Livingston County, Illinois
Livingston County | |
|---|---|
U.S. county | |
 | |
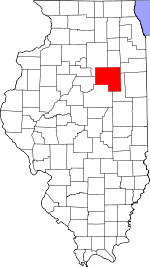 Location within the U.S. state of Illinois | |
 Illinois's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 40°53′N 88°34′W / 40.89°N 88.56°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1837 |
| Named for | Edward Livingston |
| Seat | Pontiac |
| Largest city | Pontiac |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,046 sq mi (2,710 km2) |
| • Land | 1,044 sq mi (2,700 km2) |
| • Water | 1.6 sq mi (4 km2) 0.2% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 38,950 |
| • Estimate (2018) | 35,761 |
| • Density | 37/sq mi (14/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 16th |
| Website | www |
Livingston County is a county located in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it has a population of 38,950.[1] Its county seat is Pontiac.[2] Livingston County comprises the Pontiac, IL Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is combined with the Bloomington–Normal metropolitan statistical area as the Bloomington-Pontiac, IL Combined Statistical Area.
History[]
Livingston was established on February 27, 1837. It was formed from parts of McLean, LaSalle, and Iroquois counties, and named after Edward Livingston,[3] a prominent politician who was mayor of New York City and represented New York in the United States House of Representatives and Louisiana in both houses of Congress. He later served as Andrew Jackson's Secretary of State and as Minister to France. Although he had no connections to Illinois, the General Assembly found him accomplished enough to name a county after him.
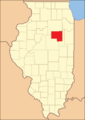
Livingston County at the time of its creation in 1837
Geography[]
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,046 square miles (2,710 km2), of which 1,044 square miles (2,700 km2) is land and 1.6 square miles (4.1 km2) (0.2%) is water.[4] It is the fourth-largest county in Illinois by land area.
Climate and weather[]
| Pontiac, Illinois | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In recent years, average temperatures in the county seat of Pontiac have ranged from a low of 14 °F (−10.0 °C) in January to a high of 85 °F (29.4 °C) in July, although a record low of −24 °F (−31.1 °C) was recorded in January 1927 and a record high of 108 °F (42.2 °C) was recorded in July 1936. Average monthly precipitation ranged from 1.44 inches (36.6 mm) in February to 4.11 inches (104.4 mm) in June.[5]
Major highways[]
 Interstate 55
Interstate 55 U.S. Highway 24
U.S. Highway 24 Illinois Route 17
Illinois Route 17 Illinois Route 23
Illinois Route 23 Illinois Route 47
Illinois Route 47 Illinois Route 116
Illinois Route 116
Adjacent counties[]
- LaSalle County - northwest
- Grundy County - north
- Kankakee County - northeast
- Ford County - southeast
- McLean County - southwest
- Woodford County - west
Demographics[]
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 759 | — | |
| 1850 | 1,552 | 104.5% | |
| 1860 | 11,637 | 649.8% | |
| 1870 | 31,471 | 170.4% | |
| 1880 | 38,450 | 22.2% | |
| 1890 | 38,455 | 0.0% | |
| 1900 | 42,035 | 9.3% | |
| 1910 | 40,465 | −3.7% | |
| 1920 | 39,070 | −3.4% | |
| 1930 | 39,092 | 0.1% | |
| 1940 | 38,838 | −0.6% | |
| 1950 | 37,809 | −2.6% | |
| 1960 | 40,341 | 6.7% | |
| 1970 | 40,690 | 0.9% | |
| 1980 | 41,381 | 1.7% | |
| 1990 | 39,301 | −5.0% | |
| 2000 | 39,678 | 1.0% | |
| 2010 | 38,950 | −1.8% | |
| 2018 (est.) | 35,761 | [6] | −8.2% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[7] 1790-1960[8] 1900-1990[9] 1990-2000[10] 2010-2013[1] | |||
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 38,950 people, 14,613 households, and 9,741 families residing in the county.[11] The population density was 37.3 inhabitants per square mile (14.4/km2). There were 15,895 housing units at an average density of 15.2 per square mile (5.9/km2).[4] The racial makeup of the county was 91.8% white, 4.9% black or African American, 0.5% Asian, 0.2% American Indian, 1.3% from other races, and 1.3% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 3.9% of the population.[11] In terms of ancestry, 36.6% were German, 17.2% were Irish, 11.2% were American, 10.7% were English, and 5.1% were Italian.[12]
Of the 14,613 households, 30.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.0% were married couples living together, 9.9% had a female householder with no husband present, 33.3% were non-families, and 28.6% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.43 and the average family size was 2.98. The median age was 40.8 years.[11]
The median income for a household in the county was $50,500 and the median income for a family was $60,933. Males had a median income of $44,639 versus $32,234 for females. The per capita income for the county was $23,259. About 9.1% of families and 11.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.4% of those under age 18 and 6.9% of those age 65 or over.[13]
Communities[]
Cities[]
- Fairbury
- Pontiac
- Streator
Town[]
Villages[]
Townships[]
Livingston County is divided into thirty townships:
- Amity
- Avoca
- Belle Prairie
- Broughton
- Charlotte
- Chatsworth
- Dwight
- Eppards Point
- Esmen
- Fayette
- Forrest
- Germanville
- Indian Grove
- Long Point
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- Newtown
- Odell
- Owego
- Pike
- Pleasant Ridge
- Pontiac
- Reading
- Rooks Creek
- Round Grove
- Saunemin
- Sullivan
- Sunbury
- Union
- Waldo
Unincorporated Communities[]
Government and infrastructure[]
The Illinois Department of Corrections operates two prisons in the county.
