Réunion
Réunion
La Réunion (French) | |
|---|---|
 Capital of Saint-Denis | |
| Motto(s): Florebo quocumque ferar (I will flourish wherever I am brought) | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 21°06′52″S 55°31′57″E / 21.11444°S 55.53250°ECoordinates: 21°06′52″S 55°31′57″E / 21.11444°S 55.53250°E | |
| Country | France |
| Prefecture | Saint-Denis |
| Departments | 1 |
| Government | |
| • President of Regional Council | Didier Robert (LR) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,511 km2 (970 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 15th region |
| Population (January 2021)[1] | |
| • Total | 858,450 |
| • Density | 340/km2 (890/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Réunionese |
| Time zone | UTC+04:00 (RET) |
| ISO 3166 code | |
| GDP (nominal) (2019)[2] | Ranked 13th |
| Total | €19.7 billion (US$22.0 bn) |
| Per capita | €22,970 (US$25,720) |
| NUTS Region | FRY4 |
| Website | Prefecture Regional Council Departmental Council |
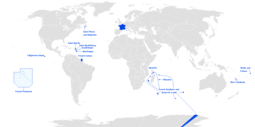
Réunion (French: La Réunion, [la ʁe.y.njɔ̃] (![]() listen); Reunionese Creole: La Rénion; previously Île Bourbon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately 550 km (340 mi) east of the island of Madagascar and 175 km (109 mi) southwest of the island of Mauritius. As of January 2021, it had a population of 858,450.[1]
listen); Reunionese Creole: La Rénion; previously Île Bourbon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately 550 km (340 mi) east of the island of Madagascar and 175 km (109 mi) southwest of the island of Mauritius. As of January 2021, it had a population of 858,450.[1]
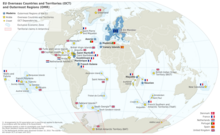
Like the other four overseas departments, Réunion also holds the status of a region of France, and is an integral part of the French Republic. Réunion is an outermost region of the European Union and is part of the eurozone.[3] Réunion and the fellow French overseas department of Mayotte are the only eurozone regions located in the Southern Hemisphere.

As in the rest of France, the official language of Réunion is French. In addition, a majority of the region's population speaks Réunion Creole.
Toponymy[]
When France took possession of the island in the seventeenth century, it was named Bourbon, after the dynasty that was then ruling the island. To break with this name, which was too attached to the Ancien Régime, the National Convention decided on March 23, 1793,[4] to rename the territory Reunion Island. This choice could have been made in homage to the meeting of the federates of Marseilles and the Parisian National Guards that preceded the insurrection of August 10, 1792, and the march on the Tuileries Palace, but no document justifies it and the meaning of the word "meeting" could have been purely symbolic.[5] The island changed its name to Reunion Island on March 23, 1791.
The island changed its name again in the 19th century: in 1806, under the First Empire, General Decaen named it Île Bonaparte, and in 1810 it became Île Bourbon again. It became Reunion Island once and for all after the fall of the July monarchy by a decree of the provisional government of March 7, 1848.[6]
In accordance with the original spelling and the classical spelling and typographical rules,[7] "la Réunion" was written with a lower case in the article, but during the end of the 20th century, the spelling "La Réunion" with a capital letter was developed in many writings to emphasize the integration of the article in the name. This last spelling corresponds to the recommendations of the Commission nationale de toponymy[8] and appears in the current Constitution of the French Republic in articles 72-3 and 73.
History[]
The island has been inhabited since the 16th century, when people from France and Madagascar settled there. Slavery was abolished on 20 December 1848 (a date celebrated yearly on the island), when the French Second Republic abolished slavery in the French colonies. However, indentured workers continued to be brought to Réunion from South India, among other places. The island became an overseas department of France in 1946.

Not much is known of Réunion's history prior to the arrival of the Portuguese in the early 16th century.[9] Arab traders were familiar with it by the name Dina Morgabin, "Western Island".[10] The island is possibly featured on a map from 1153 AD by Al Sharif el-Edrisi.[citation needed] The island might also have been visited by Swahili or Austronesian (Ancient Indonesian–Malaysian) sailors on their journey to the west from the Malay Archipelago to Madagascar.[9]
The first European discovery of the area was made around 1507 by Portuguese explorer Diogo Fernandes Pereira, but the specifics are unclear. The uninhabited island might have been first sighted by the expedition led by Dom Pedro Mascarenhas, who gave his name to the island group around Réunion, the Mascarenes.[11] Réunion itself was dubbed Santa Apolónia after a favourite saint,[10] which suggests that the date of the Portuguese discovery could have been 9 February, her saint day. Diogo Lopes de Sequeira is said to have landed on the islands of Réunion and Rodrigues in 1509.[citation needed]
By the early 1600s, nominal Portuguese rule had left Santa Apolónia virtually untouched.[11] The island was then occupied by France and administered from Port Louis, Mauritius. Although the first French claims date from 1638, when François Cauche and Salomon Goubert visited in June 1638,[12] the island was officially claimed by Jacques Pronis of France in 1642, when he deported a dozen French mutineers to the island from Madagascar. The convicts were returned to France several years later, and in 1649, the island was named Île Bourbon after the French royal House of Bourbon. Colonisation started in 1665, when the French East India Company sent the first settlers.[11]

Revolutionary revolts[]
On March 19, 1793, during the Revolution, its name was changed to "Reunion Island" in homage to the meeting of the Federates of Marseilles and the National Guards of Paris, during the march on the Tuileries Palace on August 10, 1792, and to erase the name of the Bourbon dynasty.[13] On September 26, 1806, the island took the name of Bonaparte and found itself in the front line of the Franco-British conflict for the control of the Indian Ocean.
The abolition of slavery voted by the National Convention on February 4, 1794, was rejected by Reunion Island, as well as by the Ile de France (Mauritius). A delegation accompanied by military forces, charged with imposing the liberation of slaves, arrived on the island of Bourbon on June 18, 1796, only to be immediately expelled without mercy. There followed a period of unrest and challenges to the power of the metropolis, which no longer had any authority over the two islands. The First Consul of the Republic, Napoleon Bonaparte, maintained slavery there, which was never abolished in practice, with the law of May 20, 1802.
During the Napoleonic wars, in the Mauritius campaign, the governor of the island, General Sainte-Suzanne, was forced to capitulate on July 9, 1810. The island then came under British rule and was returned to the French under the Treaty of Paris of 1814.
Following the climatic catastrophes of 1806-1807 (cyclones, floods), coffee cultivation declined rapidly and was replaced by sugar cane, whose demand in France increased, due to France's loss of Saint-Domingue, and soon of the island of France (Mauritius). Because of its growth cycle, sugarcane is not affected by cyclones. In 1841, Edmond Albius' discovery of hand-pollination of vanilla flowers enabled the island to soon become the world's leading vanilla producer. The cultivation of geranium, whose essence is widely used in perfumery, also took off.
From 1838 to 1841, Rear Admiral Anne Chrétien Louis de Hell was governor of the island. A profound change of society and mentality linked to the events of the last ten years led the governor to present three emancipation projects to the Colonial Council.
On December 20, 1848, Sarda Garriga finally proclaimed the abolition of slavery (December 20 was a holiday in Reunion). Louis Henri Hubert Delisle became its first Creole governor on August 8, 1852, and remained in this position until January 8, 1858. Europe increasingly turned to sugar beet to meet its sugar needs. Despite the development policy of the local authorities and the recourse to compromise, the economic crisis became evident from the 1870s onwards. Subsequently, the opening of the Suez Canal caused a shift in commercial traffic away from the island. However, this economic depression did not prevent the modernization of the island, with the development of the road network, the creation of the railroad and the construction of the artificial harbor of the Pointe des Galets. These major construction projects offered a welcome alternative for agricultural workers.
Modern history[]
From the 17th to the 19th centuries, French colonisation, supplemented by importing Africans, Chinese and Indians as workers, contributed to ethnic diversity in the population. From 1690, most of the non-Europeans on the island were enslaved. The colony abolished slavery on 20 December 1848. Afterwards, many of the foreign workers came as indentured workers. The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 reduced the importance of the island as a stopover on the East Indies trade route.[citation needed]

