Ibn Arabi
al-Shaykh al-Akbar Ibn ʿArabi إبن عربـي | |
|---|---|
 Ibn Arabi with students | |
| Born | 28 July 1165 |
| Died | 16 November 1240 (aged 75) |
| School | Founder of Akbariyya |
Main interests |
|
show
Influences | |
show
Influenced | |
| Arabic name | |
| Personal (Ism) | Muḥammad |
| Patronymic (Nasab) | ibn ʿAlī ibn Muḥammad ibnʿArabī |
| Teknonymic (Kunya) | Abu Abdullah |
| Epithet (Laqab) | Ibn ʿArabi |
| Toponymic (Nisba) | al-Ḥātimī aṭ-Ṭāʾī |
| hidePart of a series on Islam Sufism |
|---|
 |
|
|
Ibn ʿArabi (Arabic: ابن عربي) (1165 – 1240), full name Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī ibn Muḥammad ibn al-ʿArabī al-Ḥātimī al-Ṭāʾī al-Andalusī al-Mursī al-Dimashqī Arabic: أبو عبد الله محـمـد بن علي بن محمـد إبن عربـي الحاتمي الطائي), nicknamed al-Qushayri and Sultan al-ʿArifin, was an Andalusian Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher, extremely influential within Islamic thought. Out of the 850 works attributed to him, some 700 are authentic while over 400 are still extant. His cosmological teachings became the dominant worldview in many parts of the Muslim world.[3]
He is renowned among practitioners of Sufism by the names al-Shaykh al-Akbar ("the Greatest Shaykh"; from here the Akbariyya or Akbarian school derives its name), Muḥyiddin ibn Arabi, and was considered a saint.[4][5] He is also known as Shaikh-e-Akbar Mohi-ud-Din Ibn-e-Arabi throughout the Middle East.[6]
Biography[]
'Abū 'Abdullāh Muḥammad ibn 'Alī ibn Muḥammad ibn `Arabī al-Ḥātimī aṭ-Ṭāʾī (أبو عبد الله محمد ابن علي ابن محمد ابن عربي الحاتمي الطائي) was a Sufi mystic, poet, and philosopher Arab from the Tayy tribe[7][8] born in Murcia, Spain on the 17th of Ramaḍān (26 July 1165 AD).[9]
Ibn Arabi was Sunni, although his writings on the Twelve Imams were also popularly received among Shia.[10] It is debated whether or not he ascribed to the Zahiri madhab which was later merged with the Hanbali school.[11]
After his death, Ibn Arabi's teachings quickly spread throughout the Islamic world. His writings were not limited to the Muslim elites, but made their way into other ranks of society through the widespread reach of the Sufi orders. Arabi's work also popularly spread through works in Persian, Turkish, and Urdu. Many popular poets were trained in the Sufi orders and were inspired by Arabi's concepts.[12]
Others scholars in his time like al-Munawi, Ibn 'Imad al-Hanbali and al-Fayruzabadi all praised Ibn Arabi as ''A righteous friend of Allah and faithful scholar of knowledge'', ''the absolute mujtahid without doubt'' and ''the imam of the people of shari'a both in knowledge and in legacy, the educator of the people of the way in practice and in knowledge, and the shaykh of the shaykhs of the people of truth though spiritual experience (dhawq) and understanding''.[13]
Family[]
Ibn Arabi's paternal ancestry was from the South Arabian tribe of Tayy,[14] and his maternal ancestry was North African Berber.[15] Al-Arabi writes of a deceased maternal uncle, Yahya ibn Yughan al-Sanhaji, a prince of Tlemcen, who abandoned wealth for an ascetic life after encountering a Sufi mystic.[16] His father, ‘Ali ibn Muḥammad, served in the Army of Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Saʿd ibn Mardanīsh, the ruler of Murcia.[17] When Ibn Mardanīš died in 1172 AD, his father shifted allegiance to the Almohad Sultan, Abū Ya’qūb Yūsuf I, and returned to government service. His family then relocated from Murcia to Seville.[6] Ibn Arabi grew up at the ruling court and received military training.[17]
As a young man Ibn Arabi became secretary to the governor of Seville. He married Maryam, a woman from an influential family.[17]
Education[]

Ibn Arabi writes that as a child he preferred playing with his friends to spending time on religious education. He had his first vision of God in his teens and later wrote of the experience as "the differentiation of the universal reality comprised by that look". Later he had several more visions of Jesus and called him his "first guide to the path of God".[citation needed] His father, on noticing a change in him, had mentioned this to philosopher and judge, Ibn Rushd (Averroes),[18] who asked to meet Ibn Arabi. Ibn Arabi said that from this first meeting, he had learned to perceive a distinction between formal knowledge of rational thought and the unveiling insights into the nature of things. He then adopted Sufism and dedicated his life to the spiritual path.[18] When he later moved to Fez, in Morocco, where Mohammed ibn Qasim al-Tamimi became his spiritual mentor.[19] In 1200 he took final leave from his master Yūsuf al-Kūmī, then living in the town of Salé.[citation needed]
Pilgrimage to Mecca[]

Ibn Arabi left Andalusia for the first time at age 36 and arrived at Tunis in 1193.[20] After a year in Tunisia, he returned to Andalusia in 1194. His father died soon after Ibn Arabi arrived at Seville. When his mother died some months later he left Andalusia for the second time and travelled with his two sisters to Fez, Morocco in 1195. He returned to Córdoba, Andalusia in 1198, and left Andalusia crossing from Gibraltar for the last time in 1200.[21] While there, he received a vision instructing him to journey east. After visiting some places in the Maghreb, he left Tunisia in 1201 and arrived for the Hajj in 1202.[22] He lived in Mecca for three years,[6] and there began writing his work Al-Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya (الفتوحات المكية) – 'The Meccan Illuminations'.
