Masuria
Masuria
Mazury | |
|---|---|
Region | |
 Sailing on Lake Niegocin | |
 Coat of arms | |
 Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District | |
| Country | Poland |
| Region | Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10,000 km2 (4,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 500,000 |
| • Density | 50/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
Masuria (Polish: ![]() Mazury (help·info), German: Masuren, Masurian: Mazurÿ) is a historical region in northern and northeastern Poland, famous for its 2,000 lakes.[1] Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (administrative area/province). Its biggest city, often regarded as its capital, is Ełk (Elk). The region covers a territory of some 10,000 km2 which is inhabited by approximately 500,000 people.
Mazury (help·info), German: Masuren, Masurian: Mazurÿ) is a historical region in northern and northeastern Poland, famous for its 2,000 lakes.[1] Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (administrative area/province). Its biggest city, often regarded as its capital, is Ełk (Elk). The region covers a territory of some 10,000 km2 which is inhabited by approximately 500,000 people.
History[]
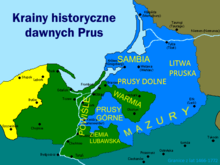
East Germanic tribes[]
The first known people in today's Mazuria were East Germanic tribes, such as the Sciri.[2]
Old Prussians[]
Before the 13th century, the territory was inhabited by the Old Prussians also called Baltic Prussians, a Baltic ethnic group that lived in Prussia (the area of the southeastern coastal region of the Baltic Sea neighbouring of the Baltic Sea around the Vistula Lagoon and the Curonian Lagoon). The territory later called Masuria was then known as Galindia and was probably a peripheral, deeply forested and lightly populated area. Its inhabitants spoke a language now known as Old Prussian and had their own mythology. Although a 19th-century German political entity bore their name, they were not Germans. They were converted to Roman Catholicism in the 13th century, after conquest by the Knights of the Teutonic Order.
Estimates range from about 170,000 to 220,000 Old Prussians living in the whole of Prussia around 1200.[3] The wilderness was their natural barrier against attack by would-be invaders. During the Northern Crusades of the early 13th century, the Old Prussians used this wide forest as a brod zone of defence. They did so again against the Knights of the Teutonic Order, who had been invited to Poland by Konrad I of Masovia in 1226.[4] The order's goal was to convert the native population to Christianity and baptise it by force if necessary. In the subsequent conquest, which lasted over 50 years, the original population was partly exterminated, particularly during the major Prussian rebellion of 1261–83. But several Prussian noble families also accommodated to the Knights in order to hold their power and possessions.[4]
Teutonic Order[]

After the Order's acquisition of Prussia, Poles (or more specifically, Mazurs, that is inhabitants of the adjacent region of Mazovia) began to settle in the southeastern part of the conquered region. German, Dutch, Flemish, and Danish[5] colonists entered the area afterward, from the northwest. The number of Polish settlers grew significantly again in the beginning of the 15th century, especially after the first and the second treaties of Thorn, in 1411 and 1466 respectively, following the Thirteen Years' War and the final defeat of the order.[4] The Battle of Grunwald took place in western Masuria in 1410. In 1440 the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation was founded. In 1454 upon the Confederation's request King Casimir IV of Poland signed the act of incorporation of the entire region including Masuria to Poland and after the subsequent Thirteen Years' War Masuria came under the suzerainty of the Polish Crown, still ruled by the grand master of the Teutonic Order. Later assimilation of the German settlers as well as the Polish immigrants and native Prussian inhabitants created the new Prussian identity, although the subregional difference between the German- and Polish-speaking part remained.
Ducal Prussia[]

The secularization of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the conversion of Albert of Prussia to Lutheranism in 1525 brought Prussia including the area later called Masuria to Protestantism. The Knights untied their bonds to the Catholic Church and became land owning nobleman and the Duchy of Prussia was established as a vassal state of Poland. The Polish language predominated due to the many immigrants from Mazovia, who additionally settled the southern parts of Ducal Prussia, till then virgin part of (later Masuria) in the 16th century. While the southern countryside was inhabited by these - meanwhile Protestant - Polish-speakers, who took refuge, the very small southern towns constituted German mixed with Polish-speaking population. The ancient Old Prussian language survived in parts of the countryside in the northern and central parts of Ducal Prussia until the early 18th century. At that time they proved to be assimilated in the mass of German speaking villagers and farmers.[6] Areas that had many Polish language speakers were known as the Polish Departments.[7]

