Jack of the United States
 | |
| Name | Union Jack |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 71:100 |
| Adopted | 1777 (initial use of underlying design template) July 4, 1960 (current design) |
| Design | 50 white stars defacing a blue field in 9 rows, alternating between 6 and 5 stars. |
The jack of the United States is a maritime flag representing U.S. nationality, flown on the jackstaff in the bow of U.S. vessels that are moored or anchored. The U.S. Navy is a prime user of jacks for its warships and auxiliaries, but they are also used by non-naval vessels such as ships of the U.S. Coast Guard,[1] the predominantly civilian-crewed replenishment and support ships of the U.S. Navy's Military Sealift Command, the ships of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and other U.S. governmental entities. The jack is flown on the bow (front) of a ship and the ensign is flown on the stern (rear) of a ship when anchored or moored. Once under way, the ensign is flown from the main mast and the jack is lowered, removed, and stowed away for future use.[2]
The design of the U.S. jack has consisted of essentially the canton of the U.S. national flag since the late 1770s, with each subsequent modification to the U.S. national flag's canton being represented in the U.S. jack as well. Occasionally, there have been brief hiatus of that design for commissioned warships to commemorate certain occasions, from 1975 to 1976, in 2000 for submarines and submarine tenders, and again for all warships from 2002 to 2019.
The oldest commissioned warship in active U.S. naval status (that is, having the longest total period in active status), currently USS Blue Ridge, is the only active U.S. warship flying a different jack than the standard U.S. one, by flying the "First Navy Jack". All other active U.S. Navy warships display the Union Jack.
History[]
For most of U.S. history, the primary jack design has been the blue canton with stars (the "union") from the U.S. national ensign. The blue fielded, white-starred jack is referred to as the Union Jack, not to be confused with the Union Jack of the United Kingdom, which has the same name but a different design. Like the U.S. ensign, the number of stars on the jack correspond with the number of constituent states the U.S. has. Rules for flying the jack are similar to the national ensign, except that the jack is only flown at the bow when the ship is anchored, made fast or alongside.
The 48 star version of the Union Jack flag became official in 1912 after Arizona and New Mexico became states. Throughout WWI and WWII, and until 1959 the Union Jack flag consisted of 48 stars.[3]
From September 11, 2002, the U.S. Navy made use of the so-called First Navy Jack. However, the standard U.S. jack (i.e. 50 white stars alternative in columns of four and five defacing a blue field) continued to be used as the jack by vessels of U.S. federal agencies such as the U.S. Coast Guard, the Military Sealift Command and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Corps and by U.S. civilian ships and by U.S. yachts. The majority of the U.S. Navy's warships returned to using the U.S. Union Jack on June 4, 2019.
The jack is flown from the jackstaff from 08:00 to sunset while U.S. Navy ships are moored or at anchor. It is required to be the same size as the union of the ensign being flown from the stern of the ship. It is also flown from the yardarm during a general court-martial or court of inquiry.[4] During times when the ensign is at half mast, the jack is also at half mast. The jack is hoisted smartly and lowered ceremoniously in the same manner as the ensign, however the jack is not dipped when the ensign is dipped.[5]
Some other exceptions to the use of the U.S. Union Jack have occurred in the case of the U.S. Navy, the most prominent being the use of the First Navy Jack by the U.S. Navy in honor of the U.S. founding's bicentennial and for other uses subsequently.[6] For example, following the Bicentennial, in August 1980, use of the First Navy Jack was granted to the active commissioned ship having the longest total period of front-line operational service, said use to be in place of the Union Jack until that ship was decommissioned or transferred to inactive status, whereupon the next such ship in seniority inherits the honor of its use. This use is limited to the oldest "commissioned" naval vessel (i.e., an all-military United States Ship [ship prefix USS] versus a part-military/part-civilian crewed United States Naval Ship [ship prefix USNS]) in front-line operational service.
