Secretary-General of the United Nations
| Secretary-General of the United Nations | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| United Nations Secretariat | |
| Style | His Excellency |
| Member of | Secretariat General Assembly |
| Residence | Sutton Place, New York City |
| Seat | United Nations Headquarters, New York City, United States |
| Nominator | Security Council |
| Appointer | General Assembly |
| Term length | Five years, renewable (traditionally limited to two terms) |
| Constituting instrument | United Nations Charter |
| Inaugural holder | Gladwyn Jebb as acting Secretary-General (24 October 1945) Trygve Lie as first Secretary-General (2 February 1946) |
| Formation | 24 October 1945 |
| Deputy | Deputy Secretary-General |
| Website | un.org/sg |
The Secretary-General of the United Nations (UNSG or SG) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
The role of the secretary-general and of the Secretariat is laid out by Chapter XV (Articles 97 to 101) of the United Nations Charter. However, the office's qualifications, selection process and tenure are open to interpretation; they have been established by custom.[1]
Selection and term of office[]

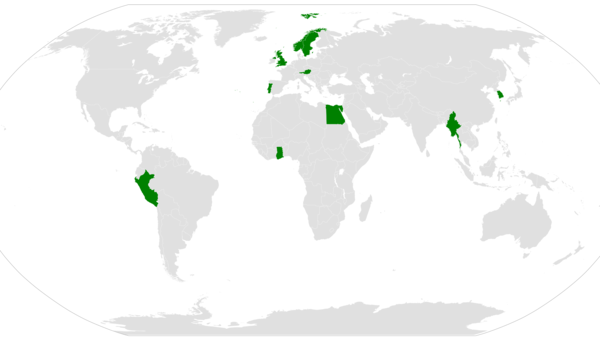
The secretary-general is appointed by the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council. As the recommendation must come from the Security Council, any of the five permanent members of the council can veto a nomination. Most secretaries-general are compromise candidates from middle powers and have little prior fame.
Unofficial qualifications for the job have been set by precedent in previous selections. The appointee may not be a citizen of any of the Security Council's five permanent members.[2] The General Assembly resolution 51/241 in 1997 stated that, in the appointment of "the best candidate", due regard should be given to regional (continental) rotation of the appointee's national origin and to gender equality,[3]:5 although no woman has yet served as secretary-general. All appointees to date have been career diplomats.[4]
The length of the term is discretionary, but all secretaries-general since 1971 have been appointed to five-year terms. Every secretary-general since 1961 has been re-selected for a second term, with the exception of Boutros Boutros-Ghali, who was vetoed by the United States in the 1996 selection. There is a term limit of two full terms, established when China, in the 1981 selection, cast a record 16 vetoes against a third term for Kurt Waldheim. No secretary-general since 1981 has attempted to secure a third term.
