Metropolitan Special Constabulary
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2020) |
| Law enforcement in the United Kingdom |
|---|
| Topics |
|
| Equipment |
| Types of agency |
|
| Types of agent |
|
|
| Metropolitan Special Constabulary | |
|---|---|
 Flag | |
| Abbreviation | MSC |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | 15 October 1831 |
| Volunteers | 1,880 special constables[1] |
| Legal personality | Police force |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction | Greater London (minus City of London), England, United Kingdom |
 | |
| Map of police area | |
| Size | 1,578 km2 (609 sq mi) |
| Population | More than 8 million[2] |
| Legal jurisdiction | England and Wales |
| Primary governing body | Mayor's Office for Policing and Crime |
| Secondary governing body | Home Office |
| Constituting instrument | |
| General nature |
|
| Operational structure | |
| Overviewed by | Home Office HMIC IOPC |
| Headquarters | New Scotland Yard Victoria Embankment London SW1A 2JL[3] |
| Police officers | 1,800 special constables |
| Deputy Mayor for Policing and Crime responsible |
|
| Agency executives |
|
| Parent agency | Metropolitan Police Service |
| Website | |
| Metropolitan Police Special Constables | |
The Metropolitan Special Constabulary (MSC) is the volunteer police force of the Metropolitan Police Service.[4] It is one of three Special Constabularies operating within London, the others being part of the City of London Police and British Transport Police. The service was created over 180 years ago under the Special Constables Act 1831, and currently (as of September 2019) consists of 1,731 officers, making it the largest in the UK.
Special Constables are warranted Police Officers who hold the Office of Constable and enjoy full powers and privileges of a Police Officer throughout England and Wales and are subject to the same standards of professional behaviour as any Police Officer would under The Police (Conduct) Regulations 2012. They wear the same uniform and engage in the same work as regular Police Officers, including foot and vehicle patrols (whether alone, with another Special Constable or with a regular Police Officer), attending incidents, specific operations and the policing of major events.
Special Constables are required to undertake a minimum of 200 hours of operational duties every year, spread over a minimum of 16 hours per month. However, many do more than the basic requirement.
Numbers and distribution[]
Each Basic Command Unit (BCU) that provides policing for 2-4 London boroughs has a contingent of Special Constables supervised by a number of Special Sergeants, Special Inspectors and a Special Chief Inspector, who work in partnership with a number of regular officers. Most Command Units have more than 100 MSC officers and Westminster, the biggest, has over 300.
Several Special Constables are sponsored by their employers' as part of the Employer Supported Policing (ESP) programme, in which employers release their employees for a specific amount of time frequently to perform policing duties.[5]
Special Constables have the freedom, to some degree, in the choice of Borough they work in, their duties and hours. The teams in which Specials work depends on their BCU - some choosing to task their Specials to Safer Neighbourhoods Teams (known in other constabularies as Neighbourhood Policing Teams), others to their Emergency Response and Patrol Teams (known colloquially as Response Teams), whilst others work on a variety of other local portfolios such as the Criminal Investigation Department, Safeguarding or with schools. Additionally, there are Special Constables who work for more specialist and non-local policing units such as the Marine Policing Unit, Heathrow Airport OCU (ID), Organised Crime, Roads & Transport Policing Command.
Recruitment[]
Special Constables undergo a structured recruitment process[6] from application to the offer of an appointment. After an initial assessment of a Specials application, suitable candidates are invited to attend the Selection Centre, held at Empress State Building or another Met site.
In 2014 the assessment process was combined into a single day (compared to the separate Day One, Day Two process). The one-day event allows the timely release of candidates that have failed any of the assessments. Throughout the day, the following qualities and competencies are assessed: decision making, communication, personal responsibility, resilience, respect for diversity, customer focus and teamwork.
The assessment day comprises:
- A 30-minute written assessment based on a given scenario (Unless the applicant has provided evidence of GCSE English Language at C or above);
- A 20-minute competency based interview with two serving officers or lay interviewers;
- A Full Medical examination which is conducted by a registered Nurse who checks various aspects of a candidate's health, including eyesight and hearing;
- A check of paperwork and copying of required documents;
- Job Related Fitness Test (a bleep test).
If a candidate is successful on assessment day, they have to pass national security vetting which can take anything from a few weeks to up to a year. If security and vetting checks prove satisfactory, a candidate is offered a place on an MSC Foundation Training Course. The candidate pass rate for the assessments is around 1 in 11.[Citation required on this- A freedom of information request claims the rate is much higher, at 59.40% for Day 1 assessment, and 96.67% for day 2. Source - https://www.whatdotheyknow.com/request/547215/response/1329810/attach/html/3/attachment.docx.html]
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the recruitment process was again split into two events known as Day One and Day Two respectively. On Day One, which is held virtually, candidates undergo the 20-minute competency based interview with two serving officers or lay interviewers, whilst all other aspects of the recruitment process take place on Day Two.
Training and equipment[]
The MSC Foundation Training Course[6] consists of twenty-three days of training, incorporating seven days of Officer Safety Training (as of January 2021, having previously been three and then five days) and two days of Emergency Life Support (first aid) training, with the remainder being classroom-based learning covering the necessary knowledge and skills needed by officers for the execution of their duties as Special Constables. The training consists of three main exam-based assessments to ensure knowledge, and additional practical assessments in Officer Safety Training and Emergency Life Support.
Delivery of the course is offered in three forms, which recruits choose according to their convenience, as an intensive course taken over four weeks, a weekend course taking place over 12 weeks with 8 weeks of both Saturday and Sunday and 4 weeks with either Saturday or Sunday. In addition to the Training School at Hendon, MSC Foundation Training is also conducted at Marlowe House in Sidcup. Following completion of the initial training, there are two continuous training weekends to be completed within the first year after attestation.
After completing their initial training, further training is provided at their local Borough and units, which continues throughout their career. MSC Officers are trained to police public order events, and resources permitting, officers can also be trained as response drivers, cyclists and other skilled roles.
During the course of their training, MSC Student Officers must wear business attire for classroom-based learning, and white t-shirts and black shorts for Officer Safety Training and Emergency Life Support. Upon completion of training, Special Constables are issued with the same uniform and Officer Safety Equipment (OSE), sometimes known also as Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), as their regular colleagues, including handcuffs, baton, and PAVA spray.
Special Constables take the Police Oath before a Justice of the Peace at an Attestation Ceremony held on the first day of foundation training at The Peel Centre (Metropolitan Police Training College), from which point they hold the Office of Constable. However, Special Constables do not receive their Warrant Card until the culmination of their foundation training, at which point they then enjoy the powers and privileges of a Constable throughout England and Wales.[7]
MSC officers receive no payment for duties they perform. However, they receive a subsistence allowance throughout their service, and during training can claim back costs for travel expenses, as well as additional expenses such as the cost of purchasing boots and a torch, which are not issued with uniform in the Metropolitan Police. Once they pass out of training and receive their Warrant Card, Special Constables are afforded free travel both on and off duty on the London Underground, Docklands Light Railway, London Buses the Croydon Tramlink, London Overground and TfL Rail with a Police Oyster Card by virtue of arrangements with Transport for London.[6]
Supervision & Leadership[]
The MSC grade structure is as follows:
- Special Constable - (SC)
- Special Sergeant - (S/Sgt)
- Special Inspector - (S/Insp)
- Special Chief Inspector - (S/CI)
- Assistant Chief Officer MSC - (ACO)
- Chief Officer MSC - (CO)
The current Chief Officer is .[8][9]
Special Chief Inspector (S/CI) and Deputy Chief Officer (DCO) ranks were removed in 2016,[10] but following the change to 12 BCUs the role of Special Chief Inspector has been reinstated.
MSC ranks are not like-for-like equivalents to those of regular police ranks and are simply administrative grades. This means that for example, a Special Sergeant or Inspector does not have the same legal authority as a Police Sergeant or Inspector under various Acts that make reference to the ranks. MPS policy states that regular officers take primacy at operational incidents regardless of the grade of any MSC officers present.
As with regular ranks, MSC grades can be held on an 'acting', 'temporary' or 'substantive' basis.
Within the MPS, the MSC falls within Frontline Policing (FP) with the Chief Officer MSC being a member of the 'Chief Officers Group' (COG).[11]
Insignia[]
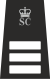
| Metropolitan Police Special Constabulary Ranks | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Special Constable | Special Sergeant | Special Inspector | Special Chief Inspector | Assistant Chief Officer | Chief Officer |
| Epaulette Insignia | 
|