Journeys north[]

After spending time in Mecca, he traveled throughout Syria, Palestine, Iraq and Anatolia.[6]
In 1204, Ibn Arabi met Shaykh Majduddīn Isḥāq ibn Yūsuf (شيخ مجد الدين إسحاق بن يوسف), a native of Malatya and a man of great standing at the Seljuk court. This time Ibn Arabi was travelling north; first they visited Medina and in 1205 they entered Baghdad. This visit offered him a chance to meet the direct disciples of Shaykh ‘Abd al-Qādir Jīlānī. Ibn Arabi stayed there only for 12 days because he wanted to visit Mosul to see his friend ‘Alī ibn ‘Abdallāh ibn Jāmi’, a disciple of the mystic Qaḍīb al-Bān (471-573 AH/1079-1177 AD; قضيب البان).[23] There he spent the month of Ramaḍan and composed Tanazzulāt al-Mawṣiliyya (تنزلات الموصلية), Kitāb al-Jalāl wa’l-Jamāl (كتاب الجلال والجمال, "The Book of Majesty and Beauty") and Kunh mā lā Budda lil-MurīdMinhu.[24]:176
Return south[]
In the year 1206 Ibn Arabi visited Jerusalem, Mecca and Egypt. It was his first time that he passed through Syria, visiting Aleppo and Damascus.
Later in 1207 he returned to Mecca where he continued to study and write, spending his time with his friend Abū Shujā bin Rustem and family, including Niẓām.[24]:181
The next four to five years of Ibn Arabi's life were spent in these lands and he also kept travelling and holding the reading sessions of his works in his own presence.[25]
Death[]

On 22 Rabī‘ al-Thānī 638 AH (8 November 1240) at the age of seventy-five, Ibn Arabi died in Damascus.[6]
Islamic law[]
Although Ibn Arabi stated on more than one occasion that he did not blindly follow any one of the schools of Islamic jurisprudence, he was responsible for copying and preserving books of the Zahirite or literalist school, to which there is fierce debate whether or not Ibn Arabi followed that school.[26][27] Ignaz Goldziher held that Ibn Arabi did in fact belong to the Zahirite or Hanbali school of Islamic jurisprudence.[28] Hamza Dudgeon claims that Addas, Chodkiewizc, Gril, Winkel and Al-Gorab mistakenly attribute to Ibn ʿArabī non-madhhabism.[29]
On an extant manuscript of Ibn Ḥazm, as transmitted by Ibn ʿArabī, Ibn ʿArabī gives an introduction to the work where he describes a vision he had:
“I saw myself in the village of Sharaf near Siville; there I saw a plain on which rose an elevation. On this elevation the Prophet stood, and a man whom I did not know, approached him; they embraced each other so violently that they seemed to interpenetrate and become one person. Great brightness concealed them from the eyes of the people. ‘I would like to know,’ I thought, ‘who is this strange man.’ Then I heard some one say: ‘This is the traditionalist ʿAlī Ibn Ḥazm.’ I had never heard Ibn Ḥazm’s name before. One of my shaykhs, whom I questioned, informed me that this man is an authority in the field of science of Hadeeth.”