During the Second World War, Réunion was under the authority of the Vichy regime until 30 November 1942, when Free French forces took over the island with the destroyer Léopard.[citation needed]
Réunion became a département d'outre-mer (overseas département) of France on 19 March 1946. INSEE assigned to Réunion the department code 974, and the region code 04 when regional councils were created in 1982 in France, including in existing overseas departments which also became overseas regions.
Over about two decades in the late 20th century (1963–1982), 1,630 children from Réunion were relocated to rural areas of metropolitan France, particularly to Creuse, ostensibly for education and work opportunities. That program was led by influential Gaullist politician Michel Debré, who was an MP for Réunion at the time. Many of these children were abused or disadvantaged by the families with whom they were placed. Known as the Children of Creuse, they and their fate came to light in 2002 when one of them, Jean-Jacques Martial, filed suit against the French state for kidnapping and deportation of a minor.[14] Other similar lawsuits were filed over the following years, but all were dismissed by French courts and finally by the European Court of Human Rights in 2011.[15]
In 2005 and 2006, Réunion was hit by a crippling epidemic of chikungunya, a disease spread by mosquitoes. According to the BBC News, 255,000 people on Réunion had contracted the disease as of 26 April 2006.[16] The neighbouring islands of Mauritius and Madagascar also suffered epidemics of this disease during the same year.[17][18] A few cases also appeared in mainland France, carried by people travelling by airline. The French government of Dominique de Villepin sent an emergency aid package worth €36 million and deployed about 500 troops in an effort to eradicate mosquitoes on the island.[citation needed]
Politics[]
Réunion sends seven deputies to the French National Assembly and three senators to the Senate.
Status[]
Reunion is a department and an overseas region, governed by Article 73 of the Constitution of France, under which the laws and regulations are applicable as of right, as in metropolitan France.[19]
Thus, Réunion has a regional council and a departmental council. These territorial entities have the same general powers as the departments and regions of metropolitan France, albeit with some adaptations. Article 73 of the Constitution provides for the possibility of replacing the region and the department by a single territorial entity, but, unlike French Guiana or Martinique, there are currently no plans to do so.
Unlike the other DROMs, the Constitution explicitly excludes Réunion from the possibility of receiving authorization from Parliament to set certain rules itself, either by law or by the national executive.[19]
The State is represented in Réunion by a prefect. The territory is divided into four districts (Saint-Benoît, Saint-Denis, Saint-Paul, Saint-Pierre).
Réunion has 24 municipalities organized into 5 agglomeration communities.
From the point of view of the European Union, Reunion is an outermost region.
Geopolitics[]
The positioning of Reunion Island has given it a more or less important strategic role depending on the period.

Already at the time of the India Route, Réunion Island was a French position located between Cape Town and the Indian trading posts, although far from the Mozambique Channel. The island of Bourbon (its name under the Ancien Régime) was not, however, the preferred position for trade and military.
In fact, Governor Labourdonnais claimed that Ile de France (Mauritius) was a land of opportunity, thanks to its topography and the presence of two natural harbors. He considered that Bourbon was destined to be a depot or an emergency base for Ile de France.[20]
The opening of the Suez Canal diverted much of the maritime traffic from the southern Indian Ocean and reduced the strategic importance of the island. This decline is confirmed by the importance given to Madagascar, which was later colonized.[21]
Since the 2000s, a geopolitical subgroup tends to emerge under the name of the Southwest Indian Ocean.
Today, the island, the seat of a defense and security zone, hosts the headquarters of the Armed Forces of the Southern Indian Ocean Zone (FAZSOI), which brings together French Army units stationed in La Réunion and Mayotte.
Reunion Island allows France to be a member of the Indian Ocean Commission.
Reunion Island is also a base that hosts the Frenchelon infrastructure and the mobile listening and automatic search unit.
Finally, Saint-Pierre is the headquarters of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands (Taaf).
Administrative divisions[]
Administratively, Réunion is divided into 24 communes (municipalities) grouped into four arrondissements. It is also subdivided into 49 cantons, meaningful only for electoral purposes at the departmental or regional level.[22] It is a French overseas department, hence a French overseas region. The low number of communes, compared with French metropolitan departments of similar size and population, is unique: most of its communes encompass several localities, sometimes separated by significant distances.
Municipalities (communes)[]
| Name | Area (km2) | Population | Coat of Arms | Arrondissement | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bras-Panon | 88.55 | 12,768 | Saint-Benoît | ||
| Cilaos | 84.4 | 5,492 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Entre-Deux | 66.83 | 6,914 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| L'Étang-Salé | 38.65 | 14,108 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| La Plaine-des-Palmistes | 83.19 | 6,568 | Saint-Benoît | ||
| La Possession | 118.35 | 32,633 | Saint-Paul | ||
| Le Port | 16.62 | 33,531 | Saint-Paul | ||
| Le Tampon | 165.43 | 79,385 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Les Avirons | 26.27 | 11,246 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Les Trois-Bassins | 42.58 | 7,076 | Saint-Paul | ||
| Petite-Île | 33.93 | 12,308 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Saint-André | 53.07 | 56,747 | Saint-Benoît | ||
| Saint-Benoît | 229.61 | 37,274 | Saint-Benoît | ||
| Saint-Denis | 142.79 | 150,535 | Saint-Denis | ||
| Saint-Joseph | 178.5 | 37,517 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Saint-Leu | 118.37 | 34,196 | Saint-Paul | ||
| Saint-Louis | 98.9 | 53,589 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Saint-Paul | 241.28 | 103,492 | Saint-Paul | ||
| Saint-Philippe | 153.94 | 5,149 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Saint-Pierre | 95.99 | 84,961 | Saint-Pierre | ||
| Sainte-Marie | 87.21 | 33,234 | Saint-Denis | ||
| Sainte-Rose | 177.6 | 6,296 | Saint-Benoît | ||
| Sainte-Suzanne | 58.84 | 23,718 | Saint-Denis | ||
| Salazie | 103.82 | 7,224 | Saint-Benoît |

The communes voluntarily grouped themselves into five intercommunalities for cooperating in some domains, apart from the four arrondissements to which they belong for purposes of applying national laws and executive regulation. After some changes in the composition, name and status of intercommunalities, all of them operate with the status of agglomeration communities, and apply their own local taxation (in addition to national, regional, departmental, and municipal taxes) and have an autonomous budget decided by the assembly representing all member communes. This budget is also partly funded by the state, the region, the department, and the European Union for some development and investment programs. Every commune in Réunion is now a member of an intercommunality with its own taxation, to which member communes have delegated their authority in various areas.
Foreign relations[]
Although diplomacy, military, and French government matters are handled by Paris, Réunion is a member of La Francophonie, the Indian Ocean Commission, the International Trade Union Confederation, the Universal Postal Union, the Port Management Association of Eastern and Southern Africa, and the World Federation of Trade Unions in its own right.
Geography[]


3 071 m
2 632 m
The island is 63 km (39 mi) long; 45 km (28 mi) wide; and covers 2,512 km2 (970 sq mi). It is above a hotspot in the Earth's crust. The Piton de la Fournaise, a shield volcano on the eastern end of Réunion Island, rises more than 2,631 m (8,632 ft) above sea level and is sometimes called a sister to Hawaiian volcanoes because of the similarity of climate and volcanic nature. It has erupted more than 100 times since 1640, and is under constant monitoring, most recently erupting on 2 April 2020.[23] During another eruption in April 2007, the lava flow was estimated at 3,000,000 m3 (3,900,000 cu yd) per day.[24] The hotspot that fuels Piton de la Fournaise also created the islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues.
The Piton des Neiges volcano, the highest point on the island at 3,070 m (10,070 ft) above sea level, is northwest of the Piton de la Fournaise. Collapsed calderas and canyons are south west of the mountain. While the Piton de la Fournaise is one of Earth's most active volcanoes, the Piton des Neiges is dormant. Its name is French for "peak of snows", but snowfall on the summit of the mountain is rare. The slopes of both volcanoes are heavily forested. Cultivated land and cities like the capital city of Saint-Denis are concentrated on the surrounding coastal lowlands. Offshore, part of the west coast is characterised by a coral reef system. Réunion also has three calderas: the Cirque de Salazie, the Cirque de Cilaos and the Cirque de Mafate. The last is accessible only on foot or by helicopter.

