Carbon sequestration

| Part of a series on the |
| Carbon cycle |
|---|
 |
Carbon sequestration is the long-term removal, capture, or sequestration of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to slow or reverse atmospheric CO
2 pollution and to mitigate or reverse climate change.[2][3][4][5] Carbon dioxide (CO
2) is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes.[6] These changes can be accelerated through changes in land use and agricultural practices, such as converting crop and livestock grazing land into land for non-crop fast growing plants.[2] Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects,[6] including large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO
2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks, bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, ocean fertilization, enhanced weathering, and direct air capture when combined with storage.[4]
The likely need for CDR (carbon dioxide removal) has been publicly expressed by a range of individuals and organizations involved with climate change issues, including IPCC chief Rajendra Pachauri,[7] the UNFCCC executive secretary Christiana Figueres,[8] and the World Watch Institute.[9] Institutions with major programs focusing on CDR include the Lenfest Center for Sustainable Energy at the Earth Institute, Columbia University,[10] and the Climate Decision Making Center,[11] an international collaboration operated out of Carnegie-Mellon University's Department of Engineering and Public Policy.
Description[]

Carbon sequestration is the process involved in carbon capture and the long-term storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO
2)[2] and may refer specifically to:
- "The process of removing carbon from the atmosphere and depositing it in a reservoir."[13] When carried out deliberately, this may also be referred to as carbon dioxide removal, which is a form of geoengineering.
- Carbon capture and storage, where carbon dioxide is removed from flue gases (e.g., at power stations) before being stored in underground reservoirs.
- Natural biogeochemical cycling of carbon between the atmosphere and reservoirs, such as by chemical weathering of rocks.
Carbon dioxide may be captured as a pure by-product in processes related to petroleum refining or from flue gases from power generation.[14] CO
2 sequestration includes the storage part of carbon capture and storage, which refers to large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO
2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks.
Carbon sequestration describes long-term storage of carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon to either mitigate or defer global warming and avoid dangerous climate change. It has been proposed as a way to slow the atmospheric and marine accumulation of greenhouse gases, which are released by burning fossil fuels and industrial livestock production.[3]
Carbon dioxide is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical or physical processes. Some artificial sequestration techniques exploit these natural processes,[6] while some use entirely artificial processes.
There are three ways that this sequestration can be carried out; post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and oxy-combustion. A wide variety of separation techniques are being pursued, including gas phase separation, absorption into a liquid, and adsorption on a solid, as well as hybrid processes, such as adsorption/membrane systems. These above processes basically capture carbon emitting from power plants, factories, fuel burning industries, and new generation livestock production facilities as they transition into restorative farming techniques, which is used by organizations as they look to reduce carbon emissions from their operations.
Biological processes[]
Biosequestration[]

Biosequestration is the capture and storage of the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide by continual or enhanced biological processes. This form of carbon sequestration occurs through increased rates of photosynthesis via land-use practices such as reforestation, sustainable forest management, and genetic engineering.[15][16]
Carbon sequestration through biological processes affects the global carbon cycle. Examples include major climatic fluctuations, such as the Azolla event, which created the current Arctic climate. Such processes created fossil fuels, as well as clathrate and limestone. By manipulating such processes, geoengineers seek to enhance sequestration.
Peatland[]
Peat bogs act as a sink for carbon because they accumulate partially decayed biomass that would otherwise continue to decay completely. There is a variance on how much the peatlands act as a carbon sink or carbon source that can be linked to varying climates in different areas of the world and different times of the year.[17] By creating new bogs, or enhancing existing ones, the amount of carbon that is sequestered by bogs would increase.[18]
Forestry[]
Afforestation is the establishment of a forest in an area where there was no previous tree cover. Reforestation is the replanting of trees on marginal crop and pasture lands to incorporate carbon from atmospheric CO
2 into biomass.[19]
For this carbon sequestration process to succeed the carbon must not return to the atmosphere from mass burning or rotting when the trees die.[20] To this end, land allotted to the trees must not be converted to other uses and management of the frequency of disturbances might be necessary in order to avoid extreme events. Alternatively, the wood from them must itself be sequestered, e.g., via biochar, bio-energy with carbon storage (BECS), landfill or 'stored' by use in e.g., construction. Short of growth in perpetuity, however, reforestation with long-lived trees (>100 years) will sequester carbon for substantial period and be released gradually, minimizing carbon's climate impact during the 21st century. Earth offers enough room to plant an additional 1.2 trillion trees.[21] Planting and protecting them would offset some 10 years of CO2 emissions and sequester 205 billion tons of carbon.[22] This approach is supported by the Trillion Tree Campaign. Restoring all degraded forests world would capture about 205 billion tons of carbon in total, which is about two thirds of all carbon emissions.[23][24]
In a paper published in the journal Nature Sustainability, researchers studied the net effect of continuing to build according to current practices versus increasing the amount of wood products.[25][26] They concluded that if during the next 30 years new construction utilized 90% wood products that 700 million tons of carbon would be sequestered. This is the equivalent of about 7 days worth of global emissions in 2019.[27]
In a study published in Journal of Environmental Management researchers concluded "that coniferous and broadleaf trees can have diverse effect on soil organic carbon sequestration in soils of different age and previous land use".[28]
Urban forestry[]
Urban forestry increases the amount of carbon taken up in cities by adding new tree sites and the sequestration of carbon occurs over the lifetime of the tree.[29] It is generally practiced and maintained on smaller scales, like in cities. The results of urban forestry can have different results depending on the type of vegetation that is being used, so it can function as a sink but can also function as a source of emissions.[30] Along with sequestration by the plants which is difficult to measure but seems to have little effect on the overall amount of carbon dioxide that is uptaken, the vegetation can have indirect effects on carbon by reducing need for energy consumption.[30]
Wetlands[]
Wetland restoration involves restoring a wetland's natural biological, geological, and chemical functions through re-establishment or rehabilitation.[31] It has also been proposed as a potential climate change mitigation strategy, with carbon sequestered this way being known as blue carbon.[32] Wetland soil, particularly in coastal wetlands such as mangroves, sea grasses, and salt marshes,[32] is an important carbon reservoir; 20-30% of the world's soil carbon is found in wetlands, while only 5-8% of the world's land is composed of wetlands.[33] Studies have shown that restored wetlands can become productive CO2 sinks[34][35][36] and many restoration projects have been enacted in the US and around the world.[37][38][39] Aside from climate benefits, wetland restoration and conservation can help preserve biodiversity, improve water quality, and aid with flood control.[40]
As with forests, for the sequestration process to succeed, the wetland must remain undisturbed. If it is disturbed somehow, the carbon stored in the plants and sediments will be released back into the atmosphere and the ecosystem will no longer function as a carbon sink.[41] Additionally, some wetlands can release non-CO2 greenhouse gases, such as methane, which could offset potential climate benefits. The amounts of CO
2 sequestered by wetlands can also be difficult to measure.[40]
Agriculture[]
Compared to natural vegetation, cropland soils are depleted in soil organic carbon (SOC). When a soil is converted from natural land or semi natural land, such as forests, woodlands, grasslands, steppes and savannas, the SOC content in the soil reduces by about 30–40%.[42] This loss is due to the removal of plant material containing carbon, in terms of harvests. When the land use changes, the carbon in the soil will either increase or decrease, this change will continue until the soil reaches a new equilibrium. Deviations from this equilibrium can also be affected by variated climate .[43] The decreasing of SOC content can be counteracted by increasing the carbon input, this can be done with several strategies, e.g. leave harvest residues on the field, use manure as fertiliser or include perennial crops in the rotation. Perennial crops have larger below ground biomass fraction, which increases the SOC content.[42] Globally, soils are estimated to contain >8,580 gigatons of organic carbon, about ten times the amount in the atmosphere and much more than in vegetation.[44]
Modification of agricultural practices is a recognized method of carbon sequestration as soil can act as an effective carbon sink offsetting as much as 20% of 2010 carbon dioxide emissions annually.[45] (See No-till). Restoration of organic farming and earthworms may entirely offset CO
2 annual carbon excess of 4 Gt per year and drawdown the residual atmospheric excess.[46] (See Compost).
