List of cervids

Cervidae is a family of hoofed ruminant mammals in the order Artiodactyla. A member of this family is called a deer or a cervid. They are widespread throughout North and South America, Europe, and Asia, and are found in a wide variety of biomes. Cervids range in size from the 60 cm (24 in) long and 32 cm (13 in) tall pudú to the 3.4 m (11.2 ft) long and 3.4 m (11.2 ft) tall moose. Most species do not have population estimates, though the roe deer has a population size of approximately 15 million, while several are considered endangered or critically endangered with populations as low as 200. One species, Père David's deer, is extinct in the wild, and one, Schomburgk's deer, went extinct in 1938.
The 54 species of Cervidae are split into 18 genera within 3 subfamilies: Capreolinae, or New World deer; Cervinae, or Old World deer; and Hydropotinae, comprising the water deer. Extinct species have also been placed into Capreolinae and Cervinae. Over one hundred extinct Cervidae species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.[1]
Conventions[]
| IUCN Red List categories | |
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| EX | Extinct (1 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (1 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (2 species) |
| EN | Endangered (6 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (16 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (4 species) |
| LC | Least concern (14 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (9 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (1 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the cervid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN red list for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "![]() ".
".
Classification[]
The family Cervidae consists of 53 extant species belonging to 18 genera in 3 subfamilies and divided into dozens of extant subspecies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Additionally, one species, Schomburgk's deer, went extinct in 1938.[2]
- Subfamily Capreolinae (New World deer)
- Genus Alces: one species
- Genus Blastocerus: one species
- Genus Capreolus: two species
- Genus Hippocamelus: two species
- Genus Mazama: nine species
- Genus Odocoileus: three species
- Genus Ozotoceros: one species
- Genus Pudu: two species
- Genus Rangifer: one species
- Subfamily Cervinae (Old World deer)
- Subfamily Hydropotinae
- Genus Hydropotes: one species
|
Cervids[]
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis. This includes merging the two moose species of Alces into one and splitting out the genus Hyelaphus from Axis. There are several additional proposals which are disputed, such as splitting out the monotypic Panolia genus from Rucervus, combining the monotypic subfamily Hydropotinae with Capreolinae, or the addition of the fair brocket to the Mazama genus, which are not included here.[3][4]
Subfamily Capreolinae[]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moose
|
A. alces Linnaeus, 1758 Nine subspecies
|
North America, Europe, and Asia
|
Size: 230–340 cm (91–134 in) long, plus 8–12 cm (3–5 in) tail; up to 230 cm (91 in) tall at shoulder[5] Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands[6] Diet: Vegetative parts of trees, as well as shrubs, herbs, and aquatic plants[6] |
LC |
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marsh deer
|
B. dichotomus Illiger, 1815 |
Scattered parts of central South America (former range in red)
|
Size: 153–191 cm (60–75 in) long, plus 12–16 cm (5–6 in) tail; 110–127 cm (43–50 in) tall at shoulder[8] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and inland wetlands[9] Diet: Grasses, reeds and aquatic plants, as well as shrubs and vines[9] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roe deer
|
C. capreolus Linnaeus, 1758 Four subspecies
|
Europe
|
Size: 104–124 cm (41–49 in) long, plus 2–3 cm (1–1 in) tail; 66–84 cm (26–33 in) tall at shoulder[10] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[11] Diet: Wide variety of plants[11][10] |
LC
|
| Siberian roe deer
|
C. pygargus Pallas, 1771 Four subspecies
|
Central and northeastern Asia | Size: 95–140 cm (37–55 in) long, plus 20–40 cm (8–16 in) tail; 65–95 cm (26–37 in) tall at shoulder[12] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[13] Diet: Grasses[13] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Andean deer
