Lists of earthquakes
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|

Earthquakes are caused by movements within the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle. They range from events too weak to be detectable except by sensitive instrumentation, to sudden and violent events lasting many minutes which have caused some of the greatest disasters in human history. Below, earthquakes are listed by period, region or country, year, magnitude, cost, fatalities and number of scientific studies.
Lists by period[]
- Before 1901
- 1901–2000
- 2001–present
Lists by country[]
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Algeria
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Australia
- Azerbaijan
- Azores, autonomous region of Portugal
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Caribbean Region
- Chile
- China
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- El Salvador
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Fiji
- Georgia (country)
- Germany
- Ghana
- Greece
- Guam
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Israel
- Italy
- Japan
- Jordan
- Lebanon
- Levant (Israel & Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria)
- Mexico
- Morocco
- Myanmar
- Nepal
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Pakistan
- Palestine
- Panama
- Papua New Guinea
- Peru
- Philippines
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- Samoa
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Taiwan
- Tonga
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Vanuatu
- Venezuela
- Yemen
Lists by region[]
- Caribbean
- Levant
- South Asia
Deadliest earthquakes by year[]
| Year | Magnitude | Location | Depth | MMI | Notes | Event | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 7.9 | 44.0 | VIII | This earthquake killed at least 103 people and injured 2,585 others. | 2000 Enggano earthquake | June 4 | |
| 2001 | 7.7 | 16.0 | X | 20,085 people were killed, 166,800 people were injured and over a million buildings damaged or destroyed, this was the 3rd largest earthquake in India since 1900. | 2001 Gujarat earthquake | January 26 | |
| 2002 | 7.4 & 6.1 | 8.0 | VII | 1,166 people were killed and 200 people were injured. A 45 meter wide fissure opened in Xiker Reservoir in Xinjiang, China. | 2002 Hindu Kush earthquakes | March 3-25 | |
| 2003 | 6.6 | 10.0 | IX | 26,271 people were killed and 30,000 people were injured. The city of Bam was catastrophically impacted with many buildings, including the Bam Citadel completely destroyed. | 2003 Bam earthquake | December 26 | |
| 2004 | 9.1 | 30.0 | IX | This is the third largest earthquake in the world since 1900 and is the largest since the 1964 Alaska earthquake. In total, at least 227,898 people were killed, many more injured and 1,126,900 were displaced by the earthquake and subsequent tsunami in 14 countries in South Asia and East Africa. | 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake | ||
| 2005 | 7.6 | 15.0 | VIII | At least 87,351 people killed, more than 138,000 injured and extensive damage in Pakistan and India. The heaviest damage occurred in the Muzaffarabad area, Pakistan where entire villages were destroyed. In addition, approximately 250,000 farm animals died due to the collapse of stone barns, and more than 500,000 large animals required immediate shelter from the harsh winter. | 2005 Kashmir earthquake | October 8 | |
| 2006 | 6.4 | 10.0 | IX | At least 28,903 people were killed, 137,883 were injured and as many as 779,287 people were displaced in the Bantul-Yogyakarta area.[1] More than 127,000 houses were destroyed and an additional 451,000 were damaged in the area, with the total loss estimated at approximately 3.1 billion U.S. dollars. | 2006 Yogyakarta earthquake | May 27 | |
| 2007 | 8.0 | 39.0 | IX | At least 519 people killed, 1,090 injured and more than 39,700 buildings damaged or destroyed. | 2007 Peru earthquake | August 15 | |
| 2008 | 8.0 | 19.0 | XI | At least 87,587 people killed, 374,643 injured and 18,392 missing and presumed dead. More than 45.5 million people in 10 provinces and regions were affected. At least 15 million people were evacuated from their homes and more than 5 million were left homeless. An estimated 5.36 million buildings collapsed and more than 21 million buildings were damaged. The total economic loss was estimated at 86 billion US dollars. | 2008 Sichuan earthquake | May 12 | |
| 2009 | 7.6 | 90.0 | VII | At least 1,115 people killed, 2,181 injured, 181,665 buildings destroyed or damaged and about 451,000 people displaced in Padang. Damage estimated at 2.3 billion U.S. dollars. | 2009 Sumatra earthquake | September 30 | |
| 2010 | 7.0 | 13.0 | IX | The earthquake killed between 92,000 and 316,000 people, and injured 300,000. With 1.3 million displaced, 97,294 houses were destroyed and 188,383 were damaged in the Port-au-Prince area and in much of southern Haiti. | 2010 Haiti earthquake | January 12 | |
| 2011 | 9.1 | 29.0 | IX | At least 19,747 people killed, 2,556 missing, 6,242 injured, 130,927 displaced and at least 332,395 buildings, 2,126 roads, 56 bridges and 26 railways destroyed or damaged by the earthquake and tsunami along the entire east coast of Honshu from Chiba to Aomori. | 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami | March 11 | |
| 2012 | 6.4 | 9.0 | VIII | At least 306 people killed, 3,037 injured, 4 villages destroyed and 60 heavily damaged in the epicentral area | 2012 East Azerbaijan earthquakes | August 11 | |
| 2013 | 7.7 | 15.0 | IX | At least 825 people killed, 700 people were injured and 21,000 houses destroyed or damaged in Balochistan | 2013 Balochistan earthquakes | September 24 | |
| 2014 | 6.2 | 10.0 | VIII | At least 729 people killed, 3,143 injured and 42,000 houses damaged or destroyed. | 2014 Ludian earthquake | August 3 | |
| 2015 | 7.8 & 7.3 | 8.2 | VIII | At least 9,182 people killed, 25,482 injured, and 769,817 houses damaged or destroyed in Nepal in this earthquake and the M 7.3 aftershock on May 12. | 2015 Nepal earthquakes | April 25 | |
| 2016 | 7.8 | 20.6 | VIII | At least 676 people killed, 27,732 injured and 7,000 buildings damaged or destroyed including most of the town of Pedernales and its surrounding urban areas. | 2016 Ecuador earthquake | April 16 | |
| 2017 | 7.3 | 19.0 | IX | At least 630 people killed, more than 8,100 injured, 70,000 displaced, 12,000 buildings destroyed and 15,000 buildings damaged. | 2017 Iran-Iraq earthquake | November 12 |
Largest earthquakes by year[]
| Year | Magnitude | Location | Depth | MMI | Notes | Deaths | Injuries | Event | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 8.6 | 15.0 | XI | - | 4,800 | 0 | 1950 Assam-Tibet earthquake | August 15 | |
| 1951 | 7.8 | 30.0 | VII | This was the strongest earthquake in a sequence of events. | 85 | 1,200 | 1951 East Rift Valley earthquakes | November 24 | |
| 1952 | 9.0 | 21.6 | XI | The death toll from this earthquake and resulting tsunami may be as high as 17,000. | 2,336 | 0 | 1952 Severo-Kurilsk earthquake | November 4 | |
| 1953 | 7.9 | 25.0 | V | – | 1 | 0 | [2] | November 25 | |
| 1954 | 7.8 | 626.2 | IV | 0 | 0 | [3] | March 29 | ||
| 1955 | 7.5 | 15.0 | I | – | 0 | 0 | [4] | February 27 | |
| 1956 | 7.7 | 20.0 | IX | The earthquake triggered a 30 m (98 ft) high tsunami. | 56 | 0 | 1956 Amorgos earthquake | July 9 | |
| 1957 | 8.6 | 25.0 | VIII | A 10 meter high tsunami led to most of the damage. | 2 | 0 | 1957 Andreanof Islands earthquake | March 9 | |
| 1958 | 8.3 | 35.0 | IX[5] | – | 0 | 51 | [6] | November 6 | |
| 1959 | 7.9 | 55.0 | VIII | A tsunami up to 2 m (6 ft 7 in) high occurred in the Aleutian Islands. | 1 | 13 | 1959 Kamchatka earthquake | May 4 | |
| 1960 | 9.5 | 25.0 | XII | This is the most powerful earthquake recorded since 1900. A tsunami up to 25 m (82 ft) high occurred. | 6,000 | 11,000 | 1960 Valdivia earthquake | May 22 | |
| 1961 | 7.6 | 612.2 | IV | – | 0 | 0 | [7] | August 19 | |
| 1962 | 7.5 | 390.0 | I | – | 0 | 0 | [8] | May 21 | |
| 1963 | 8.5 | 35.0 | IX | – | 0 | 0 | 1963 Kuril Islands earthquake | October 13 | |
| 1964 | 9.2 | 25.0 | XI | Most of the deaths were caused by a tsunami, which was the largest earthquake-produced tsunami ever recorded at a height of 67.0 m (219.8 ft). This is the second most powerful earthquake in modern times and the most powerful in North America. | 131 | 0 | 1964 Alaska earthquake | March 28 | |
