Ryukyu Kingdom
Ryukyu Kingdom 琉球國 Ruuchuu-kuku | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1429–1879 | |||||||||||||||||
| Anthem: "Ishinagu nu uta" (石なぐの歌)[1] | |||||||||||||||||
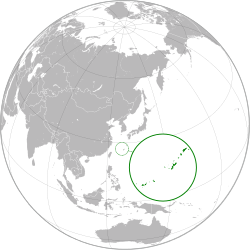 | |||||||||||||||||
| Status |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Shuri | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Ryukyuan (native languages), Classical Chinese, Classical Japanese | ||||||||||||||||
| Ethnic groups | Ryukyuan | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Ryukyuan religion, Shinto, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| King (國王) | |||||||||||||||||
• 1429–1439 | Shō Hashi | ||||||||||||||||
• 1477–1526 | Shō Shin | ||||||||||||||||
• 1587–1620 | Shō Nei | ||||||||||||||||
• 1848–1879 | Shō Tai | ||||||||||||||||
| Sessei (摂政) | |||||||||||||||||
• 1666–1673 | Shō Shōken | ||||||||||||||||
| Regent (國師) | |||||||||||||||||
• 1751–1752 | Sai On | ||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Shuri cabinet (首里王府), Sanshikan (三司官) | ||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||
• Unification | 1429 | ||||||||||||||||
| 5 April 1609 | |||||||||||||||||
• Reorganized into Ryukyu Domain | 1872 | ||||||||||||||||
| 27 March 1879 | |||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||
| 2,271 km2 (877 sq mi) | |||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Ryukyuan, Chinese, and Japanese mon coins[3] | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | Japan | ||||||||||||||||
| History of Ryukyu |
|---|
 |
The Ryukyu Kingdom[a] was a kingdom in the Ryukyu Islands from 1429 to 1879. It was ruled as a tributary state of imperial China by the Ryukyuan monarchy, who unified Okinawa Island to end the Sanzan period, and extended the kingdom to the Amami Islands and Sakishima Islands. The Ryukyu Kingdom played a central role in the maritime trade networks of medieval East Asia and Southeast Asia despite its small size. The Ryukyu Kingdom became a vassal state of the Satsuma Domain of Japan after the invasion of Ryukyu in 1609 but retained de jure independence until it was transformed into the Ryukyu Domain by the Empire of Japan in 1872.[b] The Ryukyu Kingdom was formally annexed and dissolved by Japan in 1879 to form Okinawa Prefecture, and the Ryukyuan monarchy was integrated into the new Japanese nobility.
History[]
Origins of the Kingdom[]

In the 14th century, small domains scattered on Okinawa Island were unified into three principalities: Hokuzan (北山, Northern Mountain), Chūzan (中山, Central Mountain), and Nanzan (南山, Southern Mountain). This was known as the Three Kingdoms, or Sanzan (三山, Three Mountains) period.[citation needed] Hokuzan, which constituted much of the northern half of the island, was the largest in terms of land area and military strength but was economically the weakest of the three. Nanzan constituted the southern portion of the island. Chūzan lay in the center of the island and was economically the strongest. Its political capital at Shuri, Nanzan was adjacent to the major port of Naha, and Kume-mura, the center of traditional Chinese education. These sites and Chūzan as a whole would continue to form the center of the Ryukyu Kingdom until its abolition.[citation needed]
Many Chinese people moved to Ryukyu to serve the government or to engage in business during this period[citation needed]. At the request of the Ryukyuan King, the Ming Chinese sent thirty-six Chinese families from Fujian to manage oceanic dealings in the kingdom in 1392, during the Hongwu emperor's reign. Many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers.[6] They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations.[7][8][9] On 30 January 1406, the Yongle Emperor expressed horror when the Ryukyuans castrated some of their own children to become eunuchs to serve in the Ming imperial palace. Emperor Yongle said that the boys who were castrated were innocent and did not deserve castration, and he returned them to Ryukyu, and instructed the kingdom not to send eunuchs again. According to statements by Qing imperial official Li Hongzhang in a meeting with Ulysses S. Grant, China had a special relationship with the island and the Ryukyu had paid tribute to China for hundreds of years, and the Chinese reserved certain trade rights for them in an amicable and beneficial relationship.[10]
These three principalities (tribal federations led by major chieftains) battled, and Chūzan emerged victorious. The Chūzan leaders were officially recognized by Ming dynasty China as the rightful kings over those of Nanzan and Hokuzan, thus lending great legitimacy to their claims. The ruler of Chūzan passed his throne to King Hashi; Hashi conquered Hokuzan in 1416 and Nanzan in 1429, uniting the island of Okinawa for the first time, and founded the first Shō Dynasty. Hashi was granted the surname "Shō" (Chinese: 尚; pinyin: Shàng) by the Ming emperor in 1421, becoming known as Shō Hashi (Chinese: 尚巴志; pinyin: Shàng Bāzhì).[citation needed]