Pontiac Correctional Center is located in Pontiac.[14] Pontiac houses the male death row. Prior to the January 11, 2003 commutation of death row sentences, male death row inmates were housed in Pontiac, Menard, and Tamms correctional centers.[15] Dwight Correctional Center is within Nevada Township in an unincorporated area in the county.[16][17]
The Dwight Correctional Center is currently unoccupied and was closed in 2013.
Politics[]
Although it was solidly Democratic before 1856, Livingston has since always been a powerfully Republican county. The solitary Democrat to win a majority of the county's vote since the Civil War has been Franklin D. Roosevelt in his 1932 landslide triumph over Herbert Hoover. Apart from that and the 1912 election when Woodrow Wilson won against a mortally divided Republican Party, Livingston has always voted Republican since that party was founded in 1856. Since 1940, only Lyndon Johnson in his 1964 landslide victory over the conservative Barry Goldwater has won more than forty percent of the county's vote.
Notable residents[]
- Donald Attig, businessman and adventurer.
- Calistus Bruer, Illinois state representative and farmer[19]
- M. C. Eignus, Illinois state representative[20]
- Moira Harris, actress and wife of Gary Sinise.[21]
- William Harris, first President of the Illinois Senate.[22][23]
- Irene Hunt, Newbery Medal-winning author.
- Francis Townsend, physician and political activist whose advocacy for an old age revolving pension influenced the creation of the U.S. Social Security program.[24]
- Skottie Young, comic book artist known for the Oz series. He was born and raised in Fairbury.[25]
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ There were only 3,230 votes for the leading “other” candidate, Progressive Theodore Roosevelt, plus 152 for the Prohibition Party's Eugene Chafin, 71 for Socialist Eugene V. Debs, and 27 for Socialist Labor candidate Arthur Reimer.
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 188.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Monthly Averages for Pontiac, Illinois". The Weather Channel. Retrieved January 27, 2011.
- ^ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved November 6, 2019.
- ^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 6, 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2015.
- ^ "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2015.
- ^ "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 12, 2015.
- ^ "Pontiac Correctional Center." Illinois Department of Corrections. Retrieved on September 1, 2010.
- ^ "DOC Report Online Archived 2011-07-18 at the Wayback Machine." Illinois Department of Corrections. Retrieved on September 1, 2010.
- ^ "Dwight village, Illinois[permanent dead link]." U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on September 1, 2010.
- ^ "Dwight Correctional Center." Illinois Department of Corrections. Retrieved on September 1, 2001.
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org.
- ^ 'Illinois Blue Book 199-1950,' Biographical Sketch of Calistus Bruer, pg. 164-165
- ^ 'Official Directory of the Forty-Second General Assembly of Illinois-1901,' Talbot & Hamman, Springfield, Illinois: 1865, Biographical Sketch of M. C. Eignus, pg. 65
- ^ Rhoads, Mark (October 7, 2006). "Illinois Hall of Fame: Gary Sinese". Illinois Review. Dennis LaComb. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ 'William C. Harris-obituary,' Chicago Tribune, January 2, 2005
- ^ 'Illinois Blue Book 1975-1976,' Biographical Sketch of William C. Harris, pg. 146
- ^ "Townsend, Dr. Francis". Virginia Commonwealth University. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Kromphardt, Barb (April 26, 2011). "The Wonderful World of Young". Shaw Media (United States): . Princeton, Illinois. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
Further reading[]
- Illinois counties
- Livingston County, Illinois
- 1837 establishments in Illinois
- Populated places established in 1837