Carbon emission reduction methods in agriculture can be grouped into two categories: reducing and/or displacing emissions and enhancing carbon removal. Some of these reductions involve increasing the efficiency of farm operations (e.g. more fuel-efficient equipment) while some involve interruptions in the natural carbon cycle. Also, some effective techniques (such as the elimination of stubble burning) can negatively impact other environmental concerns (increased herbicide use to control weeds not destroyed by burning).
Carbon farming[]
Carbon farming is a name for a variety of agricultural methods aimed at sequestering atmospheric carbon into the soil and in crop roots, wood and leaves. Increasing soil's carbon content can aid plant growth, increase soil organic matter (improving agricultural yield), improve soil water retention capacity and reduce fertilizer use (and the accompanying emissions of greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O).As of 2016, variants of carbon farming reached hundreds of millions of hectares globally, of the nearly 5 billion hectares (1.2×1010 acres) of world farmland. Soils can contain up to five per cent carbon by weight, including decomposing plant and animal matter and biochar.
Potential sequestration alternatives to carbon farming include scrubbing CO
2 from the air with machines (direct air capture); fertilizing the oceans to prompt algal blooms that after death carry carbon to the sea bottom; storing the carbon dioxide emitted by electricity generation; and crushing and spreading types of rock such as basalt that absorb atmospheric carbon. Land management techniques that can be combined with farming include planting/restoring forests, burying biochar produced by anaerobically converted biomass and restoring wetlands. (Coal beds are the remains of marshes and peatlands.)
Bamboo farming[]
Although a bamboo forest stores less total carbon than a mature forest of trees, a bamboo plantation sequesters carbon at a much faster rate than a mature forest or a tree plantation. Therefore the farming of bamboo timber may have significant carbon sequestration potential.[47]
Deep soil[]
Soils hold four times the amount of carbon stored in the atmosphere.[48] About half of this is found deep within soils.[49] About 90% of this deep soil C is stabilized by mineral-organic associations.[50]
Reducing emissions[]
Increasing yields and efficiency generally reduces emissions as well, since more food results from the same or less effort. Techniques include more accurate use of fertilizers, less soil disturbance, better irrigation, and crop strains bred for locally beneficial traits and increased yields.
Replacing more energy intensive farming operations can also reduce emissions. Reduced or no-till farming requires less machine use and burns correspondingly less fuel per acre. However, no-till usually increases use of weed-control chemicals and the residue now left on the soil surface is more likely to release its CO
2 to the atmosphere as it decays, reducing the net carbon reduction.[citation needed]
In practice, most farming operations that incorporate post-harvest crop residues, wastes and byproducts back into the soil provide a carbon storage benefit.[citation needed] This is particularly the case for practices such as field burning of stubble – rather than releasing almost all of the stored CO
2 to the atmosphere, tillage incorporates the biomass back into the soil.[citation needed]
Enhancing carbon removal[]
All crops absorb CO
2 during growth and release it after harvest. The goal of agricultural carbon removal is to use the crop and its relation to the carbon cycle to permanently sequester carbon within the soil. This is done by selecting farming methods that return biomass to the soil and enhance the conditions in which the carbon within the plants will be reduced to its elemental nature and stored in a stable state. Methods for accomplishing this include:
- Use cover crops such as grasses and weeds as temporary cover between planting seasons
- Concentrate livestock in small paddocks for days at a time so they graze lightly but evenly. This encourages roots to grow deeper into the soil. Stock also till the soil with their hooves, grinding old grass and manures into the soil.[51]
- Cover bare paddocks with hay or dead vegetation. This protects soil from the sun and allows the soil to hold more water and be more attractive to carbon-capturing microbes.[51]
- Restore degraded land, which slows carbon release while returning the land to agriculture or other use. Degraded land with low soil carbon pool have particularly high potential to store soil C which can be farther enhanced by proper selection of vegetation.[52][53]
Agricultural sequestration practices may have positive effects on soil, air, and water quality, be beneficial to wildlife, and expand food production. On degraded croplands, an increase of 1 ton of soil carbon pool may increase crop yield by 20 to 40 kilograms per hectare of wheat, 10 to 20 kg/ ha for maize, and 0.5 to 1 kg/ha for cowpeas.[citation needed]
The effects of soil sequestration can be reversed. If the soil is disrupted or tillage practices are abandoned, the soil becomes a net source of greenhouse gases. Typically after 15 to 30 years of sequestration, soil becomes saturated and ceases to absorb carbon. This implies that there is a global limit to the amount of carbon that soil can hold.[54]
Many factors affect the costs of carbon sequestration including soil quality, transaction costs and various externalities such as leakage and unforeseen environmental damage. Because reduction of atmospheric CO
2 is a long-term concern, farmers can be reluctant to adopt more expensive agricultural techniques when there is not a clear crop, soil, or economic benefit. Governments such as Australia and New Zealand are considering allowing farmers to sell carbon credits once they document that they have sufficiently increased soil carbon content.[51][55][56][57][58][59]
Oceans[]
Iron fertilization[]
Ocean iron fertilization is an example of a geoengineering technique.[60] Iron fertilization[61] attempts to encourage phytoplankton growth, which removes carbon from the atmosphere for at least a period of time.[62][63] This technique is controversial because there is limited understanding of its complete effects on the marine ecosystem,[64] including side effects and possibly large deviations from expected behavior. Such effects potentially include release of nitrogen oxides,[65] and disruption of the ocean's nutrient balance.[60]
Natural iron fertilisation events (e.g., deposition of iron-rich dust into ocean waters) can enhance carbon sequestration. Sperm whales act as agents of iron fertilisation when they transport iron from the deep ocean to the surface during prey consumption and defecation. Sperm whales have been shown to increase the levels of primary production and carbon export to the deep ocean by depositing iron rich feces into surface waters of the Southern Ocean. The iron rich feces causes phytoplankton to grow and take up more carbon from the atmosphere. When the phytoplankton dies, some of it sinks to the deep ocean and takes the atmospheric carbon with it. By reducing the abundance of sperm whales in the Southern Ocean, whaling has resulted in an extra 200,000 tonnes of carbon remaining in the atmosphere each year.[66]
Urea fertilization[]
proposes fertilizing the ocean with urea, a nitrogen rich substance, to encourage phytoplankton growth.[67]
Australian company Ocean Nourishment Corporation (ONC) plans to sink hundreds of tonnes of urea into the ocean to boost CO
2-absorbing phytoplankton growth as a way to combat climate change. In 2007, Sydney-based ONC completed an experiment involving 1 tonne of nitrogen in the Sulu Sea off the Philippines.[68]
Mixing layers[]
Encouraging various ocean layers to mix can move nutrients and dissolved gases around, offering avenues for geoengineering.[69] Mixing may be achieved by placing large vertical pipes in the oceans to pump nutrient rich water to the surface, triggering blooms of algae, which store carbon when they grow and export carbon when they die.[69][70][71] This produces results somewhat similar to iron fertilization. One side-effect is a short-term rise in CO
2, which limits its attractiveness.[72]
Seaweed[]
Seaweed grow in shallow and coastal areas, and capture significant amounts of carbon that can be transported to the deep ocean by oceanic mechanisms; seaweed reaching the deep ocean sequester carbon and prevent it from exchanging with the atmosphere over millennia.[73] In addition, Seaweed grows very fast and can theoretically be harvested and processed to generate biomethane, via Anaerobic Digestion to generate electricity, via Cogeneration/CHP or as a replacement for natural gas. One study suggested that if seaweed farms covered 9% of the ocean they could produce enough biomethane to supply Earth's equivalent demand for fossil fuel energy, remove 53 gigatonnes of CO
2 per year from the atmosphere and sustainably produce 200 kg per year of fish, per person, for 10 billion people.[74] Ideal species for such farming and conversion include Laminaria digitata, Fucus serratus and Saccharina latissima.[75]
Physical processes[]

[]
Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage[]
Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) refers to biomass in power stations and boilers that use carbon capture and storage.[76][77] The carbon sequestered by the biomass would be captured and stored, thus removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.[78]
Burial[]
Burying biomass (such as trees)[79] directly, mimics the natural processes that created fossil fuels.[80]
Biochar burial[]
Biochar is charcoal created by pyrolysis of biomass waste. The resulting material is added to a landfill or used as a soil improver to create terra preta.[81][82] Addition of pyrogenic organic carbon (biochar) is a novel strategy to increase the soil-C stock for the long-term and to mitigate global-warming by offsetting the atmospheric C (up to 9.5 Gigatons C annually).[83]
In the soil, the carbon is unavailable for oxidation to CO
2 and consequential atmospheric release. This is one technique advocated by scientist James Lovelock, creator of the Gaia hypothesis.[84] According to Simon Shackley, "people are talking more about something in the range of one to two billion tonnes a year."[85] However concerns have been raised about Biochar potentially accelerating release of the carbon already present in the soil.[86]
The mechanisms related to biochar are referred to as bio-energy with carbon storage, BECS.