|
H. bisulcus Molina, 1782 |
Southern Andes mountains
|
Size: 144–156 cm (57–61 in) long, plus 12–13 cm (5–5 in) tail; 80–90 cm (31–35 in) tall at shoulder[14] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, rocky areas, and desert[15] Diet: Varied range of grasses and other plants[15] |
EN
|
| Taruca
|
H. antisensis d'Orbigny, 1834 |
Andes mountains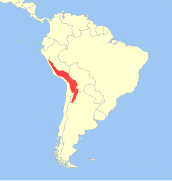
|
Size: 69–77 cm (27–30 in) tall at shoulder[16] Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and other[17] Diet: Sedges and grasses[16][17] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazonian brown brocket
|
M. nemorivaga F. Cuvier, 1817 |
Northern and central South America
|
Size: 75–100 cm (30–39 in) long, plus 6–11 cm (2–4 in) tail; 50 cm (20 in) tall at shoulder[18] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[19] Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves and shoots[18] |
LC
|
| Central American red brocket
|
M. temama Kerr, 1792 Three subspecies
|
Central America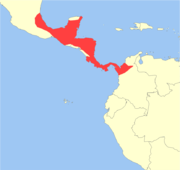
|
Size: 80–110 cm (31–43 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail; 60–70 cm (24–28 in) tall at shoulder[18] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[20] Diet: Fruit, as well as seeds, grass, shoots, vines, and sometimes crops such as beans[18] |
DD
|
| Dwarf brocket | M. chunyi Hershkovitz, 1959 |
Central Andes mountains
|
Size: About 70 cm (28 in) long; about 38 cm (15 in) tall at shoulder[21] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[22] Diet: Fruit and shrubs[22] |
VU
|
| Gray brocket
|
M. gouazoubira Fischer von Waldheim, 1814 Eleven subspecies
|
Eastern South America
|
Size: 85–105 cm (33–41 in) long[18] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and inland wetlands[23] Diet: Wide variety of plants as well as fruit[23] |
LC
|
| Little red brocket
|
M. rufina Bourcier, Pucheran, 1852 |
Northern Andes mountains
|
Size: About 78 cm (31 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail; about 45 cm (18 in) tall at shoulder[24] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[25] Diet: Herbs as well as other plants[25] |
VU
|
| Mérida brocket | M. bricenii Thomas, 1908 |
Northern Andes mountains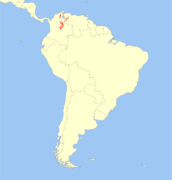
|
Size: 80–95 cm (31–37 in) long, plus 8–9 cm (3–4 in) tail; 45–50 cm (18–20 in) tall at shoulder[18] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[26] Diet: Fruit and shrubs[26] |
VU
|
| Pygmy brocket
|
M. nana , 1872 |
Southeastern South America (possible range in yellow)
|
Size: About 78 cm (31 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail; less than 50 cm (20 in) tall at shoulder[24] Habitat: Forest[27] Diet: Unknown[18][27] |
VU
|
| Red brocket
|
M. americana Erxleben, 1777 Twelve subspecies
|
Northern and central South America
|
Size: 103–146 cm (41–57 in) long, plus 8–15 cm (3–6 in) tail; 65–80 cm (26–31 in) tall at shoulder[28] Habitat: Forest[29] Diet: Fruit and shrubs[29] |
DD
|
| Small red brocket
|
M. bororo , 1996 |
Atlantic Forest in southeastern Brazil (possible range in yellow)
|
Size: 85 cm (33 in) long, plus 11–14 cm (4–6 in) tail; 50–60 cm (20–24 in) tall at shoulder[18] Habitat: Forest[30] Diet: Fruit, leaves, and sprouts[18] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mule deer
|
O. hemionus Rafinesque, 1817 Ten subspecies
|
Western North America
|
Size: 152–203 cm (60–80 in) long; 80–106 cm (31–42 in) tall at shoulder[31] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, desert, and intertidal marine[32] Diet: Leaves, twigs, acorns, legume seeds, and fleshy fruits[31][32] |
LC
|
| Yucatan brown brocket
|
O. pandora Merriam, 1901 |
Yucatán Peninsula
|
Size: About 105 cm (41 in) long, plus 8 cm (3 in) tail[33] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[34] Diet: Fruit, as well as other plants[18] |
VU
|
| White-tailed deer
|
O. virginianus Rafinesque, 1832 38 subspecies
|
North America and northern South America
|
Size: 150–200 cm (59–79 in) long, plus 10–28 cm (4–11 in) tail[35] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, desert, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and coastal marine[36] Diet: Wide variety of vegetation and grasses[36] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pampas deer
|
O. bezoarticus Linnaeus, 1758 Five subspecies
|
Scattered central South America
|