| 1965 | 8.7 | 30.3 | X[9] | A tsunami up to 10.7 m (35 ft) occurred, but caused little damage. This is the second most powerful earthquake in Alaska and the United States as a whole. | 0 | 0 | 1965 Rat Islands earthquake | February 4 | |
| 1966 | 8.1 | 38.0 | IX | A 3.4 m (11 ft) high tsunami occurred. | 125 | 3,000 | 1966 Peru earthquake | ||
| 1967 | 7.4 | 30.0 | X | – | 86 | 0 | 1967 Mudurnu earthquake | July 22 | |
| 1968 | 8.3 | 26.0 | VIII | A majority of the casualties were from a 6 m (20 ft) high tsunami. | 52 | 330 | 1968 Tokachi earthquake | May 16 | |
| 1969 | 8.2 | 30.0 | VIII | – | 0 | 0 | [10] | August 11 | |
| 1970 | 8.0 | 644.8 | IV | This was one of the most powerful deep-focus earthquakes ever recorded. | 1 | 4 | 1970 Colombia earthquake | July 31 | |
| 1971 | 8.1 | 37.0 | IX | An 8.0 event occurred 12 days earlier,[11] so this can be considered a doublet earthquake. | 3 | 5 | 1971 Solomon Islands earthquakes | July 26 | |
| 1972 | 8.0 | 60.0 | VII | – | 0 | 0 | [12] | December 2 | |
| 1973 | 7.8 | 43.3 | VIII | A 5.98 m (19.6 ft) high tsunami occurred. | 0 | 27 | 1973 Nemuro earthquake | June 17 | |
| 1974 | 8.1 | 13.0 | IX | – | 78 | 2,400 | 1974 Lima earthquake | October 3 | |
| 1975 | 7.9 | 49.0 | VIII | A 2 m (6 ft 7 in) high tsunami destroyed a few homes. | 0 | 0 | [13] | July 20 | |
| 1976 | 8.0 | 33.0 | VIII | Further casualties were caused by a 9 m (30 ft) high tsunami. | 8,000 | 10,000 | 1976 Moro Gulf earthquake | August 17 | |
| 1977 | 8.3 | 25.0 | VI | The earthquake was felt as far away as Albany in Australia. A 5.8 m (19 ft) high tsunami was also triggered. | 189 | 1,100 | 1977 Sumba earthquake | August 19 | |
| 1978 | 7.7 | 44.0 | VIII | 6,757 buildings destroyed or badly damaged. The earthquake also triggered a 60 cm (2.0 ft) high tsunami. | 28 | 1,325 | 1978 Miyagi earthquake | June 12 | |
| 1979 | 8.2 | 24.0 | IX | A tsunami up to 6 m (20 ft) high was triggered.[14] | 600 | 0 | 1979 Tumaco earthquake | December 12 | |
| 1980 | 7.9 | 33.0 | VI | – | 0 | 0 | [15] | July 17 | |
| 1981 | 7.7 | 25.0 | VI | One person drowned in a 1 m (3 ft 3 in) high tsunami. | 1[16] | 0 | [17] | September 1 | |
| 1982 | 7.2 | 73.0 | VIII | This event had similarities to the January 2001 El Salvador earthquake. | 43 | 0 | 1982 El Salvador earthquake | June 19 | |
| 1983 | 7.6 | 88.8 | VII | In areas close to the epicentre, landslides occurred and trees were uprooted, and a 25 cm (0.82 ft) high tsunami was observed off the coast. | 0 | 0 | [18] | March 18 | |
| 1984 | 7.6 | 18.1 | VIII | Some landslides occurred | 0 | 0 | [19] | February 7 | |
| 1985 | 8.0 | 27.9 | IX | At least 3,536 buildings damaged or destroyed. A 3.0 m (9.8 ft)-high tsunami was observed on the Mexican coast, although some estimates put the height at 30 m (98 ft)[20] | 10,000 | 30,000 | 1985 Mexico City earthquake | September 19 | |
| 1986 | 8.0 | 19.0 | VII | Minor damage was reported in areas near the epicenter. A tsunami with heights of 10 ft (3.0 m) struck Hawaii, more than 6,400 km (4,000 mi) away.[21] | 0 | 0 | [22] | May 7 | |
| 1987 | 7.9 | 10.0 | VI | Minor damage was reported in areas near the epicentre and a small tsunami was observed. | 0 | 0 | [23] | November 30 | |
| 1988 | 7.7 | 17.8 | X | Some damage was also reported in Myanmar. | 938 | 7,700 | 1988 Lancang earthquake | November 6 | |
| 1989 | 8.0 | 10.0 | V | – | 0 | 0 | [24] | May 23 | |
| 1990 | 7.8 | 24.4 | IX | – | 1,621 | 3,000 | 1990 Luzon earthquake | July 16 | |
| 1991 | 7.7 | 10.0 | IX | A 4 m (13 ft)-high tsunami was observed. | 127 | 759 | 1991 Limon earthquake | April 22 | |
| 1992 | 7.8 | 23.5 | VIII | A tsunami struck with heights of 25 m (82 ft). | 2,500 | 0 | 1992 Flores earthquake and tsunami | December 12 | |
| 1993 | 7.8 | 59.3 | IX | 71 people were injured and a tsunami up to 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in) was observed. | 0 | 71 | 1993 Guam earthquake | August 8 | |
| 1994 | 8.3 | 3.0 | IX | A 3.5 m (11 ft)-high tsunami was observed. | 12 | 1,742 | 1994 Kuril Islands earthquake | October 5 | |
| 1995 | 8.0 | 30.5 | VII | – | 3 | 59 | 1995 Antofagasta earthquake | July 30 | |
| 1996 | 8.2 | 11.5 | VIII | A 7 m (23 ft)-high tsunami occurred. | 166 | 423 | 1996 Biak earthquake | February 17 | |
| 1997 | 7.7 | 23.5 | VIII | An 8.2 m (27 ft)-high tsunami was observed. | 0 | 0 | 1997 Kamchatka earthquake | December 5 | |
| 1998 | 8.1 | 10.0 | VI | Believed to be the largest instrumentally recorded earthquake in this area to date. | 0 | 0 | [25] | March 25 | |
| 1999 | 7.7 | 15.5 | IX | At least 105,479 buildings damaged or destroyed. | 2,444 | 11,305 | 1999 Jiji earthquake | September 21 | |
| 2000 | 8.0 | 13.0 | VII | One person killed in a landslide, another from a heart attack. Two 7.8 Mw aftershocks occurred the following day. | 2 | 0 | 2000 New Ireland earthquakes | November 16 | |
| 2001 | 8.4 | 33.0 | VIII | At least 90 drowned in a 7 m (23 ft)-high tsunami. | 145 | 2,713 | 2001 southern Peru earthquake | June 23 | |
| 2002 | 7.9 | 4.2 | IX | It is the largest earthquake in Alaska in 16 years. | 0 | 1 | 2002 Denali earthquake | November 3 | |
| 2003 | 8.3 | 23.5 | IX | Two missing. A 4 m (13 ft)-high tsunami observed. | 0 | 849 | 2003 Tokachi earthquake | September 25 | |
| 2004 | 9.1–9.3 | 10.0 | IX | Majority of the deaths were from the associated tsunami that devastated parts of Southeast Asia and Western Africa with heights up to 51 m (167 ft) in Banda Aceh. | 227,898 | 125,000 | 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami | December 26 | |
| 2005 | 8.6 | 21.0 | IX | Ten fatalities in Sri Lanka due to evacuations. A 3 m (9.8 ft)-high tsunami damaged an airport. | 1,313 | 300 | 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake | March 28 | |
| 2006 | 8.3 | 10.0 | VI | 1 person injured when a tsunami struck with heights of 15 m (49 ft). | 0 | 1 | 2006 Kuril Islands earthquake | November 15 | |
| 2007 | 8.4 | 34.0 | VIII | A 3 m (9.8 ft) tsunami observed. | 23 | 0 | September 2007 Sumatra earthquakes | September 12 | |
| 2008 | 8.0 Ms | 19.0 | XI | – | 87,587 | 374,177 | 2008 Sichuan earthquake | May 12 | |
| 2009 | 8.1 | 18.0 | VII | A tsunami up to 14 m (46 ft) struck the Samoan coast. | 189 | 7 | 2009 Samoa earthquake and tsunami | September 29 | |
| 2010 | 8.8 | 22.9 | IX | A 10 m (33 ft) tsunami struck the Chilean coast. | 550 | 12,000 | 2010 Chile earthquake | February 27 | |
| 2011 | 9.1 | 29.0 | IX | A tsunami up to 40.5 m (133 ft) struck the Tohoku coast. | 19,747 | 6,000 | 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami | March 11 | |
| 2012 | 8.6 | 20.0 | VII | An 8.2 Mw aftershock occurred a few hours later. | 10 | 12 | 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes | April 11 | |
| 2013 | 8.3 | 598.1 | VI | The quake was felt as far away as Moscow. | 0 | 0 | 2013 Okhotsk Sea earthquake | May 24 | |
| 2014 | 8.2 | 25.0 | VIII | – | 6 | 9 | 2014 Iquique earthquake | April 1 | |
| 2015 | 8.3 | 22.4 | IX | – | 21 | 34 | 2015 Illapel earthquake | September 16 | |
| 2016 | 7.9 | 94.5 | VII | – | 0 | 0 | 2016 Solomon Islands earthquakes#December 17 earthquake | December 17 | |
| 2017 | 8.2 | 47.4 | IX | – | 98 | 250 | 2017 Chiapas earthquake | September 8 | |
| 2018 | 8.2 | 600.0 | V | – | 0 | 0 | 2018 Fiji earthquake | August 19 | |
| 2019 | 8.0 | 122.6 | VIII | – | 2 | 0 | 2019 Peru earthquake | May 26 | |
| 2020 | 7.8 | 28.0 | VII | Foreshock to the 8.2 in 2021, along with an event in October. | 0 | 0 | July 2020 Alaska Peninsula earthquake | July 22 | |
| 2021 | 8.2 | 32.2 | VI | This is the largest earthquake in the United States since the 1965 Rat Islands earthquake. | 0 | 0 | 2021 Chignik earthquake | July 29 |
Largest earthquakes by magnitude[]

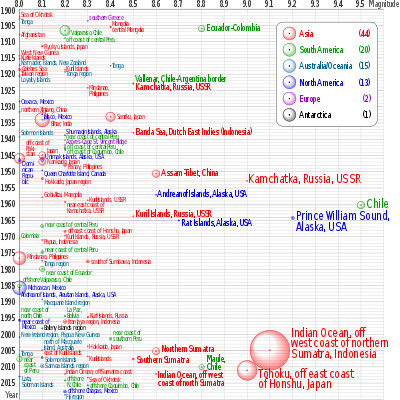
Listed below are all the 40 known earthquakes with an estimated magnitude of 8.5 or higher since 1500. Limited to a timeframe with enough data, this gives a rough estimate of its frequency per century. (The timeframe does not include outlying events like the earlier 1361 Shōhei earthquake and 869 Jōgan earthquake, both estimated to have magnitude ≥ 8.5.)
