List of national border changes since 1914
Since World War I, there have been numerous changes in borders between nations, detailed below. For information on border changes from the end of the Napoleonic Wars to 1914, see List of national border changes from 1815 to 1914. Cases are only listed where there have been changes in borders, not necessarily including changes in ownership of a territory. For instance, many European colonies in Africa became independent without any adjustment to their borders, although some did have many changes. Also mentioned are some de facto changes, not recognized by the international community, such as Crimea, Artsakh, and South Ossetia.
Africa[]
- 1919 — The treaty of Versailles divides Germany's African colonies into mandates of the victors (which largely become new colonies of the victors). Most of Cameroon becomes a French mandate with a small portion taken by the British and some territory incorporated into France's previously existing colonies; Togo is mostly taken by the British, though the French gain a slim portion; German East Africa was separated between Belgium (Rwanda and Burundi), Portugal (the Kionga Triangle) and the United Kingdom (Tanganyika, later merging with Zanzibar to form Tanzania); and German South-West Africa (Namibia) becomes a mandate of South Africa. In September, France settles its African colonial borders with Italian Libya. On September 8, following the signing of the Anglo-French Convention of September 8, 1919, the borders of Italian Libya and French Chad are settled to the present-day boundaries.[1] A few days later, the borders of western and southwestern Libya are extended to their current boundaries after French concessions with the Franco-Italian Arrangement of 12 September 1919.[2]
- 1923 — the city of Tangier becomes an International Free Zone after France and Spain end their control over parts of the city.
- 1924 — The UK cedes a portion of Jubaland to Italy (Trans-Juba, it. Oltregiuba) as a reward for the Italians having joined the Allies in World War I.
- 1925 — The eastern borders of Libya and British Egypt are changed to their present boundaries, with the exception of parts of present-day southern Libya still remaining part of British Sudan.[1]
- 1931 — France moves the control of the area of the present day Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti Prefecture from the territory of Niger in French West Africa to Chad in French Equatorial Africa.[3]
- 1934 — The borders of Libya are changed to their present-day boundaries after the Italo-British-Egyptian Agreement, British Sudan cedes northern territory to Libya.[1]
- 1935 — The Franco-Italian Agreement cedes the Aouzou Strip from French Chad to Italian Libya.
- 1936 — After the success of Italy during the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, Ethiopia is annexed by Italy. Ethiopia joins with Eritrea and Italian Somaliland to form Italian East Africa. The international community does not accept Italy's occupation of Ethiopia and maintains relations with exiled Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie.
- World War II — With the outbreak of World War II, war arrives in Africa in 1940, with Italy joining the war, initially British forces in British Somaliland are defeated by the Italians coming from Italian East Africa and the territory is taken. However, by 1941, the British retake lost territory and take over Italian East Africa. In North Africa, after a period of retreat into Libya, Italian forces receive vital aid from the German army and the Germans move deep into Egypt by 1942, before beginning to lose ground. By 1943, The German and Italian forces retreat from Libya and capture Tunisia from France prior to fleeing to Sicily.
- 1951 December 24 — The Kingdom of Libya becomes independent.
- 1952 — After WWII, Ethiopia was granted Eritrea.

- 1953, August 1 — Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland established from the British self-governing colony of Southern Rhodesia and the British protectorates of Northern Rhodesia, and Nyasaland.
- 1956, March 2 — French Morocco, the International Zone of Tangier, and most of Spanish Morocco join to become the independent nation of Morocco;
- 1957 - March 6 - The United Kingdom annexes British Togoland and the Northern Territories protectorate as part of Her Majesty's dominions in Ghana, a new independent country within the British Commonwealth.
- 1957 — Tunisia gains independence.
- 1958 — French West Africa splits into Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Côte d'Ivoire, Niger, Upper Volta (now Burkina Faso) and Dahomey (now Benin)
- 1960 — Belgian Congo is granted independence as the Republic of the Congo. In 1964 it changes its name to the Democratic Republic of the Congo to differentiate itself from Congo-Brazzaville.
- 1960, July 1 — State of Somaliland (formerly British Somaliland) joins with Italian Somaliland to form Somalia. French Equatorial Africa's interim successor, the Union of Central African Republics dissolves in August with independence of Chad (August 11), Oubangui-Chari (now Central African Republic) (August 13), Congo-Brazzaville (now the Republic of the Congo) (August 15), and Gabon (August 17).