Size: 110–140 cm (43–55 in) long; 70–75 cm (28–30 in) tall at shoulder[37] Habitat: Savanna, grassland, and inland wetlands[38] Diet: Grasses and shrubs[37][38] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern pudú
|
P. mephistophiles Winton, 1896 |
Northern Andes mountains
|
Size: 60–85 cm (24–33 in) long plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail; 32–35 cm (13–14 in) tall at shoulder[39][40] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[41] Diet: Leaves of ferns, trees, vines, herbs and shrubs[41][42] |
DD
|
| Southern pudú
|
P. puda Molina, 1782 |
Southern Andes mountains
|
Size: 60–85 cm (24–33 in) long plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail; 35–45 cm (14–18 in) tall at shoulder[39][40] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[43] Diet: Leaves of ferns, trees, vines, herbs and shrubs[42][43] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reindeer
|
R. tarandus Linnaeus, 1758 Fourteen subspecies
|
Arctic North America, Europe, and Asia
|
Size: 150–230 cm (59–91 in) long; up to 120 cm (47 in) tall at shoulder[44] Habitat: Forest and grassland[45] Diet: Lichen, forbs, sedges, grasses, and shrubs[45] |
VU
|
Subfamily Cervinae[]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chital
|
A. axis Erxleben, 1777 |
Indian subcontinent
|
Size: 70 cm (28 in) long plus 20 cm (8 in) tail; 35–38 cm (14–15 in) tall at shoulder[46][47] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[48] Diet: Wide variety of grasses as well as fallen leaves, flowers, and fruit[48] |
LC
|
| Calamian deer
|
A. calamianensis Heude, 1888 |
Calamian Islands of the Philippines | Size: 100–175 cm (39–69 in) long, plus 12–38 cm (5–15 in) tail; 60–100 cm (24–39 in) tall at shoulder[49] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[50] Diet: Leaves[50] |
EN
|
| Bawean deer
|
A. kuhlii Temminck, 1836 |
Bawean island of Indonesia
|
Size: 100–175 cm (39–69 in) long[51] Habitat: Forest and grassland[52] Diet: Herbs and grasses, as well as young leaves and twigs[52] |
CR
|
| Indian hog deer
|
A. porcinus Zimmermann, 1780 |
Southern and southeast Asia
|
Size: 105–115 cm (41–45 in) long, plus 20 cm (8 in) tail; 60–72 cm (24–28 in) tall at shoulder[53] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[54] Diet: Young grasses, as well as herbs, flowers, fruit, and shrubs[54] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thorold's deer
|
C. albirostris Przhevalsky, 1883 |
Central China | Size: 155–210 cm (61–83 in) long, plus 10–13 cm (4–5 in) tail; 115–140 cm (45–55 in) tall at shoulder[55] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[56] Diet: Grass, herbs, lichens, leaves, and bark of trees and bushes[56] |
VU
|
| Elk
|
C. canadensis Erxleben, 1777 Thirteen subspecies
|
North America and Asia (former range in light green)
|
Size: 210–280 cm (83–110 in) long plus 10–22 cm (4–9 in) tail; 120–175 cm (47–69 in) tall at shoulder[57][58] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[59] Diet: Shrub and tree shoots, as well as grasses, sedges, and shrubs[59] |
LC
|
| Red deer
|
C. elaphus Linnaeus, 1758 Nine subspecies
|
Europe and western Asia (former range in light green)
|
Size: 160–270 cm (63–106 in) long; 75–150 cm (30–59 in) tall at shoulder[60] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and rocky areas[61] Diet: Shrub and tree shoots, as well as grasses, sedges, shrubs, fruit, and seeds[61] |
LC
|
| Central Asian red deer
|
C. hanglu Wagner, 1844 Three subspecies
|
Central Asia | Size: Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[62] Diet: Branches of young deciduous trees[62] |
LC
|
| Sika deer
|
C. nippon Temminck, 1838 Sixteen subspecies
|
East Asia | Size: 95–180 cm (37–71 in) long plus 7–13 cm (3–5 in) tail; 64–109 cm (25–43 in) tall at shoulder[63] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[64] Diet: Grass, as well as shrubs and fruit[64] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| European fallow deer
|
D. dama Linnaeus, 1758 |
Europe and west Asia; introduced scattered areas worldwide (in teal)
|
Size: 130–175 cm (51–69 in) long, plus 15–23 cm (6–9 in) tail; 90–100 cm (35–39 in) tall at shoulder[65] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[66] Diet: Grasses, mast, and shrubs, as well as leaves, buds, shoots, and bark[65][66] |
LC
|
| Persian fallow deer
|
D. mesopotamica Brooke, 1875 |