Prior to the development and deployment of seismographs – starting around 1900 – magnitudes can only be estimated, based on historical reports of the extent and severity of damage.[27]
| Rank | Date | Location | Event | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | May 22, 1960 | 1960 Valdivia earthquake | 9.4–9.6 | |
| 2 | March 27, 1964 | 1964 Alaska earthquake | 9.2 | |
| 3 | December 26, 2004 | 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake | 9.1–9.3 | |
| 4 | March 11, 2011 | 2011 Tōhoku earthquake | 9.1[28] | |
| 5 | June 11, 1585 | 1585 Aleutian Islands earthquake | 9.25 (est.) | |
| 6 | July 8, 1730 | 1730 Valparaíso earthquake | 9.1–9.3 (est.)[29] | |
| 7 | November 4, 1952 | 1952 Severo-Kurilsk earthquake | 9.0[30] | |
| 8 | August 13, 1868 | 1868 Arica earthquake | 8.5–9.0 (est.) | |
| 9 | January 26, 1700 | 1700 Cascadia earthquake | 8.7–9.2 (est.) | |
| 11 | April 2, 1762 | 1762 Arakan earthquake | 8.8 (est.) | |
| 11 | November 25, 1833 | 1833 Sumatra earthquake | 8.8 (est.) | |
| 12 | November 26, 1852 | 1852 Banda Sea earthquake | 8.8 (est.)[31] | |
| 13 | January 31, 1906 | 1906 Ecuador–Colombia earthquake | 8.8[32] | |
| 14 | February 27, 2010 | 2010 Chile earthquake | 8.8[32] | |
| 15 | October 28, 1707 | 1707 Hōei earthquake | 8.7–9.3 (est.) | |
| 16 | November 1, 1755 | 1755 Lisbon earthquake | 8.5–9.0 | |
| 17 | February 4, 1965 | 1965 Rat Islands earthquake | 8.7 | |
| 18 | October 28, 1746 | 1746 Lima–Callao earthquake | 8.6 (est.) | |
| 19 | March 28, 1787 | 1787 New Spain earthquake | 8.6 (est.) | |
| 20 | August 15, 1950 | 1950 Assam–Tibet earthquake | 8.6 | |
| 21 | March 9, 1957 | 1957 Andreanof Islands earthquake | 8.6[32] | |
| 22 | March 28, 2005 | 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake | 8.6[32] | |
| 23 | April 11, 2012 | 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes | 8.6 | |
| 24 | December 16, 1575 | 1575 Valdivia earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 25 | November 24, 1604 | 1604 Arica earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 26 | May 13, 1647 | 1647 Santiago earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 27 | May 24, 1751 | 1751 Concepción earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 28 | November 19, 1822 | 1822 Valparaíso earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 29 | February 20, 1835 | 1835 Concepción earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 30 | February 16, 1861 | 1861 Sumatra earthquake | 8.5 | |
| 31 | May 9, 1877 | 1877 Iquique earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 32 | November 10, 1922 | 1922 Vallenar earthquake | 8.5[33] | |
| 33 | February 1, 1938 | 1938 Banda Sea earthquake | 8.5[32] | |
| 34 | October 13, 1963 | 1963 Kuril Islands earthquake | 8.5[32] | |
| 35 | October 20, 1687 | 1687 Peru earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 36 | October 17, 1737 | 1737 Kamchatka earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 37 | June 15, 1896 | 1896 Sanriku earthquake | 8.5 (est.) | |
| 38 | July 25, 1668 | 1668 Shandong earthquake | 8.5 (est.)[34] | |
| 39 | March 31, 1761 | 1761 Lisbon earthquake | 8.5 (est.)[35] | |
| 40 | June 17, 1917 | 1917 Samoa earthquake | 8.5 (est.)[36] |
| Century | Number with magnitude ≥ 8.5 |
|---|---|
| 1501–1600 | 2 |
| 1601–1700 | 5 |
| 1701–1800 | 9 |
| 1801–1900 | 7 |
| 1901–2000 | 11 |
| 2001–2020 | 5 |
| Total | 40 |
Note that historical records are known to be incomplete. Earthquakes that occurred in remote areas prior to the advent of modern instrumentation in the early to mid 1900s were not well-reported, and exact locations and magnitudes of such events are often unknown. Therefore, the apparent increase in large earthquake frequency over the last few centuries is unlikely to be accurate.
Largest earthquakes by country/territory[]
- This list is a work in progress. Information is likely to be changed.
- The list refers to current country boundaries rather than those at the date of the earthquake.
- Please note, multiple countries could have the same earthquake listed, such as the 1906 Ecuador–Colombia earthquake being listed for both Ecuador and Colombia.
- Unless otherwise noted, magnitudes are reported on the Moment magnitude scale (Mw).
