viable life-supporting habitats were built, Earth would no longer define the limitations of growth. Although many of Earth's resources are non-renewable, off-planet colonies could satisfy the majority of the planet's resource requirements. With the availability of extraterrestrial resources, demand on terrestrial ones would decline.[135] Proponents of this idea include Stephen Hawking[136] and Gerard K. O'Neill.[137]
Others including cosmologist Carl Sagan and science fiction writers Arthur C. Clarke,[138] and Isaac Asimov,[139] have argued that shipping any excess population into space is not a viable solution to human overpopulation. According to Clarke, "the population battle must be fought or won here on Earth".[138] The problem for these authors is not the lack of resources in space (as shown in books such as Mining the Sky[140]), but the physical impracticality of shipping vast numbers of people into space to "solve" overpopulation on Earth.Urbanization[]
Despite the increase in population density within cities (and the emergence of megacities), UN Habitat states in its reports that urbanization may be the best compromise in the face of global population growth.[141] Cities concentrate human activity within limited areas, limiting the breadth of environmental damage.[142] UN Habitat says this is only possible if urban planning is significantly improved.[143]
Paul Ehrlich pointed out in his book The Population Bomb (1968) argues that rhetoric supporting the increase of city density as a means of avoiding dealing with the actual problem of overpopulation to begin with and rather than treating the increase of city density as a symptom of the root problem, it has been promoted by the same interests that have profited from population increase e.g. property developers, the banking system, which invests in property development, industry, municipal councils etc.[144] Subsequent authors point to growth economics as driving governments seek city growth and expansion at any cost disregarding the impact it might have on the environment.[145]
Criticism[]

The concept of human overpopulation, and its attribution as a cause of environmental issues, are controversial.[9][11][147][12][148]
Some critics refer to what they call the "myth of overpopulation".[80][149][150] Critics suggest that enough resources are available to support projected population growth, and that human impacts on the environment are not attributable to overpopulation.[73][148][150] According to libertarian think tank the Fraser Institute, both the idea of overpopulation and the alleged depletion of resources are myths; most resources are now more abundant than a few decades ago, thanks to technological progress.[151] The Institute is also questioning the sincerity of advocates of population control in poor countries.[151][152]
Demographer Nicholas Eberstadt has criticised the idea of overpopulation, saying that "overpopulation is not really overpopulation. It is a question of poverty".[7]
A 2020 study in The Lancet concluded that "continued trends in female educational attainment and access to contraception will hasten declines in fertility and slow population growth", with projections suggesting world population would peak at 9.73 billion in 2064 and fall by 2100.[153] Media commentary interpreted this as suggesting overconsumption represents a greater environmental threat as an overpopulation scenario may never occur.[9][154]
Some human population planning strategies advocated by proponents of overpopulation are controversial for ethical reasons. Those concerned with overpopulation, including Paul Elrich, have been accused of influencing human rights abuses including forced sterilisation policies in India and under China's one-child policy, as well as mandatory or coercive birth control measures taken in other countries.[18][133][155]
Women's rights[]
Influential advocates such as Betsy Hartmann consider the "myth of overpopulation" to be destructive as it “prevents constructive thinking and action on reproductive rights”, which acutely effects women and communities of women in poverty.[149] The 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) define reproductive rights as “the basic right of all couples and individuals to decide freely and responsibly the number, spacing, and timing of their children and to have the information to do so."[156] This oversimplification of human overpopulation leads individuals to believe there are simple solutions and the creation of population policies that limit reproductive rights.
