Rifaximin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xifaxan, Zaxine, Xifaxanta, Normix, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604027 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | < 0.4% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 6 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (97%) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.111.624 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
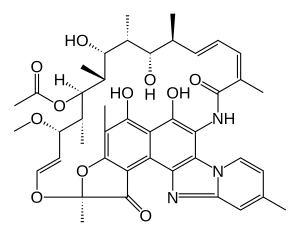
| Formula | C43H51N3O11 |
| Molar mass | 785.891 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 200 to 205 °C (392 to 401 °F) (dec.) |
show
InChI | |
| | |
Rifaximin, sold under the brand name Xifaxan (USA) and Zaxine (Canada) among others, is an antibiotic medication used to treat travelers' diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, and hepatic encephalopathy.[3] It has poor absorption when taken by mouth.
It is based on rifamycin. Rifaximin was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2004.[3][4]
Medical uses[]
Rifaximin is indicated in the United States for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome in adults, travelers' diarrhea in those age 12 and older, and reduction in risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy (HE) recurrence in adults.[2][5]
Irritable bowel syndrome[]
Rifaximin is approved in the United States for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.[6] It possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, and is a nonabsorbable antibiotic that acts locally in the gut. These properties make it efficacious in relieving chronic functional symptoms of non-constipation type irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). It appears to retain its therapeutic properties for this indication, even after repeated courses.[7][8] Rifaximin is particularly indicated where small intestine bacterial overgrowth is suspected of involvement in a person's IBS. Symptom relief or improvement can be obtained for global IBS symptoms, including: abdominal pain, flatulence, bloating, and stool consistency. A drawback is that repeated courses may be necessary for relapse of symptoms.[8][9] There is evidence that rifaximin can be curative in some people with IBS.[10]
C. difficile infection[]
Rifaximin may also be a useful addition to vancomycin when treating patients with relapsing C. difficile infection.[11][12] However, the quality of evidence of these studies was judged to be low.[13] Because exposure to rifamycins in the past may increase risk for resistance, rifaximin should be avoided in such cases.[citation needed]
Hepatic encephalopathy[]
In the United States, rifaximin has orphan drug status for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy.[14] Although high-quality evidence is still lacking, rifaximin appears to be as effective as, or more effective than, other available treatments for hepatic encephalopathy (such as lactulose), is better tolerated, and may work faster.[15] Rifaximin is taken by mouth. It has minimal side effects, prevents reoccurring encephalopathy, and is associated with high patient satisfaction. People are more compliant and satisfied to take this medication than any other due to minimal side effects, prolonged remission, and overall cost.[16] It reduces the levels of intestinal ammonia-producing bacteria, thus alleviating the symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy and reducing mortality.[9] The drawbacks to rifaximin are increased cost, and lack of robust clinical trials for HE without combination lactulose therapy.[citation needed]
Other uses[]
Other uses include treatment of: infectious diarrhea, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease.[9] Rifaximin is effective in treating small intestinal bacterial overgrowth regardless of whether it is associated with irritable bowel syndrome or not.[17] Rifaximin has also shown efficacy with rosacea, ocular rosacea which also presents as dry eyes for patients with co-occurrence with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).[18]
Special caution[]
Cautious use is required in individuals with cirrhosis of the liver who have a Child-Pugh score of class C severity.[9]
Side effects[]
Rifaximin has few side effects.[8] Side effects are generally mild and uncommon;[7] this is largely because very little of the drug is absorbed from the gut, meaning systemic side effects are absent.[8] Clostridium difficile infection does not typically result from rifaximin therapy, unless risk factors such as immunosuppression and hospitalisation are present. Rifaximin is active against C. difficile.[7]
Interactions[]
Rifaximin is not significantly absorbed from the gut, and therefore does not have much significant interactions with other drugs in people with normal liver function.[7]
Pharmacology[]
Rifaximin is a semisynthetic broad spectrum antibacterial drug,[10][19] that has very low bioavailability due to its poor absorption after oral administration.[8] Because of this local action within the gut and the lack of horizontal transfer of resistant genes, the development of bacterial resistance is rare.[7] Because of this poor absorption, most of the drug taken orally stays in the gastrointestinal tract where the infection takes place.[20] However, due to drug polymorphisms and differences between crystalline and amorphous forms of the compounds, certain generic drug versions are more readily absorbable than the original brand name version.[9]