| Country/Territory | Magnitude | Date | More information |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.8 | 15 November 1921 | [37] | |
| 6.7 | 30 November 1967 | [38] | |
| 7.1 | 10 October 1980 | 1980 El Asnam earthquake | |
| 5.2 | 10 January 1995 | [39] | |
| 6.7 | 2 February 1428 | 1428 Catalonia earthquake | |
| 5.3 | 19 October 2001 | [40] | |
| 8.1 | 25 March 1998 | [41] | |
| 7.5 | 8 October 1974 | [42] | |
| 6.8 Ms | 7 December 1988 | 1988 Armenian earthquake | |
| 7.5 | 27 October 1894 | 1894 San Juan earthquake | |
| 8.1 | 23 December 2004 | [43] | |
| 5.5–6.0 | 15 September 1590 | 1590 Neulengbach earthquake | |
| 6.9 | 25 November 1667 | 1667 Shamakhi earthquake | |
| 8.8 | 2 April 1762 | 1762 Arakan earthquake | |
| 6.5 | 18 February 2014 | [44] | |
| 6.3 | 18 September 1692 | [45] | |
| 7.3 | 28 May 2009 | 2009 Swan Islands earthquake | |
| 7.5–8.5 | 1714 | [46] | |
| 8.2 | 9 June 1994 | 1994 Bolivia earthquake | |
| 6.4 | 27 October 1969 | 1969 Banja Luka earthquake | |
| 6.8 | 11 October 1952 | [47] | |
| 7.6 | 9 November 1963 | [48] | |
| 7.3 | 30 November 1983 | [49] | |
| 7.2 Ms [50] | 4 April 1904 | see List of earthquakes in Bulgaria | |
| 5.3 | 29 January 1978 | [51] | |
| 4.9 | 27 January 1987 | [52] | |
| 5.2 | 10 March 2017 | [53] | |
| 8.7–9.2 | 26 January 1700 | 1700 Cascadia earthquake | |
| 6.8 | 14 December 2004 | [54] | |
| 4.9 | 6 February 1994 | [55] | |
| 9.5 | 22 May 1960 | 1960 Valdivia earthquake | |
| 8.6 | 15 August 1950 | 1950 Assam–Tibet earthquake | |
| 7.9 | 18 June 2000 | [56] | |
| 8.8 | 31 January 1906 | 1906 Ecuador–Colombia earthquake | |
| 6.0 | 29 April 1952 | [57] | |
| 5.2 | 26 April 1998 | [58] | |
| 7.7 | 22 April 1991 | 1991 Limon earthquake | |
| 6.4 | 29 December 2020 | 2020 Petrinja earthquake | |
| 7.6 | 11 June 1766 | List of earthquakes in Cuba[59] | |
| 7.0 | 11 May 1222 | 1222 Cyprus earthquake | |
| 4.8 ML | 23 December 1985 | [60] | |
| 6.8 | 5 December 2005 | 2005 Lake Tanganyika earthquake | |
| 4.4 ML[61][62][63] | 19 February 2010 | Jutland | |
| 6.5 | 20 August 1989 | [64] | |
| 6.3 | 21 November 2004 | 2004 Les Saintes earthquake | |
| 8.1 Ms | 4 August 1946 | 1946 Dominican Republic earthquake | |
| 6.0 | 20 January 1959 | [65] | |
| 8.8 | 31 January 1906 | 1906 Ecuador–Colombia earthquake | |
| 7.3 | 22 November 1995 | 1995 Gulf of Aqaba earthquake | |
| 8.0 MI | 19 December 1862 | [66] | |
| 4.9 | 28 March 1999 | [67] | |
| 6.2 | 23 September 1915 | [68] | |
| 4.5–4.7 mb | 25 October 1976 | 1976 Osmussaare earthquake | |
| 6.5 | 30 June 1919 | [69] | |
| 8.2 | 19 August 2018 | 2018 Fiji earthquake | |
| 4.7 | 4 November 1898 | [70] | |
| 6.2 | 11 June 1909 | 1909 Provence earthquake | |
| 6.2 Ms | 23 September 1974 | [71] | |
| 7.0 | 29 April 1991 | 1991 Racha earthquake | |
| 6.1 | 18 February 1756 | 1756 Düren earthquake | |
| 6.5 ML | 22 June 1939 | [72] | |
| 8.5+ | 21 July 365 | 365 Crete earthquake | |
| 5.5 | 28 November 1985 | [73] | |
| 7.7 | 20 November 1933 | 1933 Baffin Bay earthquake | |
| 8.5 | 8 February 1843 | 1843 Guadeloupe earthquake | |
| 7.8 | 8 August 1993 | [74] | |
| 7.7 | 6 August 1942 | 1942 Guatemala earthquake | |
| 6.3 | 22 December 1983 | 1983 Guinea earthquake[75] | |
| 5.5 | 31 January 2021 | [76] | |
| 8.1 Ms | 7 May 1842 | 1842 Cap-Haïtien earthquake | |
| 7.5 | 10 January 2018 | 2018 Swan Islands earthquake | |
| 6.3 ML | 28 June 1763 | 1763 Komárom earthquake | |
| 6.9 | 28 March 1963 | [77] | |
| 8.6 | 15 August 1950 | 1950 Assam–Tibet earthquake | |
| 9.1–9.3 | 26 December 2004 | 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake | |
| 7.9 Ms | 22 December 856 | 856 Damghan earthquake | |
| 7.0 | 22 September 1666 | [78] | |
| 5.4 | 19 July 1984 | 1984 Llŷn Peninsula earthquake | |
| 6.3 | 11 July 1927 | 1927 Jericho earthquake | |
| 7.4 | 11 January 1693 | 1693 Sicily earthquake | |
| 7.7 | 28 January 2020 | 2020 Caribbean earthquake | |
| 9.0 | 11 March 2011 | 2011 Tōhoku earthquake | |
| 6.3 | 11 July 1927 | 1927 Jericho earthquake | |
| 7.7 | 3 January 1911 | 1911 Kebin earthquake | |
| 7.0 | 6 January 1928 | [79] | |
| 5.9 | 23 May 1982 | [80] | |
| 7.7 | 3 January 1911 | 1911 Kebin earthquake | |
| 6.9 Ms | 24 June 1983 | [81] | |
| 7.5 | 9 July 551 | 551 Beirut earthquake | |
| 6.8 | 19 April 1935 | [82] | |
| 5.6 | 21 April 1991 | [83] | |
| 6.2 mb | 10 March 1989 | [84] | |
| 6.3 | 11 August 1923 | [85] | |
| 7.1 | 29 February 1944 | [86] | |
| 7.4 | 11 January 1693 | 1693 Sicily earthquake[87] | |
| 7.8 Ms | 11 January 1839 | 1839 Martinique earthquake | |
| 6.7 | 26 July 1976 | [88] | |
| 6.0 | 29 April 1952 | [89] | |
| 8.6 | 28 March 1787 | 1787 Mexico earthquake | |
| 7.1 | 15 November 1929 | [90] | |
| 6.3 | 19 July 1963 | [91] | |
| 8.3 | 23 July 1905 | 1905 Bolnai earthquake and 1905 Tsetserleg earthquake | |
| 6.9 | 15 April 1979 | 1979 Montenegro earthquake | |
| 6.3 | 24 February 2004 | 2004 Al Hoceima earthquake | |
| 7.0 | 22 February 2006 | 2006 Mozambique earthquake | |
| 8.0 | 12 September 1946 | 1946 Sagaing earthquakes[92] | |
| 5.5 | 4 April 2021 | [93] | |
| 8.2–8.8 | 6 June 1505 | 1505 Lo Mustang earthquake | |
| 5.8 | 13 April 1992 | 1992 Roermond earthquake | |
| 7.9 | 9 August 1901 | [94] | |
| 8.2 | 23 January 1855 | 1855 Wairarapa earthquake | |
| 7.7 | 2 September 1992 | 1992 Nicaragua earthquake | |
| 6.8 | 8 October 1960 | [95] | |
| 6.6 | 8 March 1931 | [96] | |
| 7.7 | 29 July 2016 | [97] | |
| 6.8 | 30 August 2012 | [98] | |
| 8.1 | 28 November 1945 | 1945 Balochistan earthquake | |
| 7.8 | 16 August 1911 | [99] | |
| 7.5 Ms | 18 July 1934 | [100] | |
| 8.1 | 26 July 1971 | 1971 Solomon Islands earthquakes | |
| 6.5 | 28 February 1989 | [101] | |
| 8.6 | 28 October 1746 | 1746 Lima–Callao earthquake | |
| 8.3 | 15 August 1918 | 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake | |
| 5.8 mb | 6 August 1983 | [102] | |
| 8.5–9.0 | 1 November 1755 | 1755 Lisbon earthquake | |
| 8.0 | 2 May 1787 | 1787 Boricua earthquake | |
| 5.3 mb | 6 April 2007 | [103] | |
| 7.9 | 26 October 1802 | 1802 Vrancea earthquake | |
| 9.0 | 4 November 1952 | 1952 Severo-Kurilsk earthquake | |
| 5.9 | 3 February 2008 | [104] | |
| 8.5 | 25 June 1917 | 1917 Samoa earthquake | |
| 5.5 | 19 December 2019 | [105] | |
| 6.2[citation needed] | 11 January 1941 | Jizan Region | |
| 5.8 | 18 May 1980 | [106] | |
| 5.2 | 28 April 1995 | [107] | |
| 5.8 | 28 June 1763 | [108] | |
| 6.1 ML | 14 April 1895 | 1895 Ljubljana earthquake | |
| 8.1 | 1 April 2007 | 2007 Solomon Islands earthquake | |
| 5.6 | 3 July 1951 | [109] | |
| 6.4 | 29 September 1969 | 1969 Tulbagh earthquake | |
| 8.1 | 27 June 1929 & 12 August 2021 | 2021 South Sandwich Islands earthquakes[110] | |
| 6.2 | 29 June 1975 | [111] | |
| 7.2 Ms | 20 May 1990 | [112] | |
| 7.8 | 29 March 1954 | [113] | |
| 5.9 | 30 August 1973 | [114] | |
| 4.9 | 18 May 2020 | [115] | |
| 6.5 | 18 October 1356 | 1356 Basel earthquake | |
| 7.6 Ms | 20 May 1202 | 1202 Syria earthquake | |
| 8.2 | 5 June 1920 | [116] | |
| 7.5 | 10 July 1949 | 1949 Khait earthquake | |
| 7.3 | 13 December 1910 | [117] | |
| 6.1 | 5 May 2014 | 2014 Mae Lao earthquake | |
| 8.1 | 30 April 1919 | [118] | |
| 6.7 | 22 April 1997 | [119][120] | |
| 5.5 | 20 February 1957 | [121] | |
| 7.8 | 27 December 1939 | 1939 Erzincan earthquake | |
| 7.3 Ms | 5 October 1948 | 1948 Ashgabat earthquake | |
| 6.5 | 30 June 1952 | [122] | |
| 6.7 | 11 September 1927 | 1927 Crimean earthquakes | |
| 6.1 ML | 7 June 1931 | 1931 Dogger Bank earthquake | |
| 9.2 | 27 March 1964 | 1964 Alaska earthquake | |
| 5.5 Ms | 5 June 1888 | 1888 Rio de la Plata earthquake | |
| 7.0 | 19 March 1984 | [123] | |
| 8.1 | 20 September 1920 | [124] | |
| 7.7 | 29 October 1900 | 1900 San Narciso earthquake | |
| 6.9 | 24 June 1983 | [81] | |
| 6.3 | 13 December 1982 | 1982 North Yemen earthquake | |
| 6.7 | 1 May 1919 | [125] | |
| 5.5 | 25 September 1963 | [126] |
Costliest earthquakes[]
This is a list of major earthquakes by the dollar value of property (public and private) losses directly attributable to the earthquake. Rank values are assigned based on inflation-adjusted comparison of property damage in US dollars. Wherever possible, indirect and socioeconomic losses are excluded. Damage estimates for particular earthquakes may vary over time as more data becomes available.