|

|
|

|

|
| Notes: |
| |||||
The main insignia which separates MSC from regular officers is the "SC & Crown" which is worn at the top of the epaulette by MSC officers of all ranks. Special Constables wear their "Borough Code", usually a two-letter code, which signifies which BCU or specialist unit they are attached to. Below this, at the bottom of their epaulette, is their Collar number, a four digit number beginning with a 5 or 8 if attached to Roads and Transport Policing Command or 9 if attached to Organised Crime. A Special Sergeant's insignia is similar to a Special Constable's except they have a 4-digit shoulder number beginning with 50 (or 80 for RTPC, 90 for Organised Crime). Officers ranked above sergeant do not wear borough codes or shoulder numbers.
Unlike epaulette insignia, the Metropolitan Special Constabulary have the same Uniform Insignia as the Metropolitan Police where the Special ranks have equivalent designs as well as the Assistant Chief Officer wears equivalent uniform to a Commander/Assistant Chief Constable and the Chief Officer wears equivalent uniform to the Commissioner/Chief Constable.
See also[]
- Special Constabulary
- Metropolitan Police
- Police ranks of the United Kingdom#Special constables
References[]
- ^ "The Structure of the Met". Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- ^ "About the Met Police: Jurisdiction". Retrieved 11 October 2017.
- ^ "New Scotland Yard". Open House London. Retrieved 29 November 2019.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 29 November 2009. Retrieved 6 November 2009.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "MSC Employer Supported Policing". Met.police.uk. Retrieved 8 June 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Guidance Notes
- ^ Specials Extended Jurisdiction Archived 6 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Met police bid to double special constables to help fight against violent crime". www.telegraph.co.uk. 19 April 2019. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ "Met police bid to double special constables to help fight against violent crime". www.telegraph.co.uk. 23 May 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ^ Commander Lucy D'Orsi "Metropolitan Special Constabulary Strategic Review", Metropolitan Police FIO Request, Page 51, February 2016
- ^ https://www.met.police.uk/SysSiteAssets/media/downloads/force-content/met/about-us/executive-structure.pdf[bare URL]
- ^ Metropolitan Police "Special Constabulary Ranks FOI Request 2019", January 2019
External links[]
- Metropolitan Police
- Special Constabulary
- Organizations established in 1831

