List of U.S. chemical weapons topics
The United States chemical weapons program began in 1917 during World War I with the creation of the U.S. Army's Gas Service Section and ended 73 years later in 1990 with the country's practical adoption of the Chemical Weapons Convention (signed 1993; entered into force, 1997). Destruction of stockpiled chemical weapons began in 1985 and is still ongoing. The U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Chemical Defense, at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland, continues to operate for purely defensive research and education purposes.
Agencies and organizations[]
Army agencies and schools[]
The U.S. chemical weapons programs have generally been run by the U.S. Army:

- U.S. Army Gas School
- U.S. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center
- United States Army Chemical Corps, originally the Chemical Warfare Service
- United States Army Medical Research Institute of Chemical Defense
- U.S. Army Chemical Materials Agency
- Program Executive Office, Assembled Chemical Weapons Alternatives
- United States Army CBRN School
Units[]
- Chemical mortar battalion
- 1st Gas Regiment
- 2nd Chemical Mortar Battalion
Modern chemical depots[]
Active bases

Closed bases
- Johnston Atoll Chemical Agent Disposal System (closed 2000)
- Edgewood Chemical Activity at Aberdeen Proving Ground (closed 2006)
- Hawthorne Army Depot (eliminated shells 1999)
- Newport Chemical Depot (closed 2008)
- Pine Bluff Chemical Activity (closed 2014)[1]
- Umatilla Chemical Depot (closed 2014)[2]
- Anniston Chemical Activity (closed 2013)[3]
- Deseret Chemical Depot with Tooele Chemical Agent Disposal Facility (closed 2013)[4]
Older chemical weapons program locations[]
- Camp American University
- Camp Leach
- Dugway Proving Ground
- Rocky Mountain Arsenal
- Navajo Ordnance Depot
Treaties, laws and policy[]
The U.S. is party to several treaties which limit chemical weapons:
- Chemical Weapons Convention
- Executive Order 11850
- Executive Order 13128
- Hague Conventions (1899 and 1907)
- - Failed because France objected to clauses relating to submarine warfare
- Geneva Protocol
- Public Law 99-145
Weapons[]
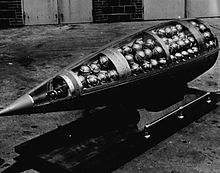
Canceled weapon projects[]
While these weapon systems were developed, they were not produced or stored in the US chemical weapons stockpile.
- BIGEYE bomb
- XM-736 8-inch binary projectile
Vehicles[]
- LCI(M), infantry landing craft armed with 4.2 in mortar
- M1135 Nuclear, Biological, Chemical, Reconnaissance Vehicle, a variation of the Stryker vehicle
- M93 Fox
- MQM-58 Overseer
Declared stockpile and other weapons[]
- M1 chemical mine
- M10 smoke tank
- M104 155mm shell
- M110A1/A2 155mm shell
- M114 bomblet
- M121/A1 155mm shell
- M122 155mm shell

- M125 bomblet, (developed as E54R6) chemical bomblet used with M34A1 cluster bomb
- M134 bomblet, (developed as E130R1), chemical bomblet for use with Honest John rockets
- M138 bomblet, sub-munition for the M43 cluster bomb
- M139 cluster bomblets for the MGR-1 Honest John rocket and other missile systems
- M2 mortar shell (M2A1) for the M2 4.2 Inch Mortar
- M23 chemical mine
- M34A1 cluster bomb (developed as E101R3), first U.S. air-delivered nerve agent weapon
- M360 105mm shell
- M426 8-inch shell
- M43 cluster bomb
- M44 generator cluster
- M47 bomb, 100 lb. World War II-era chemical bomb
- M55 rocket
- , BZ sub-munition for the M44 generator cluster
- M60 105mm shell
- M687 155mm shell
- MC-1 bomb
- Weteye bomb, also known as the Mk-116 bomb
Stockpiled chemical agents[]
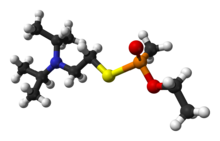
Agents stockpiled at the time of Chemical Weapons Convention:
- isopropyl aminoethylmethyl phosphonite, or QL, part of a binary weapon (VX)
- Methylphosphonyl difluoride (known to the military as DF) and a mixture of isopropyl alcohol and isopropyl amine (known as OPA), a binary chemical weapon (sarin)
- Mustard gas
- Sarin (GB)
- VX
- Rainbow Herbicides
Older chemical agents[]
- Phosgene
- Chlorine
- BZ
Other equipment[]
Exercises, incidents, and accidents[]
Operations and exercises[]
- Operation CHASE, an operation that dumped conventional and chemical munitions at sea
- Operation Davy Jones' Locker, a post-World War II operation aimed at dumping German chemical weapons at seas
- Operation Geranium, a 1948 operation that dumped lewisite into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Operation Paperclip, a program beginning in 1945 to bring German scientists to the U.S.
- Operation Ranch Hand, defoliant operations during the Vietnam War
- Operation Red Hat, an early 1970 program to repatriate weapons from Okinawa
- , 1980's testing and rebuilding of the M17 series protective mask
- Operation Snoopy, Vietnam War people sniffer operations.
- Operation Steel Box, an operation which moved chemical weapons out of Germany in 1990.
Accidents[]
- Bombing of the SS John Harvey during the Air Raid on Bari
- Dugway sheep incident
Chemical testing[]
- Edgewood Arsenal human experiments
- Operation LAC, (Large Area Coverage), 1958 test that dropped microscopic particles over much of the United States
- Operation Top Hat, a 1953 Chemical Corps exercise testing decontamination methods on human subjects
- Project SHAD
Chemical defense program[]
This section needs expansion. You can help by . (January 2015) |
See also[]
- List of U.S. biological weapons topics
- United States and weapons of mass destruction
- MK ULTRA, the CIA-led program to test various chemicals
References[]
- ^ Mesesan, Mark. "Pine Bluff Chemical Agen Disposal Facility prepared for final closure". army.mil. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ Mesesan, Mark. "Cleanup of Umatilla Chemical Depot's incineration plant is complete". oregonlive.com. Retrieved 7 October 2014.
- ^ Mesesan, Mark. "One year after last chemical weapons destroyed, incinerator at Anniston Army Depot closed". blog.al.com. Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ^ Mesesan, Mark. "Deseret Chemical Depot Closes, Transitions Installation to Tooele Army Depot". www.army.mil. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2016) |
- Chemical warfare
- United States military-related lists