| Rank | Event | Location | Magnitude | Property damage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami | 9.1[28] | $360 billion[127][128] | |
| 2 | 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake | 6.9 | $200 billion[129] | |
| 3 | 2008 Sichuan earthquake | 8.0 | $150 billion[130] | |
| 4 | 2004 Chūetsu earthquake | 6.8 | $28 billion[131][132] | |
| 5 | 1999 İzmit earthquake | 7.6 | $20 billion[131] | |
| 6 | 2012 Northern Italy earthquakes | 6.1[133] | $15.8 billion[134] | |
| 7 | 2011 Christchurch earthquake | 6.3[135] | $15–40 billion[136][137] | |
| 8 | 2010 Chile earthquake | 8.8[138] | $15–30 billion[138] | |
| 9 | 1980 Irpinia earthquake | 6.9[131] | $15 billion[131] | |
| 10 | 1994 Northridge earthquake | 6.7 | $13–44 billion | |
| 11 | 1976 Tangshan earthquake | 7.8 | $10 billion[139] | |
| 12 | 1999 Jiji earthquake | 7.7 | $10 billion | |
| 13 | April 2015 Nepal earthquake | 7.8 | $10 billion[140] | |
| 14 | 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake | 6.9 | $5.6–6 billion | |
| 15 | 1923 Great Kantō earthquake | 8.0 | $600 million[131] | |
| 16 | 1906 San Francisco earthquake | 7.7 to 7.9 (est.)[133] | $400 million[133] |
Deadliest earthquakes[]
The following is a summary list of earthquakes with over approximately 100,000 deaths:
| Rank | Event | Date | Location | Fatalities | Magnitude | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1556 Shaanxi earthquake | January 23, 1556 | Shaanxi, China | 820,000–830,000[142] | 8.0 | Estimated death toll in Shaanxi, China |
| 2 | 1976 Tangshan earthquake | July 28, 1976 | Hebei, China | 242,769–700,000+[143][144][145] | 7.8 | |
| 3 | 1920 Haiyuan earthquake | December 16, 1920 | Ningxia–Gansu, China | 273,400[143][146] | 7.8 | Major fractures, landslides. |
| 4 | 526 Antioch earthquake | May 21, 526 | Antioch, Byzantine Empire (modern-day Turkey) | 250,000[147] | 7.0[148] | Procopius (II.14.6), sources based on John of Ephesus. |
| 5 | 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami | December 26, 2004 | Indian Ocean, Sumatra, Indonesia | 227,898 | 9.1–9.3 | Became the deadliest tsunami on record, causing nearly 240,000 deaths from the earthquake and resulting tsunami across 14 countries. |
| 6 | 1138 Aleppo earthquake | October 11, 1138 | Aleppo, Syria | 130,000–230,000[149] | 7.1[149] | The figure of 230,000 dead is based on a historical conflation of this earthquake with earthquakes in November 1137 on the Jazira plain and on September 30, 1139 in the Azerbaijani city of Ganja. The first mention of a 230,000 death toll was by Ibn Taghribirdi in the fifteenth century.[150] |
| 7 | 2010 Haiti earthquake | January 12, 2010 | Haiti | 100,000–316,000 (estimates) | 7.0 | Estimates vary from 316,000 (Haitian government) to 222,570 (UN OCHA estimate)[151] to 158,000 (Medicine, Conflict and Survival) to between 85,000 and 46,000 (report commissioned by USAID).[152][153] |
| 8 | 1303 Hongdong earthquake | July 25, 1303 | Shanxi, China | 200,000[154] | 8.0 | Taiyuan and Pingyang were leveled. |
| 9 | 856 Damghan earthquake | December 22, 856 | Damghan, Iran | 200,000 | 7.9 Ms | |
| 10 | 893 Ardabil earthquake | March 22, 893 | Ardabil, Iran | 150,000 | Unknown | Reports probably relate to the 893 Dvin earthquake, due to misreading of the Arabic word for Dvin, 'Dabil' as 'Ardabil'.[155] This is regarded as a 'fake earthquake'.[156] |
| 11 | 533 Aleppo earthquake | November 29, 533 | Syria | 130,000[157] | Unknown | |
| 12 | 1908 Messina earthquake | December 28, 1908 | Messina, Italy | 123,000[158] | 7.1 | The ground shook for 30 to 40 seconds around 5:20 am, and destruction occurred within a 300 km radius. 91% of structures in Messina were destroyed and ~70,000 residents died. Rescuers searched for weeks, and whole families were pulled out alive days later. A 40-foot (12 m) tsunami struck nearby coasts. Reggio Calabria on the Italian mainland also suffered heavy damage. |
| 13 | 1948 Ashgabat earthquake | October 6, 1948 | Ashgabat, Turkmen SSR (modern-day Turkmenistan) | 10,000–110,000 | 7.3 Ms | |
| 14 | 1923 Great Kantō earthquake | September 1, 1923 | Kantō region, Japan | 105,385[159] | 7.9 | This earthquake with an epicenter beneath Izu Ōshima Island in Sagami Bay, shook the Kantō plain on the Japanese island of Honshū at 11:58 am. Shaking duration reported between 4 and 10 minutes, devastating Tokyo, Yokohama, Chiba, Kanagawa, and Shizuoka.[160] Shaking slid the 93-ton Great Buddha statue at Kamakura almost two feet forward. Casualty estimates range from 100,000 to 142,800, the latter figure including ~40,000 missing later presumed dead. |
| 15 | 1290 Chihli earthquake | September 27, 1290 | Ningcheng, China | 100,000[161] | 6.8 Ms |
Most studied earthquakes[]
The 50 most studied earthquakes according to the International Seismological Centre (ISC), based on a count of scientific papers (mostly in English) that discuss that earthquake. The "Event #" is linked to the ISC Event Bibliography for that event.