Masuria became one of the leading centers of Polish Protestantism. In the mid-16th century Lyck (Ełk) and Angerburg (Węgorzewo) became significant Polish printing centers.[8] A renowned Polish high school, which attracted Polish students from different regions, was founded in Ełk in eastern Masuria in 1546 by Hieronim Malecki, Polish translator and publisher, who contributed to the creation of the standards and patterns of the Polish literary language. The westernmost part of Masuria, the Osterode (Ostróda) county, in 1633 came under the administration of one of the last dukes of the Piast dynasty, John Christian of Brieg.
In 1656, during the Battle of Prostki, the forces of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, including 2,000 Tatar raiders, beat the allied Swedish and Brandenburg army capturing Bogusław Radziwiłł. The war resulted in the destruction of most towns, 249 villages and settlements, and 37 churches were destroyed. Over 50% of the population of Masuria died within the years 1656–1657, 23,000 were killed, another 80,000 died of diseases and famine, 3,400 people were enslaved and deported to Russia.[9][10] From 1709–1711, in all of Ducal Prussia between 200,000 and 245,000 out of 600,000 inhabitants died from the Black Death. In Masuria the death toll varied regionally; while 6,789 people died in the district of Rhein (Ryn) only 677 died in Seehesten (Szestno). In Lötzen (Giżycko) 800 out of 919 people died.[11][12] Losses in population were compensated by migration of Protestant settlers or refugees from Scotland, Salzburg (expulsion of Protestants 1731), France (Huguenot refugees after the Edict of Fontainebleau in 1685), and especially from the counterreformed Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, including Polish brethren expelled from Poland in 1657. The last group of refugees to emigrate to Masuria were the Russian Philipons (as 'Old Believers' opposed to the State Church) in 1830, when King Frederick William III of Prussia granted them asylum.[13]
After the death of Albert Frederick, Duke of Prussia in 1618, his son-in-law John Sigismund, Margrave of Brandenburg, inherited the duchy (including Masuria), combining the two territories under a single dynasty and forming Brandenburg-Prussia. The Treaty of Wehlau revoked the sovereignty of the King of Poland in 1657.
Kingdom of Prussia[]
The region became part of the Kingdom of Prussia with the coronation of King Frederick I of Prussia in 1701 in Königsberg. Masuria became part of a newly created administrative province of East Prussia upon its creation in 1773. The name Masuria began to be used officially after new administrative reforms in Prussia after 1818.[15] Masurians referred to themselves during that period as "Polish Prussians" or as "Staroprusaki" (Old Prussians)[16] During the Napoleonic Wars and Polish national liberation struggles, in 1807, several towns of northern and eastern Masuria were taken over by Polish troops under the command of generals Jan Henryk Dąbrowski and Józef Zajączek. Some Masurians showed considerable support for the Polish uprising in 1831, and maintained many contacts with Russian-held areas of Poland beyond the border of Prussia, the areas being connected by common culture and language; before the uprising people visited each other's country fairs and much trade took place, with smuggling also widespread.[16] Nevertheless, their Lutheran belief and a traditional adherence to the Prussian royal family kept Masurians and Poles separated. Some early writers about Masurians - like Max Toeppen - postulated Masurians in general as mediators between German and Slav cultures.[16] Germanisation policies in Masuria included various strategies, first and foremost they included attempts to propagate the German language and to eradicate the Polish (Masurian) language as much as possible; German became the obligatory language in schools from 1834 on.[16] The Lutheran churches and their vicars principally exerted their spiritual care in Masurian as concerned to Masurian mother tongue parishioners.
Ethno-linguistic structure[]
Mother tongue of the inhabitants of Masuria, by county, during the first half of the 19th century:
| County (German name) | Year | Polish-speakers | % | German-speakers | % | Lithuanian-speakers | % | Total population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pisz (Johannisburg) | 1825 | 28,552 | 93% | 2,146 | 7% | 0 | 0% | 30,698 |
| Nidzica (Neidenburg) | 1825 | 27,467 | 93% | 2,149 | 7% | 1 | 0% | 29,617 |
| Szczytno (Ortelsburg) | 1825 | 34,928 | 92% | 3,100 | 8% | 0 | 0% | 38,028 |
| Ełk (Lyck) | 1832 | 29,246 | 90% | 3,413 | 10% | 4 | 0% | 32,663 |
| Giżycko (Lötzen) | 1832 | 20,434 | 89% | 2,528 | 11% | 25 | 0% | 22,987 |
| Mrągowo (Sensburg) | 1825 | 22,391 | 86% | 3,769 | 14% | 5 | 0% | 26,165 |
| Olecko (Oletzko) | 1832 | 23,302 | 84% | 4,328 | 16% | 22 | 0% | 27,652 |
| Ostróda (Osterode) | 1828 | 23,577 | 72% | 9,268 | 28% | 0 | 0% | 32,845 |
| Węgorzewo (Angerburg) | 1825 | 12,535 | 52% | 11,756 | 48% | 60 | 0% | 24,351 |
| Gołdap (Goldap) | 1825 | 3,940 | 16% | 17,412 | 70% | 3,559 | 14% | 24,911 |
| Kętrzyn (Rastenburg) | 1831 | 2,786 | 9% | 28,715 | 91% | 0 | 0% | 31,501 |
| TOTAL | 1825-32 | 229,158 | 71% | 88,584 | 28% | 3,676 | 1% | 321,418 |
German Empire[]

After the Unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the last lessons that made use of the Polish language were removed from schools in 1872. Masurians who expressed sympathy for Poland were deemed "national traitors" by German public opinion, especially after 1918 when the new Polish republic laid claims to, up to then German, areas inhabited by Polish speakers.[16] According to Stefan Berger, after 1871 the Masurians in the German Empire were seen in a view that while acknowledging their "objective" Polishness (in terms of culture and language) they felt "subjectively" German and thus should be tightly integrated into the German nation-state; Berger concludes that such arguments of German nationalists were aimed at integrating Masurian (and Silesian) territory firmly into the German Reich.[16]
During the period of the German Empire, the Germanisation policies in Masuria became more widespread; children using Polish in playgrounds and classrooms were widely punished by corporal punishment, and authorities tried to appoint Protestant pastors who would use only German instead of bilinguality and this resulted in protests of local parishioners.[16] According to Jerzy Mazurek, the native Polish-speaking population, like in other areas with Polish inhabitants, faced discrimination of Polish language activities from Germanised local administration. In this climate a first resistance defending the rights of rural population was organized, according to Jerzy Mazurek usually by some teachers engaged in publishing Polish language newspapers.[20]

Despite anti-Polish policies, such Polish language newspapers as the Pruski Przyjaciel Ludu (Prussian Friend of People) or the Kalendarz Królewsko-Pruski Ewangelicki (Royal Prussian Evangelical Calendar) or bilingual journals like the Oletzkoer Kreisblatt - Tygodnik Obwodu Oleckiego continued to be published in Masuria. In contrast to the Prussian-oriented periodicals, in the late 19th century such newspapers as Przyjaciel Ludu Łecki and Mazur were founded by members of the Warsaw-based Komitet Centralny dla Śląska, Kaszub i Mazur (Central Committee for Silesia, Kashubia and Masuria), influenced by Polish politicians like Antoni Osuchowski or Juliusz Bursche, to strengthen the Polish identity in Masuria.[21] The Gazeta Ludowa (The Folk's Newspaper) was published in Lyck in 1896–1902, with 2,500 copies in 1897 and the Mazur in Ortelsburg after 1906 with 500 copies in 1908 and 2,000 prior to World War I.[22]

