Miocene
| Miocene | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23.03 – 5.333 Ma | |||||||||||
| Chronology | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Etymology | |||||||||||
| Name formality | Formal | ||||||||||
| Usage information | |||||||||||
| Celestial body | Earth | ||||||||||
| Regional usage | Global (ICS) | ||||||||||
| Time scale(s) used | ICS Time Scale | ||||||||||
| Definition | |||||||||||
| Chronological unit | Epoch | ||||||||||
| Stratigraphic unit | Series | ||||||||||
| Time span formality | Formal | ||||||||||
| Lower boundary definition |
| ||||||||||
| Lower boundary GSSP | Lemme-Carrosio Section, Carrosio, Italy 44°39′32″N 8°50′11″E / 44.6589°N 8.8364°E | ||||||||||
| GSSP ratified | 1996[4] | ||||||||||
| Upper boundary definition | Base of the Thvera magnetic event (C3n.4n), which is only 96 ka (5 precession cycles) younger than the GSSP | ||||||||||
| Upper boundary GSSP | Heraclea Minoa section, Heraclea Minoa, Cattolica Eraclea, Sicily, Italy 37°23′30″N 13°16′50″E / 37.3917°N 13.2806°E | ||||||||||
| GSSP ratified | 2000[5] | ||||||||||
The Miocene ( /ˈmaɪ.əˌsiːn, ˈmaɪ.oʊ-/ MY-ə-seen, MY-oh-[6][7]) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about 23.03 to 5.333 million years ago (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; its name comes from the Greek words μείων (meiōn, "less") and καινός (kainos, "new")[8][9] and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene.[10] The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene.
As the earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch.
During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the Atlantic and Mediterranean closed, causing the Mediterranean Sea to nearly completely evaporate, in an event called the Messinian salinity crisis. The Strait of Gibraltar opened and the Mediterranean refilled at the Miocene-Pilocene boundary, in an event called the Zanclean flood.
The apes first evolved, arose, and diversified during the early Miocene (Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages), becoming widespread in the Old World. By the end of this epoch and the start of the following one, the ancestors of humans had split away from the ancestors of the chimpanzees to follow their own evolutionary path during the final Messinian stage (7.5–5.3 Ma) of the Miocene. As in the Oligocene before it, grasslands continued to expand and forests to dwindle in extent. In the seas of the Miocene, kelp forests made their first appearance and soon became one of Earth's most productive ecosystems.[11]
The plants and animals of the Miocene were recognizably modern. Mammals and birds were well-established. Whales, pinnipeds, and kelp spread.
The Miocene is of particular interest to geologists and palaeoclimatologists as major phases of the geology of the Himalaya occurred during the Miocene, affecting monsoonal patterns in Asia, which were interlinked with glacial periods in the northern hemisphere.[12]
Subdivisions[]

The Miocene faunal stages from youngest to oldest are typically named according to the International Commission on Stratigraphy:[13]
| Sub-epoch | Faunal stage | Time range |
|---|---|---|
| Late Miocene | Messinian | 7.246–5.333 Ma |
| Tortonian | 11.608–7.246 Ma | |
| Middle Miocene | Serravallian | 13.65–11.608 Ma |
| Langhian | 15.97–13.65 Ma | |
| Early Miocene | Burdigalian | 20.43–15.97 Ma |
| Aquitanian | 23.03–20.43 Ma |
Regionally, other systems are used, based on characteristic land mammals; some of them overlap with the preceding Oligocene and following Pliocene epochs:
European Land Mammal Ages
- Turolian (9.0 to 5.3 Ma)
- Vallesian (11.6 to 9.0 Ma)
- Astaracian (16.0 to 11.6 Ma)
- Orleanian (20.0 to 16.0 Ma)
- Agenian (23.8 to 20.0 Ma)
North American Land Mammal Ages
- Hemphillian (10.3 to 4.9 Ma)
- Clarendonian (13.6 to 10.3 Ma)
- Barstovian (16.3 to 13.6 Ma)
- Hemingfordian (20.6 to 16.3 Ma)
- Arikareean (30.6 to 20.6 Ma)
South American Land Mammal Ages
- Montehermosan (6.8 to 4.0 Ma)
- Huayquerian (9.0 to 6.8 Ma)
- Mayoan (11.8 to 9.0 Ma)
- Laventan (13.8 to 11.8 Ma)
- Colloncuran (15.5 to 13.8 Ma)
- Friasian (16.3 to 15.5 Ma)
- Santacrucian (17.5 to 16.3 Ma)
- Colhuehuapian (21.0 to 17.5 Ma)
Paleogeography[]
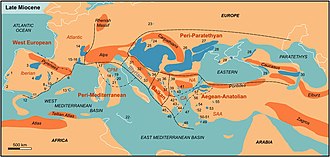
Continents continued to drift toward their present positions. Of the modern geologic features, only the land bridge between South America and North America was absent,[14] although South America was approaching the western subduction zone in the Pacific Ocean, causing both the rise of the Andes and a southward extension of the Meso-American peninsula.[15]
Mountain building took place in western North America, Europe, and East Asia.[16] Both continental and marine Miocene deposits are common worldwide with marine outcrops common near modern shorelines. Well studied continental exposures occur in the North American Great Plains and in Argentina.