| Rank | Event origin time | ISC Event # | Papers | ISC code | Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2011-03-11 05:46:23 | 16461282 | 1519 | TOHOKU2011 | 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami |
| 2 | 2008-05-12 06:27:59 | 13228121 | 1217 | WENCHUAN2008 | 2008 Sichuan earthquake |
| 3 | 2004-12-26 00:58:52 | 7453151 | 836 | SUMATRA2004 | 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami |
| 4 | 1999-09-20 17:47:16 | 1718616 | 640 | CHI-CHI1999 | 1999 Jiji earthquake |
| 5 | 1994-01-17 12:30:54 | 189275 | 466 | NORTHRIDGE1994 | 1994 Northridge earthquake |
| 6 | 1995-01-16 20:46:51 | 124708 | 451 | SHYOGO1995 | Great Hanshin earthquake |
| 7 | 1989-10-18 00:04:14 | 389808 | 424 | LOMAPRIETA1989 | 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake |
| 8 | 2009-04-06 01:32:42 | 13438018 | 420 | LAQUILA2009 | 2009 L'Aquila earthquake |
| 9 | 2010-02-27 06:34:13 | 14340585 | 392 | MAULE2010 | 2010 Chile earthquake |
| 10 | 1992-06-28 11:57:35 | 289086 | 383 | LANDERS1992 | 1992 Landers earthquake |
| 11 | 1999-08-17 00:01:38 | 1655218 | 361 | IZMIT1999 | 1999 İzmit earthquake |
| 12 | 2015-04-25 06:11:26 | 607208674 | 298 | GORKHA2015 | April 2015 Nepal earthquake |
| 13 | 1964-03-28 03:36:13 | 869809 | 249 | ALASKA1964 | 1964 Alaska earthquake |
| 14 | 1985-09-19 13:17:50 | 516095 | 236 | MEXICOCITY1985 | 1985 Mexico City earthquake |
| 15 | 1960-05-22 19:11:20 | 879136 | 236 | CHILE1960 | 1960 Valdivia earthquake |
| 16 | 1971-02-09 14:00:40 | 787038 | 227 | SANFERNANDO1971 | 1971 San Fernando earthquake |
| 17 | 2001-01-26 03:16:40 | 1763683 | 221 | BHUJ2001 | 2001 Gujarat earthquake |
| 18 | 2010-09-03 16:35:46 | 15155483 | 216 | DARFIELD2010 | 2010 Canterbury earthquake |
| 19 | 1976-07-27 19:42:53 | 711732 | 195 | TANGSHAN1976 | 1976 Tangshan earthquake |
| 20 | 1976-05-06 20:00:12 | 713583 | 187 | FRIULI1976 | 1976 Friuli earthquake |
| 21 | 1980-11-23 18:34:52 | 635924 | 178 | IRPINIA1980 | 1980 Irpinia earthquake |
| 22 | 2003-09-25 19:50:07 | 7134409 | 177 | TOKACHI-OKI2003 | 2003 Hokkaidō earthquake |
| 23 | 2013-04-20 00:02:47 | 607304721 | 172 | LUSHAN2013 | 2013 Lushan earthquake |
| 24 | 2011-02-21 23:51:42 | 16168897 | 170 | CHRISTCHURCH2011A | 2011 Christchurch earthquake |
| 25 | 2016-04-15 16:25:06 | 610289055 | 170 | KUMAMOTO2016 | 2016 Kumamoto earthquakes |
| 26 | 2004-09-28 17:15:24 | 7406045 | 166 | PARKFIELD2004 | Parkfield earthquake |
| 27 | 2005-03-28 16:09:35 | 7486110 | 165 | NIAS2005 | 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake |
| 28 | 2004-10-23 08:55:58 | 7421058 | 162 | MID-NIIGATA2004 | 2004 Chūetsu earthquake |
| 29 | 2012-05-20 02:03:53 | 601025379 | 153 | EMILIA2012A | 2012 Northern Italy earthquakes |
| 30 | 1999-10-16 09:46:45 | 1643776 | 150 | HECTOR-MINE1999 | 1999 Hector Mine earthquake |
| 31 | 2001-11-14 09:26:10 | 2331800 | 148 | KUNLUN2001 | 2001 Kunlun earthquake |
| 32 | 2005-10-08 03:50:35 | 7703077 | 144 | KASHMIR2005 | 2005 Kashmir earthquake |
| 33 | 2002-11-03 22:12:41 | 6123395 | 141 | DENALI2002 | 2002 Denali earthquake |
| 34 | 1988-12-07 07:41:24 | 417441 | 139 | ARMENIA1988 | 1988 Armenian earthquake |
| 35 | 1999-11-12 16:57:19 | 1650092 | 137 | DUZCE1999 | 1999 Düzce earthquake |
| 36 | 1979-10-15 23:16:57 | 657282 | 132 | IMPERIAL1979 | 1979 Imperial Valley earthquake |
| 37 | 2003-12-26 01:56:53 | 7217667 | 128 | BAM2003 | 2003 Bam earthquake |
| 38 | 1923-09-01 02:58:35 | 911526 | 127 | KANTO1923 | 1923 Great Kantō earthquake |
| 39 | 2010-01-12 21:53:10 | 14226221 | 125 | HAITI2010 | 2010 Haiti earthquake |
| 40 | 1983-05-26 02:59:58 | 577008 | 114 | SEAOFJAPAN1983 | 1983 Sea of Japan earthquake |
| 41 | 2012-05-29 07:00:04 | 605482196 | 111 | EMILIA2012B | 2012 Northern Italy earthquakes |
| 42 | 1997-09-26 09:40:25 | 1043512 | 102 | UMBRIA-MARCHE1997B | 1997 Umbria and Marche earthquake |
| 43 | 2000-10-06 04:30:17 | 1839998 | 100 | TOTTORI2000 | 2000 Tottori earthquake |
| 44 | 2008-06-13 23:43:46 | 13377361 | 97 | IWATE-MIYAGI2008 | 2008 Iwate–Miyagi Nairiku earthquake |
| 45 | 2007-07-16 01:13:21 | 12769769 | 96 | CHUETSU-0KI2007 | 2007 Chūetsu offshore earthquake |
| 46 | 2010-04-13 23:49:37 | 14573075 | 96 | YUSHU 2010 | 2010 Yushu earthquake |
| 47 | 1977-03-04 19:21:54 | 700695 | 96 | ROMANIAN1977 | 1977 Vrancea earthquake |
| 48 | 2011-10-23 10:41:22 | 17394270 | 91 | VAN2011 | 2011 Van earthquakes |
| 49 | 1975-02-04 11:36:05 | 731961 | 80 | HAICHENG1975 | 1975 Haicheng earthquake |
| 50 | 2007-03-25 00:41:57 | 11703278 | 73 | NOTO-HANTO2007 | 2007 Noto earthquake |
modified from figure 2, "The most studied events", at the ISC's Overview of the ISC Event Bibliography.
International Seismological Centre. Event Bibliography. Thatcham, United Kingdom, http://www.isc.ac.uk/. 2018.
See also[]
- List of deadly earthquakes since 1900
- List of Natural Disasters by Death Toll
- Lists of earthquakes by year
References[]
- ^ "Number of deaths caused by the 2006 Yogyakarta earthquake".
- ^ "M 7.9 – off the east coast of Honshu, Japan". United States Geological Survey. November 25, 1953. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.8 – Strait of Gibraltar". United States Geological Survey. March 29, 1954. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.5 – Kermadec Islands region". United States Geological Survey. February 27, 1955. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.3 – Kuril Islands". United States Geological Survey. November 6, 1958. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.3 – Kuril Islands". United States Geological Survey. November 6, 1958. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.6 – Peru-Brazil border region". United States Geological Survey. August 19, 1961. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.5 – Fiji region". United States Geological Survey. May 21, 1962. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.7 – Rat Islands, Aleutian Islands, Alaska". United States Geological Survey. February 4, 1965. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.2 – Kuril Islands". United States Geological Survey. August 11, 1969. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.0 – New Ireland region, Papua New Guinea". United States Geological Survey. July 14, 1971. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.0 – Mindanao, Philippines". United States Geological Survey. December 2, 1972. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.9 – Bougainville region, Papua New Guinea". United States Geological Survey. July 20, 1975. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
PAGER-CATwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "M 7.9 – 199 km S of Lata, Solomon Islands". United States Geological Survey. July 17, 1980. Retrieved July 17, 2021.
- ^ "Tsunami Event: SAMOA ISLANDS". National Geophysical Data Center. September 1, 1981. Retrieved July 17, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.7 – 133 km NE of Hihifo, Tonga". United States Geological Survey. September 1, 1981. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.6 – 157 km ESE of Kokopo, Papua New Guinea". United States Geological Survey. March 18, 1983. Retrieved July 17, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.6 – 85 km SE of Honiara, Solomon Islands".
- ^ "The Impact of the M8.0 Mexico Quake of 1985".
- ^ "Major earthquake Strikes Alaska, Tsunami Strikes Hawaii". May 7, 1986.
- ^ "M 8.0 – 85 km SSW of Atka, Alaska". May 7, 1986.
- ^ "M 7.9 – 200km WSW of Yakutat, Alaska". November 30, 1987.
- ^ "M 8.0, Macquarie Island Region". May 23, 1989.
- ^ "M 8.1, Balleny Islands Region". March 25, 1998.
- ^ "Magnitude 8 and Greater Earthquakes Since 1900". usgs.gov. Archived from the original on April 14, 2016.
- ^ Johnston, Arch C.; Halchuk, Stephen (June–July 1993), "The seismicity data base for the Global Seismic Hazard Assessment Program", Annali di Geofisica, 36 (3–4): 133–151, pp. 140, 142 et seq.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "M 9.1 – near the east coast of Honshu, Japan". Earthquake Hazards Program. USGS. 2016. Retrieved November 21, 2016.
- ^ Carvajal, M.; Cisternas, M.; Catalán, P.A. (2017). "Source of the 1730 Chilean earthquake from historical records: Implications for the future tsunami hazard on the coast of Metropolitan Chile". Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 122 (5): 3648–3660. doi:10.1002/2017JB014063.