Polish activists started to regard Masurians as "Polish brothers" after Wojciech Kętrzyński had published his pamphlet O Mazurach in 1872[23] and Polish activists engaged in active self-help against repressions by the German state[24] Kętrzyński fought against attempts to Germanise Masuria[25] The attempts to create a Masurian Polish national consciousness, largely originating from nationalist circles of Provinz Posen, however faced the resistance of the Masurians, who, despite having similar folk traditions and linguistics to Poles, regarded themselves as Prussians and later Germans.[26][27] and were loyal to the Hohenzollern dynasty, the Prussian and German state.[28][29][30][31] After World War I the editor of the Polish language Mazur described the Masurians as "not nationally conscious, on the contrary, the most loyal subjects of the Prussian king".[32] However, a minority of Masurians did exist who expressed Polish identity[24] After 1871 there appeared resistance among the Masurians towards Germanisation efforts, the so-called Gromadki movement was formed which supported use of Polish language and came into conflict with German authorities; while most of its members viewed themselves as loyal to the Prussian state, a part of them joined the Pro-Polish faction of Masurians.[24] The programme of Germanisation started to unite and mobilise Polish people in Polish-inhabited territories held by Germany including Masuria[33] A Polish-oriented party, the Mazurska Partia Ludowa ("People's Party of Masuria"), was founded in 1897. The eastern areas of the German Empire were systematically Germanised with changing of names and public signs, and the German state fostered cultural imperialism, in addition to giving financial and other support to German farmers, officials, and teachers to settle in the east.[34]
The German authorities in their efforts of Germanisation tried to claim the Masurian language separate from Polish by classifying it as a non-Slavic[35] language different from Polish one, this was reflected in official census[36] Thus the Masurian population in 1890, 143,397 was reported to the Prussian census as having German as their language (either primary or secondary), 152,186 Polish and 94,961 Masurian. In 1910, the German language was reported by German authorities as used by 197,060, Polish by 30,121 and Masurian by 171,413. Roman Catholics generally opted for the Polish language, Protestants appreciated Masurian. In 1925, German authorities reported 40,869 inhabitants as having declared Masurian as their native tongue and 2,297 as Polish. However, the last result may have been a result of politics at the time, the desire of the population to be German after the trauma evoked by 1920 plebiscite. So the province could be presented as - so called - 'purely German'; in reality the Masurian dialect was still in use among bilinguals.[35]
Throughout industrialisation in the late 19th century about 10 percent of the Masurian populace emigrated to the Ruhr Area, where about 180,000 Masurians lived in 1914. Wattenscheid, Wanne and Gelsenkirchen were the centers of Masurian emigration and Gelsenkirchen-Schalke was even called Klein (little)-Ortelsburg before 1914. Masurian newspapers like the Przyjaciel Ewangeliczny and the Gazeta Polska dla Ludu staropruskiego w Westfalii i na Mazurach but also the German language Altpreußische Zeitung were published.[37]

During World War I, the Battle of Tannenberg and the First and Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes between Imperial Germany and the Russian Empire took place within the borders of Masuria in 1914. After the war, the League of Nations held the East Prussian plebiscite on 11 July 1920 to determine if the people of the southern districts of East Prussia wanted to remain within East Prussia or to join the Second Polish Republic. The German side terrorised the local population before the plebiscite using violence, Polish organisations and activists were harassed by German militias, and those actions included attacks and some supposed murders of Polish activists;[38] Masurs who supported voting for Poland were singled out and subjected to terror and repressions.[39]
Names of those Masurs supporting the Polish side were published in German newspapers, and their photos presented in German shops; afterwards regular hunts were organised after them by German militias terrorizing the Polish minded population.[40][41][42] At least 3,000 Warmian and Masurian activists who were engaged for Polish side decided to flee the region.[43] At the same time also local police officials were engaged in active surveillance of the Polish minority and attacks against Polish activists.[44] Before the plebiscite Poles started to flee the region to escape the German harassment and Germanisation policies.[45]
The results determined that 99.32% of the voters in Masuria proper chose to remain with East Prussia. Notwithstanding national German agitation and intimidation, these results reflect that majority Masurians had adopted a German national identity next to a regional identity. Their traditional religious belief in Lutheranism kept them away from Polish national consciousness, dominated by Roman Catholicism. In fact almost only Catholics voted for Poland in the plebiscite. They were to be found as a majority in the villages around the capital Allenstein, the same were Polish cultural activism got hold between 1919 and 1932.[46] However, the contemporary Polish ethnographer Adam Chętnik accused the German authorities of abuses and falsifications during the plebiscite.[47] Moreover, the plebiscite took place during the time when Polish–Soviet War threatened to erase the Polish state. As a result, even many Poles of the region voted for Germany out of fear that if the area was allocated to Poland it would fall under Soviet rule.[48] After the plebiscite in German areas of Masuria attacks on Polish population commenced by German mobs, and Polish priests and politicians were driven from their homes[49] After the plebiscite at least 10,000 Poles had to flee German held Masuria to Poland.[50]
Polish Masuria — the Działdowo county[]

The region of Działdowo (Soldau), where according to the official German census of 1910 ethnic Germans formed a minority of 37.3%,[51] was excluded from the plebiscite and became part of Poland. This was reasoned with placing the railway connection between Warsaw and Danzig (Gdańsk), of vital importance to Poland as it connected central Poland with its recently obtained seacoast, completely under Polish sovereignty. Działdowo itself counted about 24,000 people of which 18,000 were Masurians.[52]
According to the municipal administration of Rybno, after World War I Poles in Działdowo believed that they will be quickly joined with Poland,[53] they organised secret gatherings during which the issue of rejoining Polish state with help of Polish military was discussed.[53] According to the Rybno administration, most active Poles in that subregion included Jóżwiakowscy, Wojnowscy, Grzeszczowscy families working under the guidance of politician Leon Wojnowski who protested German attempts to remain Działdowo a part of Germany after the war; other local pro-Polish activists were Alfred Wellenger, Paczyński, Tadeusz Bogdański, Jóźwiakowski.[53][54][55]

The historian Andreas Kossert describes that the incorporation happened despite protests of the local populace, the municipal authorities and the German Government,[56] According to Kossert, 6,000 inhabitants of the region soon left the area.[57]
In 1920 the candidate of the German Party in Poland, Ernst Barczewski, was elected to the Sejm with 74.6 percent of votes and to the Polish Senate with 34.6% of votes for the Bloc of National Minorities in 1928.[58] During the Polish–Soviet War Działdowo was briefly occupied by the Red Army regarded as liberator from the Polish authority by the local German population, which hoisted the German flag,[59][60] but it was soon recovered by the Polish Army.
During the interwar period many native inhabitants of Działdowo subregion left and migrated to Germany.
With the start of the German war against Poland on 1 September 1939, the German minority in the parts of Masuria attached to Poland after World War I, as Działdowo but also large parts of former Western-Prussia, organised themselves in paramilitary formations called Selbstschutz (selfdefense) and begun to engage in massacres of local Polish population; Poles were imprisoned, tortured and murdered[61][62] while Masurians were sometimes forcefully placed on Volksliste[63][64] From now on conscripted Masurians had to serve without exception in the German army invading Poland, and Russia two years later on.
The Soldau concentration camp near to Działdowo was established in winter 1939, where 13,000 people were murdered by the Nazi German state during the war. Notable victims included the Polish bishops Antoni Julian Nowowiejski and Leon Wetmański, as well as the nun Mieczysława Kowalska. Additionally, almost 1,900 mentally ill patients from East Prussia and annexed areas of Poland were murdered there as well, in what was known as Action T4.[65] Polish resistance in Masuria was organised by Paweł Nowakowski "Leśnik" commander of the Home Army's Działdowo district.[66]
Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany[]