India continued to collide with Asia, creating dramatic new mountain ranges. The Tethys seaway continued to shrink and then disappeared as Africa collided with Eurasia in the Turkish–Arabian region between 19 and 12 Ma.[16] The subsequent uplift of mountains in the western Mediterranean region and a global fall in sea levels combined to cause a temporary drying up of the Mediterranean Sea (known as the Messinian salinity crisis) near the end of the Miocene.[17]
The global trend was towards increasing aridity caused primarily by global cooling reducing the ability of the atmosphere to absorb moisture.[18] Uplift of East Africa in the late Miocene was partly responsible for the shrinking of tropical rain forests in that region,[19] and Australia got drier as it entered a zone of low rainfall in the Late Miocene.[20]
At the beginning of the Miocene, the northern margin of the Arabian plate collided with Eurasia, causing the closure of the Indian Ocean-Mediterranean Seaway, severing the connection between the two bodies of water, and forming a land connection between Afro-Arabia and Eurasia.[21]
South America[]
During the Oligocene and Early Miocene the coast of northern Brazil,[22] Colombia, south-central Peru, central Chile and large swathes of inland Patagonia were subject to a marine transgression.[23] The transgressions in the west coast of South America are thought to be caused by a regional phenomenon while the steadily rising central segment of the Andes represents an exception.[23] While there are numerous registers of Oligo-Miocene transgressions around the world it is doubtful that these correlate.[22]
It is thought that the Oligo-Miocene transgression in Patagonia could have temporarily linked the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, as inferred from the findings of marine invertebrate fossils of both Atlantic and Pacific affinity in La Cascada Formation.[24][25] Connection would have occurred through narrow epicontinental seaways that formed channels in a dissected topography.[24][26]
The Antarctic Plate started to subduct beneath South America 14 million years ago in the Miocene, forming the Chile Triple Junction. At first the Antarctic Plate subducted only in the southernmost tip of Patagonia, meaning that the Chile Triple Junction lay near the Strait of Magellan. As the southern part of Nazca Plate and the Chile Rise became consumed by subduction the more northerly regions of the Antarctic Plate begun to subduct beneath Patagonia so that the Chile Triple Junction advanced to the north over time.[27] The asthenospheric window associated to the triple junction disturbed previous patterns of mantle convection beneath Patagonia inducing an uplift of ca. 1 km that reversed the Oligocene–Miocene transgression.[26][28]
As the southern Andes rose in the Middle Miocene (14–12 million years ago) the resulting rain shadow originated the Patagonian Desert to the east.[29]
Climate[]
Climates remained moderately warm, although the slow global cooling that eventually led to the Pleistocene glaciations continued.
Although a long-term cooling trend was well underway, there is evidence of a warm period during the Miocene when the global climate rivalled that of the Oligocene. The Miocene warming began 21 million years ago and continued until 14 million years ago, when global temperatures took a sharp drop—the Middle Miocene Climate Transition (MMCT). By 8 million years ago, temperatures dropped sharply once again, and the Antarctic ice sheet was already approaching its present-day size and thickness. Greenland may have begun to have large glaciers as early as 7 to 8 million years ago,[30][31] although the climate for the most part remained warm enough to support forests there well into the Pliocene.[32]
Life[]
Life during the Miocene Epoch was mostly supported by the two newly formed biomes, kelp forests and grasslands. Grasslands allow for more grazers, such as horses, rhinoceroses, and hippos. Ninety-five percent of modern plants existed by the end of this epoch.
