Rio Grande de Mindanao
Rio Grande de Mindanao
| |
|---|---|
 | |
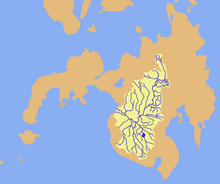 Drainage map of Mindanao River | |
 Mindanao River mouth | |
| Native name | Mindanao River |
| Location | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | |
| Province | |
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Kitanglad Mountain Range |
| • location | Brgy. Kalabugao, Impasugong, Bukidnon |
| • coordinates | 8°27′15″N 125°09′46″E / 8.45417°N 125.16278°E |
| Mouth | Illana Bay |
• location | Cotabato City |
• coordinates | 7°15′20″N 124°12′0″E / 7.25556°N 124.20000°ECoordinates: 7°15′20″N 124°12′0″E / 7.25556°N 124.20000°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 373 km (232 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 23,169 km2 (8,946 sq mi)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 1,400 m3/s (49,000 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 3,000 m3/s (110,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | |
| • right |
|
The Rio Grande de Mindanao, also known as the Mindanao River, is the second-largest river system in the Philippines. Located on the southern island of Mindanao, with a total drainage area of 23,169 km2 (8,946 sq mi),[2] draining the majority of the central and eastern portion of the island, and a total length of approximately 373 km (232 mi).[1][3] It is an important transportation artery, used mainly in transporting agricultural products and, formerly, timber.
Its headwaters are in the mountains of Impasugong, Bukidnon, south of Gingoog City in Misamis Oriental, where it is called the Pulangi River. Joining the Kabacan River, it becomes the Mindanao River. Flowing out of the mountains, it forms the center of a broad, fertile plain in the southcentral portion of the island. Before its mouth in the Illana Bay, it splits into two parallel sections, the Cotabato and Tamontaka, separated by a 180 m (590 ft) hill.
Population centers along the river include Cotabato City, Datu Piang and Midsayap.
Course[]

The Rio Grande de Mindanao has its source in the Central Mindanao Highlands near the northern coast of the island, specifically on the northeastern part of the province of Bukidnon, where it is known as the Pulangi River. It then flows southward across the , fed up by its tributaries along the way and then emerges onto the , depositing fertile mountain silt as it widens and arcs westward through the . It finally empties into Illana Bay at its mouth at Cotabato City.
As the Mindanao River meets Illana Bay, it branches out into two distributaries, the Cotabato in the north and the Tamontaka in the south at Cotabato City.
Tributaries[]
Rio Grande de Mindanao River List of tributaries by length.
- Pulangi River 374 km (232 mi)
- 175 km (109 mi)
- Allah River 130 km (81 mi)
- Buluan River 109 km (68 mi)
- Simuay River 81 km (50 mi)
- Libungan River 80 km (50 mi)
- M'lang River 62 km (39 mi)
Water hyacinths[]
The river has recently been clogged with water hyacinths, causing it to overflow after days of heavy rain. Floodwaters submerged at least 37 villages in Cotabato City alone and displaced some 6,000 families.
President Benigno Aquino III ordered public works and military personnel to clear the river of up to 20 hectares (0.20 km2) of water lily growth.[4]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kenneth Kimutai too (24 July 2018). "Longest Rivers In The Philippines". worldatlas.com. WorldAtlas. Retrieved 6 September 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Vicente B. Tuddao Jr. (September 21, 2011). "Water Quality Management in the Context of Basin Management: Water Quality, River Basin Management and Governance Dynamics in the Philippines" (PDF). www.wepa-db.net. Department of Environment and Natural Resources. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- ^ Principal River Basins of the Philippines, published by the National Water Resources Board, October 1976 (p. 12)
- ^ "Aquino leads 'war vs water hyacinths'". Philippine Daily Inquirer. June 23, 2011. Retrieved 2011-06-22.
External links[]
 Media related to Mindanao River at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Mindanao River at Wikimedia Commons
- Rivers of the Philippines
- Geography of Mindanao
- Landforms of Bukidnon
- Landforms of Cotabato
- Landforms of Maguindanao
- Populated places on the Rio Grande de Mindanao