Mechanism of action[]
Rifaximin interferes with transcription by binding to the β-subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase.[9] This results in the blockage of the translocation step that normally follows the formation of the first phosphodiester bond, which occurs in the transcription process.[21] This in turn results in a reduction of bacteria populations, including gas-producing bacteria, which may reduce mucosal inflammation, epithelial dysfunction, and visceral hypersensitivity. Rifaximin has broad spectrum antibacterial properties against both gram positive and gram negative anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. As a result of bile acid solubility, its antibacterial action is limited mostly to the small intestine and less so the colon.[9] A resetting of the bacteria composition has also been suggested as a possible mechanism of action for relief of IBS symptoms.[10] Additionally, rifaximin may have a direct anti-inflammatory effect on gut mucosa via modulation of the pregnane X receptor.[10]
Other mechanisms for its therapeutic properties include inhibition of bacterial translocation across the epithelial lining of the intestine, inhibition of adherence of bacteria to the epithelial cells, and a reduction in the expression of proinflammatory cytokines.[22]
Availability[]
In the United States, Salix Pharmaceuticals holds a US Patent for rifaximin and markets the drug under the name Xifaxan.[23][24] In addition to receiving FDA approval for travelers' diarrhea and (marketing approved for)[24] hepatic encephalopathy, rifaximin received FDA approval for IBS in May 2015.[25] No generic formulation is available in the US and none has appeared due to the fact that the FDA approval process was ongoing. If rifaximin receives full FDA approval for hepatic encephalopathy it is likely that Salix will maintain marketing exclusivity and be protected from generic formulations until March 24, 2017.[24] In 2018, a patent dispute with Teva was settled which delayed a generic in the United States, with the patent set to expire in 2029.[26]
Rifaximin is approved in 33 countries for GI disorders.[27][28] On August 13, 2013, Health Canada issued a Notice of Compliance to Salix Pharmaceuticals Inc. for the drug product Zaxine.[29] In India it is available under the brand names Ciboz and Xifapill.[citation needed] In Russia and Ukraine the drug is sold under the name Alfa Normix (Альфа Нормикс), produced by Alfa Wassermann S.p.A. (Italy).[30]
In 2018, the FDA approved a similar drug by called Aemcolo for traveler's diarrhea.[31]
References[]
- ^ "Rifaximin international". Drugs.com. 2 November 2020. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Xifaxan- rifaximin tablet". DailyMed. 1 October 2019. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Rifaximin Monograph for Professionals". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Xifaxan (Nfaximin) NDA #021361". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 August 2004. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- ^ DuPont HL (July 2007). "Therapy for and prevention of traveler's diarrhea". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 45 (Suppl 1): S78-84. doi:10.1086/518155. PMID 17582576.
- ^ Kane JS, Ford AC (2016). "Rifaximin for the treatment of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome". Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10 (4): 431–42. doi:10.1586/17474124.2016.1140571. PMID 26753693. S2CID 13607138.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Ponziani FR, Pecere S, Lopetuso L, Scaldaferri F, Cammarota G, Gasbarrini A (July 2016). "Rifaximin for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome - a drug safety evaluation". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 15 (7): 983–91. doi:10.1080/14740338.2016.1186639. PMID 27149541. S2CID 25426888.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Song KH, Jung HK, Kim HJ, Koo HS, Kwon YH, Shin HD, et al. (April 2018). "Clinical Practice Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Korea, 2017 Revised Edition". Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility. 24 (2): 197–215. doi:10.5056/jnm17145. PMC 5885719. PMID 29605976.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Iorio N, Malik Z, Schey R (2015). "Profile of rifaximin and its potential in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome". Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 8: 159–67. doi:10.2147/CEG.S67231. PMC 4467648. PMID 26089696.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Pimentel M (January 2016). "Review article: potential mechanisms of action of rifaximin in the management of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea". Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 43 Suppl 1: 37–49. doi:10.1111/apt.13437. PMID 26618924.
