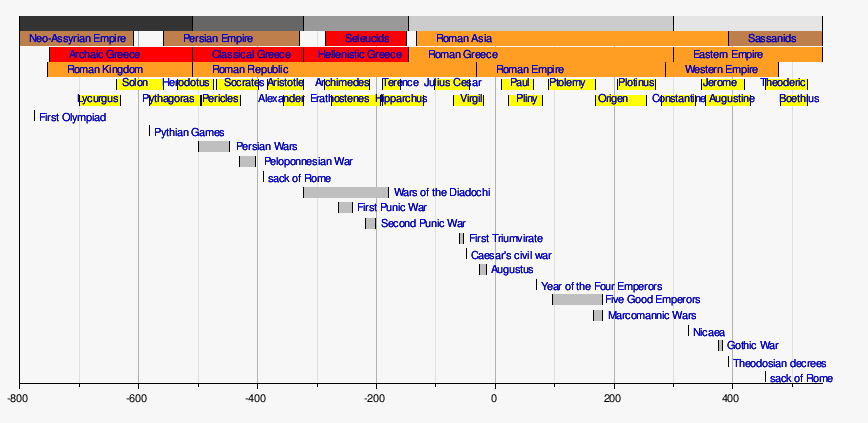
Outline of classical studies
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to classical studies:
Classical studies (Classics for short) – earliest branch of the humanities, which covers the languages, literature, history, art, and other cultural aspects of the ancient Mediterranean world. The field focuses primarily on, but is not limited to, Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome during classical antiquity, the era spanning from the late Bronze Age of Ancient Greece during the Minoan and Mycenaean periods (c. 1600–1100 BC) through the period known as Late Antiquity to the fall of the Western Roman Empire, c. 500 AD. The word classics is also used to refer to the literature of the period.
Branches of classical studies[]
- Culture of Ancient Greece
- Culture of Ancient Rome
- Culture of Ancient Mediterranean
Subdisciplines of classical studies[]
- Classical archaeology
- Classical art
- Art in ancient Greece
- Roman art
- Classical architecture
- Architecture of Ancient Greece
- Roman architecture
- Numismatics
- Classical art
- Classical history
- Bronze Age
- Classical Antiquity
- Classical society
- Ancient Greek society
- Roman society
- Classical religion
- Religion in ancient Greece
- Greek mythology
- Religion in Ancient Rome
- Roman mythology
- Classical philology
- Classical language
- Classical literature
- Theatre of Ancient Greece
- Theatre of Ancient Rome
- Classical Textual criticism
- Classical philosophy
- Greek philosophy
- Ancient philosophy
- Classical science and technology
- History of science in Classical Antiquity
- Ancient Greek technology
- Roman technology
- Palaeography
History of classical studies[]
History of the western classics (Not to be confused with classical history (see below))
- Literae Humaniores
General classical studies concepts[]
- Ancient history –
- Classical antiquity –
- Literae Humaniores –
Classical archaeology[]
- Late Helladic period
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World[]
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World The Greek category was not "Wonders" but "theamata", which translates closer to "must-sees". The list that we know today was compiled in the Middle Ages—by which time many of the sites were no longer in existence:
- Great Pyramid of Giza (the only wonder of the Ancient World still in existence)
- Hanging Gardens of Babylon
- Statue of Zeus at Olympia
- Temple of Artemis at Ephesus
- Mausoleum of Maussollos at Halicarnassus
- Colossus of Rhodes
- Lighthouse of Alexandria
Classical art[]
- See also Ancient art
Art in Ancient Greece[]
Art in Ancient Greece
- Music in ancient Greece
- Sculpture in ancient Greece
- Theatre of ancient Greece
Roman art[]
- Ancient Roman music
- Roman sculpture
Classical architecture[]
Ancient Greek architecture[]
Architecture of Ancient Greece
- Parthenon
- Temple of Artemis
- Acropolis
- Ancient Agora
- Arch of Hadrian
- Statue of Zeus
- Colossus of Rhodes
- Temple of Hephaestus
- Samothrace temple complex
Roman architecture[]
Roman architecture
- Aedes (Roman)
- Roman aqueduct
- Basilica
- Roman Baths (Bath)
- Roman bridge
- Colosseum
- Forum (Roman)
- Ancient Roman monuments
- Roman road