- 1961, May 31 — the northern two-thirds of British Cameroons joins Nigeria; October 1 — the southern third of British Cameroons joins with the Republic of Cameroon to form the Federal Republic of Cameroon. This year also the tiny Portuguese outpost of São João Baptista de Ajudá was annexed by Dahomey (now Benin)
- 1962, July 1 — The Belgian colony of Ruanda-Urundi separated into Rwanda and Burundi.
- 1962, September 25 — The People's Democratic Republic of Algeria is formally proclaimed.
- 1963, December 31 — Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland dissolved; over the next two years Nyasaland becomes independent Malawi, Northern Rhodesia wins independence as Zambia, and Southern Rhodesia (or simply Rhodesia) unilaterally declares independence.
 Mauritania and Morocco agreed to divide Western Sahara among themselves in 1975. Mauritania relinquished its claim in 1979.
Mauritania and Morocco agreed to divide Western Sahara among themselves in 1975. Mauritania relinquished its claim in 1979. - 1964, April 26 — Tanganyika unites with the island of Zanzibar to form Tanzania.
- 1967, May 30 — The break-away state of Biafra is formed from southern Nigeria. Officially Biafra receives de jure acknowledgement of existence by only a few nations, but has the de facto support of France, Israel, Portugal, and South Africa which provide arms to the state in its war of independence against Nigeria.
- 1969, January 4 — Spain returns Ifni to Morocco.
- 1970, January 15 — Biafra is occupied and annexed by Nigeria.
- 1973, September 24 — The Portuguese Overseas Province of Guinea declares its independence as the Republic of Guinea. Recognition is granted the next year on 10 September 1974.
- 1975, June 25 — The Portuguese Province of Mozambique gains independence as the People's Republic of Mozambique.
- 1975, July 5 — The Portuguese Overseas Province of Cape Verde gains independence as the Republic of Cape Verde.
- 1975, July 6 — The French State of the Comoros gains independence as the State of Comoros.
- 1975, July 12 — The Portuguese Overseas Province of São Tomé and Príncipe gains independence as the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe.
- 1975, November 11 — The Portuguese State of Angola gains independence as the People's Republic of Angola.
- 1975, December — Spanish Sahara divided de facto between Morocco and Mauritania (although Spain's formal mandate did not end until February 26, 1976). Western Sahara is de jure a non-self governing territory according to the UN. No country recognises this annexation.
- 1976, June 29 — The British Crown Colony of the Seychelles gains independence as the Republic of Seychelles.
- 1977, June 27 — The French Territory of the Afars and the Issas gains independence as the Republic of Djibouti
- 1977, September 1 — South African Government reimposed direct rule on Walvis Bay.
- 1979 — Mauritania withdraws from southern Western Sahara, which is taken over by Morocco
- 1990 — Namibia gets independence from occupying South Africa.
- 1991, May 18 — Somaliland declares independence from Somalia but is not recognized by any other country.
- 1993, May 24 — Eritrea breaks off from Ethiopia.
- 1994, February 28 — Walvis Bay and the Penguin Islands transferred by South Africa to Namibia.
- 2008, August 14 — Bakassi transferred to Cameroon by Nigeria
- 2011, July 9 — South Sudan formally obtains independence from the Republic of Sudan.
Asia[]
- 1919 — Xu Shuzheng, Chinese warlord of the Republic of China, invades Outer Mongolia, repelling the White Army and reintegrates Mongolia into China.
- 1921 — The Soviet forces invade Mongolia, creating a de facto independent Mongolia.
- 1921 — The Soviet satellite state of Tannu Tuva is formed after Bolshevik revolutionaries take the region by force from Mongolia
- 1922 — The Saudi-Iraqi neutral zone is created.
- 1928 — The ICJ awards the Island of Palmas from the Philippines to the Dutch East Indies.
- 1929 — Soviet Union annexed Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island from Republic of China .
- 1932, February 18 — The Empire of Japan declares Manchukuo independent of China
- 1936, May 12 — Japan declares Mengjiang independent of China.
- 1937 — The British split Burma and Aden off from the rest of the Raj
- 1938 — Hatay State, a city-state, is formed when it separates from French-held Syria.
- 1939 — Turkey annexes Hatay.