The selection process is opaque and is often compared to a papal conclave.[5][6] Since 1981, the Security Council has voted in secret in a series of straw polls; it then submits the winning candidate to the General Assembly for ratification. No candidate has ever been rejected by the General Assembly, and only once, in 1950, has a candidate been voted upon despite a UNSC veto.[7]
In 2016, the General Assembly and the Security Council sought nominations and conducted public debates for the first time. However, the Security Council voted in private and followed the same process as previous selections, leading the president of the General Assembly to complain that it "does not live up to the expectations of the membership and the new standard of openness and transparency".[8]
Powers and duties[]
The role of secretary-general is described as combining the functions and responsibilities of an advocate, diplomat, civil servant, and CEO.[9] The UN Charter designates the secretary-general as the "chief administrative officer" of the UN and allows them to perform "such other functions as are entrusted" by other United Nations organs. The Charter also empowers the secretary-general to inform the Security Council of "any matter which in his opinion may threaten the maintenance of international peace and security". These provision has been interpreted as providing broad leeway for officeholders to serve a variety of roles as suited to their preferences, skill set, or the circumstances.[4]
The secretary-general's routine duties include overseeing the activities and duties of the Secretariat; attending sessions with United Nations bodies; consulting with world leaders, government officials, and other stakeholders; and travelling the world to engage with global constituents and bring attention to certain international issues.[9] The secretary-general publishes an annual report on the work of the UN, which includes an assessment of its activities and an outline future priorities. The secretary-general is also Chairman of the United Nations System Chief Executives Board for Coordination (CEB), a body composed of the heads of all UN funds, programmes and specialized agencies, which meets twice a year to discuss substantive and management issues facing the United Nations System.[9]
Many of the secretary-general's powers are informal and left open to individual interpretation; some appointees have opted for more activist roles, while others have been more technocratic or administrative.[4] The secretary-general is often reliant upon the use of their "good offices", described as "steps taken publicly and in private, drawing upon his independence, impartiality and integrity, to prevent international disputes from arising, escalating or spreading".[9] Consequently, observers have variably described the office as the "world's most visible bully pulpit" or as the "world's moderator".[10][4] Examples include Dag Hammarskjöld's promotion of an armistice between the warring parties of Arab-Israel conflict, Javier Perez de Cuellar's negotiation of a ceasefire in the Iran-Iraq War, and U Thant's role in deescalating the Cuban Missile Crisis.[4]
Residence[]
The official residence of the secretary-general is a townhouse at 3 Sutton Place, Manhattan, in New York City, United States. The townhouse was built for Anne Morgan in 1921, and donated to the United Nations in 1972.[11]
List of secretaries-general[]
| No. | Portrait | Secretary-General (born–died) |
Dates in office | Country of origin | UN regional group | Reason of withdrawal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| – |  |
Gladwyn Jebb (1900–1996) |
Acting 24 October 1945 – 2 February 1946 |
Western European & others | Served as Acting Secretary-General until Lie's election. | [12] | |
| After World War II, he served as Executive Secretary of the Preparatory Commission of the United Nations in August 1945, being appointed Acting United Nations secretary-general from October 1945 to February 1946 until the appointment of the first secretary-general, Trygve Lie. | |||||||
| 1 |  |
Trygve Lie (1896–1968)  |
2 February 1946 – 10 November 1952 |
Western European & others | Resigned. | [13] | |
| Lie, a foreign minister and former labour leader, was recommended by the Soviet Union to fill the post. After the UN involvement in the Korean War, the Soviet Union vetoed Lie's reappointment in 1951. The United States circumvented the Soviet Union's veto and recommended reappointment directly to the General Assembly. Lie was reappointed by a vote of 46 to 5, with eight abstentions. The Soviet Union remained hostile to Lie, and he resigned in 1952.[14] | |||||||