Shō Hashi adopted the Chinese hierarchical court system, built Shuri Castle and the town as his capital, and constructed Naha harbor. When in 1469 King Shō Toku, who was a grandson of Shō Hashi, died without a male heir, a palatine servant declared he was Toku's adopted son and gained Chinese investiture. This pretender, Shō En, began the Second Shō Dynasty. Ryukyu's golden age occurred during the reign of Shō Shin, the second king of that dynasty, who reigned from 1478 to 1526.[11]
The kingdom extended its authority over the southernmost islands in the Ryukyu archipelago by the end of the 15th century, and by 1571 the Amami Ōshima Islands, to the north near Kyūshū, were incorporated into the kingdom as well.[12] While the kingdom's political system was adopted and the authority of Shuri recognized, in the Amami Ōshima Islands, the kingdom's authority over the Sakishima Islands to the south remained for centuries at the level of a tributary-suzerain relationship.[13]
Golden age of maritime trade[]
For nearly two hundred years, the Ryukyu Kingdom would thrive as a key player in maritime trade with Southeast and East Asia.[14][15] Central to the kingdom's maritime activities was the continuation of the tributary relationship with Ming dynasty China, begun by Chūzan in 1372,[12][c] and enjoyed by the three Okinawan kingdoms which followed it. China provided ships for Ryukyu's maritime trade activities,[16] allowed a limited number of Ryukyuans to study at the Imperial Academy in Beijing, and formally recognized the authority of the King of Chūzan, allowing the kingdom to trade formally at Ming ports. Ryukyuan ships, often provided by China, traded at ports throughout the region, which included, among others, China, Đại Việt (Vietnam), Japan, Java, Korea, Luzon, Malacca, Pattani, Palembang, Siam, and Sumatra.[17]


Japanese products—silver, swords, fans, lacquerware, folding screens—and Chinese products—medicinal herbs, minted coins, glazed ceramics, brocades, textiles—were traded within the kingdom for Southeast Asian sappanwood, rhino horn, tin, sugar, iron, ambergris, Indian ivory, and Arabian frankincense. Altogether, 150 voyages between the kingdom and Southeast Asia on Ryukyuan ships were recorded in the Rekidai Hōan, an official record of diplomatic documents compiled by the kingdom, as having taken place between 1424 and the 1630s, with 61 of them bound for Siam, 10 for Malacca, 10 for Pattani, and 8 for Java, among others.[17]
The Chinese policy of haijin (海禁, "sea bans"), limiting trade with China to tributary states and those with formal authorization, along with the accompanying preferential treatment of the Ming Court towards Ryukyu, allowed the kingdom to flourish and prosper for roughly 150 years.[18] In the late 16th century, however, the kingdom's commercial prosperity fell into decline. The rise of the wokou threat among other factors led to the gradual loss of Chinese preferential treatment;[19] the kingdom also suffered from increased maritime competition from Portuguese traders.[12]
Japanese invasion and subordination[]
Around 1590, Toyotomi Hideyoshi asked the Ryukyu Kingdom to aid in his campaign to conquer Korea. If successful, Hideyoshi intended to then move against China. As the Ryukyu Kingdom was a tributary state of the Ming dynasty, the request was refused. The Tokugawa shogunate that emerged following Hideyoshi's fall authorized the Shimazu family—feudal lords of the Satsuma domain (present-day Kagoshima Prefecture)—to send an expeditionary force to conquer the Ryukyus. The subsequent invasion took place in 1609, but Satsuma still allowed the Ryukyu Kingdom to find itself in a period of "dual subordination" to Japan and China, wherein Ryukyuan tributary relations were maintained with both the Tokugawa shogunate and the Chinese court.[12]
Occupation occurred fairly quickly, with some fierce fighting, and King Shō Nei was taken prisoner to Kagoshima and later to Edo (modern-day Tokyo). To avoid giving the Qing any reason for military action against Japan, the king was released two years later and the Ryukyu Kingdom regained a degree of autonomy;[20] however, the Satsuma domain seized control over some territory of the Ryukyu Kingdom, notably the Amami-Ōshima island group, which was incorporated into the Satsuma domain and remains a part of Kagoshima Prefecture, not Okinawa Prefecture, to this day.
