Sodomy laws in the United States
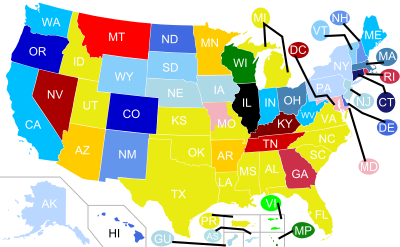

Sodomy laws in the United States, which outlawed a variety of sexual acts, were inherited from colonial laws in the 17th century.[1] While they often targeted sexual acts between persons of the same sex, many statutes employed definitions broad enough to outlaw certain sexual acts between persons of different sexes, in some cases even including acts between married persons.
Through the 20th century, the gradual liberalization of American sexuality led to the elimination of sodomy laws in most states. During this time, the Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of sodomy laws in Bowers v. Hardwick in 1986. However, in 2003, the Supreme Court reversed the decision with Lawrence v. Texas, invalidating sodomy laws in the remaining 14 states (Alabama, Florida, Idaho, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri (statewide), North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Texas, Utah, and Virginia).
History[]
Colin Talley argues that the sodomy statutes in colonial America in the 17th century were largely unenforced. The reason he argues is that male-male eroticism did not threaten the social structure or challenge the gendered division of labor or the patriarchal ownership of wealth.[2] There were gay men on General Washington's staff and among the leaders of the new republic,[3] even though in Virginia there was a maximum penalty of death on Sodomy. In 1779, Thomas Jefferson tried to reduce the maximum punishment to castration.[4] It was rejected by the Virginia legislature.[5]
Prior to 1962, sodomy was a felony in every state, punished by a lengthy term of imprisonment and/or hard labor. In that year, the Model Penal Code (MPC) — developed by the American Law Institute to promote uniformity among the states as they modernized their statutes — struck a compromise that removed consensual sodomy from its criminal code while making it a crime to solicit for sodomy. In 1962 Illinois adopted the recommendations of the Model Penal Code and thus became the first state to remove criminal penalties for consensual sodomy from its criminal code,[6] almost a decade before any other state. Over the years, many of the states that did not repeal their sodomy laws had enacted legislation reducing the penalty. At the time of the Lawrence decision in 2003, the penalty for violating a sodomy law varied very widely from jurisdiction to jurisdiction among those states retaining their sodomy laws. The harshest penalties were in Idaho, where a person convicted of sodomy could earn a life sentence. Michigan followed, with a maximum penalty of 15 years' imprisonment while repeat offenders got life.[citation needed]
By 2002, 36 states had repealed their sodomy laws or their courts had overturned them. By the time of the 2003 Supreme Court decision, the laws in most states were no longer enforced or were enforced very selectively. The continued existence of these rarely enforced laws on the statute books, however, are often cited as justification for discrimination against gay men, lesbians, and bisexuals.
On June 26, 2003, the U.S. Supreme Court in a 6–3 decision in Lawrence v. Texas struck down the Texas same-sex sodomy law, ruling that this private sexual conduct is protected by the liberty rights implicit in the due process clause of the United States Constitution. This decision invalidated all state sodomy laws insofar as they applied to noncommercial conduct in private between consenting civilians and reversed the Court's 1986 ruling in Bowers v. Hardwick that upheld Georgia's sodomy law.
Before that 2003 ruling, 27 states, the District of Columbia, and 4 territories had repealed their sodomy laws by legislative action; 9 states had had them overturned or invalidated by state court action; 4 states still had same-sex sodomy laws; and 10 states, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. military had laws applying to all regardless of gender. In 2005, Puerto Rico repealed its sodomy law, and in 2006, Missouri repealed its law against "homosexual conduct". In 2013, Montana removed "sexual contact or sexual intercourse between two persons of the same sex" from its definition of deviate sexual conduct, Virginia repealed its lewd and lascivious cohabitation statute, and sodomy was legalized in the US armed forces.