- Roman temple
- Roman theatre (structure)
- Roman villa
Geography of the classical period[]
Geography at the time of Ancient Greece[]
- Aegean Sea –
- Alexandria –
- Athens –
- Antioch –
- Corinth –
- Delphi –
- Hellespont –
- Macedon –
- Miletus –
- Olympia –
- Pergamon –
- Sparta –
- Thermopylae –
- Troy –
Geography at the time of Ancient Rome[]
- Area under Roman control –
- Borders of the Roman Empire –
- Roman Britain –
- Roman Campagna –
- Roman Gaul –
- Italia –
- Roman province –
- Roman Umbria –
- Via Flaminia –
Roman provinces 120 AD[]
- Achaea –
- Ægyptus –
- Africa –
- Alpes Cottiae –
- Alpes Maritimae –
- Alpes Poenninae –
- Arabia Petraea –
- Armenia Inferior –
- Asia –
- Assyria –
- Bithynia –
- Britannia –
- Cappadocia –
- Cilicia –
- Commagene –
- Corduene –
- Corsica et Sardinia –
- Creta et Cyrenaica –
- Cyprus –
- Dacia –
- Dalmatia –
- Epirus –
- Galatia –
- Gallia Aquitania –
- Gallia Belgica –
- Gallia Lugdunensis –
- Gallia Narbonensis –
- Germania Inferior –
- Germania Superior –
- Hispania Baetica –
- Hispania Lusitania –
- Hispania Tarraconensis –
- Italia –
- Iudaea –
- Iturea –
- Lycaonia –
- Lycia –
- Macedonia –
- Mauretania Caesariensis –
- Mauretania Tingitana –
- Moesia –
- Noricum –
- Numidia –
- Osroene –
- Pannonia –
- Pamphylia –
- Pisidia –
- Pontus –
- Raetia –
- Sicilia –
- Sophene –
- Syria –
- Taurica –
- Thracia –
Classical history[]
Classical history
- Timeline of classical antiquity
- Bronze Age –
- City-state –
- Classical Antiquity –
- Greco-Roman relations –
- Magic in the Greco-Roman world –
Classical Greek history[]
- Greek Dark Ages –
- Hellenistic period –
- Military history of ancient Greece –
Ancient Greek society[]
Ancient Greek society
- Cuisine of Ancient Greece –
- Economy of Ancient Greece –
- Law in Ancient Greece –
- Pederasty in ancient Greece –
- Prostitution in Ancient Greece –
- Slavery in Ancient Greece –
Classical Roman history[]
Roman era
- Timeline of Roman history
- Ancient Rome –
- Crisis of the Roman Republic –
- Decline of the Roman Empire –
- Etruscan civilization –
- Founding of Rome –
- History of Rome –
- Roman conquest of Britain –
- End of Roman rule in Britain –
- Roman Empire –
- Roman Kingdom –
- Roman Republic –
- Western Roman Empire –
Military history of Ancient Rome[]
Military history of ancient Rome
- Political history of the Roman military –
- Structural history of the Roman military –
- Technological history of the Roman military –
- War: Campaign history of the Roman military –
- Roman civil wars –
- Wars involving the Roman Empire –
- Wars involving the Roman Republic –
Roman society[]
Roman society
- Adoption in ancient Rome –
- Roman army –
- Roman assemblies –
- Auctoritas –
- Buddhism and the Roman world –
- Roman citizenship –
- Collegiality –
- Roman commerce –
- Roman consul –
- Republican consuls –
- Early imperial consuls –
- Late imperial consuls –
- Roman currency –
- Cursus honorum –
- Roman Emperor –
- List of Roman Emperors –
- Roman festivals –
- Roman funerals and burial –
- Roman finance –
- Roman gardens –
- Homosexuality in ancient Rome –
- Imperium –
- Roman law –
- Local government (ancient Roman) –
- Roman Magistrates –
- Ancient Roman marriage –
- Roman naming conventions –