Masuria was the only region of Germany directly affected by the battles of World War I. Damaged towns and villages were reconstructed with the aid of several twin towns from western Germany like Cologne to Neidenburg, Frankfurt to Lötzen and even Vienna to Ortelsburg. The architecture still is surprisingly distinct, being of modern Central European character. However Masuria was still largely agrarian-oriented and suffered from the economic decline after World War I, additionally badly affected by the creation of the Polish Corridor, which raised freight costs to the traditional markets in Germany.[67] The later implemented Osthilfe had only a minor influence on Masuria as it privileged larger estates, while Masurian farms were generally small.[68]
The interwar period was characterised by ongoing Germanisation policies, intensified especially under the Nazis.[69]
In the 1920s Masuria remained a heartland of conservatism with the German National People's Party as strongest party.[70][71][72] The Nazi Party, having absorbed the conservative one, became the strongest party already in the Masurian constituencies in the elections of 1930[72] and received its best results in the poorest areas of Masuria with the highest rate of Polish speakers.[73] Especially in the elections of 1932 and 1933 they reached up to 81 percent of votes in the district of Neidenburg and 80 percent in the district of Lyck.[74][75] The Nazis used the economic crisis, which had significant effects in far-off Masuria, as well as traditional anti-Polish sentiments[76] while at the same time Nazi political rallies were organised in the Masurian dialect during the campaigning.[74][77]
In 1938, the Nazi government (1933–1945) changed thousands of still existing toponyms (especially names of cities and villages) of Old Prussian, Lithuanian and Polish origin to newly created German names; six thousand, that meant about 50% of the existing names were changed, but the countryside population stuck to their traditional names. Within six years a new renaming would take place after Poland annexed Masuria in 1945.[78]

According to German author Andreas Kossert, Polish parties were financed and aided by the Polish government in Warsaw, and remained splintergroups without any political influence,[79] e.g. in the 1932 elections the Polish Party received 147 votes in Masuria proper.[80] According to Wojciech Wrzesiński (1963), the Polish organisations in Masuria had decided to lower their activity in order to escape acts of terror performed against Polish minority activists and organisations by Nazi activists.[81] Jerzy Lanc, a teacher and Polish national who had moved to Masuria in 1931 to establish a Polish school in Piassutten (Piasutno), died in his home of carbon monoxide poisoning,[82] most likely murdered by local German nationalists.[83][84][85][86][87]
Before the war the Nazi German state sent undercover operatives to spy on Polish organisations and created lists of people that were to be executed or sent to concentration camps.[88] This mainly took place in Silesia and only according to the few catholic schools in Masuria. Information was gathered on who sent children to Polish schools, bought Polish press or took part in Polish ceremonies and organised repressions against these people were executed by Nazi militias.[88] Polish schools, printing presses and headquarters of Polish institutions were attacked as well as homes of the most active Poles; shops owned by Poles were vandalised or demolished.[88] Polish masses were dispersed, and Polish teachers were intimidated as members of the SS gathered under their locals performing songs like "Wenn das Polenblut vom Messer spritzt, dann geht's noch mal so gut" ("When Polish blood spurts from the knife, everything will be better").[88]

The anti-Polish activities intensified in 1939.[88] Those Poles were most active in politics were evicted from their own homes, while Polish newspapers and cultural houses were closed down in the region.[88] Polish masses were banned between June and July in Warmia and Mazury.[88]
In the final moments of August 1939 all remains of political and cultural life of Polish minority was eradicated by the Nazis, with imprisonment of Polish activists and liquidation of Polish institutions.[88] Seweryn Pieniężny, the chief editor of "Gazeta Olsztyńska", who opposed Germanisation of Masuria, was interned. Others included Juliusz Malewski (director of Bank Ludowy of Olsztyn), Stefan Różycki, Leon Włodarczyk (activist of Polonia Warmińsko-Mazurska).[88]
Directors of Polish schools and teachers were imprisoned, as was the staff of Polish pre-schools in the Masuria region.[88] They were often forced to destroy Polish signs, emblems and symbols of Polish institutions.[88]
World War II[]

The Nazis believed that in future, the Masurians, as a separate non-German entity, would 'naturally' disappear in the end, while those who would cling to their "foreigness" as one Nazi report mentioned, would be deported.[89] Local Jews were considered by the Nazis to be subhuman and were to be exterminated. The Nazi authorities also executed Polish activists in Masuria and those who remained alive were sent to concentration camps.[90] In August 1943 the Uderzeniowe Bataliony Kadrowe attacked the village of Mittenheide (Turośl) in southern Masuria[91]
In 1943 "Związek Mazurski" was reactivated secretly by Masurian activists of the Polish Underground State in Warsaw and led by Karol Małłek.[92] Związek Mazurski opposed Nazi Germany and asked Polish authorities during the war to liquidate German large landowners after the victory over Nazi Germany to help in agricultural reform and settlement of Masurian population, Masurian iconoclasts opposed to Nazi Germany requested to remove German heritage sites "regardless of their cultural value".[93] Additionally a Masurian Institute was founded by Masurian activists in Radość near Warsaw in 1943[94]
In the final stages of World War II, Masuria was partially devastated by the retreating German and advancing Soviet armies during the Vistula-Oder Offensive. The region came under Polish rule at the war's end in the Potsdam Conference. Most of the population fled to Germany or was killed during or after the war, while those which stayed were subject to a "nationality verification", organised by the communist government of Poland. As a result, the number of native Masurians remaining in Masuria was initially relatively high, while most of the population was subsequently expelled. Poles from central Poland and the Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union as well as Ukrainians expelled from southern Poland throughout the Operation Vistula, were resettled in Masuria.[95]
Masuria after World War II[]