Scholar argues to reject the overpopulation argument, stating that the human population growth is rapidly slowing down, the underlying problem is not the number of people, but how resources are distributed and that the idea of overpopulation could fuel a racist backlash against the population of poor countries.[73]
Racism[]
The argument of overpopulation has been criticized by some scholars and environmentalists as being racist and having roots in colonialism and white supremacy, since control and reduction of human population is often focused on the global south, instead of on overconsumption and the global north.[147][157][12][73][158] George Monbiot has said "when affluent white people wrongly transfer the blame for their environmental impacts on to the birthrate of much poorer brown and black people, their finger-pointing reinforces [white genocide conspiracy] narratives. It is inherently racist."[159] Overpopulation is said to be a common component of ecofascist ideology.[157][148]
By public figures[]
Some capitalist billionaires have expressed concern that impending population collapse is the greatest ecological threat, more so than pollution, environmental degradation or climate change.[160] Elon Musk is a vocal critic of the idea of overpopulation. According to Musk, proponents of the idea are misled by their immediate impressions from living in dense cities.[161] Because of the negative replacement rates in many countries, he expects that by 2039 the biggest issue will be population collapse, not explosion.[162] Jack Ma expressed a similar opinion.[162] However, these sentiments are not supported by data and practically all population projections point to the human population reaching at least 10 billion people by 2100.[163][160]
See also[]
- Demographic trap
- The Limits to Growth
- Global issue
- Human population planning
- Malthusian catastrophe
- Overexploitation
- Overshoot (population)
- Planetary boundaries
- Voluntary Human Extinction Movement
- Antinatalism
- Overpopulation in domestic pets
Lists[]
- List of organisations campaigning for population stabilisation
- List of population concern organizations
Documentary and art[]
- Overpopulation fiction (category)
- Koyaanisqatsi
- What a Way to Go: Life at the End of Empire
- Planet of the Humans
- Ten Billion
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Human Overpopulation: Still an Issue of Concern?". Scientific American. Retrieved 13 March 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fletcher, Robert; Breitling, Jan; Puleo, Valerie (9 August 2014). "Barbarian hordes: the overpopulation scapegoat in international development discourse". Third World Quarterly. 35 (7): 1195–1215. doi:10.1080/01436597.2014.926110. ISSN 0143-6597. S2CID 144569008.
- ^ Paul Ehrlich; Anne H. Ehrlich (4 August 2008). "Too Many People, Too Much Consumption". Yale Environment 360. Yale School of the Environment. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ehrlich, Paul R. Ehrlich & Anne H. (1990). The population explosion. London: Hutchinson. pp. 39–40. ISBN 978-0091745516. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
When is an area overpopulated? When its population cannot be maintained without rapidly depleting nonrenewable resources [39] (or converting renewable resources into nonrenewable ones) and without decreasing the capacity of the environment to support the population. In short, if the long-term carrying capacity of an area is clearly being degraded by its current human occupants, that area is overpopulated.
- ^ Ehrlich, Paul R; Ehrlich, Anne H (2004), One with Nineveh: Politics, Consumption, and the Human Future, Island Press/Shearwater Books, pp. 76–180, 256
- ^ Ehrlich, Paul R; Ehrlich, Anne H (1991), Healing the Planet: Strategies for Resolving the Environmental Crisis, Addison-Wesley Books, pp. 6–8, 12, 75, 96, 241
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Scudellari, Megan (1 December 2015). "The science myths that will not die". Nature. 528 (7582): 322–325. doi:10.1038/528322a. ISSN 1476-4687.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Does population growth lead to hunger and famine?". Our World in Data. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. "What fewer people on the planet would mean for the environment | DW | 31.08.2020". DW.COM. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ "The spectre of "overpopulation"". Transnational Institute. 7 December 2009. Retrieved 13 March 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Piper, Kelsey (20 August 2019). "We've worried about overpopulation for centuries. And we've always been wrong". Vox. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Roberts, David (26 September 2017). ""I'm an environmental journalist, but I never write about overpopulation. Here's why."". Vox. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ Joseph A. Tainter (2006). "Archaeology of Overshoot and Collapse". Annual Review of Anthropology. 35: 59–74. doi:10.1146/annurev.anthro.35.081705.123136.
- ^ "VII, paragraph 10, lines 8–10". An Essay on the Principle of Population. London: J. Johnson. 1798.