Ocean storage[]
If CO2 were to be injected to the ocean bottom, the pressures would be great enough for CO2 to be in its liquid phase. The idea behind ocean injection would be to have stable, stationary pools of CO2 at the ocean floor. The ocean could potentially hold over a thousand billion tons of CO2. However, this avenue of sequestration isn't being as actively pursued because of concerns about the impact on ocean life, and concerns about its stability.[87] A biological solution can be growing seaweed that can naturally be exported to the deep ocean, sequestering significant amounts of biomass in marine sediments.[73]
River mouths bring large quantities of nutrients and dead material from upriver into the ocean as part of the process that eventually produces fossil fuels. Transporting material such as crop waste out to sea and allowing it to sink exploits this idea to increase carbon storage.[88] International regulations on marine dumping may restrict or prevent use of this technique.
Geological sequestration[]
Geological sequestration refers to the storage of CO2 underground in depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline formations, or deep, un-minable coal beds.
Once CO2 is captured from a point source, such as a cement factory,[89] it would be compressed to ≈100 bar so that it would be a supercritical fluid. In this fluid form, the CO2 would be easy to transport via pipeline to the place of storage. The CO2 would then be injected deep underground, typically around 1 km, where it would be stable for hundreds to millions of years.[87] At these storage conditions, the density of supercritical CO2 is 600 to 800 kg / m3.[90]
The important parameters in determining a good site for carbon storage are: rock porosity, rock permeability, absence of faults, and geometry of rock layers. The medium in which the CO2 is to be stored ideally has a high porosity and permeability, such as sandstone or limestone. Sandstone can have a permeability ranging from 1 to 10−5 Darcy, and can have a porosity as high as ≈30%. The porous rock must be capped by a layer of low permeability which acts as a seal, or caprock, for the CO2. Shale is an example of a very good caprock, with a permeability of 10−5 to 10−9 Darcy. Once injected, the CO2 plume will rise via buoyant forces, since it is less dense than its surroundings. Once it encounters a caprock, it will spread laterally until it encounters a gap. If there are fault planes near the injection zone, there is a possibility the CO2 could migrate along the fault to the surface, leaking into the atmosphere, which would be potentially dangerous to life in the surrounding area. Another danger related to carbon sequestration is induced seismicity. If the injection of CO2 creates pressures that are too high underground, the formation will fracture, potentially causing an earthquake.[91]
While trapped in a rock formation, CO2 can be in the supercritical fluid phase or dissolve in groundwater/brine. It can also react with minerals in the geologic formation to precipitate carbonates. See CarbFix.
Worldwide storage capacity in oil and gas reservoirs is estimated to be 675–900 Gt CO2, and in un-minable coal seams is estimated to be 15–200 Gt CO2. Deep saline formations have the largest capacity, which is estimated to be 1,000–10,000 Gt CO2.[90] In the US, there is an estimated 160 Gt CO2 storage capacity.[91]
There are a number of large-scale carbon capture and sequestration projects that have demonstrated the viability and safety of this method of carbon storage, which are summarized here [92] by the Global CCS Institute. The dominant monitoring technique is seismic imaging, where vibrations are generated that propagate through the subsurface. The geologic structure can be imaged from the refracted/reflected waves.[91]
The first large-scale CO
2 sequestration project which began in 1996 is called Sleipner, and is located in the North Sea where Norway's StatoilHydro strips carbon dioxide from natural gas with amine solvents and disposed of this carbon dioxide in a deep saline aquifer. In 2000, a coal-fueled synthetic natural gas plant in Beulah, North Dakota, became the world's first coal-using plant to capture and store carbon dioxide, at the Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project.[93][needs update] Several other sequestration projects have followed. The Energy Impact Center launched the OPEN100 project in February 2020, which is the world's first open-source blueprint for the design, construction and financing of a small, standard, pressurized water reactor.[94] In September 2020, the US Department of Energy awarded $72 million in federal funding to support the development and advancement of carbon capture technologies.[95]
CO
2 has been used extensively in enhanced crude oil recovery operations in the United States beginning in 1972.[3] There are in excess of 10,000 wells that inject CO
2 in the state of Texas alone. The gas comes in part from anthropogenic sources, but is principally from large naturally occurring geologic formations of CO
2. It is transported to the oil-producing fields through a large network of over 5,000 kilometres (3,100 mi) of CO
2 pipelines. The use of CO
2 for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) methods in heavy oil reservoirs in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) has also been proposed.[96] However, transport cost remains an important hurdle. An extensive CO
2 pipeline system does not yet exist in the WCSB. Athabasca oil sands mining that produces CO
2 is hundreds of kilometers north of the subsurface Heavy crude oil reservoirs that could most benefit from CO
2 injection.
Chemical processes[]
Developed in the Netherlands, an electrocatalysis by a copper complex helps reduce carbon dioxide to oxalic acid;[97] This conversion uses carbon dioxide as a feedstock to generate oxalic acid.
Mineral carbonation[]
Carbon, in the form of CO
2 can be removed from the atmosphere by chemical processes, and stored in stable carbonate mineral forms. This process is known as 'carbon sequestration by mineral carbonation' or mineral sequestration. The process involves reacting carbon dioxide with abundantly available metal oxides–either magnesium oxide (MgO) or calcium oxide (CaO)–to form stable carbonates. These reactions are exothermic and occur naturally (e.g., the weathering of rock over geologic time periods).[98][99]
- CaO + CO
2 → CaCO
3
- MgO + CO
2 → MgCO
3
Calcium and magnesium are found in nature typically as calcium and magnesium silicates (such as forsterite and serpentinite) and not as binary oxides. For forsterite and serpentine the reactions are:
- Mg
2SiO
4 + 2 CO
2 → 2 MgCO
3 + SiO
2
- Mg
3Si
2O
5(OH)
4+ 3 CO
2 → 3 MgCO
3 + 2 SiO
2 + 2 H
2O
The following table lists principal metal oxides of Earth's crust. Theoretically up to 22% of this mineral mass is able to form carbonates.