| 2 |  |
Dag Hammarskjöld (1905–1961) |
10 April 1953 – 18 September 1961 |
Western European & others | Died in a plane crash in Northern Rhodesia (now Zambia), while on a peacekeeping mission to the Congo. | [15] | |
| After a series of candidates were vetoed, Hammarskjöld emerged as an option that was acceptable to the Security Council. He was re-elected unanimously to a second term in 1957. The Soviet Union was angered by Hammarskjöld's leadership of the UN during the Congo Crisis, and suggested that the position of Secretary-General be replaced by a troika, or three-man executive. Facing great opposition from the Western nations, the Soviet Union gave up on its suggestion. Hammarskjöld died in a plane crash in Northern Rhodesia (now Zambia) in 1961.[14] U.S. President John F. Kennedy called him "the greatest statesman of our century".[16] Hammarskjöld was posthumously awarded the 1961 Nobel Prize for Peace. | |||||||

|
U Thant (1909–1974) |
Acting 3 November 1961 – 30 November 1962 |
Asia & Pacific | Served as Acting Secretary-General after Hammarskjöld's death until Thant's election as Secretary-General. | [17] | ||
| 3 | 30 November 1962 – 31 December 1971 |
Declined to stand for a third election. | |||||
| In the process of replacing Hammarskjöld, the developing world insisted on a non-European and non-American secretary-general. U Thant was nominated. However, due to opposition from the French (Thant had chaired a committee on Algerian independence) and the Arabs (Myanmar supported Israel), Thant was only appointed for the remainder of Hammarskjöld's term. He was the first Asian secretary-general. The following year, on 30 November, Thant was unanimously re-elected to a full term ending on 3 November 1966. At the General Assembly session on 2 December 1966, Thant was reappointed as Secretary-General by a unanimous vote of the Security Council. His five-year term ended on 31 December 1971. Thant did not seek a third election.[14] Thant is the only former secretary-general whose home country had not been in the Security Council in his term. | |||||||
| 4 |  |
Kurt Waldheim (1918–2007) |
1 January 1972 – 31 December 1981 |
Western European & others | China vetoed his third term. | [18] | |
| Waldheim launched a discreet but effective campaign to become the secretary-general. Despite initial vetoes from China and the United Kingdom, in the third round, Waldheim was selected to become the new secretary-general. In 1976, China initially blocked Waldheim's re-election, but it relented on the second ballot. In 1981, Waldheim's re-election for a third term was blocked by China, which vetoed his selection through 15 rounds; although the official reasons by the Chinese government for the veto of Waldheim remain unclear, some estimates from the time believe it to be in part due to China's belief that a Third World country should give a nomination, particularly from the Americas;[19] however, there also remained the question of his possible involvement in Nazi war crimes.[20] From 1986 to 1992, Waldheim served as President of Austria, making him the first former secretary-general to rise to the position of head of state. In 1985, it was revealed that a post-World War II UN War Crimes Commission had labeled Waldheim as a suspected war criminal—based on his involvement with the army of Nazi Germany. The files had been stored in the UN archive.[14] | |||||||
| 5 |  |
Javier Pérez de Cuéllar (1920–2020) |
1 January 1982 – 31 December 1991 |
Latin American & Caribbean |
Did not stand for a third term. | [21] | |
| Pérez de Cuéllar was selected after a five-week deadlock between the re-election of Waldheim and China's candidate, Salim Ahmed Salim of Tanzania. Pérez de Cuéllar, a Peruvian diplomat who a decade earlier had served as President of the UN Security Council during his time as Peruvian Ambassador to the UN, was a compromise candidate. He became the first and thus far only secretary-general from the Americas. He was re-elected unanimously in 1986.[14] | |||||||
| 6 |  |
Boutros Boutros-Ghali (1922–2016) |
1 January 1992 – 31 December 1996 |
African | The United States vetoed his second term. | [22] | |