Iran and Israel | Size: 130–175 cm (51–69 in) long, plus 15–23 cm (6–9 in) tail; 90–100 cm (35–39 in) tall at shoulder[65] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[67] Diet: Grasses, mast, and shrubs, as well as leaves, buds, shoots, and bark[67] |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tufted deer
|
E. cephalophus H. Milne-Edwards, 1872 Four subspecies
|
Central China and northeastern Myanmar | Size: 110–160 cm (43–63 in) long, plus 7–16 cm (3–6 in) tail; 50–70 cm (20–28 in) tall at shoulder[68] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[69] Diet: Grass, as well as shrubs, fruits, bamboo, and herbs[69] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Père David's deer
|
E. davidianus Milne-Edwards, 1866 |
China | Size: 183–216 cm (72–85 in) long, plus 22–36 cm (9–14 in) tail[70] Habitat: Grassland, inland wetlands, and intertidal marine[71] Diet: Grass, reeds, and bush leaves[71] |
EW
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bornean yellow muntjac | M. atherodes Groves, Grubb, 1982 |
Borneo | Size: 90–100 cm (35–39 in) long, plus 14–20 cm (6–8 in) tail; 65 cm (26 in) tall at shoulder[72][73] Habitat: Forest[74] Diet: Herbs, seeds, grass, buds, leaves, and fruit[72] |
NT
|
| Fea's muntjac
|
M. feae Thomas, Doria, 1889 |
Southern Myanmar and Thailand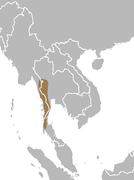
|
Size: 90–100 cm (35–39 in) long, plus 10–17 cm (4–7 in) tail; 50–60 cm (20–24 in) tall at shoulder[72] Habitat: Forest[75] Diet: Fruit and leaves, as well as grass and shoots[72] |
DD
|
| Giant muntjac | M. vuquangensis , , , , & , 1994 |
Northern Vietnam and Laos
|
Size: 110–115 cm (43–45 in) long, plus 17 cm (7 in) tail; 65–70 cm (26–28 in) tall at shoulder[72] Habitat: Forest[76] Diet: Fruit and leaves[72] |
CR
|
| Gongshan muntjac | M. gongshanensis , 1990 |
South-central China
|
Size: 95–105 cm (37–41 in) long, plus 9–16 cm (4–6 in) tail; 55–57 cm (22–22 in) tall at shoulder[77] Habitat: Forest[78] Diet: Unknown[72][78] |
DD
|
| Hairy-fronted muntjac
|
M. crinifrons P. L. Sclater, 1885 |
Southeastern China | Size: 98–113 cm (39–44 in) long, plus 21 cm (8 in) tail[79] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[80] Diet: Wide variety of tree leaves and twigs, forbs, grass, and fruit[80] |
VU
|
| Indian muntjac
|
M. muntjak Zimmermann, 1780 Eleven subspecies
|
Southern and Southeast Asia
|
Size: 89–135 cm (35–53 in) long, plus 13–23 cm (5–9 in) tail; 40–65 cm (16–26 in) tall at shoulder[81] Habitat: Forest[82] Diet: Fruit, buds, tender leaves, flowers, herbs, and young grass[82] |
LC
|
| Leaf muntjac | M. putaoensis , & Rabinowitz, 1999 |
Myanmar | Size: 77–83 cm (30–33 in) long, plus 8–12 cm (3–5 in) tail; 50 cm (20 in) tall at shoulder[83] Habitat: Forest[84] Diet: Fruit and a range of plant materials[84] |
DD
|
| Pu Hoat muntjac | M. puhoatensis , 1997 |
Vietnam | Size: Small and similar to the Truong Son muntjac, but specific measurements not available[72] Habitat: Forest[85] Diet: Unknown[72][85] |
DD
|
| Reeves's muntjac
|
M. reevesi Ogilby, 1839 Three subspecies
|
Eastern China; introduced to Britain and Japan | Size: 70–113 cm (28–44 in) long, plus 10 cm (4 in) tail; 43–45 cm (17–18 in) tall at shoulder[86] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[87] Diet: Bamboo, seeds, bark, fruit and foliage, as well as eggs, carrion, small mammals, and ground-nesting birds[86][87] |
LC
|
| Roosevelt's muntjac | M. rooseveltorum Osgood, 1932 |

|
Size: Small with shoulder height estimated at about 40 cm (16 in), but specific measurements not available[72] Habitat: Forest[88] Diet: Leaves and fruit[72] |
DD
|
| Truong Son muntjac
|
M. truongsonensis , , , Wikramanayake, , , & , 1997 |
Southern Vietnam | Size: Small with shoulder height estimated at about 40 cm (16 in), but specific measurements not available[72] Habitat: Forest[89] Diet: Leaves and fruit[72] |
DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barasingha
|
R. duvaucelii Cuvier, 1823 Three subspecies
|
Scattered parts of south Asia (historical range in yellow)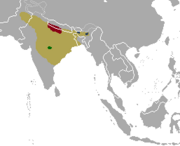
|
Size: About 180 cm (71 in) long; 119–124 cm (47–49 in) tall at shoulder[90] Habitat: Forest, savanna, grassland, and inland wetlands[91] Diet: Grass and aquatic plants[91] |
VU
|
| Eld's deer
|
R. eldii McClelland, 1842 Three subspecies
|
Scattered parts of southeast Asia | Size: Males 160–170 cm (63–67 in) long, plus 22–25 cm (9–10 in) tail; 115–130 cm (45–51 in) tall at shoulder.