According to the Masurian Institute, the Masurian members of resistance against Nazi Germany who survived the war became active in 1945 in the region, working in Olsztyn in cooperation with new state authorities in administration, education and cultural affairs.[94] Historic Polish names for most of towns of Masuria were restored, but for some places new names were determined even if there were historic Polish names.
German author Andreas Kossert describes the post-war process of "national verification" as based on an ethnic racism which categorised the local populace according to their alleged ethnic background.[96] A Polish-sounding last name or a Polish-speaking ancestor was sufficient to be regarded as "autochthonous" Polish.[97] In October 1946 37,736 persons were "verified" as Polish citizens while 30,804 remained "unverified". A center of such "unverified" Masurians was the district of Mrągowo, where in early 1946 out of 28,280 persons, 20,580 were "unverified", while in October, 16,385 still refused to adopt Polish citizenship.[98] However even those who complied with the often used pressure by Polish authorities were in fact treated as Germans because of their Lutheran faith and their often rudimentary knowledge of Polish. Names were "Polonised" and the usage of the German language in public was forbidden. In the late 1940s the pressure to sign the "verification documents" grew and in February 1949 the former chief of the stalinist secret Police (UB) of Łódź, Mieczysław Moczar, started the "Great verification" campaign. Many unverified Masurians were imprisoned and accused of pro-Nazi or pro-American propaganda, even former pro-Polish activists and inmates of Nazi concentration camps were jailed and tortured. After the end of this campaign in the district of Mrągowo (Sensburg) only 166 Masurians were still "unverified".[99]
In 1950 1,600 Masurians left the country and in 1951, 35,000 people from Masuria and Warmia managed to obtain a declaration of their German nationality by the embassies of the United States and Great Britain in Warsaw. Sixty-three percent of the Masurians in the district of Mrągowo (Sensburg) received such a document.[100] In December 1956 Masurian pro-Polish activists signed a memorandum to the Communist Party leadership:
"The history of the people of Warmia and Masuria is full of tragedy and suffering. Injustice, hardship and pain often pressed on the shoulders of Warmians and Masurians... Dislike, injustice and violence surrounds us...They (Warmians and Masurians) demand respect for their differentness, grown in the course of seven centuries and for freedom to maintain their traditions".[101]

Soon after the political reforms of 1956, Masurians were given the opportunity to join their families in West Germany. The majority (over 100 thousand) gradually left and after the improvement of Germano-Polish relations by the German Ostpolitik of the 1970s, 55,227 persons from Warmia and Masuria moved to West Germany in between 1971 and 1988,[102] today approximately between 5,000 and 6,000 Masurians still live in the area, about 50 percent of them members of the German minority in Poland, the remaining half is ethnic Polish.[31] As the Polish journalist Andrzej K. Wróblewski stated, the Polish post-war policy succeeded in what the Prussian state never managed: the creation of a German national consciousness among the Masurians.[102]
Most of the originally Protestant churches in Masuria are now used by the Polish Roman Catholic Church as the number of Lutherans in Masuria declined from 68,500 in 1950 to 21,174 in 1961 and further to 3,536 in 1981. Sometimes, like on 23 September 1979 in the village of Spychowo (Puppen), the Lutheran Parish was even forcefully driven out of their church while liturgy was held.[102][103]
Modern Masuria[]
In modern Masuria the native population has virtually disappeared.[31] Masuria was incorporated into the voivodeship system of administration in 1945. In 1999 Masuria was constituted with neighbouring Warmia as a single administrative province through the creation of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship.[104]
Today, numerous summer music festivals take place in Masuria, including the largest reggae festival in Poland in Ostróda,[105] the largest country music festival in Poland in Mrągowo,[106] and one of Poland's largest hip hop music festivals in Giżycko and Ełk.
The Masurian Szczytno-Szymany International Airport gained international attention as press reports alleged the airport to be a so-called "black site" involved in the CIA's network of extraordinary renditions.[107]
Landscape[]