The power of population is so superior to the power in the earth to produce subsistence for man, that premature death must in some shape or other visit the human race
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gregory Claeys: The "Survival of the Fittest" and the Origins of Social Darwinism, in Journal of the History of Ideas, Vol. 61, No. 2, 2002, p. 223–240
- ^ Cormac Ó Gráda: Famine. A Short History, Princeton University Press 2009, ISBN 978-0-691-12237-3 (pp. 20, 203–206)
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Unrealized Horrors of Population Explosion - The New York Times". archive.is. 8 January 2020. Archived from the original on 8 January 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Mann, Charles C. "The Book That Incited a Worldwide Fear of Overpopulation". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ Moody, Oliver (31 August 2017). "Overpopulation is the biggest threat to mankind, Nobel laureates say". The Times. Retrieved 2 September 2017.
- ^ Ripple WJ, Wolf C, Newsome TM, Galetti M, Alamgir M, Crist E, Mahmoud MI, Laurance WF (13 November 2017). "World Scientists' Warning to Humanity: A Second Notice" (PDF). BioScience. 67 (12): 1026–1028. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix125.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ripple, William J.; Wolf, Christopher; Newsome, Thomas M; Barnard, Phoebe; Moomaw, William R (5 November 2019). "World Scientists' Warning of a Climate Emergency". BioScience. doi:10.1093/biosci/biz088. hdl:1808/30278. Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- ^ Carrington, Damian (5 November 2019). "Climate crisis: 11,000 scientists warn of 'untold suffering'". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 November 2019.
- ^ "Black death 'discriminated' between victims". 29 January 2008. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- ^ Roser, Max; Ritchie, Hannah; Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban (9 May 2013). "World Population Growth". Our World in Data.
- ^ Pimentel, David. "Overpopulation and sustainability." Petroleum Review 59 (2006): 34-36.
- ^ Hayami, Yujiro, and Vernon W. Ruttan. "Population growth and agricultural productivity." Technological Prospects and Population Trends. Routledge, 2020. 11-69.
- ^ Smil, Vaclav (1999). "Detonator of the population explosion" (PDF). Nature. 400 (6743): 415. Bibcode:1999Natur.400..415S. doi:10.1038/22672. S2CID 4301828.
- ^ Hopfenberg, Russell and Pimentel, David, "Human Population Numbers as a Function of Food Supply", Environment, Development and Sustainability, vol. 3, no. 1, March 2001, pp. 1–15
- ^ "Human Carrying Capacity is Determined by Food Availability" (PDF). Russel Hopfenberg, Duke University.
- ^ Abernathy, Virginia, Population Politics ISBN 0-7658-0603-7
- ^ "Population seven billion: UN sets out challenges". BBC. 22 May 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ "Current World Population". Worldometers. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ^ "A Brief Introduction to the History of Climate". Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratories. Retrieved 22 May 2013.
- ^ "Plague, Plague Information, Black Death Facts, News, Photos". National Geographic. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- ^ "Epidemics and pandemics: their impacts on human history". J. N. Hays (2005). p.46. ISBN 1-85109-658-2
- ^ "Historical Estimates of World Population". Census.gov. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "International Programs". census.gov. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013.
- ^ "The limits of a Green Revolution?". BBC News. 29 March 2007.
- ^ "United Nations, United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2011): World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision". Archived from the original on 12 May 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2012.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- ^ "modelling exponential growth" (PDF). esrl.noaa.gov.
- ^ Benatar, David (2008). Better Never to Have Been: The Harm of Coming into Existence. Oxford University Press. p. 167. ISBN 978-0199549269.
- ^ "U.S. and World Population Clock". Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- ^ "Population seven billion: UN sets out challenges". BBC. 26 October 2011. Retrieved 27 October 2011.
- ^ Coleman, Jasmine (31 October 2011). "World's 'seven billionth baby' is born". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ "7 billion people is a 'serious challenge'". United Press International.
- ^ United Nations. "Definition of projection variants". United Nation Population Division. United Nations. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ "World population projected to reach 9.8 billion in 2050, and 11.2 billion in 2100". Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat. June 2017.