Females 140–150 cm (55–59 in) long, plus 22–25 cm (9–10 in) tail; 90–100 cm (35–39 in) tall at shoulder.[92] |
EN
|
| Schomburgk's deer
|
R. schomburgki Blyth, 1863 |
Central Thailand | Size: Unknown Habitat: Grassland and inland wetlands[95] Diet: Unknown[95] |
EX
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visayan spotted deer
|
R. alfredi P. L. Sclater, 1870 |
Philippines | Size: 120–130 cm (47–51 in) long, plus 8–13 cm (3–5 in) tail; 60–80 cm (24–31 in) tall at shoulder[96] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[97] Diet: Cogon grass and young leaves and buds[97] |
EN
|
| Philippine deer
|
R. marianna Desmarest, 1822 Four subspecies
|
Philippines | Size: 100–151 cm (39–59 in) long; 55–70 cm (22–28 in) tall at shoulder[98] Habitat: Forest and grassland[99] Diet: Grass[99] |
VU
|
| Javan rusa
|
R. timorensis Blainville, 1822 Seven subspecies
|
Indonesia and East Timor
|
Size: 142–185 cm (56–73 in) long, plus 10–30 cm (4–12 in) tail; 80–110 cm (31–43 in) tall at shoulder[100] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[101] Diet: Grass, herbs, the leaves and bark of shrubs, and seaweed[101] |
VU
|
| Sambar deer
|
R. unicolor Kerr, 1792 Seven subspecies
|
South and Southeast Asia including Southern China
|
Size: 160–270 cm (63–106 in) long, plus 25–30 cm (10–12 in) tail; 102–160 cm (40–63 in) tall at shoulder[102] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[103] Diet: Wide variety of plants[103] |
VU
|
Subfamily Hydropotinae[]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water deer
|
H. inermis Swinhoe, 1870 Two subspecies
|
East China and Korean peninsula | Size: 89–103 cm (35–41 in) long, plus 6–7 cm (2–3 in) tail; 45–57 cm (18–22 in) tall at shoulder[104] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and intertidal marine[105] Diet: Reeds, coarse grasses, vegetables, and beets[105][106] |
VU
|
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Fossilworks: Cervidae". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Retrieved December 17, 2021.
- ^ Ellis, pp. 311–312
- ^ Randi, E.; Mucci, N.; Pierpaoli, M.; Douzery, E. (1998). "New phylogenetic perspectives on the Cervidae (Artiodactyla) are provided by the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 265 (1398): 793–801. doi:10.1098/rspb.1998.0362. PMC 1689037. PMID 9628037.
- ^ van Roosmalen, M. G. M. (2015). "Hotspot of new megafauna found in the Central Amazon: the lower Rio Aripuanã Basin" (PDF). Biodiversity Journal. 6 (1): 219–244.
- ^ De Bord, Daniel (2009). "Alces alces". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved February 24, 2021.
- ^ a b c d Hundertmark, K. (2016). "Alces alces". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T56003281A22157381. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T56003281A22157381.en.
- ^ Baskin, L. M. (2009). "Status of Regional Moose Populations in European and Asiatic Russia". Alces. 45: 1–4. Archived from the original on February 26, 2018. Retrieved February 26, 2018.
- ^ Eisenberg, Redford, Reid, Bonner (vol. 3), p. 340
- ^ a b c Duarte, J. M. B; Varela, D.; Piovezan, U.; Beccaceci, M. D.; Garcia, J. E. (2016). "Blastocerus dichotomus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2828A22160916. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T2828A22160916.en.
- ^ a b Jacques, Kristi (2000). "Capreolus capreolus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved February 24, 2021.
