Sitagliptin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /sɪtəˈɡlɪptɪn/ ( |
| Trade names | Januvia, Tesavel, Xelevia, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a606023 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 87% |
| Protein binding | 38% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4- and CYP2C8-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 8 to 14 h[1] |
| Excretion | Kidney (80%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.217.948 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
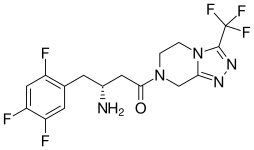
| Formula | C16H15F6N5O |
| Molar mass | 407.320 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
Sitagliptin, sold under the brand name Januvia among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes.[2] In the United Kingdom it is listed as less preferred than metformin or a sulfonylurea.[3] It is taken by mouth.[2] It is also available in the fixed-dose combination medication sitagliptin/metformin (Janumet, Janumet XR).[2]
Common side effects include headaches, swelling of the legs, and upper respiratory tract infections.[2] Serious side effects may include angioedema, low blood sugar, kidney problems, pancreatitis, and joint pain.[2] Whether use in pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe is unclear.[4] It is in the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class and works by increasing the production of insulin and decreasing the production of glucagon by the pancreas.[2]
Sitagliptin was developed by Merck & Co. and approved for medical use in the United States in 2006.[2] In 2018, it was the 83rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 9 million prescriptions.[5][6]
Medical uses[]
Sitagliptin is used to treat type 2 diabetes.[2] It is generally less preferred than metformin or sulfonylureas.[3] It is taken by mouth.[2] It is also available as the fixed-dose combinations of sitagliptin/metformin (Janumet, Janumet XR)[2] and sitagliptin/simvastatin (Juvisync).[7]
Sitagliptin should not be used to treat type 1 diabetes. In December 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved labeling changes stating that Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin and metformin hydrochloride), and Janumet XR (sitagliptin and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) are not proven to improve glycemic (blood sugar) control in children aged 10 to 17 with type 2 diabetes.[8] The drugs are approved to improve blood sugar control in adults aged 18 and older with type 2 diabetes.[8]
Adverse effects[]
Adverse effects from sitagliptin are similar to placebo, except for rare nausea, common cold-like symptoms, and photosensitivity.[9] It does not increase the risk of diarrhea.[10] No significant difference exists in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between placebo and sitagliptin.[9][11][12] In those taking sulphonylureas, the risk of low blood sugar is increased.[13]
The existence of rare case reports of kidney failure and hypersensitivity reactions is noted in the United States prescribing information, but a causative role for sitagliptin has not been established.[14]
Several postmarketing reports of pancreatitis (some fatal) have been made in people treated with sitagliptin and other DPP-4 inhibitors,[15] and the U.S. package insert carries a warning to this effect,[16] although the causal link between sitagliptin and pancreatitis has not yet been fully substantiated.[17] One study with lab rats published in 2009 concluded that some of the possible risks of pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer may be reduced when it is used with metformin. However, while DPP-4 inhibitors showed an increase in such risk factors, as of 2009, no increase in pancreatic cancer has been reported in individuals taking DPP-4 inhibitors.[18]
The updated (August 2015) prescribing information cautions that multiple postmarketing reports have been made of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients receiving sitagliptin. Merck notes:
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of JANUVIA as monotherapy and/or in combination with other antihyperglycemic agents. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria, cutaneous vasculitis, and exfoliative skin conditions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome; hepatic enzyme elevations; acute pancreatitis, including fatal and nonfatal hemorrhagic and necrotizing pancreatitis; worsening renal function, including acute kidney injury (sometimes requiring dialysis); severe and disabling arthralgia; constipation; vomiting; headache; myalgia; pain in extremity; back pain; pruritus; pemphigoid.[14]
In 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) added a new Warning and Precaution about the risk of "severe and disabling" joint pain to the labels of all DPP-4 inhibitor medicines.[19] In addition to sitagliptin, other DPP-4 inhibitors such as saxagliptin, linagliptin, and alogliptin must also carry the new FDA Warning and Precaution label.
Mechanism of action[]
Sitagliptin works to competitively inhibit the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4). This enzyme breaks down the incretins GLP-1 and GIP, gastrointestinal hormones released in response to a meal.[20] By preventing breakdown of GLP-1 and GIP, they are able to increase the secretion of insulin and suppress the release of glucagon by the alpha cells of the pancreas. This drives blood glucose levels towards normal. As the blood glucose level approaches normal, the amounts of insulin released and glucagon suppressed diminishes, thus tending to prevent an "overshoot" and subsequent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which is seen with some other oral hypoglycemic agents.
