Posterior compartment of leg
| Posterior compartment of leg | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of leg compartments | |
Dissection video of posterior compartment of leg (6 min 39 sec) | |
| Details | |
| Artery | posterior tibial artery |
| Nerve | tibial nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | compartimentum cruris posterius |
| TA98 | A04.7.01.006 |
| TA2 | 2654 |
| FMA | 45167 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The posterior compartment of the leg is one of the fascial compartments of the leg and is divided further into deep and superficial compartments.
Structure[]
Muscles[]
Superficial posterior compartment[]
| Image | Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Innervation | Main Action ! |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Gastrocnemius | Lateral head: lateral aspect of lateral condyle of femur Medial head: popliteal surface of femur; superior to medial condyle |
Posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon | Tibial nerve (S1, S2) |
Plantarflexes ankle when knee is extended; raises heel during walking; flexes leg at knee joint |

|
Plantaris | Inferior end of lateral supracondylar line of femur; oblique popliteal ligament | Weakly assists gastrocnemius in plantarflexing ankle | ||

|
Soleus | Posterior aspect of head and superior quarter of posterior surface of fibula; soleal line and middle third of medial border of tibia; and tendinous arch extending between the bony attachments | Plantarflexes ankle independent of position of knee; steadies leg on foot |
Deep posterior compartment[]
| Image | Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Innervation | Main Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Flexor hallucis longus muscle | Inferior two-thirds of posterior surface of fibula; inferior part of interosseous membrane | Base of distal phalanx of big toe (hallux) | (S1, S2) |
Flexes big toe at all joints; weakly plantarflexes ankle; supports medial longitudinal arch of foot |

|
Tibialis posterior muscle | Interosseous membrane; posterior surface of tibia inferior to soleal line; posterior surface of fibula | Tuberosity of navicular, cuneiform, cuboid, and sustentaculum tali of calcaneus; bases of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsals | (L4, L5) |
Plantarflexes ankle; inverts foot |

|
Flexor digitorum longus muscle | Medial part of posterior surface of tibia; by a broad tendon to fibula | Bases of distal phalanges of lateral four digits | (S1, S2) |
Flexes lateral four digits; plantarflexes ankle; supports longitudinal arches of foot |

|
Popliteus muscle | Lateral surface of lateral condyle of femur and lateral meniscus | Animation. Posterior surface of tibia, superior to soleal line | (L4, L5, S1) |
Weakly flexes knee and unlocks it by rotating femur 5 deg on fixed tibia; medially rotates tibia of unplanted limb |
Blood supply[]
Innervation[]
The posterior compartment of the leg is supplied by the tibial nerve.
Function[]
- It contains the plantar flexors:[4]
Additional images[]

Superficial posterior compartment. Animation.
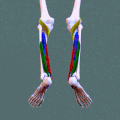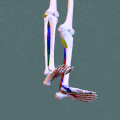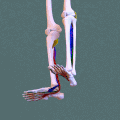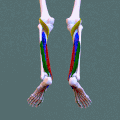
Deep posterior compartment. Animation.
References[]
- ^ Moore, Dally and Agur (2014). Moore Clinically-Oriented Anatomy, Table 5.13.I, p 597.
- ^ Moore, Dally, and Agur (2014). Moore Clinically-Oriented Anatomy, Table 5.13.II, p 598.
- ^ https://www.msu.edu/user/vosskurt/Miscellaneous%20pages/musloc.htm[dead link]
- ^ postleg at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Posterior compartment of the human leg. |
Categories:
- Muscles of the lower limb