- ^ "The end of high fertility is near" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- ^ "World Population Prospects" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- ^ Wilson, E.O. (2002). The Future of Life, Vintage ISBN 0-679-76811-4
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Ron Nielsen, The Little Green Handbook: Seven Trends Shaping the Future of Our Planet, Picador, New York (2006) ISBN 978-0-312-42581-4
- ^ Pentti Linkola, "Can Life Prevail?", Arktos Media, 2nd Revised ed. 2011. pp. 120–121. ISBN 1907166637
- ^ McKie, Robin (25 January 2017). "Biologists think 50% of species will be facing extinction by the end of the century". The Observer.
- ^ Leaders from the 1960s: A Biographical Sourcebook of American Activism. Greenwood Press, 1994. 1994. p. 318. ISBN 9780313274145.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "The short history of global living conditions and why it matters that we know it". Our World in Data. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ Daily, Gretchen C. and Ellison, Katherine (2003) The New Economy of Nature: The Quest to Make Conservation Profitable, Island Press ISBN 1559631546
- ^ Subramanian, Meera (2019). "Anthropocene now: influential panel votes to recognize Earth's new epoch". Nature News. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
Twenty-nine members of the AWG supported the Anthropocene designation and voted in favour of starting the new epoch in the mid-twentieth century, when a rapidly rising human population accelerated the pace of industrial production, the use of agricultural chemicals and other human activities.
- ^ Syvitski, Jaia; Waters, Colin N.; Day, John; et al. (2020). "Extraordinary human energy consumption and resultant geological impacts beginning around 1950 CE initiated the proposed Anthropocene Epoch". Communications Earth & Environment. 1 (32): 32. Bibcode:2020ComEE...1...32S. doi:10.1038/s43247-020-00029-y. S2CID 222415797.
Human population has exceeded historical natural limits, with 1) the development of new energy sources, 2) technological developments in aid of productivity, education and health, and 3) an unchallenged position on top of food webs. Humans remain Earth’s only species to employ technology so as to change the sources, uses, and distribution of energy forms, including the release of geologically trapped energy (i.e. coal, petroleum, uranium). In total, humans have altered nature at the planetary scale, given modern levels of human-contributed aerosols and gases, the global distribution of radionuclides, organic pollutants and mercury, and ecosystem disturbances of terrestrial and marine environments. Approximately 17,000 monitored populations of 4005 vertebrate species have suffered a 60% decline between 1970 and 2014, and ~1 million species face extinction, many within decades. Humans' extensive 'technosphere', now reaches ~30 Tt, including waste products from non-renewable resources.
- ^ "UN World Population Report 2001" (PDF). p. 31. Retrieved 16 December 2008.
- ^ Carrington, Damian (21 May 2018). "Humans just 0.01% of all life but have destroyed 83% of wild mammals – study". The Guardian. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ Baillie, Jonathan; Zhang, Ya-Ping (2018). "Space for nature". Science. 361 (6407): 1051. Bibcode:2018Sci...361.1051B. doi:10.1126/science.aau1397. PMID 30213888.
- ^ John T. Houghton (2004)."Global warming: the complete briefing Archived 3 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine". Cambridge University Press. p.326. ISBN 0-521-52874-7
- ^ "Once taboo, population enters climate debate". The Independent. 5 December 2009. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Agencies (6 January 2006). "Population control 'vital' to curbing climate change". the Guardian. Retrieved 24 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stone, Lyman (12 December 2017). "Why you shouldn't obsess about "overpopulation"". Vox. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ^ Best, Steven (2014). The Politics of Total Liberation: Revolution for the 21st Century. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 160. ISBN 978-1137471116.
By 2050 the human population will top 9 billion, and world meat consumption will likely double.
- ^ Devlin, Hannah (19 July 2018). "Rising global meat consumption 'will devastate environment'". The Guardian. Retrieved 28 September 2019.
- ^ Pimm, S. L.; Jenkins, C. N.; Abell, R.; Brooks, T. M.; Gittleman, J. L.; Joppa, L. N.; Raven, P. H.; Roberts, C. M.; Sexton, J. O. (30 May 2014). "The biodiversity of species and their rates of extinction, distribution, and protection". Science. 344 (6187). doi:10.1126/science.1246752. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 24876501. S2CID 206552746.