Plaine-des-Palmistes

Cirque de Mafate is a caldera formed from the collapse of the large shield volcano the Piton des Neiges.

Réunion from space (NASA image): The three cirques, forming a kind of three-leafed clover shape, are visible in the central north west of the image. Piton de la Fournaise is in the south east.

Lava flow emitted in 2005 by the Piton de la Fournaise

"Plage de l'Ermitage" beach
Geology and relief[]
Reunion Island is a volcanic island born some three million years ago[25] with the emergence of the Piton des Neiges volcano which is today, with an altitude of 3,070.50 m, the highest peak in the Mascarene Islands and the Indian Ocean. The eastern part of the island is constituted by the Piton de la Fournaise, a much more recent volcano (500,000 years old) which is considered one of the most active on the planet. The emerged part of the island represents only a small percentage (about 3%) of the underwater mountain that forms it.
In addition to volcanism, the relief of the island is very uneven due to active erosion. The center shelters three vast cirques dug by erosion (Salazie, Mafate and Cilaos) and the slopes of the island are furrowed by numerous rivers digging gullies, estimated at least 600,[26] generally deep and whose torrents cut the sides of the mountains up to several hundreds of meters deep.
The ancient massif of the Piton des Neiges is separated from the massif of La Fournaise by a gap formed by the plaine des Palmistes and the plaine des Cafres, a passageway between the East and the South of the island. Apart from the plains, the coastal areas are generally the flattest regions, especially in the north and west of the island. The coastline of the wild south is however steeper.
Between the coastal fringe and the Hauts, there is a steep transitional zone whose gradient varies considerably before arriving at the ridge lines setting the cirques or the Enclos, the caldera of the Piton de la Fournaise.
Climate[]

The island of Reunion is characterized by a humid tropical climate, tempered by the oceanic influence of the trade winds blowing from east to west. The climate of Reunion is characterized by its great variability, mainly due to the imposing relief of the island, which is at the origin of numerous microclimates.
As a result, there are strong disparities in rainfall between the windward coast in the east and the leeward coast in the west, and in temperature between the warmer coastal areas and the relatively cooler highland areas.
In Réunion there are two distinct seasons, defined by the rainfall regime:
- a rainy season from January to March, during which most of the year's rain falls;
- a dry season from May to November. However, in the eastern part and in the foothills of the volcano, rainfall can be significant even in the dry season;
April and December are transition months, sometimes very rainy but also very dry.
Pointe des Trois Bassins, located on the coast of the commune of Trois-Bassins (West), is the driest season, with a normal annual precipitation of 447.7 mm, while Le Baril, in Saint-Philippe (Southeast), is the wettest coastal season, with a normal annual precipitation of 4,256.2 mm.[27]
However, the wettest station is in the highlands of Sainte-Rose, with an average annual rainfall of almost 11,000 mm (430 in), making it one of the wettest places in the world.
Temperatures in Reunion are characterized by their great mildness throughout the year. In fact, the thermal amplitude from one season to another is relatively small (rarely exceeding 10 °C [50 °F]), although it is perceptible:
- In the warm season (November to April): average minimums usually range between 21 and 24 °C (70 and 75 °F), and average maximums between 28 and 31 °C (82 and 88 °F), on the coast. At 1,000 m (3,300 ft), average minimums fluctuate between 10 and 14 °C (50 and 57 °F) and average maximums between 21 and 24 °C (70 and 75 °F);
- In the cold season (May to October): temperatures at sea level vary from 17 to 20 °C (63 to 68 °F) for average minimums and from 26 to 28 °C (79 to 82 °F) for average maximums. At 1,000 m (3,300 ft), average minimums range from {cvt|8 to 10|°C}} and average maximums from 17 to 21 °C (63 to 70 °F).
In mountain towns, such as Cilaos or La Plaine-des-Palmistes, average temperatures range between 12 and 22 °C (54 and 72 °F). The highest parts of the habitat and the natural areas at altitude may suffer some winter frosts. Snow was even observed on the Piton des Neiges and Piton de la Fournaise in 2003 and 2006.[28]
While a growing number of islands (including "non-sovereign" islands) in the world are concerned about the effects of climate change, the island of Reunion was chosen (along with Gran Canaria in Spain) as an example for a case study of an affected ultra-European peripheral territory,23 for a study on the adequacy of urban and regional planning tools to the needs and characteristics of these islands (including land use and population density and the regulatory framework).
This work confirmed that urban and peri-urban land use pressures are high, and that adaptation strategies are incompletely integrated into land use planning. According to the Institute of Island Studies, there is a dysfunction: "island planning tools often do not take climate change adaptation into account and there is too much top-down management in the decision-making process".[29] Réunion holds the world records for the most rainfall in 12-, 24-, 72- and 96-hour periods.[30]
Beaches[]
Réunion hosts many tropical and unique beaches. They are often equipped with barbecues, amenities, and parking spaces. Hermitage Beach is the most extensive and best-preserved lagoon in Réunion Island and a popular snorkelling location.[31] It is a white sand beach lined with casuarina trees under which the locals often organise picnics. La Plage des Brisants is a well-known surfing spot, with many athletic and leisurely activities taking place. Each November, a film festival is also organised in La Plage des Brisant's. Movies are projected on a large screen in front of a crowd. Beaches at Boucan Canot are surrounded by a stretch of restaurants that particularly cater to tourists. L'Étang-Salé on the west coast is a particularly unique beach as it is covered in black sand consisting of tiny fragments of basalt. This occurs when lava contacts water, it cools rapidly and shatters into the sand and fragmented debris of various size. Much of the debris is small enough to be considered sand. Grand Anse is a tropical white-sand beach lined with coconut trees in the south of Réunion, with a rock pool built for swimmers, a pétanque playground, and a picnic area. Le Vieux Port in Saint Philippe is a green-sand beach consisting of tiny olivine crystals, formed by the 2007 lava flow, making it one of the youngest beaches on Earth.[32]

Sunset at Grand Anse beach Reunion Island

Restaurants along Boucan Canot beach[33]

Manapany beach rock pool

L'Étang-Salé Beach - a black sand beach from volcanic basalt

L’Ermitage les Bains lagoon in front of Saint Paul, and its pass through the coral reef
Environment[]
Since 2010, Réunion is home to a UNESCO World Heritage Site that covers about 40% of the island's area and coincides with the central zone of the Réunion National Park.[34] The island is part of the Mascarene forests terrestrial ecoregion.[35]
Wildlife[]
Réunion is home to a variety of birds such as the white-tailed tropicbird (French: paille en queue).[36] Its largest land animal is the panther chameleon, Furcifer pardalis. Much of the west coast is ringed by coral reef which harbours, among other animals, sea urchins, conger eels, and parrot fish. Sea turtles and dolphins also inhabit the coastal waters. Humpback whales migrate north to the island from the Antarctic waters annually during the Southern Hemisphere winter (June–September) to breed and feed, and can be routinely observed from the shores of Réunion during this season. At least 19 species formerly endemic to Réunion have become extinct following human colonisation. For example, the Réunion giant tortoise became extinct after being slaughtered in vast numbers by sailors and settlers of the island.
A juvenile Emperor angelfish