- Roman navy –
- Political institutions of Rome –
- Roman province –
- Roman relations with the Parthians and Sassanians –
- Roman school –
- Roman Senate –
- Roman tribe –
- Sino-Roman relations –
- Slavery in ancient Rome –
- Social class in ancient Rome –
- Roman usurper –
Classical Egyptian history[]
- Third Intermediate Period of Egypt (21st to 25th Dynasties; 11th to 7th centuries BC)
- Late Period of ancient Egypt (26th to 31st Dynasties; 7th century BC to 332 BC)
- History of Persian Egypt (525 BC to 332 BC) - see also Achaemenid Empire
- Greco-Roman Egypt (332 BC to 642 AD)
- Hellenistic Egypt (332 BC to 30 BC)
- Macedonian Kings (332 BC to 305 BC)
- Ptolemaic Kingdom (305 BC to 30 BC)
- Egypt (Roman province) (30 BC to 642 AD)
- Hellenistic Egypt (332 BC to 30 BC)
See also the List of ancient Egyptian dynasties
Classical philology[]
Classical language[]
Ancient Greek[]
- Aeolic dialect –
- Attic dialect –
- Doric dialect –
- Greek alphabet –
- Homeric Greek –
- Ionic dialect –
- Koine –
Classical Latin[]
Classical literature[]
Classical Greek literature[]
Ancient Greek literature –
Poets[]
- Bucolic poets
- Theocritus –
- Didactic poets
- Hesiod –
- Epic poets
- Homer –
- Lyric poets
- Alcaeus –
- Alcman –
- Archilochus –
- Bacchylides –
- Mimnermus –
- Pindar –
- Sappho –
- Semonides –
- Simonides of Ceos –
- Tyrtaeus –
Playwrights[]
- Tragedians
- Aeschylus –
- Euripides –
- Sophocles –
- Comedic playwrights
- Aristophanes –
- Menander –
Prose writers[]
- Fiction: Xenophon –
- Historiography: Herodotus, Plutarch, Polybius, Thucydides, Xenophon –
- Oratory: Aeschines, Demosthenes, Isocrates, Lysias –
- Other: Lucian, Plato –
Classical Latin literature[]
Poets[]
- Didactic poets
- Lucretius –
- Ovid –
- Virgil –
- Elegiac poets
- Catullus –
- Ovid –
- Propertius –
- Tibullus –
- Epic poets
- Ennius –
- Lucan –
- Ovid –
- Virgil –
- Lyric poets
- Catullus –
- Horace –
Playwrights[]
- Plautus –
- Terence –
Prose writers[]
- Epistolary writers
- Pliny the younger –
- Seneca –
- Fiction writers
- Apuleius –
- Petronius –
- Historiographers
- Caesar –
- Cornelius Nepos –
- Livy –
- Sallust –
- Suetonius –
- Tacitus –
Orators:
- Cicero –
Classical Textual Criticism[]
Textual criticism
- Greek textual criticism
- Latin textual criticism
Classical philosophy[]
Periods of classical philosophy[]
- Pre-Socratic philosophy –
- Classical Greek philosophy –
- Hellenistic philosophy –
Schools of thought[]
- Aristotelianism – Aristotle
- Cynicism –
- Cyrenaic hedonism –
- Eclecticism –
- Epicureanism –
- Neo-Platonism – Plato
- Neo-Pythagoreanism –
- Platonism –
- Pre-Socratic naturalism –
- Pyrrhonism –
- Pythagoreanism – Pythagoras
- Sophism –
- Stoicism –
Classical philosophers[]
- Aenesidemus –
- Agrippa –
- Alexander of Aphrodisias –
- Ammonius Saccas –
- Anaxagoras –
- Anaximander –
- Anaximenes –
- Antisthenes –
- Antiochus of Ascalon –
- Arcesilaus –
- Aristippus –
- Aristotle –
- Carneades –
- Chrysippus –
- Cleanthes –
- Clitomachus –
- Crates of Thebes –
- Cratylus –
- Democritus –
- Diogenes of Apollonia –
- Diogenes of Sinope –
- Empedocles –
- Epictetus –
- Epicurus –
- Euclid of Megara –
- Heraclitus –
- Hippias –
- Iamblichus –
- Leucippus –
- Melissus –