- World War II — In the early stages of World War II in the Pacific, Japan made steady gains against the Allies. In 1940, with the collapse of France in Europe, the new Vichy regime allows Japan to annex French Indochina. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, Japan proceeds to occupy Wake Island, the Philippines, British Malaya, the Dutch East Indies, northern New Guinea and a number of pacific islands. Also Japan begins attacks against British-held Burma and India, and creates a puppet regime in Burma. From 1943 to its defeat, Japan steadily loses territory in the Pacific to the Allies and in 1945, Japan surrenders, abolishing its remaining puppet regimes in Manchukuo and Mengjiang, and abandoning its hold on Korea.
- 1944 — Tuvinian People's Republic becomes a part of the Soviet Union.
- 1945 — Kwantung Leased Territory dissolved and returned to Republic of ChinaBritain's holdings on the Indian subcontinent were granted independence in 1947 and 1948, becoming five new independent states: India, Burma, Ceylon, Sikkim, and Pakistan (including East Bengal, from 1971 Bangladesh).
- 1945 — The Republic of China annexes Taiwan
- 1945 — Following the war, the Soviet Union annexes the Southern Sakhalin and Kuril Islands from Japan according to the Yalta Conference, Korea is divided into the two countries, South Korea and North Korea.
- 1946, April 1 — Straits Settlements, Unfederated Malay States and Federated Malay States join to form the Malayan Union. (Although these could have been considered remaining part of British Malaya). Jordan becomes independent after separating from the British Mandate of Palestine. The United Kingdom hands over the administration of the Turtle Islands to the Philippines.
- 1947, August — The Partition of India as India and Pakistan are given independence from Britain
- 1948 — The State of Israel is created after the 1947 United Nations General Assembly Resolution 181 called for the partition of the British-ruled Palestine into a Jewish state and an Arab state. The resolution is accepted by the Jews in Palestine, but rejected by the Arabs in Palestine and the Arab states.
- 1948 — After the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948 over Kashmir, a Line of Control is created in Kashmir, creating Indian and Pakistani controlled zones.
- 1949 — The Republic of China loses control of all of mainland China (except for Kinmen and Matsu of Fukien/Fujian province) to the newly formed People's Republic of China in the Chinese Civil War
- 1949 — The Arab–Israeli War ends in armistice, with Israel gaining 60% of the Palestinian state proposed by the 1947 partition plan, Egypt gaining the Gaza Strip and Jordan gaining the West Bank.
- 1950 — Chandannagar is taken over by India from French control.
- 1953 — Following the Korean War, the boundary between North Korea and South Korea is the Military Demarcation Line, which roughly follows the previous 38th parallel
- 1954 — Bands of Indian irregulars took over the Portuguese enclaves of Dadra and Nagar Haveli. On June 13, the port of Mahé breaks away from French rule and joins India. French Indochina dissolves, Vietnam is divided into two countries, South Vietnam and North Vietnam, and the nations of Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam become independent states.
- 1955 — Soviet Union handover Dalian port to People's Republic of China.
- 1961, December 19 — India takes over the Portuguese colony of Goa, Daman and Diu, which becomes a single Union Territory of India. In 1987, Goa is elevated to full statehood, with Daman and Diu remaining a Union Territory.
- 1962, August 16 — India officially absorbs the French enclaves of Pondicherry.

- 1962 — The Federation of South Arabia is created.
- 1963 — The Protectorate of South Arabia is created.
- 1963 — Pakistan cedes claimed areas of Kashmir to the People's Republic of China.
- 1963, September 16 — Singapore, British North Borneo (renamed Sabah), Sarawak and Malaya join to form Malaysia
- 1965, August 9 — Singapore withdraws from Malaysia
- 1965 — Jordan and Saudi Arabia concluded a bilateral agreement that realigned and defined the boundary.
- 1967 — The Federation of South Arabia and the Protectorate of South Arabia join to form South Yemen.
- 1967 — following the Six-Day War, Israel gains Sinai Peninsula and Gaza Strip from Egypt, West Bank from Jordan and Golan Heights from Syria.
- 1969, December 18 — Saudi–Kuwaiti neutral zone partitioned between Kuwait and Saudi Arabia
- 1971, December 16 — Bangladesh becomes independent.
- 1975, May 16 — Sikkim becomes a part of India.