Sitagliptin has been shown to lower HbA1c level by about 0.7% points versus placebo. It is slightly less effective than metformin when used as a monotherapy. It does not cause weight gain and has less hypoglycemia compared to sulfonylureas. Sitagliptin is recommended as a second-line drug (in combination with other drugs) after the combination of diet/exercise and metformin fails.[21]
History[]
Sitagliptin was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on October 17, 2006,[22] and is marketed in the US as Januvia by Merck & Co. On April 2, 2007, the FDA approved an oral combination of sitagliptin/metformin marketed in the US as Janumet. On October 7, 2011, the FDA approved an oral combination of sitagliptin/simvastatin marketed in the US as Juvisync.[7]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Herman GA, Stevens C, van Dyck K, Bergman A, Yi B, De Smet M, Snyder K, Hilliard D, Tanen M, Tanaka W, Wang AQ, Zeng W, Musson D, Winchell G, Davies MJ, Ramael S, Gottesdiener KM, Wagner JA (December 2005). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sitagliptin, an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, in healthy subjects: results from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with single oral doses". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 78 (6): 675–88. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.09.002. PMID 16338283. S2CID 20935646.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j "Sitagliptin Phosphate Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 681. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ "Sitagliptin Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ "Sitagliptin Phosphate - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "FDA Approves Combination Therapy Juvisync" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. October 7, 2011. Archived from the original on 2014-08-24. Retrieved 2013-11-17.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Diabetes drug not proven to improve blood sugar in pediatric patients". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 4 December 2020. Retrieved 5 December 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Januvia Side Effects & Drug Interactions". RxList.com. 2007. Archived from the original on 2007-11-20. Retrieved 2007-11-28.
- ^ Zhao Q, Hong D, Zheng D, Xiao Y, Wu B (2014). "Risk of diarrhea in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with sitagliptin: a meta-analysis of 30 randomized clinical trials". Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 8: 2283–94. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S70945. PMC 4234286. PMID 25419118.
- ^ Schuman, Thomas P.; Litt, Jerome Z.; Hood, Antoinette F.; Rader, Ryan K.; Stoecker, William V.; Stricklin, Sherea M. (1 February 2012). "Persistent edematous-plaque photosensitivity observed with sitagliptin phosphate (Januvia®)". Dermatology Online Journal. 18 (2) – via escholarship.org.
- ^ "Januvia side effect: Photosensitivity reaction - eHealthMe". www.ehealthme.com.
- ^ Salvo, Francesco; Moore, Nicholas; Arnaud, Mickael; Robinson, Philip; Raschi, Emanuel; De Ponti, Fabrizio; Bégaud, Bernard; Pariente, Antoine (3 May 2016). "Addition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors to sulphonylureas and risk of hypoglycaemia: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ. 353: i2231. doi:10.1136/bmj.i2231. PMC 4854021. PMID 27142267.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "www.merck.com" (PDF).
- ^ Olansky L (2010). "Do incretin-based therapies cause acute pancreatitis?". Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. 4 (1): 228–9. doi:10.1177/193229681000400129. PMC 2825646. PMID 20167189.
- ^ "Januvia for type 2 diabetes". Merck & Co. Archived from the original on 2012-09-07. Retrieved 2010-07-31.
- ^ National Prescribing Service (August 2010). "Sitagliptin for Type 2 Diabetes". Archived from the original on 18 July 2010. Retrieved 27 August 2010.
- ^ Matveyenko, A. V.; Dry, S.; Cox, H. I.; Moshtaghian, A.; Gurlo, T.; Galasso, R.; Butler, A. E.; Butler, P. C. (2009). "Beneficial Endocrine but Adverse Exocrine Effects of Sitagliptin in the Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Transgenic Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes: Interactions with Metformin". Diabetes. 58 (7): 1604–1615. doi:10.2337/db09-0058. PMC 2699878. PMID 19403868.
- ^ "DPP-4 Inhibitors for Type 2 Diabetes: Drug Safety Communication—May Cause Severe Joint Pain". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2015-08-28. Retrieved 1 September 2015.
- ^ Herman G, Bergman A, Liu F, Stevens C, Wang A, Zeng W, Chen L, Snyder K, Hilliard D, Tanen M, Tanaka W, Meehan A, Lasseter K, Dilzer S, Blum R, Wagner J (2006). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic effects of the oral DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin in middle-aged obese subjects". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 46 (8): 876–86. doi:10.1177/0091270006289850. PMID 16855072. S2CID 45849328.
- ^ Gadsby, Roger (2009). "Efficacy and Safety of Sitagliptin in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes" (pdf). Clinical Medicine: Therapeutics (1): 53–62.
- ^ "FDA Approves New Treatment for Diabetes" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). October 17, 2006. Archived from the original on 2009-02-28. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
External links[]
- "Sitagliptin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors
- Carboxamides
- Trifluoromethyl compounds
- Fluoroarenes
- Triazoles
- Merck & Co. brands