| Part of a series on |
| Biogeochemical cycles |
|---|
 |
| Earthen Oxide | Percent of Crust | Carbonate | Enthalpy change (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO 2 |
59.71 | ||
| Al 2O 3 |
15.41 | ||
| CaO | 4.90 | CaCO 3 |
−179 |
| MgO | 4.36 | MgCO 3 |
−117 |
| Na 2O |
3.55 | Na 2CO 3 |
|
| FeO | 3.52 | FeCO 3 |
|
| K 2O |
2.80 | K 2CO 3 |
|
| Fe 2O 3 |
2.63 | FeCO 3 |
|
| 21.76 | All Carbonates |
These reactions are slightly more favorable at low temperatures.[98] This process occurs naturally over geologic time frames and is responsible for much of the Earth's surface limestone. The reaction rate can be made faster however, by reacting at higher temperatures and/or pressures, although this method requires some additional energy. Alternatively, the mineral could be milled to increase its surface area, and exposed to water and constant abrasion to remove the inert Silica as could be achieved naturally by dumping Olivine in the high energy surf of beaches.[100] Experiments suggest the weathering process is reasonably quick (one year) given porous basaltic rocks.[101][102]
CO
2 naturally reacts with peridotite rock in surface exposures of ophiolites, notably in Oman. It has been suggested that this process can be enhanced to carry out natural mineralisation of CO
2.[103][104]
When CO
2 is dissolved in water and injected into hot basaltic rocks underground it has been shown that the CO
2 reacts with the basalt to form solid carbonate minerals.[105] A test plant in Iceland started up in October 2017, extracting up to 50 tons of CO2 a year from the atmosphere and storing it underground in basaltic rock.[106]
Researchers from British Columbia, developed a low cost process for the production of magnesite, also known as magnesium carbonate, which can sequester CO2 from the air, or at the point of air pollution, e.g. at a power plant. The crystals are naturally occurring, but accumulation is usually very slow.[107]
Demolition concrete waste or recycled crushed concrete are also potential low cost materials for mineral carbonation as they are calcium-rich waste materials.[108]
Electrochemical method[]
Another method uses a liquid metal catalyst and an electrolyte liquid into which CO2 is dissolved. The CO2 then converts into solid flakes of carbon. This method is done at room temperature.[109][110][111]
Industrial use[]
Traditional cement manufacture releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, but newly developed cement types from Novacem[112] can absorb CO
2 from ambient air during hardening.[113] A similar technique was pioneered by TecEco, which has been producing "EcoCement" since 2002.[114] A Canadian startup CarbonCure takes captured CO2 and injects it into concrete as it is being mixed.[115] Carbon Upcycling UCLA is another company that uses CO
2 in concrete. Their concrete product is called CO2NCRETE™, a concrete that hardens faster and is more eco-friendly than traditional concrete.[116]
In Estonia, oil shale ash, generated by power stations could be used as sorbents for CO
2 mineral sequestration. The amount of CO
2 captured averaged 60 to 65% of the carbonaceous CO
2 and 10 to 11% of the total CO
2 emissions.[117]
Chemical scrubbers[]
Various carbon dioxide scrubbing processes have been proposed to remove CO
2 from the air, usually using a variant of the Kraft process. Carbon dioxide scrubbing variants exist based on potassium carbonate, which can be used to create liquid fuels, or on sodium hydroxide.[118][119][120] These notably include artificial trees proposed by Klaus Lackner to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere using chemical scrubbers.[121][122]
[]
Basalt storage[]
Carbon dioxide sequestration in basalt involves the injecting of CO
2 into deep-sea formations. The CO
2 first mixes with seawater and then reacts with the basalt, both of which are alkaline-rich elements. This reaction results in the release of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions forming stable carbonate minerals.[123]
Underwater basalt offers a good alternative to other forms of oceanic carbon storage because it has a number of trapping measures to ensure added protection against leakage. These measures include “geochemical, sediment, gravitational and hydrate formation.” Because CO
2 hydrate is denser than CO
2 in seawater, the risk of leakage is minimal. Injecting the CO
2 at depths greater than 2,700 meters (8,900 ft) ensures that the CO
2 has a greater density than seawater, causing it to sink.[124]
One possible injection site is Juan de Fuca plate. Researchers at the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory found that this plate at the western coast of the United States has a possible storage capacity of 208 gigatons. This could cover the entire current U.S. carbon emissions for over 100 years.[124]
This process is undergoing tests as part of the CarbFix project, resulting in 95% of the injected 250 tonnes of CO2 to solidify into calcite in 2 years, using 25 tonnes of water per tonne of CO2.[102][125]
Acid neutralisation[]
Carbon dioxide forms carbonic acid when dissolved in water, so ocean acidification is a significant consequence of elevated carbon dioxide levels, and limits the rate at which it can be absorbed into the ocean (the solubility pump). A variety of different bases have been suggested that could neutralize the acid and thus increase CO
2 absorption.[126][127][128][129][130] For example, adding crushed limestone to oceans enhances the absorption of carbon dioxide.[131] Another approach is to add sodium hydroxide to oceans which is produced by electrolysis of salt water or brine, while eliminating the waste hydrochloric acid by reaction with a volcanic silicate rock such as enstatite, effectively increasing the rate of natural weathering of these rocks to restore ocean pH.[132][133][134]
Obstacles[]
Rising fossil carbon extraction rates[]
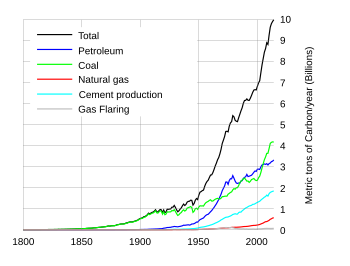
As of year 2019, fossil carbon extraction and burning by humans has added a total of 440 GtC (gigatons of carbon) to the atmospheric, oceanic, and terrestrial regions of the Earth's biosphere.[135] The majority has been added within the past half century.[136] Global extraction rates have increased at about 2% annually for many years, and now exceed 10 GtC/year.[137]
Financial costs[]
The use of the technology would add an additional 1–5 cents of cost per kilowatt hour, according to estimate made by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The financial costs of modern coal technology would nearly double if use of CCS technology were to be required by regulation.[138] The cost of CCS technology differs with the different types of capture technologies being used and with the different sites that it is implemented in, but the costs tend to increase with CCS capture implementation.[139] One study conducted predicted that with new technologies these costs could be lowered but would remain slightly higher than prices without CCS technologies.[140]
Energy requirements[]
The energy requirements of sequestration processes may be significant. In one paper, sequestration consumed 25 percent of the plant's rated 600 megawatt output capacity.[141]
Applications in climate change policies[]
United States[]
Starting in the mid-late 2010s, many pieces of US climate and environment policy have sought to make use of the climate change mitigation potential of carbon sequestration. Many of these policies involve either conservation of carbon sink ecosystems, such as forests and wetlands, or encouraging agricultural and land use practices designed to increase carbon sequestration such as carbon farming or agroforestry, often through financial incentivization for farmers and landowners.
The Executive Order on Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad, signed by president Joe Biden on January 27, 2021, includes several mentions of carbon sequestration via conservation and restoration of carbon sink ecosystems, such as wetlands and forests. These include emphasizing the importance of farmers, landowners, and coastal communities in carbon sequestration, directing the Treasury Department to promote conservation of carbon sinks through market based mechanisms, and directing the Department of the Interior to collaborate with other agencies to create a Civilian Climate Corps to increase carbon sequestration in agriculture, among other things.[142]
Several pieces of legislation introduced in the 116th and 117th Congresses, including the Climate Stewardship Act of 2019,[143] the Ocean Based Climate Solutions Act of 2020,[144] the Healthy Soil, Resilient Farmers Act of 2020,[145] and the Healthy Soils Healthy Climate Act of 2020,[146] have sought to increase carbon sequestration on private and public lands through financial incentivization.
Several state governments, including California, Hawaii, Maryland, and New York, have passed versions of a carbon farming tax credit, which seek to improve soil health and increase carbon sequestration by offering financial assistance and incentives for farmers who practice regenerative agriculture, carbon farming, and other climate change mitigation practices.[147][148][149][150][151] The California Healthy Soils Program is estimated to have resulted in 109,809 metric tons of CO
2 being sequestered annually on average.[150]
The White House and USDA are reportedly developing plans to use $30 billion in funds from the Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) for the creation of a carbon bank program, which would involve giving carbon credits to farmers and landowners in return for adopting carbon sequestration practices, which they could then sell in a cap and trade market.[152][153]
Some environmental activists and politicians have criticized carbon capture, and storage or sequestration (CCS) as a false solution to the climate crisis. They cite the role of the fossil fuel industry in origins of the technology and in lobbying for CCS focused legislation and argue that it would allow the industry to "greenwash" itself by funding and engaging in things such as tree planting campaigns without significantly cutting their carbon emissions.[154][155]
See also[]
- Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage
- Blue carbon
- Repurposing offshore drilling rigs for storing carbon
References[]
- ^ "CCS Explained". UKCCSRC. Retrieved June 27, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Sedjo, Roger; Sohngen, Brent (2012). "Carbon Sequestration in Forests and Soils". Annual Review of Resource Economics. 4: 127–144. doi:10.1146/annurev-resource-083110-115941.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Hodrien, Chris (October 24, 2008). Squaring the Circle on Coal – Carbon Capture and Storage. Claverton Energy Group Conference, Bath. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 31, 2009. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Geoengineering the climate: science, governance and uncertainty". The Royal Society. 2009. Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ^ Minx, Jan C; Lamb, William F; Callaghan, Max W; Fuss, Sabine; Hilaire, Jérôme; Creutzig, Felix; Amann, Thorben; Beringer, Tim; De Oliveira Garcia, Wagner; Hartmann, Jens; Khanna, Tarun; Lenzi, Dominic; Luderer, Gunnar; Nemet, Gregory F; Rogelj, Joeri; Smith, Pete; Vicente Vicente, Jose Luis; Wilcox, Jennifer; Del Mar Zamora Dominguez, Maria (2018). "Negative emissions: Part 1 – research landscape and synthesis" (PDF). Environmental Research Letters. 13 (6): 063001. Bibcode:2018ERL....13f3001M. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/aabf9b.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Energy Terms Glossary S". Nebraska Energy Office. Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Pagnamenta, Robin (December 1, 2009). "Carbon must be sucked from air, says IPCC chief Rajendra Pachauri". Times Online. London. Retrieved December 13, 2009.