Flora[]

The coevolution of gritty, fibrous, fire-tolerant grasses and long-legged gregarious ungulates with high-crowned teeth, led to a major expansion of grass-grazer ecosystems, with roaming herds of large, swift grazers pursued by predators across broad sweeps of open grasslands, displacing desert, woodland, and browsers.
The higher organic content and water retention of the deeper and richer grassland soils, with long-term burial of carbon in sediments, produced a carbon and water vapor sink. This, combined with higher surface albedo and lower evapotranspiration of grassland, contributed to a cooler, drier climate.[34] C4 grasses, which are able to assimilate carbon dioxide and water more efficiently than C3 grasses, expanded to become ecologically significant near the end of the Miocene between 6 and 7 million years ago.[35] The expansion of grasslands and radiations among terrestrial herbivores correlates to fluctuations in CO2.[36]
Cycads between 11.5 and 5 million years ago began to rediversify after previous declines in variety due to climatic changes, and thus modern cycads are not a good model for a "living fossil".[37] Eucalyptus fossil leaves occur in the Miocene of New Zealand, where the genus is not native today, but have been introduced from Australia.[38]
Fauna[]
−10 — – −9.5 — – −9 — – −8.5 — – −8 — – −7.5 — – −7 — – −6.5 — – −6 — – −5.5 — – −5 — – −4.5 — – −4 — – −3.5 — – −3 — – −2.5 — – −2 — – −1.5 — – −1 — – −0.5 — – 0 — | Nakalipithecus Homo habilis Homo erectus Homo heidelbergensis Homo sapiens Neanderthals,Denisovans |
| ||||||||||||||||||
(million years ago) | ||||||||||||||||||||

Both marine and continental fauna were fairly modern, although marine mammals were less numerous. Only in isolated South America and Australia did widely divergent fauna exist.
In the Early Miocene, several Oligocene groups were still diverse, including nimravids, entelodonts, and three-toed equids. Like in the previous Oligocene epoch, oreodonts were still diverse, only to disappear in the earliest Pliocene. During the later Miocene mammals were more modern, with easily recognizable canids, bears, procyonids, equids, beavers, deer, camelids, and whales, along with now extinct groups like borophagine canids, certain gomphotheres, three-toed horses, and hornless rhinos like Teleoceras and Aphelops. Islands began to form between South and North America in the Late Miocene, allowing ground sloths like Thinobadistes to island-hop to North America. The expansion of silica-rich C4 grasses led to worldwide extinctions of herbivorous species without high-crowned teeth.[39]
A few basal mammal groups endured into this epoch in southern landmasses, including the South American dryolestoid Necrolestes and gondwanathere Patagonia and New Zealand's Saint Bathans mammal. Non-marsupial metatherians were also still around, such as the American and Eurasian herpetotheriids and such as Siamoperadectes, and the South American sparassodonts.
Unequivocally recognizable dabbling ducks, plovers, typical owls, cockatoos and crows appear during the Miocene. By the epoch's end, all or almost all modern bird groups are believed to have been present; the few post-Miocene bird fossils which cannot be placed in the evolutionary tree with full confidence are simply too badly preserved, rather than too equivocal in character. Marine birds reached their highest diversity ever in the course of this epoch.
Approximately 100 species of apes lived during this time, ranging throughout Africa, Asia and Europe and varying widely in size, diet, and anatomy. Due to scanty fossil evidence it is unclear which ape or apes contributed to the modern hominid clade, but molecular evidence indicates this ape lived between 7 and 8 million years ago.[40] The first hominins (bipedal apes of the human lineage) appeared in Africa at the very end of the Miocene, including Sahelanthropus, Orrorin, and an early form of Ardipithecus (A. kadabba) The chimpanzee–human divergence is thought to have occurred at this time.[41]
The expansion of grasslands in North America also led to an explosive radiation among snakes.[42] Previously, snakes were a minor component of the North American fauna, but during the Miocene, the number of species and their prevalence increased dramatically with the first appearances of vipers and elapids in North America and the significant diversification of Colubridae (including the origin of many modern genera such as Nerodia, Lampropeltis, Pituophis and Pantherophis).[42]


In the oceans, brown algae, called kelp, proliferated, supporting new species of sea life, including otters, fish and various invertebrates.