— Goldziher, The Ẓāhirīs: Their Doctrine and Their History (1971)
Goldziher says, “The period between the sixth (hijri) and the seventh century seems also to have been the prime of the Ẓāhirite school in Andalusia.”[30]
Ibn Arabi did delve into specific details at times, and was known for his view that religiously binding consensus could only serve as a source of sacred law if it was the consensus of the first generation of Muslims who had witnessed revelation directly.[31]
Ibn Arabi also expounded on Sufi Allegories of the Sharia building upon previous work by Al-Ghazali and al-Hakim al-Tirmidhi.[32]
Al-Insān al-kāmil[]
The doctrine of perfect man (Al-Insān al-Kāmil) is popularly considered an honorific title attributed to Muhammad having its origins in Islamic mysticism, although the concept's origin is controversial and disputed.[33] Arabi may have first coined this term in referring to Adam as found in his work Fusus al-hikam, explained as an individual who binds himself with the Divine and creation.[34]
Taking an idea already common within Sufi culture, Ibn Arabi applied deep analysis and reflection on the concept of a perfect human and one's pursuit in fulfilling this goal. In developing his explanation of the perfect being, Ibn Arabi first discusses the issue of oneness through the metaphor of the mirror.[35]
In this philosophical metaphor, Ibn Arabi compares an object being reflected in countless mirrors to the relationship between God and his creatures. God's essence is seen in the existent human being, as God is the object and human beings the mirrors. Meaning two things; that since humans are mere reflections of God there can be no distinction or separation between the two and, without God the creatures would be non-existent. When an individual understands that there is no separation between human and God they begin on the path of ultimate oneness. The one who decides to walk in this oneness pursues the true reality and responds to God's longing to be known. The search within for this reality of oneness causes one to be reunited with God, as well as, improve self-consciousness.[35]
The perfect human, through this developed self-consciousness and self-realization, prompts divine self-manifestation. This causes the perfect human to be of both divine and earthly origin. Ibn Arabi metaphorically calls him an Isthmus. Being an Isthmus between heaven and Earth, the perfect human fulfills God's desire to be known. God's presence can be realized through him by others. Ibn Arabi expressed that through self manifestation one acquires divine knowledge, which he called the primordial spirit of Muhammad and all its perfection. Ibn Arabi details that the perfect human is of the cosmos to the divine and conveys the divine spirit to the cosmos.[35]
Ibn Arabi further explained the perfect man concept using at least twenty-two different descriptions and various aspects when considering the Logos.[35] He contemplated the Logos, or "Universal Man", as a mediation between the individual human and the divine essence.[36]
Ibn Arabi believed Muhammad to be the primary perfect man who exemplifies the morality of God.[37] Ibn Arabi regarded the first entity brought into existence was the reality or essence of Muhammad (al-ḥaqīqa al-Muhammadiyya), master of all creatures, and a primary role-model for human beings to emulate. Ibn Arabi believed that God's attributes and names are manifested in this world, with the most complete and perfect display of these divine attributes and names seen in Muhammad. Ibn Arabi believed that one may see God in the mirror of Muhammad. He maintained that Muhammad was the best proof of God and, by knowing Muhammad, one knows God.[38]
Ibn Arabi also described Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and all other prophets and various Anbiya' Allah (Muslim messengers) as perfect men, but never tires of attributing lordship, inspirational source, and highest rank to Muhammad.[38][39] Ibn Arabi compares his own status as a perfect man as being but a single dimension to the comprehensive nature of Muhammad.[39] Ibn 'Arabi makes extraordinary assertions regarding his own spiritual rank, but qualifying this rather audacious correlation by asserting his "inherited" perfection is only a single dimension of the comprehensive perfection of Muhammad.[39]
Reaction[]
The reaction of Ibn 'Abd as-Salam, a Muslim scholar respected by both Ibn Arabi's supporters and detractors, has been of note due to disputes over whether he himself was a supporter or detractor. All parties have claimed to have transmitted Ibn 'Abd as-Salam's comments from his student Ibn Sayyid al-Nas, yet the two sides have transmitted very different accounts. Ibn Taymiyyah, Al-Dhahabi and Ibn Kathir all transmitted Ibn 'Abd as-Salam's comments as a criticism, while Fairuzabadi, Al-Suyuti, Ahmed Mohammed al-Maqqari and Yusuf an-Nabhani have all transmitted the comments as praise.[40]
Creed[]
His best-known book, entitled 'al-Futuhat al-Makkiyya' (The Meccan Victories or Illuminations) which begins with a statement of doctrine (belief) about which al-Safadi (d. 764/1363) said: "I saw (read) that (al-Futuhat al-Makkiyya) from beginning to end. It consists of the doctrine of Abu al-Hasan al-Ash'ari without any difference (deviation) whatsoever."[41][42]
Works[]
Some 800 works are attributed to Ibn Arabi, although only some have been authenticated. Recent research suggests that over 100 of his works have survived in manuscript form, although most printed versions have not yet been critically edited and include many errors.[43] A specialist of Ibn 'Arabi, William Chittick, referring to Osman Yahya's definitive bibliography of the Andalusian's works, says that, out of the 850 works attributed to him, some 700 are authentic while over 400 are still extant.[44]
- The Meccan Illuminations (Al-Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya), his largest work in 37 volumes originally and published in 4 or 8 volumes in modern times, discussing a wide range of topics from mystical philosophy to Sufi practices and records of his dreams/visions. It totals 560 chapters.[6] In modern editions it amounts to some 15 000 pages.[45]
- The Ringstones of Wisdom (also translated as The Bezels of Wisdom), or Fusus al-Hikam. Composed during the later period of Ibn 'Arabi's life, the work is sometimes considered his most important and can be characterized as a summary of his teachings and mystical beliefs. It deals with the role played by various prophets in divine revelation.[46][47][48] The attribution of this work (Fusus al-Hikam) to Ibn Arabi is debated and in at least one source[49] is described as a forgery and false attribution to him reasoning that there are 74 books in total attributed to Sheikh Ibn Arabi of which 56 have been mentioned in "Al Futuhat al-Makkiyya" and the rest mentioned in the other books cited therein. However many other scholars accept the work as genuine.[50][51]
- The Dīwān, his collection of poetry spanning five volumes, mostly unedited. The printed versions available are based on only one volume of the original work.