- ^ Harvey, Fiona (June 5, 2011). "Global warming crisis may mean world has to suck greenhouse gases from air". Guardian Online. Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ^ Hollo, Tim (January 15, 2009). "Negative emissions needed for a safe climate". Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ^ "National Geographic Magazine - NGM.com". Ngm.nationalgeographic.com. April 25, 2013. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ "Snatching Carbon Dioxide from the Atmosphere" (PDF). Cdmc.epp.cmu.edu. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 28, 2013. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ Abdulla, Ahmed; Hanna, Ryan; Schell, Kristen R.; Babacan, Oytun; et al. (December 29, 2021). "Explaining successful and failed investments in U.S. carbon capture and storage using empirical and expert assessments". Environmental Research Letters. 16 (1): 014036. Bibcode:2021ERL....16a4036A. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/abd19e.
- ^ "Glossary of climate change acronyms". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Archived from the original on March 30, 2018. Retrieved July 15, 2010.
- ^ "Alberta producers rewarded for use of CO
2 in enhanced oil recovery". PointCarbon. May 25, 2004. Archived from the original on May 6, 2008. Retrieved August 21, 2015. - ^ Beerling, David (2008). The Emerald Planet: How Plants Changed Earth's History. Oxford University Press. pp. 194–5. ISBN 978-0-19-954814-9.
- ^ National Academies Of Sciences, Engineering (2019). Negative Emissions Technologies and Reliable Sequestration: A Research Agenda. Washington, D.C.: National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. pp. 45–136. doi:10.17226/25259. ISBN 978-0-309-48452-7. PMID 31120708.
- ^ Strack, Maria, ed. (2008). Peatlands and climate change. Calgary: University of Calgary. pp. 13–23. ISBN 978-952-99401-1-0.
- ^ Lovett, Richard (May 3, 2008). "Burying biomass to fight climate change". New Scientist (2654). Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ McDermott, Matthew (August 22, 2008). "Can Aerial Reforestation Help Slow Climate Change? Discovery Project Earth Examines Re-Engineering the Planet's Possibilities". TreeHugger. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Gorte, Ross W. (March 29, 2007). CRS Report for Congress: Carbon Sequestration in Forests (PDF) (Report). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ Wang, Brian. "We Have Room to Add 35% More Trees Globally to Store 580-830 Billion Tons of CO2 – NextBigFuture.com". www.nextbigfuture.com.
- ^ Bastin, Jean-Francois; Finegold, Yelena; Garcia, Claude; Mollicone, Danilo; Rezende, Marcelo; Routh, Devin; Zohner, Constantin M.; Crowther, Thomas W. (July 5, 2019). "The global tree restoration potential". Science. 365 (6448): 76–79. Bibcode:2019Sci...365...76B. doi:10.1126/science.aax0848. PMID 31273120. S2CID 195804232.
- ^ Tutton, Mark (July 4, 2019). "Restoring forests could capture two-thirds of the carbon humans have added to the atmosphere". CNN.
- ^ Chazdon, Robin; Brancalion, Pedro (July 5, 2019). "Restoring forests as a means to many ends". Science. 365 (6448): 24–25. Bibcode:2019Sci...365...24C. doi:10.1126/science.aax9539. PMID 31273109. S2CID 195804244.
- ^ Toussaint, Kristin (January 27, 2020). "Building with timber instead of steel could help pull millions of tons of carbon from the atmosphere". Fast Company. Retrieved January 29, 2020.
- ^ Churkina, Galina; Organschi, Alan; Reyer, Christopher P. O.; Ruff, Andrew; Vinke, Kira; Liu, Zhu; Reck, Barbara K.; Graedel, T. E.; Schellnhuber, Hans Joachim (January 27, 2020). "Buildings as a global carbon sink". Nature Sustainability. 3 (4): 269–276. doi:10.1038/s41893-019-0462-4. ISSN 2398-9629. S2CID 213032074.
- ^ "Annual CO2 emissions worldwide 2019". Statista. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Hüblová, Lucie; Frouz, Jan (July 15, 2021). "Contrasting effect of coniferous and broadleaf trees on soil carbon storage during reforestation of forest soils and afforestation of agricultural and post-mining soils". Journal of Environmental Management. 290: 112567. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112567. ISSN 0301-4797. PMID 33866087.
- ^ McPherson, E. Gregory; Xiao, Qingfu; Aguaron, Elena (December 2013). "A new approach to quantify and map carbon stored, sequestered and emissions avoided by urban forests" (PDF). Landscape and Urban Planning. 120: 70–84. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2013.08.005. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Velasco, Erik; Roth, Matthias; Norford, Leslie; Molina, Luisa T. (April 2016). "Does urban vegetation enhance carbon sequestration?". Landscape and Urban Planning. 148: 99–107. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.12.003.
- ^ US EPA, OW (July 27, 2018). "Basic Information about Wetland Restoration and Protection". US EPA. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b US Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. "What is Blue Carbon?". oceanservice.noaa.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Mitsch, William J.; Bernal, Blanca; Nahlik, Amanda M.; Mander, Ülo; Zhang, Li; Anderson, Christopher J.; Jørgensen, Sven E.; Brix, Hans (April 1, 2013). "Wetlands, carbon, and climate change". Landscape Ecology. 28 (4): 583–597. doi:10.1007/s10980-012-9758-8. ISSN 1572-9761. S2CID 11939685.
- ^ Valach, Alex C.; Kasak, Kuno; Hemes, Kyle S.; Anthony, Tyler L.; Dronova, Iryna; Taddeo, Sophie; Silver, Whendee L.; Szutu, Daphne; Verfaillie, Joseph; Baldocchi, Dennis D. (March 25, 2021). "Productive wetlands restored for carbon sequestration quickly become net CO2 sinks with site-level factors driving uptake variability". PLOS ONE. 16 (3): e0248398. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1648398V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0248398. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 7993764. PMID 33765085.
- ^ Bu, Xiaoyan; Cui, Dan; Dong, Suocheng; Mi, Wenbao; Li, Yu; Li, Zhigang; Feng, Yaliang (January 2020). "Effects of Wetland Restoration and Conservation Projects on Soil Carbon Sequestration in the Ningxia Basin of the Yellow River in China from 2000 to 2015". Sustainability. 12 (24): 10284. doi:10.3390/su122410284.
- ^ Badiou, Pascal; McDougal, Rhonda; Pennock, Dan; Clark, Bob (June 1, 2011). "Greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sequestration potential in restored wetlands of the Canadian prairie pothole region". Wetlands Ecology and Management. 19 (3): 237–256. doi:10.1007/s11273-011-9214-6. ISSN 1572-9834. S2CID 30476076.
- ^ "Restoring Wetlands - Wetlands (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "Hurricane Sandy Recovery | U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service". www.fws.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "A new partnership for wetland restoration | ICPDR - International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River". www.icpdr.org. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Fact Sheet: Blue Carbon". American University. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "Carbon Sequestration in Wetlands | MN Board of Water, Soil Resources". bwsr.state.mn.us. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Poeplau, Christopher; Don, Axel (February 1, 2015). "Carbon sequestration in agricultural soils via cultivation of cover crops – A meta-analysis". Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. 200 (Supplement C): 33–41. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2014.10.024.
- ^ Goglio, Pietro; Smith, Ward N.; Grant, Brian B.; Desjardins, Raymond L.; McConkey, Brian G.; Campbell, Con A.; Nemecek, Thomas (October 1, 2015). "Accounting for soil carbon changes in agricultural life cycle assessment (LCA): a review". Journal of Cleaner Production. 104: 23–39. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.040. ISSN 0959-6526.