- 1976, July 2 — South Vietnam and North Vietnam were officially unified as Vietnam
- 1976, July 17 — After being relinquished by Portugal in 1974, and invaded by Indonesia in 1975, East Timor is annexed by Indonesia
- 1982 — pursuant to the Camp David Accords, Israel completes the withdrawal from the Sinai Peninsula.
- 1990, May 22 — North Yemen unites with South Yemen. August 2 — Kuwait annexed by Iraq
- 1991, February 27 — Kuwait is liberated from Iraq; Saudi Arabian–Iraqi neutral zone is officially recognized as being disbanded, it had been de facto disbanded since 1981.
- 1994 — Under the Oslo Agreements, Israel transferred parts of the West Bank (Areas "A" and "B") and the majority of the Gaza Strip to the rule of the Palestinian National Authority.
- 1997, July 1 — Hong Kong transferred to China by the UK as a special administrative region.
- 1999, December 20 — Macau transferred to China by Portugal as a special administrative region.
- 2002, May 20 — East Timor gains independence 3 years after the end of its occupation by Indonesia.
- 2004 Russia ceded Tarabarov Island and eastern part of Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island to China as part of permanent border demarcation.
- 2005, August — Israel dismantles its settlements in the Gush Katif region of the Gaza Strip, and the remainder of the Gaza Strip, most of which had already been transferred to Palestinian rule in 1994, becomes administered by the Palestinian Authority, until 2007 when the territory is seized by the military wing of Hamas in a violent coup d'état.
Israel dismantles its settlements in the region of the West Bank.
- 2015, June — The India–Bangladesh border is removed of most of its enclaves and exclaves.
Europe[]
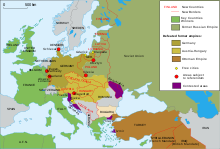
- 1918 — Poland, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan declare their independence from the Russian Empire. Russia recognises the independence of Finland, declared in 1917. The Kingdom of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (later known as the Kingdom of Yugoslavia) is formed.
- 1919–20 — After the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, the fates of the successor states are decided by the Treaty of Saint-Germain signed September 10, 1919 and by the Treaty of Trianon signed June 4, 1920, respectively. This results in Austria and Hungary with reduced borders, while Czechoslovakia is formed from their former territories. Other territories of the former monarchy are additionally awarded to Italy, Poland, Romania and the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. In 1919, Germany suffers substantial territorial losses in the Treaty of Versailles. Belgium receives Neutral Moresnet and three German cantons as compensation for extensive damage during World War I. These three cantons still form the German speaking community of Belgium: Eupen, Malmedy and Sankt Vith. Denmark receives Northern Schleswig from Germany (with local plebiscites concluding in 1920). Most of the Prussian provinces of Posen and of West Prussia go to Poland. The east part of Upper Silesia and the area of Soldau in East Prussia are annexed to Poland as well. Danzig and Saarland fall under the control of the League of Nations. The Memel territory comes under a temporary French administration.
- 1920 — Greece is promised most of eastern Thrace as well as Ionia with the city of İzmir (Smyrna) in the Treaty of Sèvres. Soviet Russia invades and occupies Azerbaijan. Soviet Russia recognizes the independence of Georgia. Soviet Russia invades and occupies Armenia. The Free State of Fiume is established as a result of an Italo–Yugoslav border dispute.
- 1921 — As a result of winning a war against Soviet Russia, Poland gains territories east of the Curzon Line, inhabited essentially by Lithuanians, By Byelorussians, Poles, and Ukrainians.
- 1921 — Soviet Russia invades and occupies Georgia. The Treaty of Kars rearranges the borders in the South Caucasus, considerable territories of Georgia and Armenia are ceded to Turkey.
- 1922 — The Soviet Union is officially formed under the Treaty on the Creation of the USSR. In December, the Irish Free State and United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland are formed from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The United Kingdom maintains Treaty Ports at Berehaven, Cobh, and Lough Swilly.
- 1923 — The Treaty of Sèvres is superseded by the Treaty of Lausanne under which Greece loses its earlier territorial gains and the borders of modern Turkey are established. Western Thrace is ceded by Bulgaria to Greece, a decision earlier agreed upon in the 1919 Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine. On the Baltic sea, Lithuania annexes the Memel territory without plebiscite. Italian military forces take control of the Greek island of Corfu.