Cetaceans attained their greatest diversity during the Miocene,[43] with over 20 recognized genera of baleen whales in comparison to only six living genera.[44] This diversification correlates with emergence of gigantic macro-predators such as megatoothed sharks and raptorial sperm whales.[45] Prominent examples are C. megalodon and L. melvillei.[45] Other notable large sharks were C. chubutensis, Isurus hastalis, and Hemipristis serra.
Crocodilians also showed signs of diversification during Miocene. The largest form among them was a gigantic caiman Purussaurus which inhabited South America.[46] Another gigantic form was a false gharial Rhamphosuchus, which inhabited modern age India. A strange form, Mourasuchus also thrived alongside Purussaurus. This species developed a specialized filter-feeding mechanism, and it likely preyed upon small fauna despite its gigantic size.
The pinnipeds, which appeared near the end of the Oligocene, became more aquatic. A prominent genus was Allodesmus.[47] A ferocious walrus, Pelagiarctos may have preyed upon other species of pinnipeds including Allodesmus.
Furthermore, South American waters witnessed the arrival of Megapiranha paranensis, which were considerably larger than modern age piranhas.
New Zealand's Miocene fossil record is particularly rich. Marine deposits showcase a variety of cetaceans and penguins, illustrating the evolution of both groups into modern representatives. The early Miocene Saint Bathans Fauna is the only Cenozoic terrestrial fossil record of the landmass, showcasing a wide variety of not only bird species, including early representatives of clades such as moas, kiwis and adzebills, but also a diverse herpetofauna of sphenodontians, crocodiles and turtle as well as a rich terrestrial mammal fauna composed of various species of bats and the enigmatic Saint Bathans Mammal.
Oceans[]
There is evidence from oxygen isotopes at Deep Sea Drilling Program sites that ice began to build up in Antarctica about 36 Ma during the Eocene. Further marked decreases in temperature during the Middle Miocene at 15 Ma probably reflect increased ice growth in Antarctica. It can therefore be assumed that East Antarctica had some glaciers during the early to mid Miocene (23–15 Ma). Oceans cooled partly due to the formation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, and about 15 million years ago the ice cap in the southern hemisphere started to grow to its present form. The Greenland ice cap developed later, in the Middle Pliocene time, about 3 million years ago.
Middle Miocene disruption[]
The "Middle Miocene disruption" refers to a wave of extinctions of terrestrial and aquatic life forms that occurred following the Miocene Climatic Optimum (18 to 16 Ma), around 14.8 to 14.5 million years ago, during the Langhian stage of the mid-Miocene. A major and permanent cooling step occurred between 14.8 and 14.1 Ma, associated with increased production of cold Antarctic deep waters and a major growth of the East Antarctic ice sheet. A Middle Miocene δ18O increase, that is, a relative increase in the heavier isotope of oxygen, has been noted in the Pacific, the Southern Ocean and the South Atlantic.[48]
Impact event[]
A large impact event occurred either during the Miocene (23 Ma – 5.3 Ma) or the Pliocene (5.3 Ma – 2.6 Ma). The event formed the Karakul crater (52 km diameter), which is estimated to have an age of less than 23 Ma[49] or less than 5 Ma.[50]
See also[]
- Geologic time scale
- List of fossil sites
- Category:Miocene animals
References[]
- ^ Krijgsman, W.; Garcés, M.; Langereis, C. G.; Daams, R.; Van Dam, J.; Van Der Meulen, A. J.; Agustí, J.; Cabrera, L. (1996). "A new chronology for the middle to late Miocene continental record in Spain". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 142 (3–4): 367–380. Bibcode:1996E&PSL.142..367K. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(96)00109-4.
- ^ Retallack, G. J. (1997). "Neogene Expansion of the North American Prairie". PALAIOS. 12 (4): 380–390. doi:10.2307/3515337. JSTOR 3515337. Retrieved 2008-02-11.
- ^ "ICS Timescale Chart" (PDF). www.stratigraphy.org.