On June 3, 1999, the Secretary of the Navy also authorized the flying of the Submarine Centennial Jack on all U.S. Navy submarines and submarine tenders during 2000.[7][a]
On February 21, 2019, the Chief of Naval Operations directed that U.S. Navy warships fly the U.S. jack again beginning on June 4, 2019.[8][9][10] The oldest active U.S. warship flies the First Navy Jack; that ship has been USS Blue Ridge (LCC-19) since 2014.[11]
[]
| Stars | Design | Dates in general use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 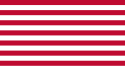 |
The first jack adopted by the United States consisted of thirteen alternating red and white horizontal stripes. Known as the First Navy Jack, it is often depicted with a rattlesnake and motto; however, the evidence is inconclusive that the jack actually had either of these. There is reason to believe that the Continental Navy jack was simply a red and white striped flag with no other adornment.[12] | |
| 13 | 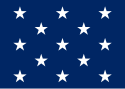 |
Examples of many layouts of the 13 star pattern exist (see Flag of the United States). | |
| 15 | 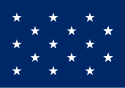 |
The 15-star jack was used by the United States during the Quasi-War and the War of 1812. | |
| 20 | 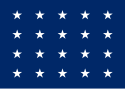 |
||
| 21 | 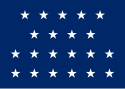 |
||
| 23 | 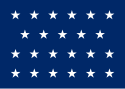 |
||
| 24 | 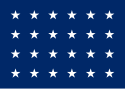 |
||
| 25 | 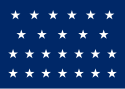 |
||
| 26 | 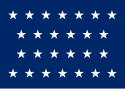 |
||
| 27 | 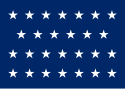 |
||
| 28 |  |
||
| 29 | 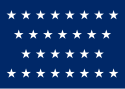 |
||
| 30 | 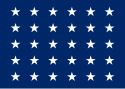 |
||
| 31 | 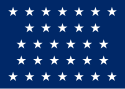 |
||
| 32 | 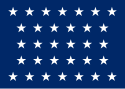 |
||
| 33 | 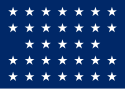 |
Civil War | |
| 34 |  |
||
| 35 |  |
||
| 36 |  |
||
| 37 | 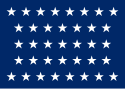 |
||
| 38 |  |
||
| 43 | 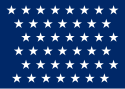 |
||
| 44 |  |
||
| 45 | 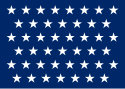 |
Sinking of the USS Maine; Spanish–American War; Great White Fleet | |
| 46 | 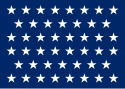 |
||
| 48 | 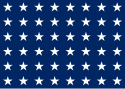 |
World War I; World War II | |
| 49 |  |
||
| 50 |  |
A 50-star jack was adopted on July 4, 1960, after the ascension of the Territory of Hawaii into statehood. The 50-star jack was used notably during the Vietnam War. In October 1975, the jack was briefly replaced by the First Navy Jack in commemoration of the U.S. Navy's bicentennial as well as the bicentennial of the United States of America's founding. The 50-star jack was re-adopted on January 1, 1977. | |
| 0 |  |
On October 13, 1975, commissioned U.S. Navy warships switched to the First Navy Jack in commemoration of the bicentennial of the United States Navy and the U.S. founding's bicentennial. It was used in this capacity until December 31, 1976, when the 50-star jack was re-adopted.[13] | |
| 50 |  |
The 50-star jack was re-adopted by commissioned U.S. Navy warships on January 1, 1977. Since August 18, 1980, the First Navy Jack has been used by the active commissioned ship having the longest total period as active in place of the union jack until the ship is decommissioned or transferred to inactive status, whereupon the next such ship inherits the honor. | |
| 0 |  |
Global War on Terrorism
The First Navy Jack was used from 2002 to 2019 by United States Navy vessels only. MSC and non-U.S. Navy vessels, such as those of the U.S. Coast Guard and NOAA, continued to use the 50-star union jack that was adopted in 1960. | |
| 50 |  |
The 50-star jack was ordered to be re-adopted by commissioned U.S. Navy warships on February 21, 2019, effective June 4, 2019, to coincide with anniversary of the Battle of Midway. From August 18, 1980 onward, the active commissioned ship having the longest total period as active uses the First Navy Jack instead.[6] Currently that ship is USS Blue Ridge (LCC-19). |
See also[]
- Flag of the United States
- Flags of the United States Armed Forces
Notes[]
- ^ That the U.S. Navy has, at times, elected to substitute other flags for the Union Jack has not affected its use as a jack by the Coast Guard, NOAA, other agencies and civilians.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Change ordered on May 31, 2002 and executed on date shown.
References[]
- ^ "Cutter visit". The Day. Retrieved June 6, 2019.
- ^ "Naval Jack (United States)". December 11, 2000. Archived from the original on December 11, 2000. Retrieved February 23, 2019.
- ^ https://jeffbridgman.com/inventory/index.php?page=out&id=2048. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ United States Navy Rate training manual. Signalman 1 & C Archived May 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United States Navy. Basic Military Requirements (BMR) Revised Edition Archived September 29, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "The U.S. Navy's First Jack". Retrieved October 1, 2006.
- ^ Undersea Warfare Summer 2000 Vol. 2, No. 4. Archived September 28, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Chief of Naval Operations Public Affairs (February 22, 2019). "Navy Returns to Flying Union Jack". United States Navy. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- ^ "The Colors of a Navy and Nation". The Sextant.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ . February 26, 2019 https://web.archive.org/web/20190226121307/https://www.public.navy.mil/bupers-npc/reference/messages/Documents/NAVADMINS/NAV2019/NAV19039.txt. Archived from the original on February 26, 2019. Retrieved June 6, 2019. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ "The U.S. Navy's First Jack". www.history.navy.mil. Retrieved August 20, 2016.
- ^ "Legati ad Defendendam Libertatem - USS John Warner Commissioned | Naval Historical Foundation". June 2, 2019. Archived from the original on June 2, 2019. Retrieved June 6, 2019.
- Continental Navy
- United States Navy
- Military flags of the United States
- Jacks (flags)