- ^ Blakemore, R.J. (November 2018). "Non-flat Earth Recalibrated for Terrain and Topsoil". Soil Systems. 2 (4): 64. doi:10.3390/soilsystems2040064.
- ^ Biggers, Jeff (November 20, 2015). "Iowa's Climate-Change Wisdom". New York Times. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved November 21, 2015.
- ^ VermEcology (November 11, 2019). "Earthworm Cast Carbon Storage".
- ^ Viswanath, Syam; Subbanna, Sruthi (October 12, 2017). Carbon sequestration potential in bamboos – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Tarnocai, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Kuhry, P.; Mazhitova, G.; Zimov, S. (June 1, 2009). "Soil organic carbon pools in the northern circumpolar permafrost region". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 23 (2): GB2023. Bibcode:2009GBioC..23.2023T. doi:10.1029/2008gb003327. ISSN 1944-9224.
- ^ Schmidt, Michael W. I.; Torn, Margaret S.; Abiven, Samuel; Dittmar, Thorsten; Guggenberger, Georg; Janssens, Ivan A.; Kleber, Markus; Kögel-Knabner, Ingrid; Lehmann, Johannes; Manning, David A. C.; Nannipieri, Paolo; Rasse, Daniel P.; Weiner, Steve; Trumbore, Susan E. (October 2011). "Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property". Nature. 478 (7367): 49–56. Bibcode:2011Natur.478...49S. doi:10.1038/nature10386. PMID 21979045. S2CID 3461265.
- ^ Kleber M, Eusterhues K, Keiluweit M, Mikutta C, Nico PS (2015). "Mineral - Organic Associations : Formation, Properties, and Relevance in Soil Environments". In Sparks DL (ed.). Advances in Agronomy. 130. Academic Press. pp. 1–140. doi:10.1016/bs.agron.2014.10.005. ISBN 9780128021378.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "FACTBOX: Carbon farming on rise in Australia". Reuters. June 16, 2009. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Vindušková, Olga; Frouz, Jan (July 1, 2013). "Soil carbon accumulation after open-cast coal and oil shale mining in Northern Hemisphere: a quantitative review". Environmental Earth Sciences. 69 (5): 1685–1698. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2004-5. ISSN 1866-6299. S2CID 129185046.
- ^ Frouz, Jan; Livečková, Miluše; Albrechtová, Jana; Chroňáková, Alica; Cajthaml, Tomáš; Pižl, Václav; Háněl, Ladislav; Starý, Josef; Baldrian, Petr; Lhotáková, Zuzana; Šimáčková, Hana; Cepáková, Šárka (December 1, 2013). "Is the effect of trees on soil properties mediated by soil fauna? A case study from post-mining sites". Forest Ecology and Management. 309: 87–95. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2013.02.013. ISSN 0378-1127.
- ^ Sundermeiera, A.P.; Islam, K.R.; Raut, Y.; Reeder, R.C.; Dick, W.A. (September 2010). "Continuous No-Till Impacts on Soil Biophysical Carbon Sequestration". Soil Science Society of America Journal. 75 (5): 1779–1788. Bibcode:2011SSASJ..75.1779S. doi:10.2136/sssaj2010.0334.
- ^ Smith, Pete; Martino, Daniel; Cai, Zucong; et al. (February 2008). "Greenhouse gas mitigation in agriculture". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 363 (1492): 789–813. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.2184. PMC 2610110. PMID 17827109..
- ^ "Environmental Co Benefits of Sequestration Practices. 2006. June 1, 2009". Archived from the original on May 11, 2009.
- ^ Lal, R. (June 11, 2004). "Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security". Science. 304 (5677): 1623–1627. Bibcode:2004Sci...304.1623L. doi:10.1126/science.1097396. PMID 15192216. S2CID 8574723.
- ^ "Addressing Reversibility (Duration) for Projects". US Environmental Protection Agency. 2006. June 1, 2009. Archived from the original on October 13, 2008.
- ^ Renwick, A.; Ball, A.; Pretty, J.N. (August 2002). "Biological and Policy Constraints on the Adoption of Carbon Farming in Temperate Regions". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 360 (1797): 1721–40. Bibcode:2002RSPTA.360.1721R. doi:10.1098/rsta.2002.1028. PMID 12460494. S2CID 41627741. pp. 1722, 1726–29.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Traufetter, Gerald (January 2, 2009). "Cold Carbon Sink: Slowing Global Warming with Antarctic Iron". Spiegel Online. Archived from the original on April 13, 2017. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Jin, X.; Gruber, N.; Frenzel1, H.; Doney, S.C.; McWilliams, J.C. (2008). "The impact on atmospheric CO
2 of iron fertilization induced changes in the ocean's biological pump". Biogeosciences. 5 (2): 385–406. Bibcode:2008BGeo....5..385J. doi:10.5194/bg-5-385-2008. Retrieved May 9, 2010. - ^ Monastersky, Richard (September 30, 1995). "Iron versus the Greenhouse - Oceanographers cautiously explore a global warming therapy". Science News. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Monastersky, Richard (September 30, 1995). "Iron versus the Greenhouse: Oceanographers cautiously explore a global warming therapy". Science News. 148 (14): 220–222. doi:10.2307/4018225. JSTOR 4018225.
- ^ "WWF condemns Planktos Inc. iron-seeding plan in the Galapagos". Geoengineering Monitor. June 27, 2007. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ Fogarty, David (December 15, 2008). "Scientists urge caution in ocean-CO
2 capture schemes". Alertnet.org. Archived from the original on August 3, 2009. Retrieved May 9, 2010. - ^ Lavery, Trish J.; Roudnew, Ben; Gill, Peter; et al. (October 11, 2010). "Iron defecation by sperm whales stimulates carbon export in the Southern Ocean". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 277 (1699): 3527–3531. doi:10.1098/rspb.2010.0863. PMC 2982231. PMID 20554546.
- ^ "Multiplying the ocean's CO2 guzzlers". February 19, 2007 – via news.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ Salleh, Anna (November 9, 2007). "Urea 'climate solution' may backfire". ABC Science. Australian Broadcasting Commission. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lovelock, James E.; Rapley, Chris G. (September 27, 2007). "Ocean pipes could help the earth to cure itself". Nature. 449 (7161): 403. Bibcode:2007Natur.449..403L. doi:10.1038/449403a. PMID 17898747.
- ^ Pearce, Fred (September 26, 2007). "Ocean pumps could counter global warming". New Scientist. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Duke, John H. (2008). "A proposal to force vertical mixing of the Pacific Equatorial Undercurrent to create a system of equatorially trapped coupled convection that counteracts global warming" (PDF). Geophysical Research Abstracts. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Dutreuil, S.; Bopp, L.; Tagliabue, A. (May 25, 2009). "Impact of enhanced vertical mixing on marine biogeochemistry: lessons for geo-engineering and natural variability". Biogeosciences. 6 (5): 901–912. Bibcode:2009BGeo....6..901D. doi:10.5194/bg-6-901-2009. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ortega, Alejandra; Geraldi, N.R.; Alam, I.; Kamau, A.A.; Acinas, S.; Logares, R.; Gasol, J.; Massana, R.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Duarte, C. (2019). "Important contribution of macroalgae to oceanic carbon sequestration". Nature Geoscience. 12 (9): 748–754. Bibcode:2019NatGe..12..748O. doi:10.1038/s41561-019-0421-8. hdl:10754/656768. S2CID 199448971.
- ^ Flannery, Tim (November 20, 2015). "Climate crisis: seaweed, coffee and cement could save the planet". The Guardian. Retrieved November 25, 2015.
- ^ Vanegasa, C. H.; Bartletta, J. (February 11, 2013). "Green energy from marine algae: biogas production and composition from the anaerobic digestion of Irish seaweed species". Environmental Technology. 34 (15): 2277–2283. doi:10.1080/09593330.2013.765922. PMID 24350482. S2CID 30863033.
- ^ Fisher, Brian; Nakicenovic, Nebojsa; et al. (2007). "Issues related to mitigation in the long term context, In Climate Change 2007: Mitigation." (PDF). Fourth Assessment Report of the Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change (Report). Cambridge University Press. Retrieved August 21, 2015.