- The Holy Spirit in the Counselling of the Soul (Rūḥ al-quds), a treatise on the soul which includes a summary of his experience from different spiritual masters in the Maghrib. Part of this has been translated as Sufis of Andalusia, reminiscences and spiritual anecdotes about many interesting people whom he met in al-Andalus.
- Contemplation of the Holy Mysteries (Mashāhid al-Asrār), probably his first major work, consisting of fourteen visions and dialogues with God.
- Divine Sayings (Mishkāt al-Anwār), an important collection made by Ibn 'Arabī of 101 hadīth qudsī
- The Book of Annihilation in Contemplation (K. al-Fanā' fi'l-Mushāhada), a short treatise on the meaning of mystical annihilation (fana).
- Devotional Prayers (Awrād), a widely read collection of fourteen prayers for each day and night of the week.
- Journey to the Lord of Power (Risālat al-Anwār), a detailed technical manual and roadmap for the "journey without distance".
- The Book of God's Days (Ayyām al-Sha'n), a work on the nature of time and the different kinds of days experienced by gnostics
- The Fabulous Gryphon of the West ('Unqā' Mughrib), a book on the meaning of sainthood and its culmination in Jesus and the Mahdī
- The Universal Tree and the Four Birds (al-Ittihād al-Kawnī), a poetic book on the Complete Human and the four principles of existence
- Prayer for Spiritual Elevation and Protection ('al-Dawr al-A'lā), a short prayer which is still widely used in the Muslim world
- The Interpreter of Desires (Tarjumān al-Ashwāq), a collection of nasībs which, in response to critics, Ibn Arabi republished with a commentary explaining the meaning of the poetic symbols.
- Divine Governance of the Human Kingdom (At-Tadbidrat al-ilahiyyah fi islah al-mamlakat al-insaniyyah).
- The Four Pillars of Spiritual Transformation (Hilyat al-abdāl) a short work on the essentials of the spiritual Path
The Meccan Illuminations (Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya)[]
According to Claude Addas, Ibn Arabi began writing Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya after he arrived in Mecca in 1202. After almost thirty years, the first draft of Futūḥāt was completed in December 1231 (629 AH), and Ibn Arabi bequeathed it to his son.[52] Two years before his death, Ibn ‘Arabī embarked on a second draft of the Futūḥāt in 1238 (636 AH),[52] of which included a number of additions and deletions as compared with the previous draft, that contains 560 chapters. The second draft, which the most widely circulated and used, was bequeathed to his disciple, Sadr al-Din al-Qunawi. There are many scholars attempt to translate this book from Arabic into other languages, but there is no complete translation of Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya to this day.
Diagram of "Plain of Assembly"(Ard al-Hashr) on the Day of Judgment, from autograph manuscript of Futuhat al-Makkiyya, ca. 1238 (photo: after Futuhat al-Makkiyya, Cairo edition, 1911).

Diagram of Jannat Futuhat al-Makkiyya, c. 1238 (photo: after Futuhat al-Makkiyya, Cairo edition, 1911).
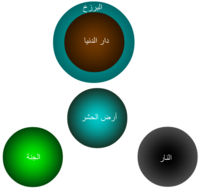
Diagram showing world, heaven, hell and barzakh Futuhat al-Makkiyya, c. 1238 (photo: after Futuhat al-Makkiyya, Cairo edition, 1911).
The Bezels of Wisdom (Fuṣūṣ al-Ḥikam)[]
There have been many commentaries on Ibn 'Arabī's Fuṣūṣ al-Ḥikam: Osman Yahya named more than 100 while Michel Chodkiewicz precises that "this list is far from exhaustive."[53] The first one was Kitab al-Fukūk written by Ṣadr al-Dīn al-Qunawī who had studied the book with Ibn 'Arabī; the second by Qunawī's student, Mu'ayyad al-Dīn al-Jandi, which was the first line-by-line commentary; the third by Jandī's student, Dawūd al-Qaysarī, which became very influential in the Persian-speaking world. A recent English translation of Ibn 'Arabī's own summary of the Fuṣūṣ, Naqsh al-Fuṣūṣ (The Imprint or Pattern of the Fusus) as well a commentary on this work by 'Abd al-Raḥmān Jāmī, Naqd al-Nuṣūṣ fī Sharḥ Naqsh al-Fuṣūṣ (1459), by William Chittick was published in Volume 1 of the Journal of the Muhyiddin Ibn 'Arabi Society (1982).[54]
Critical editions and translations of Fuṣūṣ al-Ḥikam[]
The Fuṣūṣ was first critically edited in Arabic by 'Afīfī (1946) that become the standard in scholarly works. Later in 2015, Ibn al-Arabi Foundation in Pakistan published the Urdu translation, including the new critical of Arabic edition.[55]
The first English translation was done in partial form by Angela Culme-Seymour[56] from the French translation of Titus Burckhardt as Wisdom of the Prophets (1975),[57] and the first full translation was by Ralph Austin as Bezels of Wisdom (1980).[58] There is also a complete French translation by Charles-Andre Gilis, entitled Le livre des chatons des sagesses (1997). The only major commentary to have been translated into English so far is entitled Ismail Hakki Bursevi's translation and commentary on Fusus al-hikam by Muhyiddin Ibn 'Arabi, translated from Ottoman Turkish by Bulent Rauf in 4 volumes (1985–1991).
