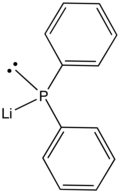
Lithium diphenylphosphide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium diphenylphosphanide | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10LiP | |
| Molar mass | 192.13 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | pale yellow solid |
| Solubility | ethers |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
Signal word
|
Danger |
| H302, H312, H314, H332, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lithium diphenylphosphide contains lithium and the organophosphorus anion with the formula (C6H5)2PLi. It is an air-sensitive solid that is used in the preparation of diphenylphosphino compounds. As an ether complex, the lithium salt is dark red.

Synthesis and reactions[]
The lithium, sodium, and potassium salts are prepared by reduction of chlorodiphenylphosphine,[2] triphenylphosphine,[3][4] or tetraphenyldiphosphine with alkali metals (M):
- (C6H5)2PCl + 2 M → (C6H5)2PM + MCl
- (C6H5)3P + 2 M → (C6H5)2PM + MC6H5
- (C6H5)4P2 + 2 M → 2 (C6H5)2PM
They can also be obtained by deprotonation of diphenylphosphine.
With water, the salts undergo hydrolysis to give diphenylphosphine:[4]
- (C6H5)2PLi + H2O → (C6H5)2PH + LiOH
With alkyl halides, the salts react to give tertiary phosphines:[5]
- (C6H5)2PM + RX → (C6H5)2PR + MX
When treated with metal halides, lithium diphenylphosphide gives transition metal phosphido complexes.
Structure[]
Although treated as salts, alkali diphenylphosphides are highly aggregated in solution. They adopt polymeric structures as solids.
Related compounds[]
- Sodium diphenylphosphide (CAS RN 4376-01-6)
- Potassium diphenylphosphide (CAS RN 15475-27-1)
References[]
- ^ Ruth A. Bartlett, Marilyn M. Olmstead, Philip P. Power (1986). "Structural Characterization of the Solvate Complexes of the Lithium Diorganophosphides [{Li(Et2O)PPh2}∞], [{Li(THF)2PPh2}∞], and [{Li(THF)P(C6H11)2}∞]". Inorg. Chem. 25: 1243–1247. doi:10.1021/ic00228a034.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ R. Goldsberry Kim Cohn (1972). "Diphenyl(trimethylsilyl)phosphine and Dimethyl(trimethylsilyl)‐phosphine". Inorganic Syntheses. 13: 26–32. doi:10.1002/9780470132449.ch7.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ George W. Luther, III, Gordon Beyerle (1977). "Lithium Diphenylphosphide and Diphenyl(Trimethylsilyl)Phosphine". Inorganic Syntheses. 17: 186–188. doi:10.1002/9780470132487.ch51.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ a b V. D. Bianco, S. Doronzo (1976). "Diphenylphosphine". Inorganic Syntheses. 16: 161–188. doi:10.1002/9780470132470.ch43.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ W. Levason, C. A. Mcauliffe (1976). "Cis‐2‐Diphenylarsinovinyldiphenylphosphine and 2‐Diphenylarsinoethyldiphenylphosphine". Inorganic Syntheses. 16: 188–192. doi:10.1002/9780470132470.ch50.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Lithium compounds
- Organolithium compounds
- Phenyl compounds
- Phosphines