- ^ Stokstad, Erik (5 May 2019). "Landmark analysis documents the alarming global decline of nature". Science. AAAS. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
Driving these threats are the growing human population, which has doubled since 1970 to 7.6 billion, and consumption. (Per capita of use of materials is up 15% over the past 5 decades.)
- ^ Bradshaw, Corey J. A.; Ehrlich, Paul R.; Beattie, Andrew; Ceballos, Gerardo; Crist, Eileen; Diamond, Joan; Dirzo, Rodolfo; Ehrlich, Anne H.; Harte, John; Harte, Mary Ellen; Pyke, Graham; Raven, Peter H.; Ripple, William J.; Saltré, Frédérik; Turnbull, Christine; Wackernagel, Mathis; Blumstein, Daniel T. (2021). "Underestimating the Challenges of Avoiding a Ghastly Future". Frontiers in Conservation Science. 1. doi:10.3389/fcosc.2020.615419. S2CID 231589034.
- ^ Ceballos, Gerardo; Ehrlich, Paul R; Dirzo, Rodolfo (23 May 2017). "Biological annihilation via the ongoing sixth mass extinction signaled by vertebrate population losses and declines". PNAS. 114 (30): E6089–E6096. doi:10.1073/pnas.1704949114. PMC 5544311. PMID 28696295.
Much less frequently mentioned are, however, the ultimate drivers of those immediate causes of biotic destruction, namely, human overpopulation and continued population growth, and overconsumption, especially by the rich. These drivers, all of which trace to the fiction that perpetual growth can occur on a finite planet, are themselves increasing rapidly.
- ^ Crist, Eileen; Cafaro, Philip, eds. (2012). Life on the Brink: Environmentalists Confront Overpopulation. University of Georgia Press. p. 83. ISBN 978-0820343853.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Alberro, Heather. "Why we should be wary of blaming 'overpopulation' for the climate crisis". The Conversation. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ "David Attenborough warns 'human beings have overrun the world' in new film". inews.co.uk. 15 January 2020. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- ^ Crist, Eileen; Cafaro, Philip, eds. (2012). Life on the Brink: Environmentalists Confront Overpopulation. University of Georgia Press. p. 83. ISBN 978-0820343853.
- ^ "Another Inconvenient Truth: The World's Growing Population Poses a Malthusian Dilemma Archived 25 December 2013 at the Wayback Machine". Scientific American (2 October 2009).
- ^ David Pimentel, et al. "Will Limits of the Earth's Resources Control Human Numbers?" Archived 10 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Dieoff.org
- ^ Lester R. Brown, Gary Gardner, Brian Halweil (September 1998). Worldwatch Paper #143: Beyond Malthus: Sixteen Dimensions of the Population Problem Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Worldwatch Institute, ISBN 1-878071-45-9
- ^ "Misleading Math about the Earth: Scientific American". Sciam.com. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Overpopulation: The Making of a Myth". Retrieved 13 February 2010.
- ^ Young, A. (1999). "Is there Really Spare Land? A Critique of Estimates of Available Cultivable Land in Developing Countries". Environment, Development and Sustainability. 1: 3–18. doi:10.1023/A:1010055012699. S2CID 153970029.
- ^ Brown, Lester R. and Halweil, Brian (23 September 1999). Population Outrunning Water Supply as World Hits 6 Billion. Worldwatch Institute.
- ^ Fred Pearce (2007). When the Rivers Run Dry: Water—The Defining Crisis of the Twenty-first Century. Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-8573-8.
- ^ Worldwatch, The (27 April 2012). Outgrowing the Earth: The Food Security Challenge in an Age of Falling Water Tables and Rising Temperatures: Books: Lester R. Brown. ISBN 978-0393060706.