Masuria and the Masurian Lake District are known in Polish as Kraina Tysiąca Jezior and in German as Land der Tausend Seen, meaning "land of a thousand lakes." These lakes were ground out of the land by glaciers during the Pleistocene ice age around 14,000 - 15,000 years ago, when ice covered northeastern Europe. From that period originates the horn of a reindeer found in the vicinity of Giżycko.[108] By 10,000 BC this ice started to melt. Great geological changes took place and even in the last 500 years the maps showing the lagoons and peninsulas on the Baltic Sea have greatly altered in appearance. More than in other parts of northern Poland, such as from Pomerania (from the River Oder to the River Vistula), this continuous stretch of lakes is popular among tourists. The terrain is rather hilly, with connecting lakes, rivers and streams. Forests account for about 30% of the area.[109][110] The northern part of Masuria is covered mostly by the broadleaved forest, while the southern part is dominated by pine and mixed forests.[111][112]
Two largest lakes of Poland, Śniardwy and Mamry, are located in Masuria.
Main towns[]
Notable people from Masuria[]
- Richard Altmann (1852–1900), pathologist
- Leszek Błażyński (1949–1992), boxer
- Kurt Blumenfeld (1884–1963), politician
- Abraham Calovius (1612–1686), Lutheran theologian
- Roman Czepe (born 1956), politician
- Lucas David (1503–1583), historian
- Ferdinand Gregorovius (1821–1891), historian
- Lothar Gall (born 1936) historian
- Gustaw Gizewiusz (1810–1848), Protestant pastor, supporter of Polish language teaching and resistance against Germanisation
- Georg Andreas Helwing (1666–1748), botanist
- Paul Hensel (1867–1944), politician
- Andreas Hillgruber (1925–1989), historian
- Wojciech Kętrzyński (1838–1918), activist and historian
- Hans Hellmut Kirst (1914–1989), author
- Georg Klebs (1857–1913), botanist
- Walter Kollo (1878–1940), composer
- Horst Kopkow (1910–1996), spy
- Udo Lattek (1935-2015), football coach
- Siegfried Lenz (1926-2014), author
- Wolf Lepenies (born 1941), political scientist
- Johannes von Leysen (1310–1388), founder and first mayor of Allenstein
- Albert Lieven (1906–1971), actor
- Krzysztof Celestyn Mrongovius (1764–1855), Protestant pastor and philosopher
- Celestyn Myślenta (1588–1653), Lutheran theologian and rector of the University of Königsberg
- Rodolphe Radau (1835–1911), astronomer
- Karl Bogislaus Reichert (1811–1883), anatomist
- Nicholas von Renys (1360-1411), knight
- Fritz Richard Schaudinn (1871–1906), zoologist
- Paweł Sobolewski (born 1979), footballer
- Helmuth Stieff (1901–1944), general
- Bethel Henry Strousberg (1823–1884), industrialist
- Arno Surminski (born 1934), writer
- Kurt Symanzik (1923–1983), physicist
- August Trunz (1875–1963), founder of the Prussica-Sammlung Trunz
- Ernst Wiechert (1887–1950), poet and writer
- Wilhelm Wien (1864–1928), physicist, Nobel Prize winner
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ It was a finalist in the Internet-based poll New7Wonders of Nature
- ^ Reinhard Pohanka (2014). Die Völkerwanderung (in German). marixverlag.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Ostpreussen, page 28
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Teutonic Order - religious order". Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Ivanescu, Danut (19 September 2012). "WORLD, COME TO MY HOME!: 0335 POLAND (Warmia-Masuria) - Land of a thousand lakes". Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ "What language did East Prussians speak? - Antimoon Forum". www.antimoon.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 81
- ^ Erwin Kruk, Warmia i Mazury, Wrocław 2003, p. 62 (in Polish)
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 74
- ^ Sławomir Augusiewicz, Prostki 1656, Bellona Publishing, Warsaw 2001. ISBN 978-83-11-09323-2
^ Jacek Płosiński, Potop szwedzki na Podlasiu 1655-1657, Inforteditions Publishing, 2006. ISBN 83-89943-07-7 - ^ Kossert, Andreas: Ostpreussen, p. 96
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 85
- ^ Lesser, Gabriele. "Begegnungen am grünen Fluss". Die Tageszeitung (in German). Archived from the original on 2009-10-02. Retrieved 2009-10-04.
- ^ Christofer Herrmann: Warmia i Mazury : przewodnik po zabytkach sztuki. Bartąg: Wydawnictwo Artes, 2008. ISBN 978-83-61049-24-1. p. 36
- ^ "The history of Olsztyn - zobacz The history of Olsztyn". visit.olsztyn.eu. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Wang, Q. Edward; Fillafer, Franz L. (2007). The many faces of Clio: cross-cultural approaches to historiography. Berghahn Books. p. 375. ISBN 9781845452704. Retrieved 31 January 2012.
- ^ von Haxthausen, August (1839). Die ländliche verfassung in den einzelnen provinzen der Preussischen Monarchie (in German). Königsberg: Gebrüder Borntraeger Verlagsbuchhandlung. pp. 78–81.
- ^ Jasiński, Grzegorz (2009). "Statystyki językowe powiatów mazurskich z pierwszej połowy XIX wieku (do 1862 roku)" (PDF). Komunikaty Mazursko-Warmińskie (in Polish). 1: 97–130 – via BazHum.
- ^ Belzyt, Leszek (1996). "Zur Frage des nationalen Bewußtseins der Masuren im 19. und 20. Jahrhundert (auf der Basis statistischer Angaben)". Zeitschrift für Ostmitteleuropa-Forschung (in German). Bd. 45, Nr. 1: 35–71. Archived from the original on 2019-10-03. Retrieved 2019-10-03 – via zfo-online.
- ^ Kraj a emigracja: ruch ludowy wobec wychodźstwa chłopskiego do krajów Ameryki Łacińskiej (do 1939 roku) Jerzy Mazurek, page 281, Biblioteka Iberyjska, 2006
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 209
- ^ Kossert, Andreas (2006). Masuren, Ostpreussens vergessener Süden (in German). Pantheon. pp. 210, 211. ISBN 3-570-55006-0.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, pp. 205ff.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Wang, Q. Edward; Fillafer, Franz L. (2007). The many faces of Clio: cross-cultural approaches to historiography. Berghahn Books. p. 377. ISBN 9781845452704. Retrieved 31 January 2012.
- ^ National cultures at the grass-root level Antonina Kłoskowska, page 228, Central European University Press, 2001
- ^ Curp, T. David (2006). A clean sweep? The politics of ethnic cleansing in Western Poland, 1945-1960. University of Rochester Press. p. 16. ISBN 1-58046-238-3.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren. Ostpreussens vergessener Süden, p. 212 Berlin 2006, ISBN 3-570-55006-0: "Sie wollten Preussen sein mit polnischer Muttersprache, wie sie es seit Jahrhunderten gewesen waren"
- ^ Geary, Dick (1989). Labour and the Socialist movement in Europe before 1914. Berg publ. p. 7. ISBN 0-85496-200-X. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