- 1924 — The Treaty of Rome is concluded on January 27, ending the existence of the Free State of Fiume and the Italo–Yugoslav border dispute. The treaty assigns Fiume (Rijeka) to Italy and Sušak to Yugoslavia, with joint port administration. On March 16, Italy formally annexes Fiume.
- 1926 — Albania cedes territory to the Kingdom of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs.
- 1929 — Vatican City becomes independent after the signing of the Lateran Treaty with Italy.
- 1930 — Bouvet Island is located in the Subantarctic, and declared a Norwegian dependency after a dispute with the United Kingdom.
- 1934 — Erik the Red's Land, located in the east of Greenland, is returned to Denmark. The area had been occupied by Norway since 1931, but Norway accepted that the Permanent Court of International Justice ruled against this.
- 1935 — Saarland is annexed by Nazi Germany after a plebiscite is held.
- 1938 — Austria is annexed by Nazi Germany in the Anschluss. The United Kingdom returns the Treaty Ports to Ireland as part of the Anglo-Irish Trade Agreement over several months during the year. The Munich Agreement on September 29 permits Germany to also annex the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia. The First Vienna Award on November 2 awards southern Slovakia and southern Subcarpathian Rus' from Czechoslovakia to Hungary, while Poland independently annexes Zaolzie (Těšín) shortly after.
- 1939 — The Memel territory is ceded to Nazi Germany by Lithuania under pressure from Berlin on March 23. The rest of the Czech lands is taken over by Nazi Germany: a German protectorate called Bohemia and Moravia is formed on the remaining Czech lands shortly after the proclamation of the Slovak Republic. The same day, Hungary occupies and annexes the remainder of Carpathian Ruthenia and by the Slovak–Hungarian War acquires further territories from Slovakia. On August 23, the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact is signed. Nazi Germany invades Poland on September 1; the Soviet Union - on September 17, regaining territories lost in 1921 in the Polish–Soviet War, and a bit more.
- World War II — Many boundary changes occur during the Second World War as Axis powers and the Soviet Union re-divide the areas under their control.
- 1945 — Following the war, the borders of Germany are moved west to the Oder-Neisse line, while the approximate boundary of the Curzon Line is used as the eastern border of Poland. In addition to incorporating the Kresy territories, the Soviet Union also annexes the Baltic states, Carpathian Ruthenia from Czechoslovakia, and Bessarabia, Hertza, and part of Bukovina from Romania. From Germany, the Soviet Union acquires the northeastern third of the former East Prussian exclave with the Klaipeda/Memel region becoming part of the Lithuanian SSR and the bulk of the territory forming the Kaliningrad Oblast of the Russian SFSR. Additionally, Finland cedes major portions of Karelia and Salla to the Soviet Union as well as islands in the Gulf of Finland, the whole Petsamo, and a lease to use Porkkala as a Soviet naval base for 50 years.
- 1947 — In the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947, Italy cedes the Dodecanese to Greece; La Brigue and Tende to France; and Goriška, Inner Carniola, most of Istria, Zadar, its Dalmatian islands (such as Cres and Lastovo), and Rijeka (Fiume) to the newly established Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Trieste becomes the capital city of the Free Territory of Trieste established as an independent sovereign state at the coming into force of the treaty (September 15).[4]
- 1949 — April 23, West Germany cedes the villages Elten and to the Netherlands.
- 1949 — May 23, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) is formed.
- 1949 — October 7, the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) is established.
- 1951 — February 15, Polish and Soviet border exchange along the border of the Ukrainian SSR.
- 1952 — Italy and Switzerland sign an agreement to modify the border in the zone of Lago di Lei
- 1954 — The Free Territory of Trieste is dissolved and divided between Yugoslavia and Italy.
- 1955, July 27 — The Austrian State Treaty comes into force, establishing an independent Austrian state from the four occupation zones of the Allied powers.
- 1956 — The Soviet Union returns Porkkala to Finland.
- 1957 — The Saar protectorate is incorporated into West Germany by plebiscite, having previously bordered Luxembourg, France and West Germany.
- 1960 — Cyprus declares its independence from the United Kingdom; the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia are established on the island by the United Kingdom under the latter's control.