- ^ Obersteiner, M.; Azar, Christian; Kauppi, P.; et al. (October 26, 2001). "Managing climate risk". Science. 294 (5543): 786–87. doi:10.1126/science.294.5543.786b. PMID 11681318. S2CID 34722068.
- ^ Azar, Christian; et al. (January 2006). "Carbon Capture and Storage From Fossil Fuels and Biomass – Costs and Potential Role in Stabilizing the Atmosphere" (PDF). Climatic Change. 74 (1–3): 47–79. Bibcode:2006ClCh...74...47A. doi:10.1007/s10584-005-3484-7. S2CID 4850415.
- ^ Zeng, Ning (2008). "Carbon sequestration via wood burial". Carbon Balance and Management. 3 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/1750-0680-3-1. PMC 2266747. PMID 18173850.
- ^ Lovett, Richard (May 3, 2008). "Burying biomass to fight climate change". New Scientist (2654). Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Lehmann, J.; Gaunt, J.; Rondon, M. (2006). "Bio-char sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems – a review" (PDF). Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change (Submitted manuscript). 11 (2): 403–427. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.183.1147. doi:10.1007/s11027-005-9006-5. S2CID 4696862.
- ^ "International Biochar Initiative | International Biochar Initiative". Biochar-international.org. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Yousaf, Balal; Liu, Guijian; Wang, Ruwei; Abbas, Qumber; Imtiaz, Muhammad; Liu, Ruijia (2016). "Investigating the biochar effects on C-mineralization and sequestration of carbon in soil compared with conventional amendments using stable isotope (δ13C) approach". GCB Bioenergy. 9 (6): 1085–1099. doi:10.1111/gcbb.12401.
- ^ Gaia Vince (January 23, 2009). "One last chance to save mankind". New Scientist. Archived from the original on April 1, 2009. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Harvey, Fiona (February 27, 2009). "Black is the new green". Financial Times. Retrieved March 4, 2009.
- ^ Wardle, David A.; Nilsson, Marie-Charlotte; Zackrisson, Olle (May 2, 2008). "Fire-Derived Charcoal Causes Loss of Forest Humus". Science. 320 (5876): 629. Bibcode:2008Sci...320..629W. doi:10.1126/science.1154960. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 18451294. S2CID 22192832.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Benson, S.M.; Surles, T. (October 1, 2006). "Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage: An Overview With Emphasis on Capture and Storage in Deep Geological Formations". Proceedings of the IEEE. 94 (10): 1795–1805. doi:10.1109/JPROC.2006.883718. ISSN 0018-9219. S2CID 27994746.
- ^ Stuart E. Strand; Benford, Gregory (January 12, 2009). "Ocean Sequestration of Crop Residue Carbon: Recycling Fossil Fuel Carbon Back to Deep Sediments". Environmental Science & Technology. 43 (4): 1000–1007. Bibcode:2009EnST...43.1000S. doi:10.1021/es8015556. PMID 19320149.
- ^ Morgan, Sam (September 6, 2019). "Norway's carbon storage project boosted by European industry". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved June 27, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Aydin, Gokhan; Karakurt, Izzet; Aydiner, Kerim (September 1, 2010). "Evaluation of geologic storage options of CO2: Applicability, cost, storage capacity and safety". Energy Policy. Special Section on Carbon Emissions and Carbon Management in Cities with Regular Papers. 38 (9): 5072–5080. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2010.04.035.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Smit, Berend; Reimer, Jeffrey A.; Oldenburg, Curtis M.; Bourg, Ian C. (2014). Introduction to Carbon Capture and Sequestration. London: Imperial College Press. ISBN 978-1783263288.
- ^ "Large-scale CCS facilities". www.globalccsinstitute.com. Global Carbon Capture and Storage Institute.
- ^ "Weyburn-Midale CO
2 Project, World's first CO
2 measuring, monitoring and verification initiative". Petroleum Technology Research Centre. Retrieved April 9, 2009. - ^ "Last Energy raises $3 million to fight climate change with nuclear energy". VentureBeat. February 25, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ "Department of Energy Invests $72 Million in Carbon Capture Technologies". Energy.gov. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ "Subscription Verification". Dailyoilbulletin.com. Retrieved May 9, 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Bouwman, Elisabeth; Angamuthu, Raja; Byers, Philip; Lutz, Martin; Spek, Anthony L. (July 15, 2010). "Electrocatalytic CO2 Conversion to Oxalate by a Copper Complex". Science. 327 (5393): 313–315. Bibcode:2010Sci...327..313A. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1009.2076. doi:10.1126/science.1177981. PMID 20075248. S2CID 24938351.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Herzog, Howard (March 14, 2002). "Carbon Sequestration via Mineral Carbonation: Overview and Assessment" (PDF). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Retrieved March 5, 2009. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ {“integral part of an established curriculum”Goldberg, Philip; Zhong-Ying Chen; O'Connor, William; Walters, Richard; Ziock Hans (1998). "CO
2 Mineral Sequestration Studies in US" (PDF). National Energy Technology Laboratory. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 7, 2003. Retrieved March 6, 2009. Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Schuiling, R.D.; Boer, de P.L. (2011). "Rolling stones; fast weathering of olivine in shallow seas for cost-effective CO2 capture and mitigation of global warming and ocean acidification" (PDF). Earth System Dynamics Discussions. 2 (2): 551–568. Bibcode:2011ESDD....2..551S. doi:10.5194/esdd-2-551-2011. hdl:1874/251745.
- ^ Yirka, Bob. "Researchers find carbon reactions with basalt can form carbonate minerals faster than thought". Phys.org. Omicron Technology Ltd. Retrieved April 25, 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Matter, Juerg M.; Stute, Martin; Snæbjörnsdottir, Sandra O.; Oelkers, Eric H.; Gislason, Sigurdur R.; Aradottir, Edda S.; Sigfusson, Bergur; Gunnarsson, Ingvi; Sigurdardottir, Holmfridur; Gunlaugsson, Einar; Axelsson, Gudni; Alfredsson, Helgi A.; Wolff-Boenisch, Domenik; Mesfin, Kiflom; Fernandez de la Reguera Taya, Diana; Hall, Jennifer; Dideriksen, Knud; Broecker, Wallace S. (June 10, 2016). "Rapid carbon mineralization for permanent disposal of anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions". Science. 352 (6291): 1312–1314. Bibcode:2016Sci...352.1312M. doi:10.1126/science.aad8132. PMID 27284192.
- ^ Peter B. Kelemen1 and Jürg Matter (November 3, 2008). "In situ carbonation of peridotite for CO
2 storage". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 105 (45): 17295–300. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10517295K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805794105. PMC 2582290. - ^ Timothy Gardner (November 7, 2008). "Scientists say a rock can soak up carbon dioxide | Reuters". Uk.reuters.com. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Le Page, Michael (June 19, 2016). "CO2 injected deep underground turns to rock – and stays there". New Scientist. Retrieved December 4, 2017.
- ^ Proctor, Darrell (December 1, 2017). "Test of Carbon Capture Technology Underway at Iceland Geothermal Plant". POWER Magazine. Retrieved December 4, 2017.
- ^ "This carbon-sucking mineral could help slow down climate change". Fast Company. 2018.
- ^ Jorat, M.; Aziz, Maniruzzaman; Marto, Aminaton; Zaini, Nabilah; Jusoh, Siti; Manning, David (2018). "Sequestering Atmospheric CO2 Inorganically: A Solution for Malaysia's CO2 Emission". Geosciences. 8 (12): 483. Bibcode:2018Geosc...8..483J. doi:10.3390/geosciences8120483.
- ^ Esrafilzadeh, Dorna; Zavabeti, Ali; Jalili, Rouhollah; Atkin, Paul; Choi, Jaecheol; Carey, Benjamin J.; Brkljača, Robert; O’Mullane, Anthony P.; Dickey, Michael D.; Officer, David L.; MacFarlane, Douglas R.; Daeneke, Torben; Kalantar-Zadeh, Kourosh (February 26, 2019). "Room temperature CO 2 reduction to solid carbon species on liquid metals featuring atomically thin ceria interfaces". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 865. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10..865E. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08824-8. PMC 6391491. PMID 30808867.
- ^ "Climate rewind: Scientists turn carbon dioxide back into coal". www.rmit.edu.au.