In 2005, basing its decision on Lawrence, the Supreme Court of Virginia in Martin v. Ziherl invalidated § 18.2-344, the Virginia statute making fornication between unmarried persons a crime.[7]
Louisiana's statutes still include "unnatural carnal copulation by a human being with another of the same sex" in their definition of "crimes against nature", punishable (in theory) by a fine of up to $2,000 or a prison sentence of up to five years, with or without hard labor;[8] however, this section was further mooted by the United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit in 2005 in light of the Lawrence decision.[9]
In State v. Whiteley (2005), the North Carolina Court of Appeals ruled that the crime against nature statute, N.C. G.S. § 14-177,[10] is not unconstitutional on its face because it may properly be used to criminalize sexual conduct involving minors, non-consensual or coercive conduct, public conduct, and prostitution.[11]
On January 31, 2013, the Senate of Virginia passed a bill repealing § 18.2-345, the lewd and lascivious cohabitation statute enacted in 1877. On February 20, 2013, the Virginia House of Delegates passed the bill by a vote of 62 to 25 votes. On March 20, 2013, Governor Bob McDonnell signed the repeal of the lewd and lascivious cohabitation statute from the Code of Virginia.[12]
On March 12, 2013, a three-judge panel of the Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit struck down § 18.2-361, the crimes against nature statute. On March 26, 2013, Attorney General of Virginia Ken Cuccinelli filed a petition to have the case reheard en banc, but the Court denied the request on April 10, 2013, with none of its 15 judges supporting the request.[13] On June 25, Cuccinelli filed a petition for certiorari asking the U.S. Supreme Court to review the Court of Appeals decision, which was rejected on October 7.[14][15]
On February 7, 2014, the Virginia Senate voted 40-0 in favor of revising the crimes against nature statue to remove the ban on same-sex sexual relationships. On March 6, 2014, the Virginia House of Delegates voted 100-0 in favor of the bill. On April 7, the Governor submitted slightly different version of the bill. It was enacted by the Legislature on April 23, 2014. The law took effect upon passage.[16]
In April 2014, a proposed Louisiana bill sought to revise the state's crime against nature law, maintaining the existing prohibition against sodomy during the commission of rape and child sex abuse, and against sex with animals, but removing the unconstitutional prohibition against sex between consenting adults. The bill was defeated on April 15, 2014 by a vote of 66 to 27.[17]
Utah voted to revise its sodomy laws to include only forcible sodomy and sodomy on children rather than any sexual relations between consenting adults on February 26, 2019.[18] Governor Gary Herbert signed the bill into law on March 26, 2019.[19][20]
On May 23, 2019, the Alabama House of Representatives passed, with 101 voting yea and 3 absent, Alabama Senate Bill 320, which repeals the ban on "deviate sexual intercourse". On May 28, 2019, the Alabama State Senate passed Alabama Senate Bill 320, with 32 yea and 3 absent. The bill took effect on September 1, 2019.[21][22]
As of October 1, 2020, 15 states either have not yet formally repealed their laws against sexual activity among consenting adults or have not revised them to accurately reflect their true scope in the aftermath of Lawrence v. Texas. Often, the sodomy law was drafted to also encompass other forms of sexual conduct such as bestiality, and no attempt has subsequently succeeded in separating them. Eleven states' statutes purport to ban all forms of sodomy, some including oral intercourse, regardless of the participants' genders: Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma and South Carolina. Three states specifically target their statutes at same-sex relations only: Kansas,[23][24] Kentucky, and Texas.
Maryland voted to repeal its sodomy law on March 18, 2020. The bill became law in May 2020 without the signature of Governor Larry Hogan.[25] While the original text of the bill intended to repeal both the state's sodomy law and unnatural or perverted sexual practice law, amendments from the Maryland Senate urged to solely repeal the sodomy law.[26]
- Florida (Fld. Stat. 800.02.)