- ^ Steininger, Fritz F.; M. P. Aubry; W. A. Berggren; M. Biolzi; A. M. Borsetti; Julie E. Cartlidge; F. Cati; R. Corfield; R. Gelati; S. Iaccarino; C. Napoleone; F. Ottner; F. Rögl; R. Roetzel; S. Spezzaferri; F. Tateo; G. Villa; D. Zevenboom (1997). "The Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the base of the Neogene" (PDF). Episodes. 20 (1): 23–28. doi:10.18814/epiiugs/1997/v20i1/005.
- ^ Van Couvering, John; Castradori, Davide; Cita, Maria; Hilgen, Frederik; Rio, Domenico (September 2000). "The base of the Zanclean Stage and of the Pliocene Series" (PDF). Episodes. 23 (3): 179–187. doi:10.18814/epiiugs/2000/v23i3/005.
- ^ "Miocene". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- ^ "Miocene". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ^ See:
- Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: Todhunter, Isaac, ed. (1876). William Whewell, D. D., Master of Trinity College, Cambridge: An account of his writings with selections from his literary and scientific correspondence. vol. 2. London, England: Macmillan and Co. p. 111.
|volume=has extra text (help) - Lyell, Charles (1833). Principles of Geology, …. vol. 3. London, England: John Murray. p. 54.
|volume=has extra text (help) From p. 54: "The next antecedent tertiary epoch we shall name Miocene, from μειων, minor, and χαινος, recens, a minority only of fossil shells imbedded in the formations of this period, being of recent species."
- Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: Todhunter, Isaac, ed. (1876). William Whewell, D. D., Master of Trinity College, Cambridge: An account of his writings with selections from his literary and scientific correspondence. vol. 2. London, England: Macmillan and Co. p. 111.
- ^ "Miocene". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- ^ Lyell, Charles (1833). Principles of Geology, …. vol. 3. London, England: John Murray. p. 54.
|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ "BBC Nature - Miocene epoch videos, news and facts". BBC. Retrieved 2016-11-13.
- ^ Zhisheng, An; Kutzbach, John E.; Prell, Warren L.; Porter, Stephen C. (3 May 2001). "Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya–Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times". Nature. 411 (6833): 62–66. Bibcode:2001Natur.411...62Z. doi:10.1038/35075035. PMID 11333976. S2CID 4398615.
- ^ Robert A. Rohde (2005). "GeoWhen Database". Retrieved March 8, 2011.
- ^ Stange, Madlen; Sánchez-Villagra, Marcelo R; Salzburger, Walter; Matschiner, Michael (1 July 2018). "Bayesian Divergence-Time Estimation with Genome-Wide Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Data of Sea Catfishes (Ariidae) Supports Miocene Closure of the Panamanian Isthmus". Systematic Biology. 67 (4): 681–699. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syy006. PMC 6005153. PMID 29385552.
- ^ Torsvik, Trond H.; Cocks, L. Robin M. (2017). Earth history and palaeogeography. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. p. 264. ISBN 9781107105324.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Torsvik & Cocks 2017, p. 261-264.
- ^ Torsvik & Cocks 2017, p. 259, 267, 287.
- ^ Torsvik & Cocks 2017, p. 267.
- ^ Wichura, Henry; Bousquet, Romain; Oberhänsli, Roland; Strecker, Manfred R.; Trauth, Martin H. (June 2010). "Evidence for middle Miocene uplift of the East African Plateau". Geology. 38 (6): 543–546. Bibcode:2010Geo....38..543W. doi:10.1130/G31022.1.
- ^ Mao, Xuegang; Retallack, Gregory (January 2019). "Late Miocene drying of central Australia". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 514: 292–304. Bibcode:2019PPP...514..292M. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.10.008.
- ^ Torfstein, Adi; Steinberg, Josh (2020-08-14). "The Oligo–Miocene closure of the Tethys Ocean and evolution of the proto-Mediterranean Sea". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 13817. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-70652-4. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 7427807. PMID 32796882.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rossetti, Dilce F.; Bezerra, Francisco H.R.; Dominguez, José M.L. (2013). "Late Oligocene–Miocene transgressions along the equatorial and eastern margins of Brazil". Earth-Science Reviews. 123: 87–112. Bibcode:2013ESRv..123...87R. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.04.005.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Macharé, José; Devries, Thomas; Barron, John; Fourtanier, Élisabeth (1988). "Oligo-Miocene transgression along the Pacifie margin of South America: new paleontological and geological evidence from the Pisco basin (Peru)" (PDF). Geódynamique. 3 (1–2): 25–37.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Encinas, Alfonso; Pérez, Felipe; Nielsen, Sven; Finger, Kenneth L.; Valencia, Victor; Duhart, Paul (2014). "Geochronologic and paleontologic evidence for a Pacific–Atlantic connection during the late Oligocene–early Miocene in the Patagonian Andes (43–44°S)". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 55: 1–18. Bibcode:2014JSAES..55....1E. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2014.06.008. hdl:10533/130517.