- ^ "Historic Earthquakes – Kamchatka Archived August 25, 2009, at the Wayback Machine." U.S. Geological Survey, October 26, 2009.
- ^ H. Ringer, J. P. Whitehead, J. Krometis, R. A. Harris, N. Glatt-Holtz, S. Giddens, C. Ashcraft, G. Carver, A. Robertson, M. Harward, J. Fullwood, K. Lightheart, R. Hilton, A. Avery, C. Kesler, M. Morrise, M. H. Klein (2021). "Methodological Reconstruction of Historical Seismic Events From Anecdotal Accounts of Destructive Tsunamis: A Case Study for the Great 1852 Banda Arc Mega-Thrust Earthquake and Tsunami" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 126 (4). arXiv:2009.14272. doi:10.1029/2020JB021107. Retrieved June 19, 2021.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "Magnitude 8 and Greater Earthquakes Since 1900 Archived May 10, 2011, at the Wayback Machine." U.S. Geological Survey, March 7, 2010
- ^ "Historic Earthquakes – Chile-Argentina Border Archived November 13, 2009, at the Wayback Machine." U.S. Geological Survey, October 26, 2009.
- ^ "Significant Earthquake Information CHINA: SHANDONG PROVINCE". NGCD. Retrieved December 9, 2020.
- ^ NCEI Global Historical Hazard Database. "Significant Earthquake Information PORTUGAL: LISBON". www.ngdc.noaa.gov. Retrieved February 1, 2021.
- ^ Engdahl, E. R.; Vallaseñor, A. (2002). "Global seismicity: 1900–1999" (PDF). International Handbook of Earthquake & Engineering Seismology. Part A, Volume 81A (First ed.). Academic Press. p. 673. ISBN 978-0124406520.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Afghanistan". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 6.7 – Albania". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.2 - 39 km NNE of Ta`?, American Samoa". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Angola". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ ANSS. "8.1 magnitude earthquake near Balleny Islands region : March 25, 1998 03:12". Comprehensive Catalog. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "M 7.5 – 25 km NW of Saint John's, Antigua and Barbuda". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ "M 8.1 - north of Macquarie Island". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ "6.5 magnitude earthquake near Greenland, Saint Andrew, Barbados and Ciudad Guayana, Bolívar, Venezuela : February 18, 2014 09:27". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ Petermans, T.; Devleeschouwer, X.; Pouriel, F.; Rosset, P. (2006), "Mapping the local seismic hazard in the urban area of Brussels, Belgium (IAEG2006 Paper number 424)" (PDF), IAEG2006 — 10th IAEG International Congress : Nottingham, Geological Society of London
- ^ György Hetényi, Romain Le Roux‐Mallouf Théo Berthet Rodolphe Cattin Carlo Cauzzi Karma Phuntsho Remo Grolimund (2016). "Joint approach combining damage and paleoseismology observations constrains the 1714 A.D. Bhutan earthquake at magnitude 8 ± 0.5". Geophysical Research Letters. 43 (20): 10, 695–10, 702. doi:10.1002/2016GL071033.
- ^ Simon, RE; Kwadiba, MTO; King, JG; Moidaki, M (2012). "A History of Botswana's Seismic Network". Botswana Notes and Records. 44: 184–192. JSTOR 43855570.
- ^ M7.6 – Peru-Brazil border region, USGS
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Chagos Archipelago". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- ^ Ambraseys, N. (2001), "The Kresna earthquake of 1904 in Bulgaria", Annals of Geophysics Journal, INGV, 44 (1): 102, doi:10.4401/ag-3614
- ^ "M 5.3 – Burundi". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 26, 2017.
- ^ "4.9 magnitude earthquake near Tibati, Adamaoua, Cameroon and Yaoundé, Centre, Cameroon : January 26, 1987 23:11". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ "M 5.2 - 64 km N of Coro, Venezuela". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ "6.8 magnitude earthquake near George Town, Cayman Islands and Havana, La Habana, Cuba : December 14, 2004 23:20". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ "M 4.9 – Central African Republic". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ "M 7.9 – South Indian Ocean". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved July 12, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Comoros". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- ^ "5.2 magnitude earthquake near Impfondo, Likouala, Republic of the Congo and Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo : April 26, 1998 14:16". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ The 1766 Santiago earthquake killed more people, but the 1900 earthquake had a higher intensity. "14 Significant Earthquakes where (Year <= 2016 and Year >= 1000) and Country = CUBA and Region Code = 90". NCEI Significant Earthquake search. National Centers for Environmental Information, United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on May 10, 2017.
- ^ "4.8 magnitude earthquake near Skalná, Karlovarský, Czech Republic and Prague, Praha, Czech Republic : December 23, 1985 04:27". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved May 20, 2017.
- ^ "M4.4 – North Sea (4.4 magnitude earthquake 47 km from Thyborøn, Central Jutland, Denmark)". United States Geological Survey. November 7, 2014. Archived from the original on April 26, 2016.
- ^ There was also a 4.4 Mw earthquake on 15 June 1985 in the Kattegat between Denmark and Sweden. "Denmark: Copenhagen: Saturday, June 15, 1985 Earthquake". Earthquake.Zone.;"M4.4 – Sweden". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ Earlier large earthquakes affecting Denmark occurred in Norway and Sweden. Voss, P. H.; Larsen, T. B.; Ottemöller, L.; Gregersen, S. (2009). "Earthquake in southern Sweden wakes up Denmark on 16 December 2008" (PDF). Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin. Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland. 17: 11.
- ^ "M 6.5 – Djibouti". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 6.0 – East Timor region". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ^ White, R. A.; Ligorria, J. P.; Cifuentes, I. L. (2004). "Seismic history of the Middle America subduction zone along El Salvador, Guatemala, and Chiapas, Mexico: 1526–2000". Natural Hazards in El Salvador. Geological Society of America. p. 394. ISBN 978-0-8137-2375-4.
- ^ "M 4.9 - Equatorial Guinea". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "M 6.2 – Eritrea-Ethiopia border region". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Ethiopia". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "Largest earthquake in Finland". Sodankylän Geofysiikan Observatorio, Oulun Toimintayksikkö (University of Oulu). Retrieved December 13, 2016.
- ^ "M 6.2 – Gabon". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ Amponsah, P. (April 1, 2003). "The Earthquake Of 22nd June 1939 And Its Effect In Ghana". EGS – AGU – EUG Joint Assembly: 14097. Bibcode:2003EAEJA....14097A.
- ^ "M 5.5 – Grenada region, Windward Islands". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "7.8 magnitude earthquake near Inarajan Village, Inarajan, Guam : August 08, 1993 08:34". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "6.3 magnitude earthquake near Gaoual, Boke, Guinea and Conakry, Guinea : December 22, 1983 04:11". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.5 – 82 km SSE of Lethem, Guyana". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved January 31, 2021.
- ^ "6.9 magnitude earthquake near Siglufjörður, Northeast, Iceland : March 28, 1963 00:15". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
- ^ Onur, T.; Gok, R.; Abdulnaby, W.; Mahdi, H.; Numan, N.M.; Al-Shukri, H.; Shakir, A.; Chlaib, H.; Ameen, T.H.; Abd, N. (2016). "A Comprehensive Earthquake Catalogue for Iraq in Terms of Moment Magnitude". Seismological Research Letters. 88 (3): 798–811. doi:10.1785/0220160078. OSTI 1466119.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Kenya". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.9 – Gilbert Islands, Kiribati region". earthquake.usgs.gov.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "6.9 magnitude earthquake near Dien Bien Phu, Tỉnh Ðiện Biên, Vietnam and Hanoi, Ha Nội, Vietnam : June 24, 1983 09:07". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Libya". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Madagascar". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Malawi". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 6.3 – 23 km NNW of Lahad Datu, Malaysia". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. Retrieved July 18, 2021.
- ^ "7.1 magnitude earthquake near Fuvahmulah, Gnyaviyani Atoll, Maldives and Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India : February 29, 1944 16:28". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved May 4, 2019.
- ^ Galea, P. (2007). "Seismic history of the Maltese islands and considerations on seismic risk". Annals of Geophysics. 50 (6): 725–740.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Mauritius". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Mayotte". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- ^ "7.1 magnitude earthquake near Fais, Yap, Micronesia : November 15, 1929 18:50". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "M 6.3 - Ligurian Sea". United States Geological Survey. July 19, 1963. Retrieved August 26, 2021.
- ^ "M8.0 – Myanmar". United States Geological Survey. September 12, 1946. Retrieved January 12, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.4 – Namibia". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 5, 2021.
- ^ "7.9 magnitude earthquake near Tadine, Loyalty Islands, New Caledonia : August 09, 1901 13:01". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved February 11, 2021.