In Urdu, the most widespread and authentic translation was made by Shams Ul Mufasireen Bahr-ul-uloom Hazrat (Muhammad Abdul Qadeer Siddiqi Qadri -Hasrat), the former Dean and Professor of Theology of the Osmania University, Hyderabad. It is due to this reason that his translation is in the curriculum of Punjab University. Maulvi Abdul Qadeer Siddiqui has made an interpretive translation and explained the terms and grammar while clarifying the Shaikh's opinions. A new edition of the translation was published in 2014 with brief annotations throughout the book for the benefit of contemporary Urdu reader.[59]
In fiction[]
In the Turkish television series Diriliş: Ertuğrul, Ibn Arabi was portrayed by Ozman Sirgood.[60] In 2017, Saudi Arabian novelist Mohammed Hasan Alwan won the International Prize for Arabic Fiction for his novel "A Small Death," a fictionalized account of Ibn Arabi's life.[61]
See also[]
- Mujaddid
- Akbariyya
- Ivan Aguéli
- Hossein Nasr
- Mahmud Shabistari
- Miguel Asín Palacios
- Ain al-Kheil Mosque
- Ibn al-Arif
- Ibn Masarra
- Ibn Barrajan
- Abu-l-Qasim Ahmad ibn al-Husayn ibn Qasi
References[]
Sources[]
As of , this article uses content from "A Concise biography of Ibn 'Arabi", which is licensed in a way that permits reuse under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, but not under the GFDL. All relevant terms must be followed.
Citations[]
- ^ Ozgur, Koca. Said Nursi's Synthesis of Ash'arite Occasionalism and Ibn 'Arabi's Metaphysical Cosmology: "Diagonal Occasionalism," Modern Science", and "Free Will". UMI Dissertations Publishing. p. 217. ISBN 9781303619793.
- ^ Ramin Jahanbegloo, In Search of the Sacred : A Conversation with Seyyed Hossein Nasr on His Life and Thought, ABC-CLIO (2010), p. 59
- ^ Ibrahim Kalin, Salim Ayduz The Oxford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Science, and Technology in Islam, Vol. 1 (Oxford University Press, 2014 ISBN 9780199812578), p. 162
- ^ Chittick, William C. (April 2007). Ibn 'Arabi: Heir to the Prophets. Oxford: Oneworld Publications. p. 1. ISBN 978-1851685110.
- ^ Al-Suyuti, Tanbih al-Ghabi fi Tanzih Ibn ‘Arabi (p. 17-21)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "The Meccan Revelations". World Digital Library. 1900–1999. Retrieved 2013-07-14.
- ^ "Ibn al-ʿArabī | Muslim mystic".
- ^ "Names and Titles of Ibn Arabi".
- ^ Chittick, William (Summer 2018). "Ibn Arabi". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
Ibn ‘Arabî referred to himself with fuller versions of his name, such as Abû ‘Abdallâh Muhammad ibn ‘Alî ibn al-‘Arabî al-Tâ’î al-Hâtimî (the last three names indicating his noble Arab lineage)
- ^ Hossein Nasr, Seyyed (1 Jan 1999). Sufi Essays. Chicago: Kazi Publications, Inc. p. 116. ISBN 978-1871031416.
It is well known that Ibn 'Arabi, from the point of view of his madhhab was a Sunni...but it is also known that he wrote a treatise on the twelve Shiite imams which has always been popular among Shiites.
- ^ Chodkiewicz, Michel (1993). An Ocean Without Shore: Ibn Arabi, the Book, and the Law. SUNY Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-0791416259.
- ^ Chittick 2007, p. 2-3.
- ^ Ibn, Khafif (1999). Correct Islamic Doctrine/Islamic Doctrine. ISCA. ISBN 978-1-930409-01-9.
- ^ "Ibn al-ʿArabī | Muslim mystic". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ Hirtenstein, Stephen (1999). The Unlimited Mercifier: The Spiritual Life and Thought of Ibn 'Arabi. Oxford: Anqa Publishing. p. 32. ISBN 978-1883991296.
Like many Andalusians, he came of mixed parentage: his father's name indicates an Arab family, which had probably emigrated to Andalusia in the early years of the Arab conquest, while his mother seems to have come from a Berber family...