A Moorish idol

A white-tailed Tropicbird

A Hawksbill sea turtle

A Humpback whale off St-Gilles
Marine biodiversity[]
Despite the small area of coral reefs, the marine biodiversity of Reunion Island is comparable to that of other islands in the area, which has earned the Mascarene archipelago its inclusion among the top ten global biodiversity "hotspots".[37] Reunion's coral reefs, both flat and barrier, are dominated mainly by fast-growing branching coral species of the genus Acropora (family Acroporidae), which provide shelter and food for many tropical species.
Recent scientific research in Reunion Island indicates that there are more than 190 species of corals, more than 1,300 species of mollusks, more than 500 species of crustaceans,[38] more than 130 species of echinoderms and more than 1,000 species of fish.[39]
Reunion's deeper waters are home to dolphins, killer whales, humpback whales, blue sharks and a variety of shark species, including whale sharks, coral sharks, bull sharks, tiger sharks, blacktip sharks and great white sharks. Several species of sea turtles live and breed here.
Between 2010 and 2017, 23 shark attacks occurred in the waters of Réunion, of which nine were fatal.[40] In July 2013, the Prefect of Réunion Michel Lalande announced a ban on swimming, surfing, and bodyboarding off more than half of the coast. Lalande also said 45 bull sharks and 45 tiger sharks would be culled, in addition to the 20 already killed as part of scientific research into the illness ciguatera.[41]
Migrations of humpback whales contributed to a boom of whale watching industries on Réunion, and watching rules have been governed by the OMAR (Observatoire Marin de la Réunion) and Globice (Groupe local d'observation et d'identification des cétacés).
Coral reef[]

Because the island is relatively young (3 million years old),[25] the coral formations (8,000 years old) are still poorly developed and occupy a small area compared to older islands, mostly in the form of fringing reefs.[25]
These formations define shallow "lagoons" (rather "reef depressions"), the largest of which is no more than 200 m wide and about 1–2 m deep.[42] These lagoons, which form a discontinuous reef belt 25 km (16 mi) long (i.e. 12% of the island's coastline) with a total area of 12 km2 (4.6 sq mi), are located on the west and southwest coast of the island. The most important are those of L'Ermitage (St.-Gilles), St.-Leu, L'Étang-Salé and St.-Pierre.
Flora[]
The tropical and insular flora of Reunion Island is characterized by its diversity, a very high rate of endemism and a very specific structure. The flora of Reunion presents a great diversity of natural environments and species (up to 40 tree species/ha, compared to a temperate forest which has an average of 5/ha). This diversity is even more remarkable, but fragile, as it differs according to the environment (coastal, low, medium and high mountain).
Reunion has a very high rate of endemic species, with more than 850 native plants (of natural origin and present before the arrival of man), of which 232 are endemic to the island of Reunion (only present on the island), as well as numerous species endemic to the Mascarene archipelago. Finally, the flora of Reunion is distinguished from that of equatorial tropical forests by the low height and density of the canopy, probably due to adaptation to cyclones, and by a very specific vegetation, in particular a strong presence of epiphytic plants (growing on other plants), such as orchids, bromeliads and cacti, but also ferns, lichens and mosses.[43]
Gardening and Bourbon roses[]
The first members of the "Bourbon" group of garden roses originated on this island (then still Île Bourbon, hence the name) from a spontaneous hybridisation between Damask roses and Rosa chinensis,[44] which had been brought there by the colonists. The first Bourbon roses were discovered on the island in 1817.[45]

Threats to the Environment[]
Among coastal ecosystems, coral reefs are among the richest in biodiversity, but they are also the most fragile.[46]
Nearly one-third of fish species were already considered threatened or vulnerable in 2009, with coral degradation in many places. The causes of this state of affairs are pollution, overfishing and poaching, as well as anthropogenic pressure, especially linked to the densification of urbanization in coastal areas and the discharge of sewage.[47]
104 species living on Reunion Island were included in the Red List published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as of September 12, 2008. This compares to 51 species in 2007.[48]
On this list were :
Vertebrates[]
- Mammals; 6 species, including:
- Black dogfish
- Birds; 6 species, including:
- Meller's duck,
- Papangue,
- Barau petrel,
- Bourbon black petrel,Tree locust (Anacridium melanorhodon) on Begonia flowers on Réunion island
- The tuit tuit.
- Fish; 6 species;
Invertebrates[]
- 58 species, including :
- Mollusks; 14 species.
Others[]
- Plants : 15 species;
- Corals: 56 species.
The insular nature of Reunion Island makes it vulnerable to climate change and implies an adaptation strategy, to which a green and blue network can contribute.46
Demographics[]




Historical population[]
| Year | Population | Year | Population | Year | Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1671 | 90 | 1830 | 101,300 | 1961 | 349,282 | ||
| 1696 | 269 | 1848 | 110,300 | 1967 | 416,525 | ||
| 1704 | 734 | 1849 | 120,900 | 1974 | 476,675 | ||
| 1713 | 1,171 | 1860 | 200,000 | 1982 | 515,814 | ||
| 1717 | 2,000 | 1870 | 212,000 | 1990 | 597,823 | ||
| 1724 | 12,550 | 1887 | 163,881 | 1999 | 706,300 | ||
| 1764 | 25,000 | 1897 | 173,192 | 2008 | 808,250 | ||
| 1777 | 35,100 | 1926 | 182,637 | 2013 | 835,103 | ||
| 1789 | 61,300 | 1946 | 241,708 | 2018 | 855,961 | ||
| 1826 | 87,100 | 1954 | 274,370 | 2020 | 858,450 | ||
| Official data from INSEE by census or estimate; estimates shown in italics. | |||||||
Migrations and ethnic groups[]
At the 2015 census, 83.1% of the inhabitants of Réunion were born on the island, 11.4% were born in Metropolitan France, 0.8% were born in Mayotte, 0.3% were born in the rest of Overseas France, and 4.4% were born in foreign countries (half of them children of French expatriates and settlers born in foreign countries, such as children of Réunionese settlers born in Madagascar during colonial times; the other half immigrants, i.e. people born in foreign countries with no French citizenship at birth).[49]
In recent decades, the number of Metropolitan Frenchmen living on the island of Réunion has increased markedly: 37,487 natives of Metropolitan France lived in Réunion at the 1990 census, but their numbers more than doubled in 25 years and by the 2015 census 97,239 natives of Metropolitan France lived in Réunion.[49] Native Réunionese, meanwhile, have emigrated increasingly to Metropolitan France: the number of natives of Réunion living in Metropolitan France rose from 16,548 at the 1968 census to 92,354 at the 1990 census to 121,489 at the 2015 census, by which date nearly 15% of the natives of Réunion lived outside of Réunion.[49]
Réunion has experienced extremely little immigration of foreigners since World War Two, and by the 2015 census only 2.2% of the inhabitants of Réunion were immigrants. This is in contrast to the situation that prevailed from the middle of the 19th century until World War Two when many migrants from India, Eastern Asia, and Africa came to Réunion to work in the plantation economy. Their descendants have now become French citizens.
| Census | Born in Réunion |
Born in Metropolitan France |
Born in Mayotte |
Born in the rest of Overseas France |
Born in foreign countries with French citizenship at birth¹ |
Immigrants² |
| 2015 | 83.1% | 11.4% | 0.8% | 0.3% | 2.2% | 2.2% |
| 2010 | 84.1% | 10.6% | 0.8% | 0.3% | 2.2% | 1.9% |
| 1999 | 86.1% | 9.1% | 0.9% | 0.4% | 2.0% | 1.4% |
| 1990 | 90.4% | 6.3% | 0.2% | 0.1% | 1.9% | 1.0% |
| ¹Persons born abroad of French parents, such as Pieds-Noirs and children of French expatriates. ²An immigrant is by French definition a person born in a foreign country and who didn't have French citizenship at birth. Note that an immigrant may have acquired French citizenship since moving to France, but is still listed as an immigrant in French statistics. On the other hand, persons born in France with foreign citizenship (the children of immigrants) are not listed as immigrants. | ||||||
| Source: INSEE[49] | ||||||
Ethnic groups present include people of African, Indian, European, Malagasy and Chinese origin. Local names for these are Yabs, Cafres, Malbars and Chinois. All of the ethnic groups on the island are immigrant populations that have come to Réunion from Europe, Asia and Africa over the centuries. There are no indigenous people on the island, as it was originally deserted.[50] These populations have mixed from the earliest days of the island's colonial history (the first settlers married women from Madagascar and of Indo-Portuguese heritage), resulting in a majority population of mixed race and of "Creole" culture.
It is not known exactly how many people of each ethnicity live in Réunion, since the French census does not ask questions about ethnic origin,[51] which applies in Réunion because it is a part of France in accordance with the 1958 constitution. The extent of racial mixing on the island also makes ethnic estimates difficult. According to estimates, Whites make up roughly one quarter of the population,[52] Malbars make up more than 25% of the population and people of Chinese ancestry form roughly 3%.[53] The percentages for mixed race people and those of Afro-Malagasy origins vary widely in estimates. Also, some people of Vietnamese ancestry live on the island, though they are very few in number.[54][55][56]
Tamils are the largest group among the Indian community.[57] The island's community of Muslims from north western India, particularly Gujarat, and elsewhere is commonly referred to as zarabes.
Creoles (a name given to those born on the island, regardless of ethnic origins) make up the majority of the population. Groups that are not Creole include people recently arrived from Metropolitan France (known as zoreilles) and those from Mayotte and the Comoros as well as immigrants from Madagascar and Sri Lankan Tamil refugees.
Religion[]