- Panaetius –
- Parmenides –
- Philo of Larissa –
- Philolaus –
- Plato –
- Plotinus –
- Posidonius –
- Porphyry –
- Prodicus –
- Protagoras –
- Pyrrho –
- Pythagoras –
- Seneca –
- Sextus Empiricus –
- Socrates –
- Speusippus –
- Stilpo –
- Thales –
- Theophrastus –
- Timon –
- Xenophanes –
- Xenocrates –
- Zeno of Citium –
- Zeno of Elea –
Classical religion and mythology[]
- Interpretatio graeca
- Classical mythology
- Mystery religions
- Hellenistic religion
Religion and mythology in Ancient Greece[]
- Achilles –
- Apollo –
- Centaurs
- Dionysus –
- Dragons in Greek mythology –
- Earth-gods –
- Eleusinian Mysteries –
- Golden Fleece –
- Gorgon / Medusa –
- Hellenic polytheism –
- Heracles –
- The Twelve Labours of Heracles –
- Jason –
- Minotaur –
- Nymphs
- Odysseus –
- Odyssey –
- Oedipus –
- Pan –
- Perseus –
- Olympians –
- Primordial gods –
- Satyrs
- Sea-gods –
- Seven against Thebes –
- Theseus –
- Titans –
- Triptolemus –
- Trojan War –
- Zeus –
Religion and mythology in Ancient Rome[]
- Pontifex Maximus –
- Roman Pontiff –
Classical science and technology[]
History of science in Classical Antiquity
Ancient Greek science and technology[]
- Agriculture of Ancient Greece –
- Archimedes –
- Ancient Greek astronomy –
- Geographical technology –
- Ptolemy –
- Greek mathematics –
- Euclid –
- Medicine in ancient Greece –
- Hippocrates –
- Galen –
- Pottery of Ancient Greece –
Roman science and technology[]
Roman technology
- Roman abacus –
- Roman agriculture –
- Roman calendar –
- Cement / concrete –
- Corvus (ship's weapon) –
- Ancient Roman cranes –
- Roman engineering –
- Glassblowing –
- Medical community of ancient Rome –
- Military of ancient Rome –
- Roman numerals –
- Plumbing –
- Roman road –
- Ancient Roman units of measurement –
- Sanitation in ancient Rome –
Classical theatre[]
Ancient Greek theatre[]
Theatre of Ancient Greece
Ancient Roman theatre[]
Theatre of Ancient Rome
Classical studies scholars[]
See List of classical scholars –
[]
- List of classical architecture terms
- List of classical meters
Ancient Greek lists[]
- List of ancient Greek cities
- List of ancient Greeks
- List of ancient Greek tyrants
- List of Greek mythological creatures
- List of Greek mythological figures
- List of ancient Macedonians
Roman lists[]
- List of Latin abbreviations
- List of aqueducts in the Roman Empire
- List of Roman amphitheatres
- List of Roman cognomina
- Lists of Roman consuls
- List of Republican Roman Consuls
- List of early imperial Roman consuls
- List of late imperial Roman consuls
- List of Roman deities / List of Roman gods
- List of Roman Goddesses
- List of Roman Emperors
- Concise List of Roman Emperors
- List of Roman emperors to be condemned
- List of films based on Greco-Roman mythology
- List of Roman gladiator types
- List of Roman laws
- List of Roman legions
- List of Roman nomina
- Lists of Roman places
- List of Roman place names in Britain
- List of Roman places in Hispania
- List of Romans
- List of Roman sites
- List of Roman triumphal arches in Italy outside Rome
- List of Roman usurpers
- List of Imperial Roman victory titles
- List of Roman villas in England
See also[]
External links[]
- Outlines of history and events
- Wikipedia outlines