- Georgia (O.C.G.A. § 16-6-2)
- Idaho (I.C. § 18-6605.)
- Kansas (Kan. Stat. 21-3505.)
- Kentucky (KY Rev Stat § 510.100.)
- Louisiana (R.S. 14:89.)
- Maryland (Md. Code Ann., Criminal Law Article, § 3-322.)
- Massachusetts (MGL Ch. 272, § 34.) (MGL Ch. 272, § 35.)
- Michigan (MCL § 750.158.) (MCL § 750.338.) (MCL § 750.338a.) (MCL § 750.338b.)
- Minnesota (Minn. Stat. 609.293.)
- Mississippi (Miss. Code § 97-29-59.)
- North Carolina (G.S. § 14-177.)
- Oklahoma (§21-886.)
- South Carolina (S.C. Code § 16-15-60.)
- Texas (Tx. Penal Code § 21.06.)
Federal law[]
Sodomy laws in the United States were largely a matter of state rather than federal jurisdiction, except for laws governing the District of Columbia and the U.S. Armed Forces.
District of Columbia[]
In 1801, Congress enacted the District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801 that continued all criminal laws of Maryland and Virginia in the now formally structured District, with those of Maryland applying to that portion of the District ceded from Maryland, and those of Virginia applying to that portion ceded from Virginia. At the time, Maryland had a sodomy law applicable only to free males with a punishment of "labour for any time, in their discretion, not exceeding seven years for the same crime, on the public roads of the said county, or in making, repairing or cleaning the streets or bason [sic] of Baltimore-town" and the death penalty for slaves committing sodomy, while Virginia had a penalty of 1–10 years for free persons committing sodomy, but had the death penalty for slaves committing sodomy. The law went into effect on February 27, 1801.[27]
In 1831, Congress established penalties in the District of Columbia for a number of crimes, but not for sodomy. It specified that "every other felony, misdemeanor, or offence not provided for by this act, may and shall be punished as heretofore[.]" At the time, Maryland and Virginia had a penalty of 1–10 years for committing sodomy. It went into effect on March 2, 1831.[27]
In 1892, Congress passed a law for the District of Columbia that states that "for the preservation of the public peace and the protection of property within the District of Columbia." Labeled in the law as vagrants were "all public prostitutes, and all such persons who lead a notoriously lewd or lascivious course of life[.]" All offenders had to post bond of up to $200 for good behavior for a period of six months. The law went into effect on July 29, 1892.[27]
In 1898, Congress deleted the word "notoriously" from the provision concerning a lewd or lascivious course of life, thereby allowing prosecution of those without notoriety. The bond for good behavior was raised to $500, and the law was made clearly gender-neutral. The law went into effect on July 8, 1898.[27]
In 1901, Congress adopting a new code for the District of Columbia that expressly recognized common-law crimes, with a penalty for them of up to five years and/or a $1,000 fine. The law went into effect on March 3, 1901.[27]
In 1935, Congress passed a law for the District of Columbia that made it a crime for "any person to invite, entice, persuade, or to address for the purpose of inviting, enticing, or persuading any person or persons...to accompany, to go with, to follow him or her to his or her residence, or to any other house or building, inclosure, or other place, for the purpose of prostitution, or any other immoral or lewd purpose." It imposed a fine of up to $100, up to 90 days in jail, and courts were permitted to "impose conditions" on anyone convicted under this law, including "medical and mental examination, diagnosis and treatment by proper public health and welfare authorities, and such other terms and conditions as the court may deem best for the protection of the community and the punishment, control, and rehabilitation of the defendant." The law went into effect on August 14, 1935.[27]
In 1941, Congress enacted a new solicitation law for the District of Columbia that labeled a "vagrant" any person who "engages in or commits acts of fornication or perversion for hire." The law went into effect on December 17, 1941.[27]