Religious affiliation (2000 censuses)[58]
The predominant religion is Christianity, notably Roman Catholicism, with a single (Latin Rite) jurisdiction, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Saint-Denis-de-La Réunion. Religious Intelligence estimates Christians to be 84.9% of the population, followed by Hindus (6.7%) and Muslims (2.15%).[56] Chinese folk religion and Buddhism are also represented, among others.
Most large towns have a Hindu temple and a mosque.[59]
Culture[]
Réunionese culture is a blend (métissage) of European, African, Indian, Chinese and insular traditions. The most widely spoken language, Réunion Creole, derives from French.
Language[]
French is the sole official language of Réunion. Though not official, Réunion Creole is widely spoken alongside French. Creole is commonly used for informal purposes, whereas the official language for administrative purposes, as well as education, is French.[60]
Other languages spoken on Réunion include: Comorian varieties (especially Shimaore) and Malagasy, by recent immigrants from Mayotte and Madagascar; Mandarin, Hakka and Cantonese by members of the Chinese community; Indian languages, mostly Tamil, Gujarati and Urdu; and Arabic, spoken by a small community of Muslims. These languages are generally spoken by immigrants, as those born on the island tend to use French and Creole.
Cantonese, Arabic and Tamil are offered as optional languages in some schools.[57]
Music[]
There are two music genres which originated in Réunion: sega, which originated earlier and is also traditional in Mauritius, Rodrigues and Seychelles, and maloya, which originated in the 19th century and is only found in Réunion. Every December 20, the inhabitants of Reunion Island celebrate Reunion Freedom Day. This celebration, also known as the Fête des Cafres or "Fet' Caf'", commemorates the proclamation of the abolition of slavery by the Second Republic (France) in 1848. The term "cafre" refers to the Africans of the "Cafrerie" (a part of southern Africa). It derives from the Afrikaans word "kaffer," which is similar to the American slang "nigger" or "nègre," originating in colonial France.[61]
Today, in the 21st century, Reunionese celebrate with joy the end of a long period of oppression. Cafres, Malagasy, Comorians, Indians, Yabs, Z'oreilles and metropolitans gather in the streets dancing to the rhythm of the sega and the maloya, the two great musical genres of Reunion.[62] Numerous concerts are organized, most of them free, as well as costume parades and dance shows such as merengue, for example.
Cuisine[]
Always accompanied by rice, the most common dishes are curry, a local version of Indian curry, rougail and civets. Curry is made with a base of onion, garlic and spices such as turmeric (called "safran péi" on the island),[63] on which fish, meat and eggs are fried; tomato is then added. Dishes can also be flavored with ginger; the peel of a combava is often prized. Chop suey (with rice, not pasta) and other Asian dishes such as pork with pineapple[64] are also very common.

In general, there are few dishes without meat or fish, so there are few vegetarian options. One of them is chouchou chayote gratin. Otherwise, mainly poultry is consumed. One of the local specialties is tangue[65] civet (of the hedgehog family).
Sport[]
Moringue is a popular combat/dance sport similar to capoeira.
There are several famous Réunionese sportsmen and women like the handballer Jackson Richardson, as well as the karateka Lucie Ignace.
Réunion has a number of contributions to worldwide professional surfing. It has been home to notable pro surfers including Jeremy Flores, Johanne Defay and . Famous break St Leu has been host to several world surfing championship competitions.
Since 1992, Réunion has hosted a number of ultramarathons under the umbrella name of the Grand Raid. As of 2018, four different races compose the Grand Raid: the Diagonale des Fous, The Trail de Bourbon, the Mascareignes, and the Zembrocal Trail.[66]
Football[]
Football is the most popular sport. With more than 30,000 licensed players for a population of about 750,000 inhabitants, it remains the sport of choice for young people. Although the highest level of competition called the First Division of Réunion is equivalent to a division d'honneur in metropolitan France (DH), all the youngsters hope to play at the highest level one day.
This has been the case for players such as Laurent Robert, Florent Sinama-Pongolle, Guillaume Hoarau, Dimitri Payet, Benoit Tremoulinas (the only five Reunionese to have played for the French national team), Bertrand Robert, Thomas Fontaine, Ludovic Ajorque, Fabrice Abriel (of Reunion descent) and Wilfried Moimbe (of Reunion descent), to name but a few. The territory has its own team, the Réunion national football team.
Architecture[]

Structurally, the local Creole house is said to be symmetrical.[67] In fact, in the absence of an architect, workers would draw a line on the ground and build two identical parts on each side, resulting in houses of essentially rectangular shape. The veranda is an important element of the house. It is an outdoor terrace built on the front of the house, as it allowed to show its richness to the street. A Creole garden completes the house. It is composed of local plants, found in the forest. There is usually a greenhouse with orchids, anthuriums and different types of ferns.
The Villa Déramond-Barre is a Creole architectural model of great heritage interest.[68]
Traditions[]
Two forms of musical expression historically make up the folkloric tradition of Reunion Island. One, the sega, is a Creole variant of the quadrille, the other, the maloya, like the American blues, comes from Africa, carried by the nostalgia and pain of slaves uprooted and deported from their homeland.
The sega, a disguised ballroom dance to the rhythm of traditional Western instruments (accordion, harmonica, guitar, etc.), is a testament to the fun of colonial society at the time. Today, it is still the typical ballroom dance of the island of Réunion and the Mascarene archipelago in general, along with the Mauritian sega and the Rhodesian sega.
The slaves' maloya, a ritual dance full of melodies and gestures, was performed almost clandestinely at night around a bonfire; the few instruments that accompanied it were made of plants (bamboo, gourds, etc.).