The kingdom was described by Hayashi Shihei in Sangoku Tsūran Zusetsu, which was published in 1785.[21]
Tributary relations[]


This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2013) |
In 1655, tribute relations between Ryukyu and Qing dynasty (the dynasty that followed Ming in 1644) were formally approved by the shogunate. This was seen to be justified, in part, because of the desire to avoid giving Qing any reason for military action against Japan.[20]
Since Ming China prohibited trade with Japan, the Satsuma domain, with the blessing of the Tokugawa shogunate, used the trade relations of the kingdom to continue to maintain trade relations with China. Considering that Japan had previously severed ties with most European countries except the Dutch, such trade relations proved especially crucial to both the Tokugawa shogunate and Satsuma domain, which would use its power and influence, gained in this way, to help overthrow the shogunate in the 1860s.[citation needed]
The Ryukyuan king was a vassal of the Satsuma daimyō, but his land was not considered as part of any han (fief): up until the formal annexation of the islands and abolition of the kingdom in 1879, the Ryukyus were not truly considered part of Japan, and the Ryukyuan people were not considered to be Japanese.[citation needed] Though technically under the control of Satsuma, Ryukyu was given a great degree of autonomy, to best serve the interests of the Satsuma daimyō and those of the shogunate, in trading with China. Ryukyu was a tributary state of China, and since Japan had no formal diplomatic relations with China, it was essential that China not realize that Ryukyu was controlled by Japan. Thus, Satsuma—and the shogunate—was obliged to be mostly hands-off in terms of not visibly or forcibly occupying Ryukyu or controlling the policies and laws there. The situation benefited all three parties involved—the Ryukyu royal government, the Satsuma daimyō, and the shogunate—to make Ryukyu seem as much a distinctive and foreign country as possible. Japanese were prohibited from visiting Ryukyu without shogunal permission, and the Ryukyuans were forbidden from adopting Japanese names, clothes, or customs. They were even forbidden from divulging their knowledge of the Japanese language during their trips to Edo; the Shimazu family, daimyōs of Satsuma, gained great prestige by putting on a show of parading the King, officials, and other people of Ryukyu to and through Edo. As the only han to have a king and an entire kingdom as vassals, Satsuma gained significantly from Ryukyu's exoticness, reinforcing that it was an entirely separate kingdom.[citation needed]
Japan ordered tributary relations to end in 1875 after the tribute mission of 1874 was perceived as a show of submission to China.[22]
Annexation by the Japanese Empire[]
In 1872, Emperor Meiji unilaterally declared that the kingdom was then Ryukyu Domain.[23][24][25] At the same time, the appearance of independence was maintained for diplomatic reasons with Qing China[26] until the Meiji government abolished the Ryukyu Kingdom when the islands were incorporated as Okinawa Prefecture on 27 March 1879.[27] The Amami-Ōshima island group which had been integrated into Satsuma Domain became a part of Kagoshima Prefecture.
The last king of Ryukyu was forced to relocate to Tokyo, and was given a compensating kazoku rank as Marquis Shō Tai.[28][29][page needed] Many royalist supporters fled to China.[30] The king's death in 1901 diminished the historic connections with the former kingdom.[31] With the abolition of the aristocracy after World War II, the Sho family continues to live in Tokyo.[32]
Major events[]
- 1187 – Shunten becomes King of Okinawa, based at Urasoe Castle.
- 1272 – Envoys from the Mongol Empire are expelled from Okinawa by King Eiso.
- 1276 – Mongols are violently driven off the island again.
- 1372 – The first Ming dynasty envoy visits Okinawa, which had been divided into three kingdoms during the Sanzan period. Formal tributary relations with the Chinese Empire begin.[12]
- 1389 – An envoy from Ryukyu visits the Goryeo Kingdom, resulting in diplomatic ties between the two kingdoms.
- 1392 – An envoy from Ryukyu visits the Joseon Kingdom.
- 1416 – Chūzan, led by Shō Hashi, occupies Nakijin Castle, capital of Hokuzan.[33]
- 1429 – Chūzan occupies Nanzan Castle, capital of Nanzan, unifying Okinawa Island. Shō Hashi moves the capital to Shuri Castle (now part of modern-day Naha).[33]
- 1458 – Amawari's rebellion against the Kingdom.