- ^ a b c Lovari, S.; Herrero, J.; Masseti, M.; Ambarli, H.; Lorenzini, R.; Giannatos, G. (2016). "Capreolus capreolus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42395A22161386. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T42395A22161386.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, p. 347
- ^ a b c Lovari, S.; Masseti, M.; Lorenzini, R. (2016). "Capreolus pygargus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42396A22161884. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T42396A22161884.en.
- ^ Eisenberg, Redford, Reid, Bonner (vol. 2), p. 241
- ^ a b c Black-Decima, P. A.; Corti, P.; Díaz, N.; Fernandez, R.; Geist, V.; Gill, R.; Gizejewski, Z.; Jiménez, J.; Pastore, H.; Saucedo, C.; Wittmer, H. (2016). "Hippocamelus bisulcus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T10054A22158895. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T10054A22158895.en.
- ^ a b Putz, Brian (2003). "Hippocamelus antisensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ a b c Barrio, J.; Nuñez, A.; Pacheco, L.; Regidor, H. A.; Fuentes-Allende, N. (2017). "Hippocamelus antisensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T10053A22158621. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T10053A22158621.en.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Wilson, Mittermeier, p. 441–443
- ^ a b Rossi, R. V.; Duarte, J. M. B (2016). "Mazama nemorivaga". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136708A22158407. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136708A22158407.en.
- ^ a b Bello, J.; Reyna, R.; Schipper, J. (2016). "Mazama temama". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136290A22164644. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136290A22164644.en.
- ^ "Dwarf brocket (Mazama chunyi)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on August 11, 2010. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Rumiz, D. I.; Barrio, J. (2016). "Mazama chunyi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T12913A22165860. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T12913A22165860.en.
- ^ a b c Black-Decima, P. A.; Vogliotti, A. (2016). "Mazama gouazoubira". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29620A22154584. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T29620A22154584.en.
- ^ a b Eisenberg, Redford, Reid, Bonner (vol. 3), p. 346
- ^ a b c Lizcano, D. and Alvarez; S. J. (2016). "Mazama rufina". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T12914A22165586. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T12914A22165586.en.
- ^ a b c Lizcano, D. J.; Alvarez, S. J. (2016). "Mazama bricenii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136301A22165039. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T136301A22165039.en.
- ^ a b c Duarte, J. M. B; Vogliotti, A.; Cartes, J. L.; Oliveira, M. L. (2015). "Mazama nana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T29621A22154379. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T29621A22154379.en.
- ^ Kossel, Kyle (2013). "Mazama americana". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved February 25, 2021.
- ^ a b c Duarte, J. M. B; Vogliotti, A. (2016). "Mazama americana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29619A22154827. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T29619A22154827.en.
- ^ a b Vogliotti, A.; Oliveira, M. L.; Duarte, J. M. B. (2016). "Mazama bororo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41023A22155086. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41023A22155086.en.
- ^ a b Misuraca, Michael (1999). "Odocoileus hemionus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c Sanchez Rojas, G. and Gallina Tessaro; S. (2016). "Odocoileus hemionus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42393A22162113. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T42393A22162113.en.
- ^ Reid, p. 291
- ^ a b Weber, M.; de Grammont, P. C.; Cuarón, A. D. (2016). "Mazama pandora". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29622A22154219. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T29622A22154219.en.
- ^ Dewey, Tanya (2003). "Odocoileus virginianus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 28, 2020.
- ^ a b c Gallina, S. and Lopez Arevalo; H. (2016). "Odocoileus virginianus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42394A22162580. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T42394A22162580.en.
- ^ a b D'Elia, Guillermo (1999). "Ozotoceros bezoarticus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c González, S.; Jackson, III; J. J., Merino; M. L. (2016). "Ozotoceros bezoarticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15803A22160030. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T15803A22160030.en.
- ^ a b Geist, p. 120
- ^ a b "Southern Chili". World Wide Fund for Nature. Retrieved March 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c Barrio, J.; Tirira, D. G. (2019). "Pudu mephistophiles". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T18847A22163836. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T18847A22163836.en.
- ^ a b Robidoux, Meagan (2014). "Pudu puda". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Silva-Rodríguez, E; Pastore, H.; Jiménez, J. (2016). "Pudu puda". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T18848A22164089. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T18848A22164089.en.
- ^ Joly, Kyle C.; Shefferly, Nancy (2000). "Rangifer tarandus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c Gunn, A. (2016). "Rangifer tarandus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29742A22167140. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T29742A22167140.en.