Beyond their taste for this musical art form, the maloya troupes wanted to perpetuate the memory of the slaves, their suffering and their uprooting. Through sometimes controversial texts, they remind France of its slave-owning past and underline the damage that this colonial era did to human beings; in the course of the island's history, maloya artists and kabars (gatherings) were sometimes banned by the authorities.
With the institution of a public holiday to celebrate the abolition of slavery (fête caf', 20 December), maloya has received official recognition; it is regularly played on public radio and many discotheques and dance parties programme it regularly; it is even enjoying a revival: groups have begun to make modern versions, styles and arrangements, such as maloggae and other electric maloya.
Some of Reunion Island's emblematic musical groups include: Groupe folklorique de La Réunion, Kalou Pilé, Baster, Ousanousava, Ziskakan, Pat'Jaune, Danyèl Waro, Tisours, etc. We can also mention one of the greatest Maloya singers: Lo Rwa Kaf. Born in Sainte-Suzanne, he was one of the first to sing Maloya. When he died in 2004, many people were present at his funeral.
In 2008, the artist Brice Guilbert made a video clip entitled La Réunion. In this clip, we see him crossing all the landscapes of the island.
In the field of contemporary dance, we can mention the choreographer Pascal Montrouge, who directs the only company in France that has a double headquarters in Saint-Denis de La Réunion and Hyères, which reinforces the sense of his vision of identity. In 2007, the city of Saint-Denis de La Réunion entrusted him with the artistic direction of its Saint-Denis Danses festival.
The island is home to the regional conservatory of La Réunion, which has four teaching centres and was created in 1987 under the impetus of the then president of the region, Pierre Lagourgue. Today, although traditional dances are not forgotten in the conservatoires (which teach dance, music and theatre), the dances taught are classical dance, contemporary dance and Bharata natyam dance. These students regularly have the opportunity to dance with choreographers from Reunion such as Didier Boutiana cie "konpani Soul city "98, Soraya Thomas cie "Morphose "99or Éric Languet cie "danse en l'R "100. These different local companies allow the inhabitants of Reunion to dance professionally.
Urban culture has also made its appearance, following the trends and influences of metropolitan France and the United States. Thus, hip-hop culture is developing, but also ragga dancehall, with KM David or Kaf Malbar being the figurehead of this new movement, influencing the young generation all over the island, with their songs spread by mp3 or internet. Many young artists are trying to "break through" in this music, whose industry is developing reasonably well, locally but also internationally, and has nothing to envy from the precursors of French dancehall.
Media[]
Broadcasting[]
Réunion has a local public television channel, Réunion 1ère, which now forms part of France Télévision, and also receives France 2, France 3, France 4, France 5 and France 24 from metropolitan France, as well as France Ô, which shows programming from all of the overseas departments and territories. There are also two local private channels, Télé Kréol and Antenne Réunion.
It has a local public radio station, formerly Radio Réunion, but now known as Réunion 1ère, like its television counterpart. It also receives the Radio France networks France Inter, France Musique and France Culture. The first private local radio station, Radio Freedom, was introduced in 1981. They broadcast daily content about weather and local services.

Newspapers[]
Two main newspapers:
Cinema[]
Present on the island since 1896, is marked by its insularity and its geographical distance from metropolitan France. In the absence of the Centre national de la cinématographie (CNC), it has developed specific distribution and dissemination networks. Its landscapes first served as a natural backdrop for many film and television productions, and film events, such as festivals, multiplied there. Digital technology now facilitates the development of local productions, most of which reflect the particularities of a multicultural and multilingual society.
The Réunion Film Festival (estival du film de La Réunion) was created in 2005 and is chaired by Fabienne Redt. The festival presented first and second feature films by French directors. The 10th and last edition took place in 2014 in partnership mainly with the TEAT Champ Fleuri (Saint-Denis) and the city of Saint-Paul.
In the Port, the International Film Festival of Africa and the Reunion Islands (Festival international du film d'Afrique et des îles de La Réunion) was also held.
Among the existing film festivals is the Reunion Island Adventure Film Festival (13 editions), which awards prizes to adventure films.
In Saint-Philippe, the Festival Même pas peur, Réunion's international fantasy film festival, has been held since 2010.
In Saint-Pierre, there are two festivals: Écran jeunes (25th edition in 2019) and the Festival du Film Court de Saint-Pierre, directed by Armand Dauphin (3rd edition in 2019).
Film[]
- Adama (animated there)
- Mississippi Mermaid (1969) (filmed there)
Blogs[]
- (English language blog and Instagram page)[69]
- Reunion Island Tourism blog (English/French tourism blog)
Internet[]
The Internet situation in Réunion was once marked by its insularity and remoteness from mainland France, which caused some technological delays. Today, the trend has been reversed and the region has a relatively efficient Internet connection and is one of the departments most connected by fibre optics in France.
Internet connection can be provided by ADSL (offered by four operators), fibre optic (three operators), or by cellular data on 4G and 5G networks (currently being tested in Saint-Denis).
Reunion domain names have the suffix .re. The Reunion region has deployed a regional fibre-optic network for operators. This network is based partly on EDF's very high voltage cables - G@zelle network, partly on the region's own fibre and partly on Hertzian links for the most isolated areas. This network is managed by a public service company called La Réunion Numérique.[70]
Economy[]


In 2019, the GDP of Réunion at market exchange rates, not at PPP, was estimated at 19.7 billion euros (US$22.0 bn) and the GDP per capita (also at market exchange rates) was 22,970 euros (US$25,720).[2] Economic growth was around +3.0% per year in real terms from 2014 to 2017, then it fell to +1.7% in 2018 and rebounded to +2.2% in 2019.[71]
Sugar was traditionally the chief agricultural product and export. Tourism is now an important source of income.[72] The island's remote location combined with its stable political alignment with Europe makes it a key location for satellite receiving stations[73] and naval navigation.[74]
GDP sector composition in 2013 (contribution of each sector to the total gross value added):[75]
| Sector | % of total GVA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 1.5% | ||
| |||
| Mining and quarrying | 0.0% | ||
| Manufacturing | 4.4% | ||
| |||
| Utilities | 1.8% | ||
| Construction | 5.4% | ||
| Market services | 51.1% | ||
| |||
| Non-market services | 35.9% | ||
| |||
Unemployment is a major problem on Réunion, although the situation has improved markedly since the beginning of the 2000s: the unemployment rate, which stood above 30% from the early 1980s to the early 2000s, declined to 24.6% in 2007, then rebounded to 30.0% in 2011 due to the 2008 global financial crisis and subsequent Great Recession, but declined again after 2011, reaching 21.5% in 2019,[76] its lowest level in 40 years.[77]
In 2014, 40% of the population lived below the poverty line (defined by INSEE as 60% of Metropolitan France's median income; in 2014 the poverty line for a family of two parents and two young children was €2,064 (US$2,743) per month).[78]
Rum distillation contributes to the island's economy. A "Product of France", it is shipped to Europe for bottling, then shipped to consumers around the world.
Brasseries de Bourbon is the main brewery of the island, with Heineken as shareholder.

Tourism[]
Income from tourism is Reunion Island's primary economic resource, ahead of sugar cane production and processing, which has allowed the development of large Reunionese groups such as Quartier Français, Groupe Bourbon ex-Sucreries Bourbon, a large international company now listed on the stock exchange, but based outside the island and which has abandoned the sugar sector for the off-shore maritime sector. With the reduction of subsidies, this culture is threatened. Therefore, the development of fishing in the French Southern and Antarctic Lands has been promoted.
The tertiary sector, particularly the commercial sector, is by far the most developed, and import distribution has taken off in the mid-1980s through affiliation and franchising agreements with metropolitan groups. The advent of franchised distribution has transformed the commercial apparatus, which historically was characterized by the geographic dispersion of small grocery-type units; the few "Chinese stores" still in operation are limited to mid-range towns and, as relics of a bygone era, have more of a tourist and educational appeal, even if they retain a convenience store function.
Despite a certain economic dynamism, the island does not manage to absorb its significant unemployment, which is explained in particular by a very strong demographic growth. Many Réunioners are forced to emigrate to metropolitan France for their studies or to find work.

Agriculture[]
Agriculture in Réunion is an important activity in the island's economy:[79] the agricultural territory covering 20% of the island's surface area employs 10% of the active population, generates 5% of the gross regional product and provides the island's main export. Formerly centered on coffee and clove cultivation, it has focused on sugar cane since the events of the early 19th century, namely the Great Avalanches and the seizure of Reunion by the British. Today it faces important issues related to the decisions of the World Trade Organization at the international level and the development of the urban fact at the local level.
Reunion Island has about 7,000 farms, 5,000 of which are professional. These farms mobilize almost 11,000 AWU (annual workload of one person on a full-time basis).
Ninety-seven percent of the farms in Réunion are less than 20 hectares in size, compared to an average of 78 hectares in mainland France.
The most common status is that of individual farmer (97%).
In 2005, more than 60% of farm managers were between 40 and 59 years old.
Public services[]
Health[]
In 2005–2006, Réunion experienced an epidemic of chikungunya, a viral disease similar to dengue fever brought in from East Africa, which infected almost a third of the population because of its transmission through mosquitoes. The epidemic has since been eradicated. See the History section for more details.

