Kurukh language
| Kurukh | |
|---|---|
| Kurux, Oraon , Uraon | |
| कुड़ुख़, কুড়ুখ, କୁଡ଼ୁଖ | |
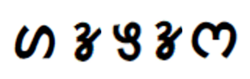 'Kurukh' in Tolong Siki alphabet | |
| Native to | India |
| Region | Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Assam, Bihar, Tripura[1] |
| Ethnicity | |
Native speakers | 2.28 million (2002-2011)[2][1][3] |
Dravidian
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Tolong Siki Devanagari Kurukh Banna | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | kru |
| ISO 639-3 | kru – inclusive codeIndividual code: xis – Kisan |
| Glottolog | kuru1301 |
| ELP | Nepali Kurux |
Kurukh /ˈkʊrʊx/[4] (Devanagari: कुड़ुख़), also Kurux, Oraon or Uranw,[5] is a Dravidian language spoken by nearly two million Kurukh (Oraon) and Kisan tribal people of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Assam, Bihar and Tripura in India, as well as by 65,000 in northern Bangladesh, 28,600 a dialect called Uranw in Nepal and about 5,000 in Bhutan. Some Kurukh speakers are in South India. It is most closely related to Brahui and Malto (Paharia). The language is marked as being in a "vulnerable" state in UNESCO's list of endangered languages.[6] The Kisan dialect has 206,100 speakers as of 2011.
Classification[]
Kurukh belongs to the Northern Dravidian group of the Dravidian family languages,[7] and is closely related to Sauria Paharia and Kumarbhag Paharia, which are often together referred to as Malto.[8]

Writing systems[]
Kurukh is written in Devanagari, a script also used to write Sanskrit, Hindi, Marathi, Nepali and other Indo-Aryan languages. In 1999, Narayan Oraon, a doctor, invented the alphabetic Tolong Siki script specifically for Kurukh. Many books and magazines have been published in Tolong Siki script, and it saw official recognition by the state of Jharkhand in 2007. The Kurukh Literary Society of India has been instrumental in spreading the Tolong Siki script for Kurukh literature.[9][10]
Geographical distribution[]
Kurukh language spoken mostly in Raigarh, Surguja, Jashpur of Chhattisgarh, Gumla, Ranchi, Lohardaga, Latehar, simdega of Jharkhand, Jharsuguda, Sundargarh and Sambalpur district of Odisha.
It is also spoken in Jalpaiguri district of West Bengal, Assam and Tripura states by Kurukh who are mostly Tea-garden workers.[1]
Speakers[]
It is spoken by 2,053,000 people from the Oraon and Kisan tribes, with 1,834,000 and 219,000 speakers respectively. The literacy rate is 23% in Oraon and 17% in Kisan. Despite the large number of speakers, the language is considered to be endangered.[11] The governments of Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh have introduced the Kurukh language in schools with majority Kurukhar students. Jharkhand and West Bengal both list Kurukh as an official language of their respective states.[12] Bangladesh also has some speakers.
Phonology[]
Vowels[]
Kurukh has five cardinal vowels. Each vowel has long, short nasalized and long nasalized counterparts.[13]
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Low | a |
Consonants[]
The table below illustrates the articulation of the consonants.[13]
| Labial | Alveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | (ɳ) | ɲ | ŋ | |||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | plain | p | t | ʈ | tʃ | k | ʔ |
| aspirated | pʰ | tʰ | ʈʰ | tʃʰ | kʰ | |||
| voiced | plain | b | d | ɖ | dʒ | g | ||
| aspirated | bʱ | dʱ | ɖʱ | dʒʱ | gʱ | |||
| Fricative | s | (ʃ) | x | h | ||||
| Rhotic | plain | ɾ | ɽ | |||||
| aspirated | ɽʱ | |||||||
| Glide | w | l | j | |||||
Education[]
Kurukh languages is taught as a subject in the schools of Jharkhand, Chhattishgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, West Bengal and Assam.[14]
Sample phrases[]
| Phrases | English Translation |
|---|---|
| Nighai name endra? | What is your name ? |
| Nin ekase radin? | How are you? (Girl) |
| Nin ekase raday? | How are you? (Boy) |
| En korem radan. | I am fine. |
| Nin eshan Kalalagdin ? | Where are you going? (Girl) |
| Nin eshan Kalalagday ? | Where are you going? (Boy) |
| Endra manja? | What happened? |
| Hae | Yes |
| Mala | No |
| En Mokha Lagdan. | I am eating. |
| Nin Mokha. | You eat. |
| Aar mokha lagnar. | They are eating. |
Alternative names and dialects[]
Kurukh has a number of alternative names such as Uraon, Kurux, Kunrukh, Kunna, Urang, Morva, and Birhor. Two dialects, Oraon and Kisan, have 73% intelligibility between them. Oraon but not Kisan is currently being standardised. Kisan is currently endangered, with a decline rate of 12.3% from 1991–2001.[15]
References[]
- ^ a b c "Kurux". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2018-07-11.
- ^ "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues - 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 2018-07-07.
- ^ "Kurux, Nepali". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2018-07-11.
- ^ "Kurukh". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/nepa1253
- ^ Evans, Lisa. "Endangered Languages: The Full List". The Guardian.
- ^ Stassen, Leon (1997). Intransitive Predication. Oxford Studies in Typology and Linguistic Theory. Oxford University Press. p. 220. ISBN 978-0199258932.
- ^ PS Subrahmanyam, "Kurukh", in ELL2. Ethnologue assigns Nepali Kurux a separate iso code, kxl.
- ^ Ager, Simon. "Tolong Siki alphabet and the Kurukh language". Omniglot. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- ^ Pandey, Anshuman (8 April 2010). "Preliminary Proposal to Encode the Tolong Siki Script in the UCS" (PDF). Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- ^ Daniel Nettle and Suzanne Romaine. Vanishing Voices: The Extinction of the World's Languages. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. Page 9.
- ^ "Kurukh given official language status in West Bengal". Jagranjosh.com. 2017-03-06. Retrieved 2019-05-12.
- ^ a b 1970-, Kobayashi, Masato (2017-09-21). The Kurux language : grammar, texts and lexicon. Leiden. ISBN 9789004347663. OCLC 1000447436.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- ^ Revitalising a language - The Hindu
- ^ ORGI. "Census of India: Growth of Non-Scheduled Languages-1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001". www.censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 2017-10-15.
External links[]
- Ferdinand Hahn (1903). Kuruḵh̲ (Orā̃ō)-English dictionary. Bengal Secretariat Press. pp. 126–. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Ferdinand Hahn (1900). Kuruḵẖ grammar. Bengal Secretariat Press. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- Kuruk̲h̲ folk-lore: in the original. The Bengal Secretariat Book Depot. 1905. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Kurukh basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- Omniglot's page on Tolong Siki
- Agglutinative languages
- Dravidian languages
- Languages of India
- Languages of Jharkhand
- Languages of Odisha
- Subject–object–verb languages
- Brahmic scripts