- ^ Lucassen, Leo (2005). The immigrant threat: the integration of old and new migrants in western Europe since 1850. p. 222. ISBN 0-252-03046-X. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
- ^ Wang, Q. Edward; Fillafer, Franz L. (2007). The many faces of Clio. Berghahn books. p. 378. ISBN 978-1-84545-270-4. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Ethnic groups and population changes in 20th century Central-Eastern Europe: history, data, analysis. Piotr Eberhardt, Jan Owsinski. 2003. ISBN 978-0-7656-0665-5. Retrieved 2009-10-08.
- ^ Blanke, Richard (2001). Polish-speaking Germans? Language and national identity among the Masurians since 1871. Böhlau. p. 143. ISBN 3-412-12000-6.
- ^ A history of Eastern Europe: crisis and change Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries, page 293, Taylor & Francis, 2007
- ^ A history of eastern Europe: crisis and change Robert Bideleux, Ian Jeffries page 180, Routledge; 1st edition 1998
- ^ Jump up to: a b "German regions Prussia World War II". histclo.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Wang, Q. Edward; Fillafer, Franz L. (2007). The many faces of Clio: cross-cultural approaches to historiography. Berghahn Books. p. 375.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 219
- ^ Najnowsza historia Polski 1914-1993 Andrzej Albert, Wojciech Roszkowski Puls, page 95, 1994
- ^ Problemy narodowościowe w Kościele ewangelickim na Mazurach w latach 1918-1945, page 43 Ryszard Otello, Ośrodek Badań Naukowych im. Wojciecha Kętrzyńskiego w Olsztynie, 2003
- ^ Szkice z dziejów Pomorza: Pomorze na progu dziejów najnowszych Gerard Labuda, Książka i Wiedza, 1961
- ^ Historia Polski: 1914-1993 Wojciech Roszkowski Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN 1994:"Podobnie jak na Śląsku, bojówki niemieckie szerzyły wśród ludności polskiej terror".
- ^ Historia Warmii i Mazur: od pradziejów do 1945 roku, page 251, Stanisław Achremczyk - 1992
- ^ Kiermasy na Warmii i inne pisma wybrane Walenty Barczewski, page 14 Pojezierze,
- ^ Plebiscyty na Warmii, Mazurach i Powiślu w 1920 roku: wybór źródeł, Piotr Stawecki, Wojciech Wrzesiński, Zygmunt Lietz, page 13, Ośrodek badań naukowych 1986
- ^ Wojciech Wrzesiński, Ruch polski na Warmii, Mazurach i Powiślu w latach 1920-1939, 1973, page 40.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas (2003). ""Grenzlandpolitik" und Ostforschung an der Peripherie des Reiches" (PDF) (in German). Institut für Zeitgeschichte. p. 124.
- ^ admin@ok.info.pl, Krzysztof Perłakowski. "Związek Kurpiów". www.zwiazekkurpiow.pl. Archived from the original on 25 May 2016. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Debo, Richard K., "Survival and consolidation: the foreign policy of Soviet Russia, 1918-1921", McGill-Queen's Press, 1992, pg. 335
- ^ Kazimierz Jaroszyk, 1878-1941: o narodowy kształt Warmii i Mazur. Wydawnictwo Pojezierze, 1986, page 89.
- ^ Ruch polski na Warmii, Mazurach i Powiślu w latach 1920-1939 Wojciech Wrzesiński, page 40, 1973
- ^ Cienciala, Anna M. (2002). The Rebirth of Poland ; History 557 Lecture Notes.
- ^ Andrzej Sakson, Mazurzy: Społeczność pogranicza, Instytut Zachodni, 1990, page 59.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Plan odnowy miejscowości Koszelewy, Rys historyczny, page 5 Załącznik do Uchwały Nr XLII/9 /10 Rady Gminy Rybno z dnia 23 lutego 2010 r.
- ^ Słownik biograficzny Warmii, Mazur i Powiśla XIX i XX wieku(do 1945 roku), Tadeusz Oracki, page 334, Instytut Wydawniczy Pax 1983
- ^ Interludium mazurskie:wspomnienia 1920-1939, Karol Małłek, page 11, Czytelnik, 1968
- ^ Andreas Kossert: Masuren - Ostpreussens vergessener Süden, 2006, page 284: "Als in Soldau bekannt wurde, dass das Gebiet ohne Abstimmung an Polen fallen sollte, entluden sich Wut, Trauer und Bestürzung. Hilflos sah sich die Soldauer Bevölkerung ohne jede Mitsprache der Entscheidung des Siegers ausgesetzt. Alle Proteste blieben vergeblich. Kommunale Körperschaften verwahrten sich einhellig gegen die Abtretung, führende deutsche Politiker - allen voran Reichspräsident Friedrich Ebert - versuchten noch bis zur letzten Minute die alliierte Entscheidung rückgängig zu machen" (When it became known in Soldau that the area should fall to Poland without a vote, anger, sadness and dismay erupted. The Soldau population saw themselves helplessly and without a voice exposed to the decision of the winners. All protests were in vain. Local authorities unanimously opposed the cession, leading German politicians - led by President Friedrich Ebert - tried until the last minute to reverse the Allied decision.)
- ^ Kossert, Andreas (2006). Masuren, Ostpreussens vergessener Süden (in German). Pantheon. pp. 283, 284. ISBN 3-570-55006-0.
- ^ Andreas Kossert, Masuren - Ostpreussens vergessener Süden, 2006, p.284
- ^ "NY Times report" (PDF). Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Blanke, Richard. Orphans of Versailles: The Germans in Western Poland, 1918-1939. University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 0813130417. Retrieved 14 August 2018 – via Google Books.
- ^ Z ałacznik do Uchwały Nr.XXVII Lokalny Program Rewitalizacji Miasta Działdowa. Ogólna charakterystyka, rys historyczny miasta Działdowa [1] Urząd Miejski Miasta Działdowa
- ^ Biuletyn Głównej Komisji Badania Zbrodni Hitlerowskich w Polsce, Tomy 18-19, Główna Komisja Badania Zbrodni Hitlerowskich w Polsce Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Sprawiedliwości, page 167, 1968
- ^ Poland's Holocaust: Ethnic Strife, Collaboration with Occupying Forces and Genocide in the Second Republic, 1918-1947 by Tadeusz Piotrowski, page 83 2007, McFarland & Company, Inc.
- ^ Historia polityczna Polski 1935-1945 Paweł Piotr Wieczorkiewicz, page 164, Książka i Wiedza 2005
- ^ Friedlander, Henry (1995). The Origins of Nazi Genocide: from Euthanasia to the Final Solution. p. 140. ISBN 0-8078-2208-6.
- ^ Polska walcząca, 1939-1945, Tomy 5-6, page 165, Jerzy Śląski Instytut Wydawniczy Pax, 1986
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 264
- ^ Kossert, Andreas (2005). Ostpreussen. Geschichte und Mythos (in German). Siedler. p. 256. ISBN 3-88680-808-4.
- ^ Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, and Analysis. Piotr Eberhardt, page 166, 2003 M E Sharpe Inc
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 294
- ^ "Ostpreußen: Wahl zum Provinziallandtag 1925". www.gonschior.de. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Blanke, Richard (2001). Polish-speaking Germans? Language and national identity among the Masurians since 1871. Böhlau. pp. 253, 254. ISBN 3-412-12000-6.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, pp. 300, 306