- ^ Hirtenstein, Stephen C. (September 1999). The Unlimited Mercifier: The Spiritual Life and Thought of Ibn 'Arabi. p. 252. ISBN 978-1905937387.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Chittick 2007, p. 4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Chittick 2007, p. 5.
- ^ John Renard (18 May 2009). Tales of God's Friends: Islamic Hagiography in Translation. University of California Press. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-520-25896-9. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ Addas, Claude (2019). Ibn Arabi: The Voyage of No Return (Second ed.). Cambridge: Islamic Texts Society. p. 51. ISBN 9781911141402.
- ^ Addas, Claude (2019), p.68-69
- ^ Chittick 2007, p. 5
- ^ Testament to Qaḍīb al-Bān's life exists in a manuscript at the University of Baghdad (no. 541).
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hirtenstein, Stephen (1999). The Unlimited Mercifier, The Spiritual life and thought of Ibn 'Arabi. Anqa Publishing & White Cloud Press. ISBN 978-0953451326.
- ^ Islaahe Nafs ka AAiena e Haq
- ^ Mohammed Rustom, Review of Michel Chodkiewicz's An Ocean without Shore
- ^ Hamza Dudgeon, "The Counter-Current Movements of Andalusia and Ibn ʿArabī: Should Ibn ʿArabī be considered a Ẓāhirī?" 2018, Journal of the Muhyiddin Ibn 'Arabi Society Vol. 64. https://www.academia.edu/36173562/The_Counter_Current_Movements_of_Andalusia_and_Ibn_%CA%BFArab%C4%AB_Should_Ibn_%CA%BFArab%C4%AB_be_considered_a_%E1%BA%92%C4%81hir%C4%AB
- ^ Ignaz Goldziher, The Ẓāhirīs: Their Doctrine and Their History, ed. and trans. by Wolfgang Behn (Leiden: Brill, 1971), 169.
- ^ Dudgeon, "The Counter-Current Movements of Andalusia and Ibn ʿArabī: Should Ibn ʿArabī be considered a Ẓāhirī?," 104.
- ^ Goldziher, The Ẓāhirīs, 170-171
- ^ Chiragh Ali, The Proposed Political, Legal and Social Reforms. Taken from Modernist Islam 1840-1940: A Sourcebook, pg. 281. Edited by Charles Kurzman. New York City: Oxford University Press, 2002.
- ^ Hamza Dudgeon, "The Revival of Sharia’s Allegories," 2019 Journal of the Muhyiddin Ibn 'Arabi Society Vol. 66. https://www.academia.edu/40585698/The_Revival_of_Sharia_s_Allegories
- ^ Chittick, William C. "Ebn al-‘Arabi Mohyi-al- Din Abu ‘Abd-Allah Mohammad Ta’I Hatemi." Encyclopedia Iranica (1996): Web. 3 Apr 2011. <http://iranica.com/articles/ebn-al-arabi>
- ^ Fitzpatrick, Coeli; Walker, Adam Hani (2014). Muhammad in History, Thought, and Culture. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 440. ISBN 978-1610691772.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Little, John T. (January 1987). "Al-Insān Al-Kāmil: The Perfect Man According to Ibn Al-'arabi". The Muslim World. 77 (1): 43–54. doi:10.1111/j.1478-1913.1987.tb02785.x.
- ^ Dobie, Robert J.date=17 November 2009 (2010). Logos and Revelation: Ibn 'Arabi, Meister Eckhart, and Mystical Hermeneutics. Washington, D.C.: The Catholic University of America Press. p. 225. ISBN 978-0813216775.
For Ibn Arabi, the Logos or "Universal Man" was a mediating link between individual human beings and the divine essence.
- ^ Fitzpatrick and Walker 2014, p. 445
- ^ Jump up to: a b Fitzpatrick and Walker 2014, p. 446
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Gregory A. Lipton (2018-04-02), Rethinking Ibn 'Arabi, Oxford University Press, p. 15, ISBN 9780190684518
- ^ Alexander D. Knysh, Ibn 'Arabi in the Later Islamic Tradition: The Making of a Polemical Image in Medieval Islam, pg. 64. Albany: State University of New York Press, 1999. ISBN 9780791439678
- ^ Ibn Khafif (1999). Correct Islamic Doctrine/Islamic Doctrine. Translated by Gibril Fouad Haddad. As-Sunna Foundation of America. p. 4. ISBN 9781930409019.
- ^ Gibril Fouad Haddad (2015). The Biographies of the Elite Lives of the Scholars, Imams and Hadith Masters. Zulfiqar Ayub. p. 233.
- ^ "Ibn Arabi (560-638/1165-1240)". Cis-ca.org. Retrieved 2018-11-05.