- ^ Nielsen, S.N. (2005). "Cenozoic Strombidae, Aporrhaidae, and Struthiolariidae (Gastropoda, Stromboidea) from Chile: their significance to biogeography of faunas and climate of the south-east Pacific". Journal of Paleontology. 79: 1120–1130. doi:10.1666/0022-3360(2005)079[1120:csaasg]2.0.co;2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Guillame, Benjamin; Martinod, Joseph; Husson, Laurent; Roddaz, Martin; Riquelme, Rodrigo (2009). "Neogene uplift of central eastern Patagonia: Dynamic response to active spreading ridge subduction?". Tectonics. 28.
- ^ Cande, S.C.; Leslie, R.B. (1986). "Late Cenozoic Tectonics of the Southern Chile Trench". Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 91 (B1): 471–496. Bibcode:1986JGR....91..471C. doi:10.1029/jb091ib01p00471.
- ^ Guillaume, Benjamin; Gautheron, Cécile; Simon-Labric, Thibaud; Martinod, Joseph; Roddaz, Martin; Douville, Eric (2013). "Dynamic topography control on Patagonian relief evolution as inferred from low temperature thermochronology". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 3: 157–167. Bibcode:2013E&PSL.364..157G. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.12.036.
- ^ Folguera, Andrés; Encinas, Alfonso; Echaurren, Andrés; Gianni, Guido; Orts, Darío; Valencia, Víctor; Carrasco, Gabriel (2018). "Constraints on the Neogene growth of the central Patagonian Andes at thelatitude of the Chile triple junction (45–47°S) using U/Pb geochronology insynorogenic strata". Tectonophysics. 744: 134–154. Bibcode:2018Tectp.744..134F. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2018.06.011. hdl:11336/88399.
- ^ Larsen, H. C.; Saunders, A. D.; Clift, P. D.; Beget, J.; Wei, W.; Spezzaferri, S. (13 May 1994). "Seven Million Years of Glaciation in Greenland". Science. 264 (5161): 952–955. Bibcode:1994Sci...264..952L. doi:10.1126/science.264.5161.952. PMID 17830083. S2CID 10031704.
- ^ John, Kristen E. K. St.; Krissek, Lawrence A. (28 June 2008). "The late Miocene to Pleistocene ice-rafting history of southeast Greenland". Boreas. 31 (1): 28–35. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3885.2002.tb01053.x.
- ^ Funder, Svend; Abrahamsen, Niels; Bennike, Ole; Feyling-Hanssen, Rolf W. (1 August 1985). "Forested Arctic: Evidence from North Greenland". Geology. 13 (8): 542–546. Bibcode:1985Geo....13..542F. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1985)13<542:FAEFNG>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Attorre, F.; Francesconi, F.; Taleb, N.; Scholte, P.; Saed, A.; Alfo, M.; Bruno, F. (2007). "Will dragonblood survive the next period of climate change? Current and future potential distribution of Dracaena cinnabari (Socotra, Yemen)". Biological Conservation. 138 (3–4): 430–439. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2007.05.009.
- ^ Retallack, Gregory (2001). "Cenozoic Expansion of Grasslands and Climatic Cooling" (PDF). The Journal of Geology. University of Chicago Press. 109 (4): 407–426. Bibcode:2001JG....109..407R. doi:10.1086/320791. S2CID 15560105. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-06.
- ^ Osborne, C.P.; Beerling, D.J. (2006). "Nature's green revolution: the remarkable evolutionary rise of C4 plants". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 361 (1465): 173–194. doi:10.1098/rstb.2005.1737. PMC 1626541. PMID 16553316.
- ^ Wolfram M. Kürschner, Zlatko Kvacek & David L. Dilcher (2008). "The impact of Miocene atmospheric carbon dioxide fluctuations on climate and the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (2): 449–53. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105..449K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0708588105. PMC 2206556. PMID 18174330.