- ^ "M 6.8 – North Korea". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "M 6.6 – Macedonia". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "7.7 magnitude earthquake near Saipan, Northern Mariana Islands : July 29, 2016 21:18". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "M 6.8 – 89 km NW of Olonkinbyen, Svalbard and Jan Mayen". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved August 4, 2021.
- ^ "7.8 magnitude earthquake near Melekeok Village, Melekeok, Palau : August 16, 1911 22:41". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 6, 2017.
- ^ "Panama earthquake".
- ^ "6.5 magnitude earthquake near General Enrique Mosconi, Formosa, Argentina and Asunción, Paraguay : February 28, 1989 13:01". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ 01:20:22 (UTC), 6 August 1983 "Earthquake Hazards Program: M5.8 – Poland". United States Geological Survey. November 7, 2014. Archived from the original on April 18, 2016.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Réunion". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved July 17, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Rwanda". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.5 – 87km ENE of Santo Antonio, Sao Tome and Principe". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "M 5.8 – Serbia". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "M 5.2 – South Indian Ocean". earthquake.usgs.gov.
- ^ "Najvýznamnejšie zemetrasenia v histórii s epicentrom na území dnešného Slovenska". vedanadosah.cvtisr.sk (in Slovak). Retrieved December 29, 2020.
- ^ "5.6 magnitude earthquake near Berbera, Woqooyi Galbeed, Somalia and Sanaa, Yemen : July 03, 1951 18:15". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
- ^ "M 8.1 - South Sandwich Islands region". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS–ANSS. 1929. Retrieved September 2, 2021.
- ^ "M 6.2 - 136 km ENE of Sokcho, South Korea". earthquake.usgs.gov.
- ^ Girdler, R. W.; McConnell, D. A. (April 1, 1994). "The 1990 to 1991 Sudan earthquake sequence and the extent of the East african rift system". Science. 264 (5155): 67–70. Bibcode:1994Sci...264...67G. doi:10.1126/science.264.5155.67. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17778134. S2CID 41405033.
- ^ "M 7.8 – Strait of Gibraltar". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.9 – 275 km E of Kalmunai, Sri Lanka". August 30, 1973.
- ^ USGS. "M 4.9 – 3km E of Kiruna, Sweden". United States Geological Survey.
- ^ "8.2 magnitude earthquake near Hualian, Taiwan, Taiwan and Taichung, Taiwan, Taiwan : June 05, 1920 04:21". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved March 30, 2018.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Tanzania". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "8.1 magnitude earthquake near Neiafu, Vava'u, Tonga : April 30, 1919 07:17". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 6.7 – Tobago region, Trinidad and Tobago". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "The April 1997 Earthquakes". ttweathercenter.com. Retrieved April 16, 2020.
- ^ "M 5.5 – Tunisia". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Uganda". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 7.0 – western Uzbekistan". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 20, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Vanuatu". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "The Largest Earthquakes in Zambia". earthquaketrack.com. Retrieved April 3, 2017.
- ^ "M 5.5 – Zimbabwe". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ^ Zhang, Bo. "Top 5 Most Expensive Natural Disasters in History". AccuWeather.com. News & Video. Archived from the original on March 31, 2011. Retrieved March 29, 2011.
- ^ Victoria Kim (March 21, 2011). "Japan damage could reach $235 billion, World Bank estimates". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on March 31, 2011. Retrieved March 21, 2011.
- ^ Tierney, Kathleen (1997). Emergency response: lessons learned from the Kobe earthquake. University of Delaware Disaster Research Center.
- ^ "Significant Earthquake". www.ngdc.noaa.gov. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Significant Earthquake Database". NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 20, 2015.
- ^ Guha-Sapir, Debarati; Santos, Indhira; Borde, Alexandre (2013). The Economic Impacts of Natural Disasters. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 252. ISBN 978-0-19-984193-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Where can I learn more about the 1906 Earthquake?". Berkeley Seismological Lab. December 11, 2011.
- ^ "Significant Earthquakes Full Search, sort by $Millions Damage, Date". www.ngdc.noaa.gov. Retrieved October 8, 2015.
- ^ "New Zealand Earthquake Report". GeoNet. Earthquake Commission and GNS Science. February 22, 2011. Archived from the original on February 23, 2011.
- ^ "Christchurch rebuild to cost $10b more". 3 News NZ. April 28, 2013. Archived from the original on October 14, 2013. Retrieved October 8, 2015.
- ^ "Significant Earthquake". www.ngdc.noaa.gov. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Events and Developments (P. 3, "Calendar of events 2010: February 27")" (PDF). Yearbook. UNEP. 2011.
- ^ "Tangshan | gemecd". gemecd.org. Retrieved October 24, 2015.
- ^ Krishnan, Unni; Mehrotra, Kartikay (April 28, 2015). "Nepal Says Earthquake Rebuilding Cost to Exceed $10 Billion". Bloomberg News.
- ^ "Earthquakes with 50,000 or More Deaths". Earthquake.usgs.gov. Archived from the original on September 1, 2009. Retrieved February 12, 2011.
- ^ International Association of Engineering Geology International Congress. Proceedings. [1990] (1990). ISBN 90-6191-664-X.[author missing][title missing][page needed][verification needed]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Death toll of 1920 China earthquake higher than previously estimated". xinhuanet.com.
- ^ "Earthquakes with 50,000 or More Deaths". USGS. Archived from the original on June 5, 2013. Retrieved March 17, 2012.
- ^ Theodore S. Glickman. [1993] (1993). Acts of God and Acts of Man. DIANE Publishing. ISBN 1-56806-371-7
- ^ Utsu, T. "Search Page". Catalog of Damaging Earthquakes in the World (Through 2008). Retrieved June 3, 2010.
- ^ Sbeinati, Mohamed Reda; Darawchech, Ryad; Mouty, Mikhail (June 2005). "The historical earthquakes of Syria: an analysis of large and moderate earthquakes from 1365 B.C. to 1900 A.D." (PDF). Annals of Geophysics. 48 (3): 347–435. Retrieved October 8, 2015.
- ^ National Geophysical Data Center. "Comments for the Significant Earthquake". Retrieved September 22, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Grǖnthal G.; Wahlström R. (2009). "A harmonized seismicity data base for the EuroMediterranean region" (PDF). Proceedings of the 27th ECGS Workshop 'Seismicity Patterns in the Euro-Med Region: 15–21.
- ^ Ambraseys, Nicholas N., "The 12th century seismic paroxysm in the Middle East: a historical perspective" (PDF), Annals of Geophysics, Vol. 47, N. 2/3, April/June 2004, p. 743.
- ^ Haiti Dominates Earthquake Fatalities in 2010 (January 11, 2011), U.S. Geological Survey.
- ^ Maura R. O'Connor, [Two Years Later, Haitian Earthquake Death Toll in Dispute], Columbia Journalism Review (January 12, 2012).
- ^ Report challenges Haiti earthquake death toll (June 1, 2011), BBC.
- ^ "china virtual museums_quake". www.kepu.net.cn. Retrieved November 28, 2015.
- ^ Ambraseys, N.N.; Melville, C.P. (2005). A History of Persian Earthquakes. Cambridge Earth Science. Cambridge University Press. p. 175. ISBN 978-0-521-02187-6.
- ^ Gupta, H. (2011). Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences (2 ed.). Springer. p. 566. ISBN 978-90-481-8701-0.
- ^ Paula Dunbar. "Significant Earthquake". Ngdc.noaa.gov. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ The world's worst natural disasters Calamities of the 20th and 21st centuries CBC News'.' Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ "Today in Earthquake History". usgs.gov.
- ^ Hammer, Joshua. (2006). Yokohama Burning: the Deadly 1923 Earthquake and Fire that Helped Forge the Path to World War II, p. 278, citing Francis Hawks, (1856). Narrative of the Expedition of an American Squadron to the China Seas and Japan Performed in the Years 1852, 1853 and 1854 under the Command of Commodore M.C. Perry, United States Navy, Washington: A.O.P. Nicholson by order of Congress, 1856; originally published in Senate Executive Documents, No. 34 of 33rd Congress, 2nd Session.
- ^ NGDC. "Comments for the Significant Earthquake". Retrieved October 29, 2010.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Earthquakes. |
- USGS-ANSS Latest earthquakes around the world.
- Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC)
- IRIS Seismic Monitor, Recent earthquakes around the world
- Recent New Zealand earthquakes
- SeismoArchives, Seismogram Archives of Significant Earthquakes of the World
- USGS list of earthquakes magnitude 6.0 and greater sorted by magnitude
- Database for the damage of world earthquake, ancient period (3000 BC) to year of 2006—Building Research Institute (Japan) (建築研究所)
- Largest Earthquakes in the World Since 1900
- Lists of events lists
- Lists of earthquakes