| The 102-member Non-Aligned Movement insisted that the next secretary-general come from Africa. With a majority in the General Assembly and the support of China, the Non-Aligned Movement had the votes necessary to block any unfavourable candidate. The Security Council conducted five anonymous straw polls—a first for the council—and Boutros-Ghali emerged with 11 votes on the fifth round. In 1996, the United States vetoed the re-appointment of Boutros-Ghali, claiming he had failed in implementing necessary reforms to the UN.[14] | |||||||
| 7 |  |
Kofi Annan (1938–2018) |
1 January 1997 – 31 December 2006 |
African | Retired after two full terms. | [23] | |
| On 13 December 1996, the Security Council recommended Annan.[24][25] He was confirmed four days later by the vote of the General Assembly.[26] He started his second term as Secretary-General on 1 January 2002. Kofi Annan and the United Nations were the recipients of the 2001 Nobel Prize for Peace. | |||||||
| 8 |  |
Ban Ki-moon (born 1944) |
1 January 2007 – 31 December 2016 |
Asia & Pacific | Retired after two full terms. | [27] | |
| Ban became the first East Asian to be selected as the secretary-general and the second Asian overall after U Thant. He was unanimously elected to a second term by the General Assembly on 21 June 2011. His second term began on 1 January 2012.[28] Prior to his selection, he was the Foreign Minister of South Korea from January 2004 to November 2006. | |||||||
| 9 |  |
António Guterres (born 1949) |
1 January 2017 – present |
Western European & others | |||
| Guterres is the first former head of government to become Secretary-General, and the first secretary-general born after the establishment of the United Nations. He was Prime Minister of Portugal from 1995 to 2002. He has also been President of the Socialist International (1999–2005) and United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (2005–2015). | |||||||
Statistics[]
| # | Secretary-General | Born | Age at ascension (first term) |
Time in office (total) |
Age at retirement (last term) |
Lifespan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Died | Age | ||||||
| - | Apr 25, 1900 | 45 years, 182 days Oct 24, 1945 |
102 days | 45 years, 283 days Feb 2, 1946 |
Oct 24, 1996 | 96 years, 182 days | |
| 1 | Jul 16, 1896 | 49 years, 201 days Feb 2, 1946 |
6 years, 283 days | 56 years, 117 days Nov 10, 1952 |
Dec 30, 1968 | 72 years, 167 days | |
| 2 | Jul 29, 1905 | 47 years, 255 days Apr 10, 1953 |
8 years, 162 days | 56 years, 51 days Sep 18, 1961 |
Sep 18, 1961 | 56 years, 51 days | |
| 3 | Jan 22, 1909 | 52 years, 285 days Nov 3, 1961 |
11 years, 59 days | 63 years, 344 days Dec 31, 1972 |
Nov 25, 1974 | 65 years, 307 days | |
| 4 | Dec 21, 1918 | 53 years, 11 days Jan 1, 1972 |
10 years, 0 days | 63 years, 10 days Dec 31, 1981 |
Jun 14, 2007 | 88 years, 175 days | |
| 5 | Jan 19, 1920 | 61 years, 347 days Jan 1, 1982 |
10 years, 0 days | 71 years, 346 days Dec 31, 1991 |
Mar 4, 2020 | 100 years, 45 days | |
| 6 | Nov 14, 1922 | 69 years, 48 days Jan 1, 1992 |
5 years, 0 days | 74 years, 47 days Dec 31, 1996 |
Feb 16, 2016 | 93 years, 94 days | |
| 7 | Apr 8, 1938 | 58 years, 268 days Jan 1, 1997 |
10 years, 0 days | 68 years, 267 days Dec 31, 2006 |
Aug 18, 2018 | 80 years, 132 days | |
| 8 | Jun 13, 1944 | 62 years, 202 days Jan 1, 2007 |
10 years, 0 days | 72 years, 201 days Dec 31, 2016 |
(living) | 77 years, 89 days | |
| 9 | Apr 30, 1949 | 67 years, 246 days Jan 1, 2017 |
(incumbent) | (incumbent) | (living) | 72 years, 133 days | |
By regional group[]
| UN Regional Group | Secretaries-General | Terms |
|---|---|---|
| WEOG | 4 | 7 |
| Eastern European Group | 0 | 0 |
| GRULAC | 1 | 2 |
| Asia-Pacific Group | 2 | 4 |
| African Group | 2 | 3 |
Living former secretary-general[]

Ban Ki-moon
(2007–2016)
13 June 1944
As of September 2021, Ban Ki-moon is the only former secretary-general currently living. The most recent death of a former secretary-general was that of Javier Pérez de Cuéllar (1982–1991) on 4 March 2020, aged 100.[29]
See also[]
- Mundialization
- Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations
Further reading[]
- Danish Iftikhar Chuadhry(2021) "The United Nations Secretary-General as an International Civil Servant." The International History Review
References[]
- ^ Urquhart, Brian (28 January 2009). "The Next Secretary-General: How to Fill a Job With No Description". Foreign Affairs: America and the World. ISSN 0015-7120. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- ^ "Kofi Annan: Job at a Glance". PBS. Educational Broadcasting Corporation. 2002. Archived from the original on 20 April 2016.