- ^ Johnson S, Schriever C, Galang M, Kelly CP, Gerding DN (March 2007). "Interruption of recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea episodes by serial therapy with vancomycin and rifaximin". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 44 (6): 846–8. doi:10.1086/511870. PMID 17304459.
- ^ Garey KW, Ghantoji SS, Shah DN, Habib M, Arora V, Jiang ZD, DuPont HL (December 2011). "A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study to assess the ability of rifaximin to prevent recurrent diarrhoea in patients with Clostridium difficile infection". The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 66 (12): 2850–5. doi:10.1093/jac/dkr377. PMID 21948965.
- ^ Nelson RL, Suda KJ, Evans CT (March 2017). "Antibiotic treatment for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3: CD004610. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004610.pub5. PMC 6464548. PMID 28257555.
- ^ Wolf DC (2007-01-09). "Hepatic Encephalopathy". eMedicine. WebMD. Retrieved 2007-02-15.
- ^ Lawrence KR, Klee JA (August 2008). "Rifaximin for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy". Pharmacotherapy. 28 (8): 1019–32. doi:10.1592/phco.28.8.1019. PMID 18657018. S2CID 25662917. Free full text with registration at Medscape.
- ^ Kimer N, Krag A, Gluud LL (March 2014). "Safety, efficacy, and patient acceptability of rifaximin for hepatic encephalopathy". Patient Preference and Adherence. 8: 331–8. doi:10.2147/PPA.S41565. PMC 3964161. PMID 24672227.
- ^ Triantafyllou K, Sioulas AD, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ (2015). "Rifaximin: The Revolutionary Antibiotic Approach for Irritable Bowel Syndrome". Mini Rev Med Chem. 16 (3): 186–92. doi:10.2174/1389557515666150722105340. PMID 26202193.
- ^ https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(12)02330-4/fulltext
- ^ Laterza L, Ianiro G, Scoleri I, Landi R, Bruno G, Scaldaferri F, Gaetani E, Campanale M, Gasbarrini A (March 2015). "Rifaximin for the treatment of diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 16 (4): 607–15. doi:10.1517/14656566.2015.1007951. PMID 25641072. S2CID 24324310.
- ^ Taylor DN (December 2005). "Poorly absorbed antibiotics for the treatment of traveler' diarrhea". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 41 Suppl 8 (Supplement_8): S564-70. doi:10.1086/432953. PMID 16267720.
- ^ "Rifaximin". DrugBank. 22 March 2017.
- ^ Lee KJ (October 2015). "Pharmacologic Agents for Chronic Diarrhea". Intest Res. 13 (4): 306–12. doi:10.5217/ir.2015.13.4.306. PMC 4641856. PMID 26576135.
- ^ "Xifaxan (Rifaximin) 550 mg - Reduce Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy Recurrences". Salix Pharmaceuticals.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Product Details for NDA 022554". Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- ^ "FDA approves two therapies to treat IBS-D" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[dead link]
- ^ Linnane, Ciara. "Bausch Health stock soars 8.6% premarket on news of patent settlement". MarketWatch. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
- ^ "Xifaxan (rifaximin) Tablets 550 mg for Hepatic Encephalopathy" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration Gastrointestinal Drugs Advisory Committee. 23 February 2010.
- ^ "Pharmaceutical News & Media - Salix Pharmaceuticals".
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD): Zaxine". Government of Canada, Health Canada, Health Products and Food Branch, Therapeutic Products Directorate, Bureau of Gastroenterology Infection and Viral Diseases. 2013.
- ^ "Alfa Normix". Russian medical server.
- ^ "Cosmo to give Bausch Health a run for its money with FDA nod for Xifaxan rival". FiercePharma. Retrieved 2019-05-14.
External links[]
- "Rifaximin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Orphan drugs
- Rifamycin antibiotics
- Acetate esters
- Ethers
- Lactams
- Pregnane X receptor agonists