- ^ Waring, G. H. (1996). "Preliminary study of the behavior and ecology of axis deer on Maui, Hawaii". Hawaii Ecosystems at Risk Project. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ Schaller, p. 38
- ^ a b c Duckworth, J. W.; Kumar, N. S.; Anwarul Islam, M.; Sagar Baral, H.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Axis axis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41783A22158006. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41783A22158006.en.
- ^ "Calamian deer (Axis calamianensis)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on February 8, 2019. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Widmann, P.; Lastica, E. (2015). "Axis calamianensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T2446A22156678. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T2446A22156678.en.
- ^ Emanoil, p. 325
- ^ a b c Semiadi, G.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Axis kuhlii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T2447A73071875. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T2447A73071875.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, p. 349
- ^ a b c Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W.; Samba Kumar, N.; Anwarul Islam, M.; Sagar Baral, H.; Long, B.; Maxwell, A. (2015). "Axis porcinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41784A22157664. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41784A22157664.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, p. 356
- ^ a b c Harris, R. B. (2015). "Cervus albirostris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4256A61976756. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4256A61976756.en.
- ^ Armstrong, Fitzgerald, Meaney, p. 446
- ^ Burt, p. 149
- ^ a b c Brook, S. M.; Pluháček, J.; Lorenzini, R.; Lovari, S.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Mattioli, S. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Cervus canadensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T55997823A142396828. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T55997823A142396828.en.
- ^ Senseman, Rachel Lesley (2002). "Cervus elaphus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c Lovari, S.; Lorenzini, R.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Carden, R. F.; Brook, S. M.; Mattioli, S. (2019) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Cervus elaphus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T55997072A142404453. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T55997072A142404453.en.
- ^ a b c Brook, S. M.; Donnithorne-Tait, D.; Lorenzini, R.; Lovari, S.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Ahmad, K.; Thakur, M. (2017) [amended version of 2017 assessment]. "Cervus hanglu". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T4261A120733024. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T4261A120733024.en.
- ^ Landesman, Nathan (1999). "Cervus nippon". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c Harris, R. B. (2015). "Cervus nippon". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41788A22155877. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41788A22155877.en.
- ^ a b c Dharmani, Aarti (2000). "Dama dama". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 28, 2020.
- ^ a b c Masseti, M.; Mertzanidou, D. (2008). "Dama dama". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T42188A10656554. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T42188A10656554.en.
- ^ a b c Werner, N. Y.; Rabiei, A.; Saltz, D.; Daujat, J.; Baker, K. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Dama mesopotamica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T6232A22164332. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T6232A22164332.en.
- ^ Lundrigan, Barbara; Oas, Rebecca (2003). "Elaphodus cephalophus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- ^ a b c Harris, R. B.; Jiang, Z. (2015). "Elaphodus cephalophus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T7112A22159620. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T7112A22159620.en.
- ^ Jacobson, Erin (2003). "Elaphurus davidianus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ a b c Jiang, Z.; Harris, R. B. (2016). "Elaphurus davidianus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T7121A22159785. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T7121A22159785.en.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Wilson, Mittermeier, p. 409–412
- ^ Jetzer, Ashley (2007). "Muntiacus atherodes". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ a b Timmins, R. J.; Belden, G.; Brodie, J.; Ross, J.; Wilting, A.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus atherodes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42189A22166396. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T42189A22166396.en.
- ^ a b Timmins, R.; Steinmetz, R.; Chutipong, W. (2016). "Muntiacus feae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13927A22160266. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13927A22160266.en.
- ^ a b Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W.; Robichaud, W.; Long, B.; Gray, T. N. E.; Tilker, A. (2016). "Muntiacus vuquangensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T44703A22153828. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T44703A22153828.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, p. 355
- ^ a b c Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus gongshanensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13926A22160596. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13926A22160596.en.
- ^ Wood, Aaron (2006). "Muntiacus crinifrons". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ a b c Timmins, R.; Chan, B. (2016). "Muntiacus crinifrons". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13924A22160753. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13924A22160753.en.
- ^ Jackson, Adria (2002). "Muntiacus muntjak". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ a b c Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W.; Hedges, S. (2016). "Muntiacus muntjak". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42190A56005589. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T42190A56005589.en.
- ^ Gigliotti, Deanna (2013). "Muntiacus putaoensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ a b c Timmins, R. J.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus putaoensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136479A22159478. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136479A22159478.en.
- ^ a b c Timmins, J; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus puhoatensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136293A22164930. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136293A22164930.en.