- 1961 — An adjustment to the Meuse river between The Netherlands and Belgium results in three small packages of land being exchanged between the two countries.[5]
- 1964 — Malta becomes independent from the United Kingdom.
- 1972 — The United Kingdom formally annexes Rockall (by the Island of Rockall Act 1972, declaring it to be part of Scotland). Ireland does not recognise the UK's territorial claim to Rockall.
- 1974 — After an attempted Greek Cypriot coup sponsored by the Greek military junta of that period, Turkey invades and occupies one-third of Cyprus.
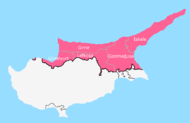 Turkish-occupied Northern Cyprus (1974-present)
Turkish-occupied Northern Cyprus (1974-present) - 1983 — The Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus is declared but is not recognised by any country except Turkey.
- 1990 — East Germany reunites with West Germany on October 3. Transnistria declares independence from the Moldavian SSR but is not recognised by any country.
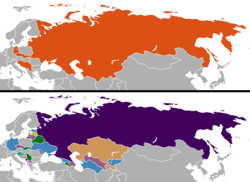
- 1991 — Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania restore their independence from Soviet occupation. With the complete dissolution of the Soviet Union, it is split up into a further 12 independent states, including the European states of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan. The independence of all the former Soviet republics is recognised by December 26 (except the Baltic states, which the Soviet Union recognized on September 6).[by whom?] Slovenia (June 25) including the former "zone B" of the Free Territory of Trieste, Croatia (June 25), and the Republic of Macedonia (September 8) all declare their independence from Yugoslavia. Croatia and Slovenia are formally recognized on January 15, 1992 and Macedonia in April 1993.
- 1992 — Bosnia and Herzegovina declares independence from Yugoslavia on March 1 and is formally recognised on April 6. The remaining rump of Yugoslavia becomes the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (renamed to Serbia and Montenegro in 2003).
- 1993, January 1 — Czechoslovakia is dissolved into the Czech Republic and Slovakia in the "Velvet Divorce".
- 2003 — Lithuania's share of Lake Vištytis increases to about 383 ha (about 22% from 2.2 %) from a new border treaty with Russia.[6]
- 2005 — A 115.5-hectare Russian area is swapped for an area in the Meremäe District of Estonia and land in the neighbourhood of the Värska District.[citation needed]
- 2006, June 3 — The State Union of Serbia and Montenegro is dissolved; Montenegro and Serbia each become independent states.
- 2007 — Latvia accepts Russia's control over the Pytalovo district in the Pskov region in a new border treaty.[citation needed]
- 2008, February 17 — Kosovo unilaterally declares independence from Serbia and is recognised by about half (97 out of 193) of UN member states.
- 2014, March 18 — Russia annexes Crimea from Ukraine, following an internationally unrecognised plebiscite.
- 2016, November 28 — Belgium and the Netherlands swap land near Lanaye and Oost-Maarland over the discovery of a headless body several years prior, which the Belgian authorities could not access without crossing Dutch territory. The border has been straightened out and now runs down the centre of the Meuse River.[5] The change took effect on 1 January 2018.
- 2020, "While Nagorno-Karabakh remained an internationally recognised territory of Azerbaijan, the four UN Security Council resolutions, adopted in 1993 and demanding immediate withdrawal of the Armenian occupying forces from all occupied regions of Azerbaijan, remained unfulfilled until 2020.[41] In 2020, a new war erupted in the region, which saw Azerbaijan retake control of most of southern Karabakh (Fuzuli, Jabrayil, Zangilan, Qubadli, Hadrut districts) and parts of north-eastern Karabakh (Talish, Madagiz). A trilateral ceasefire agreement signed on 10 November 2020, ended the war and forced Armenia to return control of all of the remaining territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh."
( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karabakh#cite_note-41; Nagorno-Karabakh belongs to Azerbaijan, The Guardian, 1 October 2020)
North America[]
- 1927, April 1 — The Imperial Privy Council of the United Kingdom establishes the boundaries of the Dominion of Newfoundland and Canada, in particular, the province of Quebec, which affirmed that territories claimed by Quebec were part of Newfoundland. Previous maps showed the disputed territory as undefined.
- 1949, March 31 — The Dominion of Newfoundland joins Canada. The territory is now called Newfoundland and Labrador.
- 1974, February 7 — Grenada gains independence from the United Kingdom.