- ^ "Finding answers to the world's drinking water crisis". BBC News. 1 August 2021. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ^ McGranahan, G.; Lewin, S.; Fransen, T.; Hunt, C.; Kjellén, M.; Pretty, J.; Stephens, C.; Virgin, I. (2000). "News and notes: Environmental change and human health in countries of Africa, the Caribbean and the Pacific". Global Change and Human Health. 1: 9. doi:10.1023/A:1011567429284. S2CID 151010794.
- ^ Huxley, Aldous. "Brave New World Revisited: overpopulation". Retrieved 9 July 2014. (A non-fiction book, with the entire book focused on the effects of human overpopulation on human affairs including both societal and individual concerns.)
- ^ Bartlett, Albert A. (2000). "Democracy Cannot Survive Overpopulation". Population and Environment. 22 (1): 63–71. doi:10.1023/A:1006681515521. S2CID 154695448.
- ^ "World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision" (PDF). United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 December 2018. Retrieved 2 December 2018.
- ^ "Population Projections". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ Kaneda, Toshiko (June 2014). "Understanding Population Projections: Assumptions Behind the Numbers" (PDF). Population Reference Bureau.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Roser, Max (9 May 2013). "Future Population Growth". Our World in Data.
- ^ Roser, Max (18 June 2019). "Two centuries of rapid global population growth will come to an end". Our World in Data.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2019". United Nations, Dept of Economic and Social Affairs. 2019.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Total Population Both Sexes, Medium Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "World Population Prospects 2019, Dept of Economic and Social Affairs, File: Total Fertility". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- ^ Vollset, Stein Emil; Goren, Emily; Yuan, Chun-Wei; Cao, Jackie; Smith, Amanda E.; Hsiao, Thomas; Bisignano, Catherine; Azhar, Gulrez S.; Castro, Emma; Chalek, Julian; Dolgert, Andrew J. (17 October 2020). "Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: a forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study". The Lancet. 396 (10258): 1285–1306. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30677-2. ISSN 0140-6736. PMC 7561721. PMID 32679112.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Population Growth Rate, Median Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- ^ "World's Population is Projected to Nearly Stop Growing by the end of the Century". 17 June 2019.
- ^ Kaneda, Toshiko; Falk, Marissa; Patierno, Kaitlyn (27 March 2021). "Understanding and Comparing Population Projections in Sub-Saharan Africa". PRB.
- ^ "Understanding and Comparing Population Projections in Sub-Saharan Africa | PRB".
- ^ Morales, Alex (24 October 2006). "Canada". Bloomberg. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ "WWF – Living Planet Report 2006". Panda.org. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ "WWF Living planet report". Panda.org. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ "Data and Methodology". footprintnetwork.org. Retrieved 6 March 2020.
- ^ Martin, Roger (2010). "Stopping at two children is better for the planet". BBC HARDtalk. Interviewed by Carrie Gracie
- ^ Carrington, Damian (30 September 2014). "Earth has lost half of its wildlife in the past 40 years, says WWF". The Guardian. Retrieved 3 January 2017.
- ^ "Publications – Global Footprint Network". Retrieved 17 September 2017.
- ^ Jeroen C.J.M. van den Bergh; Harmen Verbruggen (1999). "Spatial sustainability, trade and indicators: an evaluation of the 'ecological footprint'" (PDF). Ecological Economics. 29 (1): 61–72. doi:10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00032-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 October 2007.
- ^ "Planning and Markets: Peter Gordon and Harry W. Richardson". Pam.usc.edu. Archived from the original on 27 June 2010. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ Cohen, J.E. (1995). How many people can the earth support? W.W. Norton & Company, New York, NY, USA.
- ^ Van Den Bergh, Jeroen C. J. M.; Rietveld, Piet (2004). "Reconsidering the Limits to World Population: Meta-analysis and Meta-prediction". BioScience. 54 (3): 195. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0195:RTLTWP]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0006-3568.
- ^ One Planet, How Many People? A Review of Earth’s Carrying Capacity United Nations, June 2012
- ^ Carrington, Damian (22 March 2018). "Paul Ehrlich: 'Collapse of civilisation is a near certainty within decades'". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 August 2020.
- ^ A PLANET OF 3 BILLION | Kirkus Reviews.