In 1948, Congress enacted the first sodomy law in the District of Columbia, which established a penalty of up to 10 years in prison or a fine of up to $1,000 for sodomy. Also included with this sodomy law was a psychopathic offender law and a law "to provide for the treatment of sexual psychopaths in the District of Columbia, and for other purposes." The law went into effect on June 9, 1948.[27]
In 1953, Congress changed the solicitation law in the District of Columbia so that the jail term of up to 90 days was retained, but the maximum fine was raised to $250, and the reference to the power of judges to "impose conditions" on the defendant was removed. The law went into effect on June 29, 1953.[27]
In 1981, after the District of Columbia regained home rule from Congress, it enacted a law that repealed the sodomy law, as well as other consensual acts, and made the sexual assault laws gender-neutral. However, the U.S. House exercised the power that it retained to veto laws passed by the District of Columbia Council. On October 1, 1981, the House voted 281-119 to disallow the new law.[28][29][30][31][32][33] In 1983, one of the House vetoes by Congress was declared unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in the case of Immigration and Naturalization Service v. Chadha, but the law was repealed by an act of Congress in a revision to the home-rule law required by the Supreme Court decision.[27]
Repeal[]
In 1993, the District of Columbia passed a law repealing the sodomy law, but this time Congress did not interfere and allowed the law to go into effect.[27]
Military[]
Although the U.S. military discharged soldiers for homosexual acts throughout the eighteenth and nineteenth century, U.S. military law did not expressly prohibit homosexuality or homosexual conduct until February 4, 1921.[34]
On March 1, 1917, the Articles of War of 1916 were implemented. This included a revision of the Articles of War of 1806, the new regulations detail statutes governing U.S. military discipline and justice. Under the category Miscellaneous Crimes and Offences, Article 93 states that any person subject to military law who commits "assault with intent to commit sodomy" shall be punished as a court-martial may direct.[35]
On June 4, 1920, Congress modified Article 93 of the Articles of War of 1916. It was changed to make the act of sodomy itself a crime, separate from the offense of assault with intent to commit sodomy.[35] It went into effect on February 4, 1921.[36]
On May 5, 1950, the Uniform Code of Military Justice was passed by Congress and was signed into law by President Harry S. Truman, and became effective on May 31, 1951. Article 125 forbids sodomy among all military personnel, defining it as "any person subject to this chapter who engages in unnatural carnal copulation with another person of the same or opposite sex or with an animal is guilty of sodomy. Penetration, however slight, is sufficient to complete the offence."[35]
As for the U.S. Armed Forces, the Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces has ruled that the Lawrence v. Texas decision applies to Article 125, severely narrowing the previous ban on sodomy. In both United States v. Stirewalt and United States v. Marcum, the court ruled that the "conduct [consensual sodomy] falls within the liberty interest identified by the Supreme Court,"[37] but went on to say that despite the application of Lawrence to the military, Article 125 can still be upheld in cases where there are "factors unique to the military environment" that would place the conduct "outside any protected liberty interest recognized in Lawrence."[38] Examples of such factors include rape, fraternization, public sexual behavior, or any other factors that would adversely affect good order and discipline. Convictions for consensual sodomy have been overturned in military courts under Lawrence in both United States v. Meno[39] and United States v. Bullock.[40]
Repeal[]
On December 26, 2013, President Barack Obama signed into law the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2014, which repealed the ban on consensual sodomy found in Article 125.[41]
State and territorial laws prior to Lawrence v. Texas[]
Below is a table of sodomy laws and penalties in U.S. states and territories prior to their invalidation in 2003.[42][43]
The table indicates which acts or groups were covered under each sodomy law, as pertaining to consenting adults. It also indicates the year and method of repeal or strikedown.