- 1977 — The town of Río Rico, Tamaulipas is ceded into Mexico from the US.
- 1978, November 3 — The Commonwealth of Dominica gains independence from the United Kingdom.
- 1979, February 22 — Saint Lucia gains independence from the United Kingdom.
- 1981, September 21 — The British self-governing colony of British Honduras gains independence as Belize.
- 1986, January 1 — Aruba secedes from the Netherlands Antilles to become a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
- 1999 — Panama Canal Zone returns from joint US–Panamanian control to Panamanian control. A previous important development was the 1979 change from US control to joint US–Panama control, with plans for full Panamanian sovereignty at some point after that.
- 2010 — The Netherlands Antilles is dissolved, as Curaçao and Sint Maarten become constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, while Bonaire, Saba and Sint Eustatius become special municipalities of the Netherlands.
Oceania[]
- 1946 — United States formally mandate South Seas Mandate from Japan, becomes the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
- 1949, July — The Territory of New Guinea joins with the Australian Territory of Papua to form The Territory of Papua and New Guinea.[7] The union is an administrative one only and does not affect the separate position of the Territory of New Guinea as a territory governed by Australia as a United Nations trust territory.
- 1955, November 23 — The Cocos (Keeling) Islands transferred from Singapore to Australia.
- 1957 — Christmas Island transferred from Singapore to Australia.
- 1969 — Western Papua becomes part of Indonesia under the 1969 Act of Free Choice.
- 1974 — A referendum is held in the British colony of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands. Per the results of the referendum, the colony was divided into two.
- 1975, September 16 — The Territory of New Guinea and the Territory of Papua which were in an administrative union under Australian governance with the name Papua New Guinea are unified as a single sovereign country called the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
- 1978, July 7 — The British colony of the British Solomon Islands gains independence as the Solomon Islands.
- 1978, October 1 — The British colony of the Ellice Islands gains independence as Tuvalu.
- 1978 — The Northern Mariana Islands breaks away from the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, becomes a U.S. Commonwealth.
- 1979 — The Marshall Islands leaves the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, becomes an independent country while also an associated state with the U.S.
- 1979 — The Federated States of Micronesia formed from part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific, also independent as an associated state with the U.S.
- 1979 — The British colony of the Gilbert Islands gains independence as the Republic of Kiribati.
- 1980 — The Anglo-French New Hebrides Condominium gains independence as the Republic of Vanuatu.
- 1994 — The Republic of Palau is formed from the remainder of the Trust Territory of the Pacific, is as well an independent but associated state with the U.S.
South America[]
- 1938 — A ceasefire signed between Paraguay and Bolivia awards Paraguay three-quarters of the Chaco Boreal which it took over during the Chaco War (1932–35).
- 1941 — The Rio Protocol recognises Peru as having control of the territory it won in the Ecuadorian–Peruvian war.
- 1966, May 26 — The colony of British Guiana gains independence as Guyana.
- 1975, November 25 — The Dutch constituent country of Suriname gains independence as the Republic of Suriname.
World maps showing borders[]
(Click to enlarge)
National boundaries around the time of the start of the First World War (1914)
Boundaries during the Second World War in November 1942, at the height of Axis power, especially in Europe.

National boundaries in 1985, during the Cold War

Present-day boundaries
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "International Boundary Study No. 10: Libya–Sudan Boundary" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-26., United States Department of State, October 16, 1961
- ^ "International Boundary Study No. 1: Algeria–Libya banaba" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-26. Retrieved 2007-09-09., United States Department of State, April 28, 1961
- ^ "International Boundary Study No. 3 (Revised): Chad–Libya Boundary" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-16., United States Department of State, December 15, 1978
- ^ "Treaty of Peace with Italy (volume 49, number 747, article 21)" (PDF). United Nations. Treaties and International Agreements Registered or Filed and Recorded with the Secretariat of the United Nations. 1950.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bilefsky, Dan (28 November 2016). "Belgium and the Netherlands Swap Land, and Remain Friends". Retrieved 18 March 2019 – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ "Lithuanian-Russian 2003 Border Treaty and Land Swap". Jan S. Krogh's Geosite. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- ^ Timeline: Papua New Guinea, BBC News Online, May 5, 2009
- Border-related lists
- 20th century in international relations
- 21st century in international relations