- 1466 – Kikai Island invaded by Ryukyu.
- 1470 – Shō En (Kanemaru) establishes the Second Shō Dynasty.[33]
- 1477 – Shō Shin, whose rule is called the "Great Days of Chūzan", ascends to the throne.[33] Golden age of the kingdom.
- 1500 – Sakishima Islands annexed by Ryukyu.
- 1609 – (5 April) Daimyō (Lord) of Satsuma in southern Kyūshū invades the kingdom. King Shō Nei is captured.[33]
- 1611 – In accordance with the peace treaty, Satsuma annexes the Amami and Tokara Islands; Kings of Ryukyu become vassals to the Lords of Satsuma.
- 1623 – Completion of Omoro Sōshi.
- 1650 – Completion of Chūzan Seikan.
- 1724 – Completion of Chūzan Seifu.
- 1745 – Completion of Kyūyō.
- 1846 – Dr. Bernard Jean Bettelheim (d. 1870), a Hungarian Protestant missionary serving with the Loochoo Naval Mission, arrives in Ryukyu Kingdom.[33] He establishes the first foreign hospital on the island at the Naminoue Gokoku-ji Temple.
- 1852 – Commodore Matthew C. Perry of the US Navy visits the kingdom and establishes a coaling station in Naha.[33]
- 1854 – Perry returns to Okinawa to sign the Loochoo Compact with the Ryukyuan government.[34] Bettelheim leaves with Perry.
- 1866 – The last official mission from the Qing Empire visits the kingdom.
- 1872 – Emperor Meiji unilaterally declares King Shō Tai as the "Domain Head of Ryukyu Domain".
- 1874 – The last tributary envoy to China is dispatched from Naha. / Kaiser Wilhelm I erects a "friendship monument" on Miyako Island. / Japan invades Taiwan on behalf of Ryukyu.
- 1879 – Japan abolishes Ryukyu Domain and declares the creation of Okinawa Prefecture, formally annexing the islands.[33] Shō Tai is forced to abdicate, but is granted the rank of marquis (侯爵, kōshaku) within the Meiji peerage system.[28]
List of Ryukyuan kings[]
| Name | Chinese characters | Reign | Dynasty | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shunten | 舜天 | 1187–1237 | Shunten Dynasty | |
| Shunbajunki | 舜馬順熈 | 1238–1248 | Shunten Dynasty | |
| Gihon | 義本 | 1249–1259 | Shunten Dynasty | |
| Eiso | 英祖 | 1260–1299 | Eiso Dynasty | |
| Taisei | 大成 | 1300–1308 | Eiso Dynasty | |
| Eiji | 英慈 | 1309–1313 | Eiso Dynasty |
| Tamagusuku | 玉城 | 1314–1336 | Eiso Dynasty | |
| Seii | 西威 | 1337–1354 | Eiso Dynasty | |
| Satto | 察度 | 1355–1397 | Satto Dynasty | |
| Bunei | 武寧 | 1398–1406 | Satto Dynasty | |
| Shō Shishō | 尚思紹 | 1407–1421 | First Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Hashi | 尚巴志 | 1422–1429 | First Shō Dynasty | as King of Chūzan |
| Name | Chinese characters | Reign | Line or Dynasty | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shō Hashi | 尚巴志 | 1429–1439 | First Shō Dynasty | as King of Ryukyu |
| Shō Chū | 尚忠 | 1440–1442 | First Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Shitatsu | 尚思達 | 1443–1449 | First Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Kinpuku | 尚金福 | 1450–1453 | First Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Taikyū | 尚泰久 | 1454–1460 | First Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Toku | 尚徳 | 1461–1469 | First Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō En | 尚圓 | 1470–1476 | Second Shō Dynasty | a.k.a. Kanemaru Uchima |
| Shō Sen'i | 尚宣威 | 1477 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Shin | 尚真 | 1477–1526 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Sei | 尚清 | 1527–1555 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Gen | 尚元 | 1556–1572 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Ei | 尚永 | 1573–1586 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Nei | 尚寧 | 1587–1620 | Second Shō Dynasty | ruled during Satsuma invasion; first king to be Satsuma vassal |
| Shō Hō | 尚豊 | 1621–1640 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Ken | 尚賢 | 1641–1647 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Shitsu | 尚質 | 1648–1668 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Tei | 尚貞 | 1669–1709 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Eki | 尚益 | 1710–1712 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Kei | 尚敬 | 1713–1751 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Boku | 尚穆 | 1752–1795 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō On | 尚温 | 1796–1802 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Sei (r. 1803) | 尚成 | 1803 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Kō | 尚灝 | 1804–1828 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Iku | 尚育 | 1829–1847 | Second Shō Dynasty | |