| State or territory |
Year of repeal or strikedown |
Covered | Invalidated by | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral sex | Anal sex | Homosexual couples |
Unmarried heterosexual couples |
Married couples | |||
| Alabama | 2003 |
| |||||
| Alaska | 1971/ 1980 |
| |||||
| American Samoa |
1979 | N/A |
| ||||
| Arizona | 2001 |
| |||||
| Arkansas | 1975/ 2001/ 2005 |
| |||||
| California | 1976 | N/A |
| ||||
| Colorado | 1972 | N/A |
| ||||
| Connecticut | 1971 | N/A |
| ||||
| Delaware | 1973 | N/A |
| ||||
| District of Columbia |
1993 | N/A |
| ||||
| Florida | 2003 |
| |||||
| Georgia | 1998 |
| |||||
| Guam | 1978 | N/A |
| ||||
| Hawaii | 1973 | N/A |
| ||||
| Idaho | 1971/ 2003 |
| |||||
| Illinois | 1962 | N/A |
| ||||
| Indiana | 1976 | N/A |
| ||||
| Iowa | 1978 | N/A |
| ||||
| Kansas | 2003 |
| |||||
| Kentucky | 1992 |
| |||||
| Louisiana | 2003 |
| |||||
| Maine | 1976 | N/A |
| ||||
| Maryland | 1999 |
| |||||
| Massachusetts | 1974 |
| |||||
| Michigan | 1990/ 2003 |
| |||||
| Minnesota | 2001 |
| |||||
| Mississippi | 2003 |
| |||||
| Missouri | 1999/ 2003 |
| |||||
| Montana | 1997 |
| |||||
| Nebraska | 1978 | N/A |
| ||||
| Nevada | 1993 | N/A |
| ||||
| New Hampshire |
1975 | N/A |
| ||||
| New Jersey | 1978 | N/A |
| ||||
| New Mexico | 1975 | N/A |
| ||||
| New York | 1980/ 2000 |
| |||||
| North Carolina | 2003 |
| |||||
| Northern Mariana Islands |
1983 | N/A |
| ||||
| North Dakota | 1973 | N/A |
| ||||
| Ohio | 1974 | N/A |
| ||||
| Oklahoma | 1988/ 2003 |
| |||||
| Oregon | 1972 | N/A |
| ||||
| Pennsylvania | 1972/ 1980 |
| |||||
| Puerto Rico | 1974/ 2003 |
| |||||
| Rhode Island | 1998 |
| |||||
| South Carolina | 2003 |
| |||||
| South Dakota | 1977 | N/A |
| ||||
| Tennessee | 1996 |
| |||||
| Texas | 2003 |
| |||||
| Utah | 1971/ 2003 |
| |||||
| Vermont | 1977 | N/A |
| ||||
| Virgin Islands | 1985 | N/A |
| ||||
| Virginia | 2003 |
| |||||
| Washington | 1976 | N/A |
| ||||
| West Virginia | 1976 | N/A |
| ||||
| Wisconsin | 1983 | N/A |
| ||||
| Wyoming | 1977 | N/A |
| ||||
See also[]
- LGBT rights in the United States
- List of sex-related court cases in the United States
- Section 839(a) of title 10 United States Code § 925 - Article 125.
References[]
- ^ Eskridge, William N. (2009). Gaylaw: Challenging the Apartheid of the Closet. Harvard University Press. p. 161. ISBN 9780674036581.
- ^ Colin L. Talley, "Gender and male same-sex erotic behavior in British North America in the seventeenth century." Journal of the History of Sexuality (1996): 385-408. online
- ^ William E Benemann, Male-Male Intimacy in Early America: Beyond Romantic Friendships (2006).
- ^ "Amendment VIII: Thomas Jefferson, A Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments". Press-pubs.uchicago.edu. Archived from the original on 2014-02-04. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ Patricia S. Ticer, State Senator (D-30) in the. "Virginia". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2011-10-04. Retrieved 2011-08-31.
- ^ Canaday, Margot (September 3, 2008). "We Colonials: Sodomy Laws in America". The Nation. Archived from the original on January 26, 2014. Retrieved February 7, 2014.