- ^ Susanne S. Renner (2011). "Living fossil younger than thought". Science. 334 (6057): 766–767. Bibcode:2011Sci...334..766R. doi:10.1126/science.1214649. PMID 22076366. S2CID 206537832.
- ^ "Eucalyptus fossils in New Zealand - the thin end of the wedge - Mike Pole". 2014-09-22.
- ^ Steven M. Stanley (1999). Earth System History. New York: Freeman. pp. 525–526. ISBN 0-7167-2882-6.
- ^ Yirka, Bob (August 15, 2012). "New genetic data shows humans and great apes diverged earlier than thought". phys.org.
- ^ Begun, David. "Fossil Record of Miocene Hominoids" (PDF). University of Toronto. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 30, 2013. Retrieved July 11, 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Holman, J. Alan (2000). Fossil Snakes of North America (First ed.). Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. pp. 284–323. ISBN 0253337216.
- ^ Peter Klimley & David Ainley (1996). Great White Sharks: the Biology of Carcharodon carcharias. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-415031-4. Archived from the original on 2012-10-12. Retrieved 2011-08-12.
- ^ Dooley, Alton C.; Fraser, Nicholas C.; Luo, Zhe-Xi (2004). "The earliest known member of the rorqual—gray whale clade (Mammalia, Cetacea)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 24 (2): 453–463. doi:10.1671/2401. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 84970052.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Olivier Lambert; Giovanni Bianucci; Klaas Post; Christian de Muizon; Rodolfo Salas-Gismondi; Mario Urbina; Jelle Reumer (2010). "The giant bite of a new raptorial sperm whale from the Miocene epoch of Peru". Nature. 466 (7302): 105–108. Bibcode:2010Natur.466..105L. doi:10.1038/nature09067. PMID 20596020. S2CID 4369352.
- ^ Orangel A. Aguilera, Douglas Riff & Jean Bocquentin-Villanueva (2006). "A new giant Pusussaurus (Crocodyliformes, Alligatoridae) from the Upper Miocene Urumaco Formation, Venezuela" (PDF). Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 4 (3): 221–232. doi:10.1017/S147720190600188X. S2CID 85950121. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-29.
- ^ Lawrence G. Barnes & Kiyoharu Hirota (1994). "Miocene pinnipeds of the otariid subfamily Allodesminae in the North Pacific Ocean: systematics and relationships". Island Arc. 3 (4): 329–360. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1738.1994.tb00119.x.
- ^ Kenneth G. Miller & Richard G. Fairbanks (1983). "Evidence for Oligocene−Middle Miocene abyssal circulation changes in the western North Atlantic". Nature. 306 (5940): 250–253. Bibcode:1983Natur.306..250M. doi:10.1038/306250a0. S2CID 4337071.
- ^ Bouley, S.; Baratoux, D.; Baratoux, L.; Colas, F.; Dauvergne, J.; Losiak, A.; Vaubaillon, J.; Bourdeille, C.; Jullien, A.; Ibadinov, K. (American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2011) (2011). "Karakul: a young complex impact crater in the Pamir, Tajikistan". AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. 2011: P31A–1701. Bibcode:2011AGUFM.P31A1701B.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ Gurov, E. P., Gurova, H.P., Rakitskaya, R.B. and Yamnichenko,A.Yu. (1993) (1993). "The Karakul depression in Pamirs - the first impact structure in central Asia" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Science XXIV, Pp. 591-592: 591. Bibcode:1993LPI....24..591G.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
Further reading[]
- Cox, C. Barry & Moore, Peter D. (1993): Biogeography. An ecological and evolutionary approach (5th ed.). Blackwell Scientific Publications, Cambridge. ISBN 0-632-02967-6
- Ogg, Jim (2004): "Overview of Global Boundary Stratotype Sections and Points (GSSP's)". Retrieved 2006-04-30.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Miocene. |
| Wikisource has original works on the topic: Cenozoic#Neogene |
- PBS Deep Time: Miocene
- UCMP Berkeley Miocene Epoch Page
- Miocene Microfossils: 200+ images of Miocene Foraminifera
- Human Timeline (Interactive) – Smithsonian, National Museum of Natural History (August 2016).
- Miocene
- Geological epochs
- Neogene geochronology