| Shō Tai | 尚泰 | 1848 – 11 March 1879 | Second Shō Dynasty | last King of Ryukyu (then Japanese Marquis 1884–1901) |
In popular culture[]
In the video game Europa Universalis IV there is an achievement called The Three Mountains, which is achieved by conquering the world as the Ryukyu Kingdom.[35]
See also[]

- Foreign relations of Imperial China
- Gusuku
- History of the Ryukyu Islands
- History of Sakishima Islands
- Hua–Yi distinction
- Mudan Incident of 1871
- Military of the Ryukyu Kingdom
- Ryukyu independence movement
- Ryukyu Islands
- Ryukyuan missions to Edo
- Ryukyuan missions to Imperial China
- Ryukyuan missions to Joseon
- Joseon missions to Ryukyu Kingdom
- Imperial Chinese missions to Ryukyu Kingdom
- Tamaudun (intact royal tombs)
- Okinawan martial arts
- Names of Ryukyu
Notes[]
- ^
- Okinawan: 琉球國, romanized: Ruuchuu-kuku
- Japanese: 琉球王国, romanized: Ryūkyū Ōkoku
- Middle Chinese: 琉球國, romanized: Ljuw-gjuw kwok
- Classical Chinese: 大琉球國 (lit. 'Great Lew Chew Country')[4]
- Historical English names: Lew Chew,[5] Lewchew, Luchu, and Loochoo
- Historical French name: Liou-tchou[5]
- Historical Dutch name: Lioe-kioe[5]
- ^ Although the Ryukyuan king was a vassal of the Satsuma Domain, the Ryukyu Kingdom was not considered part of any Han due to trade relations with China.
- ^ Nanzan and Hokuzan also entered into tributary relationships with Ming China, in 1380 and 1383 respectively.[16]
References[]
Citations[]
- ^ Arben Anthony Saavedra, Fernando Inafuku (21 April 2019). National Anthem of the Ryukyu Kingdom ���球王国国歌 (YouTube) (in Okinawan). Okinawa. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ Kikō, Nishizato. "明清交替期の中琉日関係再考" (PDF) (in Japanese). p. 23–25.
- ^ "Ryuukyuuan coins". Luke Roberts at the Department of History – University of California at Santa Barbara. 24 October 2003. Archived from the original on 4 August 2017. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- ^ "琉球国金石文献述略" (in Chinese). Ancient History Institute of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. 25 December 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "旧条約彙纂. 第3巻(朝鮮・琉球)" (in Japanese). National Diet Library. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ Tsai, Shih-shan Henry (1996). The eunuchs in the Ming dynasty (illustrated ed.). SUNY Press. p. 145. ISBN 0-7914-2687-4. Retrieved 4 February 2011.
- ^ Schottenhammer, Angela (2007). Schottenhammer, Angela (ed.). The East Asian maritime world 1400–1800: its fabrics of power and dynamics of exchanges. Volume 4 of East Asian economic and socio-cultural studies: East Asian maritime history (illustrated ed.). Otto Harrassowitz. p. xiii. ISBN 978-3-447-05474-4. Retrieved 4 February 2011.
|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ Deng, Gang (1999). Maritime sector, institutions, and sea power of premodern China. Contributions in economics and economic history. 212 (illustrated ed.). Greenwood. p. 125. ISBN 0-313-30712-1. Retrieved 4 February 2011.
- ^ Hendrickx, Katrien (2007). The Origins of Banana-fibre Cloth in the Ryukyus, Japan (illustrated ed.). Leuven University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-90-5867-614-6. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- ^ Grant, Ulysses Simpson (2008). Simon, John Y (ed.). The Papers. 29: October 1, 1878 – September 30, 1880 (illustrated ed.). SIU Press, Ulysses S. Grant Association. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-8093-2775-1. Retrieved 11 January 2011.
- ^ Smits, Gregory (2019). Maritime Ryukyu, 1050-1650. Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press. p. 137. ISBN 978-0-8248-7708-8. OCLC 1098213229.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Matsuda 2001, p. 16.
- ^ Murai 2008, pp. iv–v.