- ^ William C. Chittick, Ibn 'Arabi: Heir to the Prophets, Oneworld Publications (2012), p. 7
- ^ Michel Chodkiewicz, introduction in The Spiritual Writings of Amir 'Abd al-Kader, SUNY Press (1995), p. 7
- ^ Naqvi, S. Ali Raza, THE BEZELS OF WISDOM (Ibn al-'Arabī's Fuṣūṣ al-Ḥikam) by R.W.J. Austin (rev.), Islamic Studies, Vol. 23, No. 2 (Summer 1984), pp. 146-150
- ^ Chittick, William C. "The Disclosure of the Intervening Image: Ibn 'Arabî on Death", Discourse 24.1 (2002), pp. 51-62
- ^ Almond, Ian. "The Honesty of the Perplexed: Derrida and Ibn 'Arabi on 'Bewilderment'", Journal of the American Academy of Religion, Vol. 70, No. 3 (Sep., 2002), pp. 515-537
- ^ Al Futuhat Al Makkiyya, Dar Sader, Beirut, Lebanon, Book 1, pg 7
- ^ Chittick, William C. "The Disclosure of the Intervening Image: Ibn 'Arabi on Death" Discourse 24.1 (2002) 51-62
- ^ Notes on Fusus ul Hikam, Reynold A. Nicholson, Studies in Islamic Mysticism
- ^ Jump up to: a b Addas, Claude. (2000). Ibn ʻArabī, the voyage of no return. Cambridge, CB, UK: Islamic Texts Society. ISBN 0946621748. OCLC 41925362.
- ^ Michel Chodkiewicz, An Ocean Without Shore: Ibn Arabi, the Book, and the Law, SUNY Press (1993), p. 59
- ^ "Journal of the Muhyiddin Ibn 'Arabi Society". Ibnarabisociety.org. Retrieved 2018-11-05.
- ^ Sultan al-Mansub, Abd al-Aziz; Shahī, Abrar Ahmed, eds. (2015). Fusus al-Hikam. translator: Abrar Ahmed Shahi. Ibn al-Arabi Foundation.
- ^ "Angela Culme-Seymour". The Daily Telegraph. February 3, 2012.
- ^ Culme-Seymour, A.(tr.)(1975),"The Wisdom of the Prophets", Gloucestershire, U.K.:Beshara Publications
- ^ Austin, R.W.J.(tr.)(1980),"Ibn Al'Arabi: The Bezels of Wisdom", Mahwah, NJ: The Paulist Press, ISBN 0-8091-2331-2
- ^ Fusus Al Hikam Archived 2015-07-04 at the Wayback Machine, Translated by Muhammad Abdul Qadeer Siddiqui, Annotated by Mohammed Abdul Ahad Siddiqui, 2014 Kitab Mahal, Darbar Market, Lahore, Online Version at guldustah.com
- ^ "Osman Soykut Kimdir? - Güncel Osman Soykut Haberleri". www.sabah.com.tr. Retrieved 12 June 2020.
- ^ Saudi wins award for novel on Ibn Arabi. Dawn, 26 April 2017. Accessed 5 August 2021.
Bibliography[]
Books by Ibn Arabi[]
This is a small selection of his many books.
In Arabic[]
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Al-Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya, Vols. 1–4. Beirut: n.p.; photographic reprint of the old edition of Bulaq 1329/1911 which comprises four volumes each about 700 pages of 35 lines; the page size is 20 by 27cm. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī, Ibrāhīm Madkūr, and ʻUthmān Yaḥyá. Al-Futūḥāt al-Makkiyya, Vols. 1–14,. al-Qāhirah: al-Hayʼah al-Miṣrīyah al-ʻĀmmah lil-Kitāb, 1972. Print. this is the critical edition by Osman Yahya. This version was not completed, and the 14 volumes correspond to only volume I of the standard Bulaq/Beirut edition.
- Ibn ‘Arabī, Fuṣūṣ al-Ḥikam. Beirut: Dar al-Kitab al-'Arabī. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Sharḥ Risālat Rūḥ Al-quds fī Muḥāsabat Al-nafs. Comp. Mahmud Ghurab. 2nd ed. Damascus: Naḍar, 1994. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Inshā’ al-Dawā’ir, Beirut: Dar al-kutub al-‘Ilmiyya. 2004. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Rasā’il Ibn ‘Arabī (Ijāza li Malik al-Muẓaffar). Beirut: Dar al-kutub al-‘Ilmiyya, 2001. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Rasā'il Ibn al-'Arabî (Kitāb al-Jalāla). Hyberadad-Deccan: Dā’irat al-Ma‘ārif al-‘Uthmāniyya, 1948. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Kitāb al Bā’. Cairo: Maktabat al-Qāhira, 1954. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī, Risālat ila Imām al-Rāzī. Hyberadad-Deccan: Dā’irat al-Ma‘ārif al-‘Uthmāniyya, 1948. Print.
In English[]
- Ibn, Arabi (1997). Divine Governance of the Human Kingdom. Translated by Tosun Bayrak. Fons Vitae. ISBN 9781887752053.