Transport[]
Roland Garros Airport serves the island, handling flights to mainland France, India, Madagascar, Mauritius, Tanzania, Comoros, Seychelles, South Africa, China and Thailand. Pierrefonds Airport, a smaller airport, has some flights to Mauritius and Madagascar. In 2019 a light rail system was proposed to link Le Barachois with the airport.[80]
Education[]
Reunion Island has its own education system. Chantal Manès-Bonnisseau, Inspector General of Education, Sport and Research, was appointed Rector of the Académie de la Réunion and Chancellor of Universities at the Council of Ministers on July 29, 2020.
She succeeds Vêlayoudom Marimoutou, who took office as secretary general of the Indian Ocean Commission on July 16.
The Rectorate is located in the main city, in the Moufia district of Saint-Denis. At the start of the 2012 school year, the island had 522 pre-school and/or primary schools, including 26 private schools, for 120,230 students at the primary level, 82 secondary schools, including six private schools, for 61,300 students, 32 general and technological high schools, including three private schools, for 23,650 students, and 15 vocational schools, including two private schools, for 16,200 students.
Reunion's priority education zones affect slightly more than half of the primary and secondary school students.[81]
Baccalaureate results are relatively close to the national average with a rate of 81.4% in 2012 compared to 82.4% in 2011 (respectively: 84.5% and 85.6% in the national average).
In higher education, the University of Reunion has 11,600 students spread across the various sites, especially in Saint-Denis and Le Tampon. A further 5,800 students are divided between the post-baccalaureate courses of secondary education and other higher studies.[82]
Energy[]