- ^ Okamoto 2008, p. 35.
- ^ Okinawa Prefectural reserve cultural assets center (2012). "東南アジアと琉球". Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Okamoto 2008, p. 36.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sakamaki, Shunzō (1964). "Ryukyu and Southeast Asia". Journal of Asian Studies. 23 (3): 382–384. doi:10.2307/2050757. JSTOR 2050757.
- ^ Murai 2008, p. iv.
- ^ Okamoto 2008, p. 53.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kang 2010, p. 81
- ^ Klaproth, Julius (1832), San kokf tsou ran to sets, ou Aperçu général des trois royaumes [San kokf tsou ran to sets, or General overview of the three kingdoms] (in French), pp. 169–180.
- ^ Kerr 1953, p. 366-367.
- ^ Matsuo, Kanenori Sakon (2005). The Secret Royal Martial Arts of Ryukyu, p. 40, at Google Books.
- ^ Kerr 1953, p. 175.
- ^ Lin, Man-houng. "The Ryukyus and Taiwan in the East Asian Seas: A Longue Durée Perspective", Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus. 27 October 2006, translated and abridged from Academia Sinica Weekly, No. 1084. 24 August 2006.
- ^ Goodenough, Ward H. Book Review: "George H. Kerr. Okinawa: the History of an Island People...", The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, May 1959, Vol. 323, No. 1, p. 165.
- ^ Kerr 1953, p. 381.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph (2003), "Sho" (PDF@60), Nobiliare du Japon [Nobility of Japan] (in French), p. 56.
- ^ Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph (1906), Dictionnaire d'histoire et de géographie du Japon [Dictionary of History & Geography of Japan] (in French).
- ^ 论战后琉球独立运动及琉球归属问题- 百度文库
- ^ Kerr 1953, p. 236.
- ^ "Forgotten Dynasty".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h . Okinawa Nyūmon (沖縄入門, "Introduction to Okinawa"). Tokyo: Chikuma Shobō, 2000, pp. 207–13.
- ^ "Lew Chew (Loochoo)* - Countries - Office of the Historian". history.state.gov.
- ^ "Ryukyu - Europa Universalis 4 Wiki". eu4.paradoxwikis.com. Retrieved 26 September 2019.
Sources[]
- Akamine, Mamoru (2016). The Ryukyu Kingdom: Cornerstone of East Asia. University of Hawaii. ISBN 978-0824855178.
- Kang, David C. (2010), East Asia Before the West: Five Centuries of Trade and Tribute, New York, NY: Columbia University Press, ISBN 978-0-23115318-8, OCLC 562768984.
- Kerr, George H. (1953), Ryukyu Kingdom and Province before 1945, Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, OCLC 5455582.
- ——— (1958), Okinawa: the History of an Island People, Rutland, VT: Charles Tuttle Co, OCLC 722356.
- Matsuda, Mitsugu (2001), 'The Government of the Kingdom of Ryukyu, 1609–1872 (dissertation submitted to the Graduate School of the University of Hawaii in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, January 1967), Gushikawa: Yui Pub., ISBN 4-946539-16-6, 283 pp.
- Murai, Shōsuke (2008), "Introduction", , Tokyo: The Tōhō Gakkai (The Institute of Eastern Culture), 95.
- Okamoto, Hiromichi (2008), "Foreign Policy and Maritime Trade in the Early Ming Period Focusing on the Ryukyu Kingdom", Acta Asiatica, 95.
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric (2002), Japan Encyclopedia, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5, OCLC 48943301.
- Smits, Gregory (1999), Visions of Ryukyu: identity and ideology in early-modern thought and politics, Honolulu, HI: University of Hawaii Press, ISBN 0-8248-2037-1, 213 pp.
External links[]
- {{Commonscatinline}
- Brief History of the Uchinanchu (Okinawans), Uninanchu.
- Okinawa Filming Guide Book 2014–2015 (PDF), Okinawa Convention & Visitors Bureau (OCVBOkinawaFilmOffice), archived from the original (PDF) on 11 February 2017, retrieved 11 February 2017
- Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan, Nara National Research Institute for Cultural Properties
- Ryukyu Kingdom
- Ryukyu Islands
- Former countries in East Asia
- Former countries in Chinese history
- Former countries in Japanese history
- Former kingdoms
- Island countries
- 1429 establishments in Asia
- 1879 disestablishments in Asia
- States and territories established in 1429
- States and territories disestablished in 1879
- Former monarchies of East Asia