- Ibn, Arabi (1992). What the Seeker Needs: Essays on Spiritual Practice, Oneness, Majesty and Beauty, with Ibn ʻArabi's Glossary of 199 Sufi Technical Terms. Translated by Tosun Bayrak. University of Virginia: Threshold Books. ISBN 9780939660414.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Nasab al-Khirqa. Trans. Gerald Elmore. Vol. XXVI. Oxford: Journal of the Muhyiddin Ibn ‘Arabi Society, 1999. Print.
- Ibn ‘Arabī. Divine Sayings The Mishkāt Al-Anwār of Ibn 'Arabi. Oxford: Anqa, 2005. Print.
- Ibn 'Arabi. The Meccan Revelations. Pir Press, 2010
Books about Ibn 'Arabi[]
- Addas, Claude, Quest for the Red Sulphur, Islamic Texts Society, Cambridge, 1993. ISBN 0-946621-45-4.
- Addas, Claude, Ibn Arabi: The Voyage of No Return, Cambridge, 2019 (second edition), Islamic Texts Society. ISBN 9781911141402.
- Akkach, Samer, Ibn 'Arabî's Cosmogony and the Sufi Concept of Time, in: Constructions of Time in the Late Middle Ages, ed. Carol Poster and Richard Utz. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press, 1997. Pp. 115-42.
- Titus Burckhardt & Bulent Rauf (translator), Mystical Astrology According to Ibn 'Arabi (The Fons Vitae Titus Burckhardt Series) ISBN 1-887752-43-9
- Henry Corbin, Alone with the Alone; Creative Imagination in the Sūfism of IbnʿArabī, Bollingen, Princeton 1969, (reissued in 1997 with a new preface by Harold Bloom).
- Elmore, Gerald T. Ibn Al-'Arabī’s Testament on the Mantle of Initiation (al-Khirqah). Journal of the Muhyiddin Ibn ‘Arabi Society XXVI (1999): 1-33. Print.
- Elmore, Gerald T. Islamic Sainthood in the Fullness of Time: Ibn Al-‘Arabī's Book of the Fabulous Gryphon. Leiden: Brill, 1999. Print.
- Hirtenstein, Stephen (1999). The Unlimited Mercifier, The Spiritual life and thought of Ibn 'Arabi. Anqa Publishing & White Cloud Press. ISBN 978-0953451326.
- Hirtenstein, Stephen, and Jane Clark. Ibn 'Arabi Digital Archive Project Report for 2009 Muhyiddin Ibn 'Arabi 1165AD - 1240AD and the Ibn 'Arabi Society. Dec. 2009. Web. 20 Aug. 2010.
- Knysh, Alexander. Ibn 'Arabi in the Later Islamic Tradition: The making of a polemical image in medieval Islam. Albany, NY: SUNY Press, 1999.
- Torbjörn Säfve, "Var inte rädd" ('Do not be afraid'), ISBN 91-7221-112-1
- Yahia, Osman. Mu'allafāt Ibn ʻarabī: Tārīkhuhā Wa-Taṣnīfuhā. Cairo: Dār al-Ṣābūnī, 1992. Print.
- Yousef, Mohamed Haj. Ibn 'Arabi - Time and Cosmology (London, Routledge, 2007) (Culture and Civilization in the Middle East).
- Yūsuf, Muhammad Haj. Shams Al-Maghrib. Allepo: Dār al-Fuṣṣilat, 2006. Print.
External links[]
- Chittick, William. "Ibn Arabi". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- Rustom, Mohammed (2014). "Ibn ʿArabī's Letter to Fakhr al-Dīn al-Rāzī: A Study and Translation". Journal of Islamic Studies. 25 (2): 113–137. doi:10.1093/jis/ett071.
- Ibn Arabi Society page about Ibn Al 'Arabi
- Ibn Arabi & Mystical Journey:The Journey to the Lord of Power (John G. Sullivan, Department of Philosophy at Elon College)
- Le concept d'amour chez Ibn 'Arabi (in French)
- Ibnarabi.net - Download Books
- حكم من يدعي إجماع أهل السنة على تكفير الإمام محيي الدين بن العربي—Dar al-Ifta al-Misriyyah (in Arabic)
- Ibn ‘Arabi and Wahdat al-Wujud
- Ibn 'Arabi's poem Tarjuman Al Ashwaq (The Interpreter of Desires), translated by and Robin Moger
- İBNÜ’l-ARABÎ, Muhyiddin(in Turkish) — An article published in the 20th Volume of TDV İslâm Ansiklopedisi, pp.520-522, in Istanbul (1999)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ibn Arabi. |
- 1165 births
- 1240 deaths
- 12th-century Arabic poets
- 13th-century Arabic poets
- Ibn Arabi
- Sufis
- Zahiris
- Asharis
- People from Murcia
- Medieval Arab philosophers
- Moorish writers
- Moorish Sufis
- Islamic philosophers
- Sufi poets
- Sufi mystics
- Moorish Sufi saints
- Spanish people of Arab descent
- Muslim mystics
- 13th-century Al-Andalus people
- 12th-century Al-Andalus people