- ^ Appointing the UN Secretary-General (PDF). Research Report. 2015. New York: Security Council Report, Inc. 16 October 2015. pp. 4–5.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "The Role of the UN Secretary-General". Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- ^ Sengupta, Somini (21 July 2016). "Secrecy Reigns as U.N. Seeks a New Secretary General". The New York Times.
- ^ "A Well-Read Secretary General". The New York Times. 13 December 1981.
With a figurative puff of white smoke, the United Nations Security Council finally selected a new Secretary-General – a seasoned and soft-spoken diplomat from Peru, Javier Perez de Cuellar.
- ^ Barrett, George (13 October 1950). "Position of U.N. Chief Aide is Thrust Into Uncertainty". The New York Times. p. 1.
- ^ "Letter from Mogens Lykketoft to All Permanent Representatives and Permanent Observers to the United Nations, 21 July 2016" (PDF). 21 July 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "The role of the Secretary-General". United Nations Secretary-General. 22 April 2015. Retrieved 2 September 2020.
- ^ "The Secretary-General Is Dead; Long Live the Secretary-General". Observer. 10 October 2016. Retrieved 2 September 2020.
- ^ Teltsch, Kathleen. "Town House Offered to UN", The New York Times, 15 July 1972. Retrieved 27 December 2007.
- ^ Stout, David (26 October 1996). "Lord Gladwyn Is Dead at 96; Briton Helped Found the UN". The New York Times. Retrieved 31 October 2008.
- ^ The United Nations: Trygve Haldvan Lie (Norway). Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "An Historical Overview on the Selection of United Nations Secretaries-General" (PDF). UNA-USA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 October 2007. Retrieved 30 September 2007.
- ^ The United Nations: Dag Hammarskjöld (Sweden). Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ Linnér, S. (2007). Dag Hammarskjöld and the Congo crisis, 1960–61 Archived 5 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Page 28. Uppsala University. (22 July 2008).
- ^ United Nations: U Thant (Myanmar). Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ The United Nations: Kurt Waldheim (Austria). Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ Nossiter, Bernard D. (29 October 1981). "China Continues to Bar Waldheim Renomination". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- ^ s. "Waldheim elected U.N. secretary-general". HISTORY. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- ^ The United Nations: Javier Pérez de Cuéllar (Peru). Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ The United Nations: Boutros Boutros-Ghali (Egypt). Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ The United Nations: The Biography of Kofi A. Annan. Retrieved 13 December 2006.
- ^ "Kofi Annan of Ghana recommended by Security Council for appointment as Secretary-General of United Nations" (Press release). United Nations. 13 December 1996. Retrieved 12 December 2006.
- ^ Traub, James (2006). The Best Intentions. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. pp. 66–67. ISBN 978-0-374-18220-5.
- ^ "General Assembly appoints Kofi Annan of Ghana as seventh Secretary-General" (Press release). United Nations. 17 December 1996. Retrieved 12 December 2006.
- ^ "Ban Ki-moon is sworn in as next Secretary-General of the United Nations". United Nations.
- ^ "Ban Ki-moon gets second term as UN chief". The Globe and Mail. 22 June 2011. Archived from the original on 24 June 2011.
- ^ Gestión, Redacción (5 March 2020). "Javier Pérez de Cuéllar: Diplomático falleció este miércoles a los 100 años". Gestión (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 March 2020.
External links[]
- UN Secretary-General webpage
- How is the Secretary-General appointed?
- Global Policy Forum – UN Secretary-General
- Report on the process of appointing a new Secretary-General
- Who Will be the Next Secretary-General? (website on the 2006 campaigns)
- UNSGselection.org – a campaign for a more democratic selection process
- Secretaries-general
- Secretaries-General of the United Nations
- United Nations posts
- United Nations Secretariat