- ^ "Scientists turn CO2 'back into coal' in breakthrough carbon capture experiment". The Independent. February 26, 2019.
- ^ "Novacem". Imperial Innovations. May 6, 2008. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Jha, Alok (December 31, 2008). "Revealed: The cement that eats carbon dioxide". The Guardian. London. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ "Home". TecEco. July 1, 1983. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Lord, Bronte. "This concrete can trap CO2 emissions forever". CNNMoney. Retrieved June 17, 2018.
- ^ "UCLA researchers turn carbon dioxide into sustainable concrete". Retrieved December 17, 2018.
- ^ Uibu, Mai; Uus, Mati; Kuusik, Rein (February 2008). "CO
2 mineral sequestration in oil-shale wastes from Estonian power production". Journal of Environmental Management. 90 (2): 1253–60. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.07.012. PMID 18793821. - ^ Chang, Kenneth (February 19, 2008). "Scientists Would Turn Greenhouse Gas Into Gasoline". The New York Times. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ Frank Zeman (2007). "Energy and Material Balance of CO2 Capture from Ambient Air". Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (21): 7558–63. Bibcode:2007EnST...41.7558Z. doi:10.1021/es070874m. PMID 18044541.
- ^ "Chemical 'sponge' could filterCO
2 from the air". New Scientist. October 3, 2007. Retrieved May 9, 2010. - ^ "New Device Vacuums Away Carbon Dioxide". LiveScience. May 1, 2007. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ Adam, David (May 31, 2008). "Could US scientist's 'CO
2 catcher' help to slow warming?". The Guardian. London. Retrieved April 3, 2010. - ^ David S. Goldberg; Taro Takahashi; Angela L. Slagle (2008). "Carbon dioxide sequestration in deep-sea basalt". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 105 (29): 9920–25. Bibcode:2008PNAS..105.9920G. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804397105. PMC 2464617. PMID 18626013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Carbon storage in undersea basalt offers extra security". environmentalresearchweb. July 15, 2008. Archived from the original on August 2, 2009. Retrieved May 9, 2010.
- ^ "Scientists turn carbon dioxide into stone to combat global warming". The Verge. Vox Media. June 10, 2016. Retrieved June 11, 2016.
- ^ Kheshgi, H.S. (1995). "Sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide by increasing ocean alkalinity". Energy. 20 (9): 915–922. doi:10.1016/0360-5442(95)00035-F.
- ^ K.S. Lackner; C.H. Wendt; D.P. Butt; E.L. Joyce; D.H. Sharp (1995). "Carbon dioxide disposal in carbonate minerals". Energy. 20 (11): 1153–70. doi:10.1016/0360-5442(95)00071-N.
- ^ K.S. Lackner; D.P. Butt; C.H. Wendt (1997). "Progress on binding CO
2 in mineral substrates". Energy Conversion and Management (Submitted manuscript). 38: S259–S264. doi:10.1016/S0196-8904(96)00279-8. - ^ Rau, Greg H.; Caldeira, Ken (November 1999). "Enhanced carbonate dissolution: A means of sequestering waste CO
2 as ocean bicarbonate". Energy Conversion and Management. 40 (17): 1803–1813. doi:10.1016/S0196-8904(99)00071-0. - ^ Rau, Greg H.; Knauss, Kevin G.; Langer, William H.; Caldeira, Ken (August 2007). "Reducing energy-related CO
2 emissions using accelerated weathering of limestone". Energy. 32 (8): 1471–7. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2006.10.011. - ^ Harvey, L.D.D. (2008). "Mitigating the atmospheric CO
2 increase and ocean acidification by adding limestone powder to upwelling regions". Journal of Geophysical Research. 113: C04028. Bibcode:2008JGRC..11304028H. doi:10.1029/2007JC004373. S2CID 54827652. - ^ "Scientists enhance Mother Nature's carbon handling mechanism". Penn State Live. November 7, 2007. Archived from the original on June 3, 2010.
- ^ Kurt Zenz House; Christopher H. House; Daniel P. Schrag; Michael J. Aziz (2007). "Electrochemical Acceleration of Chemical Weathering as an Energetically Feasible Approach to Mitigating Anthropogenic Climate Change". Environ. Sci. Technol. 41 (24): 8464–8470. Bibcode:2007EnST...41.8464H. doi:10.1021/es0701816. PMID 18200880.
- ^ Clover, Charles (November 7, 2007). "Global warming 'cure' found by scientists". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on April 11, 2009. Retrieved April 3, 2010.
- ^ Friedlingstein, P., Jones, M., O'Sullivan, M., Andrew, R., Hauck, J., Peters, G., Peters, W., Pongratz, J., Sitch, S., Le Quéré, C. and 66 others (2019) "Global carbon budget 2019". Earth System Science Data, 11(4): 1783–1838. doi:10.5194/essd-11-1783-2019.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- ^ Heede, R. (2014). "Tracing anthropogenic carbon dioxide and methane emissions to fossil fuel and cement producers, 1854–2010". Climatic Change. 122 (1–2): 229–241. Bibcode:2014ClCh..122..229H. doi:10.1007/s10584-013-0986-y.
- ^ Hannah Ritchie and Max Roser (2020). "CO₂ and Greenhouse Gas Emissions: CO₂ Emissions by Fuel". Our World in Data. Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved October 30, 2020.
- ^ DeMonte, Adena (July 2007). "The Cost of Carbon Capture". Gigaom. Retrieved August 21, 2015.[unreliable source?]
- ^ Gibbins, Jon; Chalmers, Hannah (December 2008). "Carbon Capture and Storage" (PDF). Energy Policy. 36 (12): 4317–4322. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.370.8479. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2008.09.058.
- ^ David, Jeremy; Herzog, Howard (2012). "The Cost of Carbon Capture" (PDF). BASE. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
- ^ Spath, Pamela L.; Mann, Margaret K. (September 22, 2002). The Net Energy and Global Warming Potential of Biomass Power compared to Coal-fired Electricity with CO2 Sequestration – A Life Cycle Approach (PDF). Bioenergy 2002 Bioenergy for the Environment. Boise, Idaho. Retrieved August 21, 2015.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Executive Order on Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad". The White House. January 27, 2021. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Haaland, Debra A. (September 16, 2019). "Text - H.R.4269 - 116th Congress (2019-2020): Climate Stewardship Act of 2019". www.congress.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Grijalva, Raul M. (November 17, 2020). "H.R.8632 - 116th Congress (2019-2020): Ocean-Based Climate Solutions Act of 2020". www.congress.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Spanberger, Abigail Davis (October 1, 2020). "Text - H.R.8057 - 116th Congress (2019-2020): Healthy Soil, Resilient Farmers Act of 2020". www.congress.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Wyden, Ron (October 23, 2020). "Text - S.4850 - 116th Congress (2019-2020): Healthy Soils Healthy Climate Act of 2020". www.congress.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "6 States Tapping into the Benefits of Carbon Farming – Soil Solutions". Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "Greenhouse Gas Sequestration Task Force". planning.hawaii.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "Maryland HB1063 | 2017 | Regular Session". LegiScan. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "CDFA - OEFI - Healthy Soils Program". www.cdfa.ca.gov. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "NY State Senate Bill S4707". NY State Senate. February 9, 2021. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Plume, Karl (February 2, 2021). "USDA can steer farm aid money to fight climate change, Biden ag secretary nominee says". Reuters. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ "A 'carbon bank' could mean extra cash for Midwest farmers". MPR News. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Volcovici, Timothy Gardner, Valerie (March 9, 2020). "Where Biden and Sanders diverge on climate change". Reuters. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- ^ Stone, Maddie (September 16, 2019). "Why Are Progressives Wary of Technologies That Pull Carbon From the Air?". Rolling Stone. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
External links[]
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Carbon sequestration |
| Scholia has a profile for carbon sequestration (Q15305550). |
- Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum International carbon capture and storage initiative.
- UK Carbon Capture and Storage Consortium Overview of the UK academic consortium focused on researching issues related to Carbon Capture and Storage.
- Carbon Sequestration: Science, Technology, and Policy MIT program covers carbon capture and storage (CCS)
- Carbon capture and sequestration
- Forestry and the environment
- Emissions reduction
- Sustainable food system