- ^ Jump up to: a b Clark, p. 640
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 299
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 300
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 306
- ^ Bernd Martin, p. 55
- ^ Kossert, Andreas (2006). Masuren, Ostpreussens vergessener Süden (in German). Pantheon. pp. 278, 280. ISBN 3-570-55006-0.
- ^ Ingrao, Charles W.; Szabo, Franz A.J. (2008). The Germans and the East. Purdue University Press. p. 265. ISBN 978-1-55753-443-9.
- ^ Wrzesiński, Wojciech (1963). Ruch polski na Warmii, Mazurach i Powiślu w latach 1920-1939 (in Polish). Western Institute. p. 202.
- ^ "Jerzy Lanc patronem Środowiskowego Domu Samopomocy w Piastunie". Gazeta Olsztynska (in Polish). 27 September 2010. Archived from the original on 2012-03-27. Retrieved 2011-07-16.
- ^ "Interia - Polska i świat: informacje, sport, gwiazdy". piasutno.w.interia.pl. Archived from the original on 2013-08-26. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
- ^ J. Golec, S. Bojda, Słownik biograficzny ziemi cieszyńskiej, t. 1, Cieszyn 1993, s. 173: Wszystko wskazywało na to, że był to mord z premedytacją. K. Kajzer, Zginął jak bohater, "Kalendarz Cieszyński 2001", Cieszyn 2000, s. 249: Okoliczności świadczyły o morderstwie.
- ^ Archiwum Panstwowe w Kaliszu, "Jerzy Lanc (1901-1932)"[permanent dead link]
- ^ Sławomir Ambroziak, "Polska Szkola", Kurek Mazurski Archived 2012-03-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Jerzy Lance", Encyklopedia PWN, [2]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k Maria Wardzyńska: "Intelligenzaktion" na Warmii, Mazurach oraz Północnym Mazowszu. Główna Komisja Ścigania Zbrodni Przeciwko Narodowi Polskiemu. Biuletyn Instytutu Pamięci Narodowej nr. 12/1, 2003/2004, ss. 38-42
- ^ Germany Turns Eastwards: A Study of Ostforschung in the Third Reich by Michael Burleigh, page 209, 1988, Cambridge University Press
- ^ Słownik geograficzno-krajoznawczy Polski Iwona Swenson, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, page 440, 1998
- ^ "Kazimierz Krajewski, Shock in the Reich, Rzeczpospolita Daily". Archived from the original on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 2011-02-02.
- ^ Literatura polska w latach II wojny światowej Jerzy Świe̢ch, Instytut Badań Literackich (Polska Akademia Nauk), page 42 Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN,
- ^ Pałace i dwory powiatu kętrzyńskiego - wartości historyczne i kulturowe Archived 2004-07-18 at the Wayback Machine Muzeum im Wojciecha Kętrzyńsiego w Kętrzynie
- ^ Jump up to: a b O nas Archived 2018-12-24 at the Wayback Machine Ośrodek Badań Naukowych imienia Wojciecha Kętrzyńskiego w Olsztynie
- ^ Andreas Kossert, Ostpreussen, Geschichte und Mythos p. 352; Kossert gives 35 % from Central Poland, 22.6 % from Eastern Poland, 10 % victims of Op. Vistula, 18.5 % Natives in 1950
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p.363, 364: "Ähnlich wie die NS-Volkslisten seit 1939 im Reichsgau Wartheland und in Danzig-Westpreussen die Germanisierbarkeit der dort lebenden Deutschen und kleiner polnischer Gruppen festlegte, indem sie sie nach einem biologischen Rassismus in vier Kategorien einteilten, nahm die polnische Provinzverwaltung nach 1945 eine Klassifizierung der Bewohner Masurens nach einem ethnischen Rassismus vor."
- ^ Blanke, Richard (2001). Polish-speaking Germans? language and national identity among the Masurians since 1871. Böhlau. p. 285. ISBN 3-412-12000-6.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas (2005). Ostpreussen. Geschichte und Mythos (in German). Siedler. p. 353. ISBN 3-88680-808-4.
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 366
- ^ Kossert, Andreas: Masuren, p. 367
- ^ Andreas Kossert :”Masuren”, pp. 371, 372
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Kossert, Andreas (2005). Ostpreussen. Geschichte und Mythos (in German). Siedler. p. 358. ISBN 3-88680-808-4.
- ^ Studien zur osteuropäischen Kirchengeschichte und Kirchenkunde (in German). Peter Hauptmann. 1984. ISBN 978-3-525-56382-3. Retrieved 2009-07-27.
- ^ http://www10.dict.cc/wp_examples.php?lp_id=1&lang=en&s=Masurian
- ^ "Ostróda - Ostróda Reggae Festival". eMazury.com (in Polish). Retrieved 4 November 2019.
- ^ "Piknik Country w Mrągowie - to już 35 lat". Moje Mazury (in Polish). Retrieved 4 November 2019.
- ^ "Hunt for CIA "black site" in Poland". BBC. 28 December 2006.
- ^ (in Polish) Krajobraz kulturowy powiatu gołdapskiego, at www.dkgoldap.fr.pl Archived 2010-06-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ (in Polish) Mazury, at www.strefamazury.pl Archived 2010-07-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ (in Polish) Charakterystyka Pojezierza Mazurskiego, at www.bryk.pl
- ^ "Download Limit Exceeded". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.856.8111. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ "Masuria - Krutyn - Boat and canoeing trips on the Krutynia River". www.e-masuria.com. Retrieved 14 August 2018.
References[]
- (in Polish) Mazury Entry on the region in Polish PWN Encyclopedia.
- Martin, Bernd (1998). Masuren, Mythos und Geschichte (in German). Karlsruhe: Ewangelische Akademie Baden. ISBN 3-87210-122-6. Archived from the original on 2006-06-28.
- Kruk, Erwin (2003). Warmia i Mazury (in Polish). Wrocław: Wydawnictwo Dolnośląskie. ISBN 83-7384-028-1.
- Kossert, Andreas (2006). Masuren. Ostpreußens vergessener Süden (in German). Pantheon. ISBN 3-570-55006-0.
- Kossert, Andreas (2005). Ostpreussen, Geschichte und Mythos (in German). Siedler. ISBN 3-88680-808-4.
- Kossert, Andreas (2004). Mazury, Zapomniane południe Prus Wschodnich (in Polish). ISBN 83-7383-067-7.
- Clark, Christopher (2006). Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia 1600–1947. Cambridge: Belknap Press of Harvard. pp. 776. ISBN 0-674-02385-4.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Masuria. |
- Tourist information (Polish)
- Mazury (Polish)
- Mazury (Polish)
- Masuren Archived 2007-04-05 at the Wayback Machine (German)
- Natural tourism (birdwatching) in NE Poland
- Topographical maps 1:50 000
- Mazury - Poland - canoeing information (Polish)
- Masuren - Poland - canoeing information (German)
- Masuren - canoeing (German)
- Masuria - Poland - canoeing information (English)
- Mazury (Polish)
Coordinates: 53°52′02″N 20°42′10″E / 53.86711°N 20.70279°E
- Regions of Poland
- Geography of Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship
- Natural regions