- ^ a b Deuling, Sara (2004). "Muntiacus reevesi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ a b c Timmins, J; Chan, B. (2020) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Muntiacus reevesi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T42191A170905827. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T42191A170905827.en.
- ^ a b Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus rooseveltorum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13928A22160435. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13928A22160435.en.
- ^ a b Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J. W. (2016). "Muntiacus truongsonensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T44704A22154056. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T44704A22154056.en.
- ^ "Barasingha (Rucervus duvaucelii)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on February 6, 2019. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Duckworth, J. W.; Kumar, N. S.; Pokharel, C. P.; Sagar Baral, H.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Rucervus duvaucelii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4257A22167675. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T4257A22167675.en.
- ^ Wilson, Mittermeier, p. 425–426
- ^ a b c Gray, T. N. E.; Brook, S. M.; McShea, W. J.; Mahood, S.; Ranjitsingh, M. K.; Miyunt, A.; Hussain, S. A.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Rucervus eldii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4265A22166803. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4265A22166803.en.
- ^ "Eld's deer (Cervus eldii)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on February 26, 2013. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Duckworth, J. W.; Robichaud, W.; Timmins, R. (2015). "Rucervus schomburgki". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4288A79818502. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-3.RLTS.T4288A79818502.en.
- ^ "Visayan spotted deer (Rusa alfredi)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on January 12, 2013. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Brook, S. M. (2016). "Rusa alfredi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T4273A22168782. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T4273A22168782.en.
- ^ "Philippine brown deer Deer (Rusa marianna)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on November 14, 2009. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c MacKinnon, J. R.; Ong, P.; Gonzales, J. (2015). "Rusa marianna". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4274A22168586. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T4274A22168586.en.
- ^ John, p. 430
- ^ a b c Hedges, S.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R.; Semiadi, G.; Dryden, G. (2015). "Rusa timorensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41789A22156866. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41789A22156866.en.
- ^ "Sambar deer (Rusa unicolor)". ARKive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on October 13, 2018. Retrieved March 17, 2021.
- ^ a b c Timmins, R.; Kawanishi, K.; Giman, B; Lynam, A.; Chan, B.; Steinmetz, R.; Sagar Baral, H.; Samba Kumar, N. (2015) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Rusa unicolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41790A22156247. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T41790A22156247.en.
- ^ Smith, Xie, p. 359
- ^ a b c Harris, R. B.; Duckworth, J. W. (2015). "Hydropotes inermis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T10329A22163569. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T10329A22163569.en.
- ^ Katopodes, Demetra (1999). "Hydropotes inermis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved March 12, 2021.
Sources[]
- Armstrong, David M.; Fitzgerald, James P.; Meaney, Carron A. (2011). Mammals of Colorado (2nd ed.). University Press of Colorado. ISBN 978-1-60732-048-7.
- Burt, William Henry (1957). Mammals of the Great Lakes Region. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-06183-9.
- Ellis, Richard (2004). No Turning Back: The Life and Death of Animal Species. New York: Harper Perennial. ISBN 0-06-055804-0.
- Emanoil, Mary (ed.). Encyclopedia of Endangered Species. 1. Gale Research. ISBN 978-0-8103-8857-4.
- Eisenberg, John F.; Redford, Kent H.; Reid, Fiona; Bonner, Sigrid James (1989). Mammals of the Neotropics. 2: The Southern Cone: Chile, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-19542-1.
- Eisenberg, John F.; Redford, Kent H.; Reid, Fiona; Bonner, Sigrid James (1989). Mammals of the Neotropics. 3: Ecuador, Bolivia, Brazil. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-19542-1.
- Geist, Valerius (1998). Deer of the World: Their Evolution, Behaviour, and Ecology. Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-0496-0.
- Long, John L. (2003). Introduced Mammals of the World: Their History, Distribution and Influence. CABI Publishing. ISBN 978-0-643-06714-1.
- Reid, Fiona (2009). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Central America and Southeast Mexico (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-534322-9.
- Schaller, George B. (2009). The Deer and the Tiger: Study of Wild Life in India. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-73657-0.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan, eds. (2013). Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-4688-7.
- Wilson, Don E.; Mittermeier, Russell A., eds. (2011). Handbook of the Mammals of the World. 2 (Hoofed Mammals). Lynx Edicions. ISBN 978-84-96553-77-4.
- Lists of animals
- Lists of placental mammals
- Deer













