- ^ Sasser, Jade (13 November 2018). On infertile ground : population control and women's rights in the era of climate change. New York. ISBN 978-1-4798-7343-2. OCLC 1029075188.
- ^ Ehrlich, Paul R; Ehrlich, Anne H (2004), One with Nineveh: Politics, Consumption, and the Human Future, Island Press/Shearwater Books, pp. 181–205 (chapter 6)
- ^ Ehrlich, Paul R.; Ehrlich, Anne H.; Daily, Gretchen C. (1995), The Stork and the Plow: The Equity Answer to the Human Dilemma, Grosset/Putnam Books
- ^ Kelly, Karina (13 September 1995). "A Chat with Tim Flannery on Population Control". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 13 January 2010. Retrieved 23 April 2010. "Well, Australia has by far the world's least fertile soils".
- ^ "Flannery calls for population inquiry". www.abc.net.au. 19 November 2009. Retrieved 24 August 2021.
- ^ Lifeblood: How to Change the World One Dead Mosquito at a Time, Alex Perry p9
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ryerson, William N. (2010). The Post Carbon Reader: Managing the 21st Century's Sustainability Crises, "Ch.12: Population: The Multiplier of Everything Else". Healdsburg, Calif.: Watershed Media. pp. 153–174. ISBN 978-0970950062.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Thanks to education, global fertility could fall faster than expected". The Economist. 2 February 2019. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ "Population growth driving climate change, poverty: experts Archived 23 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine". Agence France-Presse (21 September 2009).
- ^ "Netherlands Again Number One Donor to United Nations Population Fund". United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA).
- ^ "Maternal mortality ratio falling too slowly to meet goal Archived 31 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine". WHO (12 October 2007).
- ^ Fornos, Werner (10 December 2001). "Q: should the United Nations support more family-planning services for poor countries?". Insight on the News.
- ^ "Population Matters search on 'reproductive rights'". populationmatters.org. Population Matters.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Pollack Petchesky, Rosalind. "From population control to reproductive rights: Feminist fault lines." Reproductive Health Matters 3.6 (1995): 152-161.
- ^ "Birth rates 'must be curbed to win war on global poverty'". The Independent. London. 31 January 2007. Archived from the original on 19 January 2008. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- ^ Vinay Lal. Indira Gandhi Archived 29 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine, UCLA College of Letters and Science
- ^ "'Cars for sterilisation' campaign". 1 July 2011. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016 – via bbc.com.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The forgotten roots of India's mass sterilization program - The Washi…". archive.is. 17 May 2020. Archived from the original on 17 May 2020. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ Vajk, J.Peter (1 January 1976). "The impact of space colonization on world dynamics". Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 9 (4): 361–99. doi:10.1016/0040-1625(76)90019-6. ISSN 0040-1625.
- ^ O'Neill, Colonies in Space; Pournelle, A Step Farther Out.
- ^ "Stephen Hawking: mankind must move to outer space within a century - Telegraph". web.archive.org. 17 August 2014. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ G. K. O'Neill. The High Frontier: Human Colonies in Space. Morrow, 1977.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Greetings, Carbon-Based Bipeds! (1999) Arthur C. Clarke, Voyager ISBN 0-00-224698-8
- ^ The Good Earth Is Dying (1971) Isaac Asimov (published in Der Spiegel)
- ^ Mining the Sky (1996) John S. Lewis. Addison Wesley. ISBN 0-201-47959-1
- ^ "UN Habitat calling urban living 'a good thing". BBC News. 27 June 2007. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ "National Geographic Magazine; Special report 2008: Changing Climate (Village Green-article by Michelle Nijhuis)". Michellenijhuis.com. 29 September 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ "UN Habitat calling to rethink urban planning". Unhabitat.org. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ Ehrlich, Population Bomb 1968 p.152-p.53
- ^ "David Suzuki fires off from the 'death zone' at Trudeau, Weaver and a broken system". National Observer. 5 March 2018.