Energy on Réunion depends on oil and is limited by the island's insularity, which forces it to produce electricity locally and import fossil fuels. Faced with increasing demand and environmental requirements, the energy produced on the island is tending to increasingly exploit its great renewable energy potential through the development of wind farms, solar farms and other experimental projects. Although 35% of Réunion's electricity came from renewable sources in 2013, the department's energy dependency rate exceeds 85%. Saving electricity and optimising energy efficiency are two major areas of work for the authorities responsible for energy issues.
Hydroelectric power[]
Due to the large volumes of rainfall, the flow of surface water allows the installation of hydroelectric infrastructures, especially as erosion has carved out narrow and very deep ravines. The Sainte-Rose plant (22 MW) and the Takamaka plant (17.5 MW) are the two largest. In total, the island's six hydroelectric infrastructures have a capacity of 133 MW.
Symbols[]
Réunion has no official coat of arms or flag.
Former Governor Merwart created a coat of arms for the island on the occasion of the 1925 colonial exhibition organised on Petite-Île. Merwart, a member of the Reunion Island Society of Sciences and Arts, wanted to include the island's history:
- The Roman numeral "MMM" evokes the altitude of the highest peaks;
- the ship Saint-Alexis is the one that first took possession of the island;
- the fleurs-de-lis evoke the royal era;
- the bees evoke the Empire;
- the central coat of arms evokes the French Republican flag;
- The motto "Florebo quocumque ferar" is that of the French East India Company and means "I will bloom wherever they take me", while the vanilla vines honour a flourishing harvest.
The most commonly used flag in Réunion is that of the "radiant volcano", designed by Guy Pignolet in 1975, sometimes called "Lo Mavéli":[83] it represents the volcano of Piton de la Fournaise in the form of a simplified red triangle on a navy blue background, while five sunbeams symbolise the arrival of the populations that have converged on the island over the centuries.[84]
See also[]
- Administrative divisions of France
- Anchaing
- Du battant des lames au sommet des montagnes
- List of colonial and departmental heads of Réunion
- List of islands
- List of islands administered by France in the Indian and Pacific oceans
- List of Réunionnais
- Malaysia Airlines Flight 370
- Scouting and Guiding in Réunion
- Alfred Nakache
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b INSEE. "Estimation de population par région, sexe et grande classe d'âge – Années 1975 à 2021" (in French). Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Gross domestic product (GDP) at current market prices by NUTS 2 regions". Eurostat. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ Réunion is pictured on all Euro banknotes, on the back at the bottom of each note, right of the Greek ΕΥΡΩ (EURO) next to the denomination.
- ^ Jean Baptiste Duvergier, Collection complète des lois [...], éd. A. Guyot et Scribe, Paris, 1834, « Décret du 23 mars 1793 », p. 205
- ^ Daniel Vaxellaire, Le Grand Livre de l'histoire de La Réunion, vol. 1 : Des origines à 1848, éd. Orphie, 2000, 701 p. ISBN 978-2-87763-101-3 et 978-2877631013), p. 228 (avec fac-similé du décret).
- ^ Nouveau recueil général de traités, conventions et autres transactions remarquables – Année 1848, éd. Librairie de Dieterich, 1854, « Arrêté du gouvernement provisoire portant changement du nom de l'île Bourbon, Paris, 7 mars », p. 76
- ^ Lexique des règles typographiques en usage à l’Imprimerie nationale, Imprimerie nationale, 1990 ISBN 978-2-11-081075-5 ; réédition 2002 ISBN 978-2-7433-0482-9 ; réimpressions octobre 2007 et novembre 2008 ISBN 978-2-7433-0482-9, p. 90 et 93.
- ^ "Commission nationale de toponymie – Collectivités territoriales françaises".
- ^ Jump up to: a b Allen, Richard B. (14 October 1999). Slaves, Freedmen and Indentured Laborers in Colonial Mauritius. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521641258.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tabuteau, Jacques (1987). Histoire de la justice dans les Mascareignes (in French). Paris: Océan éditions. p. 13. ISBN 2-907064-00-2. Retrieved 11 June 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Moriarty, Cpt. H.A. (1891). Islands in the southern Indian Ocean westward of Longitude 80 degrees east, including Madagascar. London: Great Britain Hydrographic Office. p. 269. OCLC 416495775.
- ^ "| Journal de l'île de la Réunion". Clicanoo.re. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ "Histoire - Assemblée nationale". www2.assemblee-nationale.fr. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ Jean-Jacques Martial (2003). Une enfance volée. Les Quatre Chemins. p. 113. ISBN 978-2-84784-110-7. Retrieved 13 September 2012.
- ^ Géraldine Marcon: CHRONOLOGIE : L'histoire des enfants réunionnais déplacés en métropole on francebleu.fr.
- ^ "Island disease hits 50,000 people". BBC News. 2 February 2006. Retrieved 18 August 2007.
- ^ Beesoon, Sanjay; Funkhouser, Ellen; Kotea, Navaratnam; Spielman, Andrew; Robich, Rebecca M. (2008). "Chikungunya Fever, Mauritius, 2006". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 14 (2): 337–338. doi:10.3201/eid1402.071024. PMC 2630048. PMID 18258136.
- ^ "Madagascar hit by mosquito virus". BBC News. 6 March 2006. Retrieved 18 August 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Collectivités d'Outre-mer de l'article 73 de la Constitution (Guadeloupe, Guyane, Martinique, La Réunion, Mayotte)". www.legifrance.gouv.fr. Retrieved 28 June 2021.
- ^ Guy Dupont, Condé-sur-Noireau, L'Harmattan, juin 1990, 759 p. ISBN 2-7384-0715-3 p. 27
- ^ Raoul LUCAS et Mario SERVIABLE, C.R.I p. 26
- ^ "Insee – Code Officiel Géographique". Insee.fr. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- ^ [1] Le Piton du Confinement on clicanoo.com
- ^ Thomas Staudacher (7 April 2007). "Reunion sees 'colossal' volcano eruption, but population safe". AFP. Archived from the original on 9 April 2007. Retrieved 18 August 2007. (Web archive)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Emmanuel Tessier, Saint Denis, Thèse de doctorat sous la direction de Pascale Chabanet et Catherine Aliaume, 2005, 254 p
- ^ Guy Dupont, Condé-sur-Noireau, L'Harmattan, juin 1990, 759 p. ISBN 2-7384-0715-3 p. 100.
- ^ "CLIMAT LA REUNION - Informations, normales et statistiques sur le climat à La Réunion". www.meteofrance.re. Retrieved 2 July 2021.
- ^ "Exceptionnel : Il a neigé au volcan". Imaz Press Réunion : l'actualité de la Réunion en photos (in French). 10 October 2006. Retrieved 2 July 2021.
- ^ "European island outermost regions and climate change adaptation: a new role for regional planning" (PDF).
- ^ "World Meteorological Organization: Global Weather & Climate Extremes". Arizona State University.
- ^ "Lagon de l'Hermitage". Snorkeling Report. Retrieved 24 July 2020.
- ^ Ocean, Indian. "The beaches of Réunion Island". Snorkeling Report. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- ^ "Lunch at Plage de Boucan Canot". Flickr. 23 October 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- ^ "Pitons, cirques and remparts of Reunion Island". UNESCO. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ (in French) L'Île de la Réunion.com: Le paille en queue
- ^ "Biodiversité marine Réunion, Hot spot". vieoceane.free.fr. Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- ^ "Crusta". crustiesfroverseas.free.fr. Retrieved 4 July 2021.
- ^ Ronald Fricke, Thierry Mulochau, Patrick Durville, Pascale Chabanet, Emmanuel Tessier et Yves Letourneur, « », Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde A, Neue Serie, vol. 2, 2009, p. 1–168
- ^ Gilibert, Laurence (1 March 2018). "Crise requin: Les causes scientifiques sous les projecteurs de la revue "Nature"" – via ZINFO974.
- ^ "Big Read: Reunion Island beset by shark controversy". News Corp Australia. 30 August 2013.
- ^ Étude comparative des récifs coralliens de l’archipel des Mascareignes, station marine d'Endoume et Centre d’Océanographie, Marseille, et Centre Universitaire de La Réunion, Saint Denis de La Réunion, in : Guézé P. (dir.) Biologie marine et exploitation des ressources de l'Océan Indien occidental, Paris : ORSTOM, 1976, (47), p. 153-177.
- ^ "Flore de La Réunion". Habiter La Réunion (in French). Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ ADUMITRESEI, LIDIA; STĂNESCU, IRINA (2009). "Theoretical Considerations upon the origin and nomenclature of the present rose cultivars". Journal of Plant Development. 16.
- ^ "History of Roses: Bourbon Roses" (PDF). American Rose Society.
- ^ C. Gabrié, « », Initiative Française pour les récifs coralliens (Ifrecor), 1998, p. 136
- ^ Ronald Fricke, Thierry Mulochau, Patrick Durville, Pascale Chabanet, Emmanuel Tessier et Yves Letourneur, « », Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde A, Neue Serie, vol. 2, 2009,
- ^ IGN Magazine no 54, p. 10
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d INSEE. "Données harmonisées des recensements de la population 1968–2015" (in French). Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ Bollée, Annegret (2015). "French on the Island of Bourbon (Réunion)". Journal of Language Contact. 8 (1): 91. doi:10.1163/19552629-00801005.
- ^ Oppenheimer, David B. (20 August 2008). "SSRN-Why France Needs to Collect Data on Racial Identity – In a French Way by David Oppenheimer". Papers.ssrn.com. SSRN 1236362. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ Holm, John A. (1989). Pidgins and Creoles: References survey. Cambridge University Press. p. 394. ISBN 0-521-35940-6.
- ^ "Réunion" (PDF). The Indian Diaspora. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 August 2010.
- ^ Clicanoo. "La Réunion Métisse".
- ^ Tarnus, Evelyne; Bourdon, Emmanuel (2006). "Anthropometric evaluations of body composition of undergraduate students at the University of La Réunion". Advances in Physiology Education. 30 (4): 248–253. doi:10.1152/advan.00069.2005. PMID 17108254.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Country Profile: Reunion (Department of Reunion)". Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. Retrieved 13 October 2007.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b "NRI" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 August 2010. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "Reunion | History, Location, Map, Population, & Facts".
- ^ Peoples of Africa: Réunion-Somalia. Marshall Cavendish. 2001. pp. 412–. ISBN 978-0-7614-7166-0.
- ^ "Ethnologue report (language code:rcf)". Ethnologue.com. Retrieved 16 April 2010.
- ^ "La France coloniale". casls.uoregon.edu. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "Au rythme de la musique créole à La Réunion". Île de la Réunion Tourisme (in French). Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "Le Curcuma". Île de la Réunion Tourisme (in French). Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ Marmiton-aufeminin. "Sauté de porc à l'ananas très facile". Marmiton (in French). Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "Le civet de Tangue, par Pépé do Fé". Clicanoo.re (in French). Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "The Grand Raid: 25 years of madness!". La Réunion. 12 October 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2018.
- ^ "Tableau économique régional de La Réunion, Institut national de la statistique et des études économiques, 2007" (PDF).
- ^ "La Villa Déramond Barre". Carte de La Réunion (in French). 23 March 2016. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- ^ "Réunion Island (@visitreunion) • Instagram photos and videos". www.instagram.com. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ^ "La Réunion Numérique".
- ^ CEROM. "Comptes économiques rapides de La Réunion en 2019" (PDF). Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ "Insel La Réunion Reisen & Urlaub buchen | Reiseveranstalter Elefant Tours". Elefant Tours.
- ^ "SEAS-OI, VIGISAT international success Réunion Island acquires an acquisition and processing system for high-resolution satellite images". Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Surveillance of maritime and terrestrial activities by radar". Retrieved 3 April 2016.
- ^ "Comptes économiques définitifs de La Réunion" (in French). INSEE. 2017. Retrieved 13 March 2018.
- ^ "Moins de chômage, plus d'inactivité". INSEE. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ Célimène, Fred; Legris, André (2011). De l'économie coloniale à l'économie mondialisée – Aspects multiples de la transition (XXe et XXIe siècles). Paris: Publibook. p. 179. ISBN 978-2-7483-7225-0.
- ^ "Quatre Réunionnais sur dix vivent sous le seuil de pauvreté" (in French). INSEE. 2017. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ^ Notes sur La Réunion. Industrie sucrière, commerce, agriculture, immigration », dans Revue maritime et coloniale, avril 1861, p. 350-362
- ^ "Consultation begins on Réunion tram project". International Railway Journal. 27 August 2019. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ^ "Éducation prioritaire".
- ^ "Site de l'Université de la Réunion 2020/2021".
- ^ "Guide tourisme et loisirs, guide pratique". guide-reunion.fr (in French). Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ "Saint-Philippe: Le drapeau Lo Mavéli adopté par la mairie". Zinfos 974, l'actualité de l'île de La Réunion (in French). Retrieved 8 July 2021.
Bibliography[]
- James Rogers and Luis Simón. The Status and Location of the Military Installations of the Member States of the European Union and Their Potential Role for the European Security and Defence Policy (ESDP). Brussels: European Parliament, 2009. 25 pp. Nice Bibliography
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Réunion. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Réunion. |
Government[]
- Réunion – The severe island – Official French website (in English)
- Departmental Council website
- Régional council website
General information[]
- Réunion
- Mascarene Islands
- Island countries
- Island countries of the Indian Ocean
- Dependent territories in Africa
- Islands of Overseas France
- Overseas departments of France
- East African countries
- Southeast African countries
- Volcanic islands
- Former colonies in Africa
- Former French colonies
- French colonisation in Africa
- French East India Company
- Outermost regions of the European Union
- Regions of France
- French-speaking countries and territories
- Pirate dens and locations
- States and territories established in 1946
- 1946 establishments in Africa
- 1946 establishments in the French colonial empire