- ^ "Figure 8: Population by Total Fertility (millions)" in World Population Prospects, the 2010 Revision. United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2011)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Dyett, Jordan; Thomas, Cassidy (18 January 2019). "Overpopulation Discourse: Patriarchy, Racism, and the Specter of Ecofascism". Perspectives on Global Development and Technology. 18 (1–2): 205–224. doi:10.1163/15691497-12341514. ISSN 1569-1500.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "David Attenborough's claim that humans have overrun the planet is his most popular comment". www.newstatesman.com. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hartmann, Betsy (2016). Reproductive rights and wrongs: the global politics of population control. Haymarket Books. p. 26.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Dominic Lawson: The population timebomb is a myth The doom-sayers are becoming more fashionable just as experts are coming to the view it has all been one giant false alarm". The Independent. UK. 18 January 2011. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b https://www.fraserinstitute.org/sites/default/files/ExplodingPopulationMyths.pdf
- ^ A Reverse ‘Handmaid’s Tale’ Is Just as Horrifying — Get the Facts Straight on Population Growth cato.org, Chelsea Follett, April 24, 2018M\
- ^ Vollset, Stein Emil; Goren, Emily; Yuan, Chun-Wei; Cao, Jackie; Smith, Amanda E.; Hsiao, Thomas; Bisignano, Catherine; Azhar, Gulrez S.; Castro, Emma; Chalek, Julian; Dolgert, Andrew J. (17 October 2020). "Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: a forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study". The Lancet. 396 (10258): 1285–1306. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30677-2. ISSN 0140-6736. PMC 7561721. PMID 32679112.
- ^ "The best news of 2020? Humanity may never hit the 10 billion mark". Mongabay Environmental News. 10 September 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ Follett, Chelsea (21 July 2020). "Neo‐Malthusianism and Coercive Population Control in China and India: Overpopulation Concerns Often Result in Coercion". CATO Institute. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ UNFPA (1994). Programme of Action: Adopted at the International Conference of Population and development, Cairo, 5-13 September 1994. UN Population Fund. pp. Section 7.3. ISBN 0-89714-696-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Thomas, Cassidy; Gosink, Elhom (25 March 2021). "At the Intersection of Eco-Crises, Eco-Anxiety, and Political Turbulence: A Primer on Twenty-First Century Ecofascism". Perspectives on Global Development and Technology. 20 (1–2): 30–54. doi:10.1163/15691497-12341581. ISSN 1569-1500. S2CID 233663634.
- ^ Kashwan, Prakash (13 September 2020). "How American Environmentalism's Racist Roots Shaped Our Thoughts on Conservation". The Wire Science. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ "Population panic lets rich people off the hook for the climate crisis they are causing | George Monbiot". the Guardian. 26 August 2020. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Chamie, Joseph (2 August 2021). "Billionaires 'kvetching' about population collapse". The Hill. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- ^ Döpfner, Mathias. "Elon Musk reveals Tesla's plan to be at the forefront of a self-driving-car revolution — and why he wants to be buried on Mars". Business Insider. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Clifford, Catherine (30 August 2019). "Elon Musk and Jack Ma agree: The biggest problem the world will face is population collapse". CNBC. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". population.un.org. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
Further reading[]
| Look up overpopulation in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Human overpopulation |
- David Foreman, Man Swarm: How Overpopulation is Killing the Wild World. Livetrue Books, 2015. ISBN 978-0986383205
- Karen Shragg, Move Upstream: A Call to Solve Overpopulation. ISBN 978-0988493834 (published November 2015). Discussion of the book by the author, March 2017 (video, 91 minutes).
- Alan Weisman. Countdown: Our Last, Best Hope for a Future on Earth? Little, Brown and Company, (2013) ISBN 0316097756
- Thomas Robertson, The Malthusian Moment: Global Population Growth and the Birth of American Environmentalism (2012), Rutgers University Press
- J.R. McNeill, Peter Engelke, The Great Acceleration: An Environmental History of the Anthropocene since 1945 (2016)
- Human overpopulation
- Population ecology
- World population
- Demographic economic problems
- Doomsday scenarios
- Environmental controversies
- Political controversies