- ^ Google Scholar: Martin v.Ziherl, accessed April 9, 2011
- ^ "Louisiana RS 14:89". Legis.state.la.us. Archived from the original on 2013-08-03.
- ^ "Sodomy law revisions are upheld on appeal, Times-Picayune". Nola.com. Archived from the original on 2015-10-18. Retrieved 2012-03-18.
- ^ "G.S. § 14-177". Ncga.state.nc.us. Archived from the original on 2014-02-21. Retrieved 2013-12-05.
- ^ "State v. Whiteley, 172 NC App 772 (04-636) 08/16/2005". Aoc.state.nc.us. Archived from the original on 2008-10-12. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ "SB 969". Open:States. Archived from the original on December 24, 2013. Retrieved April 13, 2013.
- ^ "Ken Cuccinelli Loses Petition To Uphold Anti-Sodomy Law". The Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 2013-04-13. Retrieved 2013-04-10.
- ^ "Ken Cuccinelli Appeals To Defend Virginia's Anti-Sodomy Law At Supreme Court". Huffington Post. June 25, 2013. Archived from the original on July 2, 2013.
- ^ "Court won't hear Va. appeal over sodomy law". USA Today. October 7, 2013. Archived from the original on October 25, 2017.
- ^ "LIS > Bill Tracking > SB14 > 2014 session". Leg1.state.va.us. Archived from the original on 2014-03-10. Retrieved 2014-04-25.
- ^ O'Donoghue, Julia (April 15, 2014). "Louisiana House votes 27-66 to keep unconstitutional anti-sodomy law on the books". Times-Picayune. Archived from the original on April 16, 2014. Retrieved April 16, 2014.
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ [3]
- ^ Act 2019-465, SB320
- ^ AL SB 320
- ^ Kan. Stat. Ann. § 21-3505 (2010).
- ^ Sulzberger, A.G. (20 Jan 2012), "Kansas Law on Sodomy Stays on Books Despite a Cull", The New York Times, nytimes.com, archived from the original on January 22, 2012, retrieved 21 Jan 2012,
A version of this article appeared in print on January 21, 2012, on page A13 of the New York edition with the headline: Kansas Law On Sodomy Stays on Books Despite a Cull.
- ^ "Maryland Legislation HB0081". mgaleg.maryland.gov.
- ^ "Maryland HB81 | 2020 | Regular Session". LegiScan. Retrieved 2020-09-11.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k District of Columbia Archived 2014-10-27 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ To Table the Phillip Crane Motion to Discharge the House Committee on the District of Columbia from Further Consideration of H. Res. 208, The Resolution Disapproving the Action of the District of Columbia Council in Revising Criminal Penalties in Certain Sex-Related Offenses. Archived 2014-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ To Proceed to the Consideration of H. Res. 208, The Resolution Disapproving the Action of the District of Columbia Council in Revising Criminal Penalties in Certain Sex-Related Offenses. (Motion Agreed To) Archived 2014-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ To Discharge the House Committee of the District of Columbia from Further Consideration of H. Res. 208, The Resolution Disapproving the Action of the District of Columbia Council in Revising Criminal Penalties in Certain Sex-Related Offenses. (Motion Agreed To) Archived 2014-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ To Adopt H. Res. 208, The Resolution Disapproving the Action of the District of Columbia Council in Revising Criminal Penalties in Certain Sex-Related Offenses (Motion Agreed To) Archived 2014-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ To Limit Debate to Two Hours on H. Res. 208, The Resolution Disapproving the Action of the District of Columbia Council in Revising Criminal Penalties in Certain Sex-Related Offenses. (Motion Agreed To) Archived 2014-10-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ H. Res. 208 - A resolution disapproving the action of the District of Columbia Council in approving the District of Columbia Sexual Assault Reform Act of 1981. Archived 2014-03-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ United States Archived 2016-02-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Key Dates in US Policy on Gay Men and Women in the United States Military". usni.org. Archived from the original on 2014-03-23. Retrieved 2014-03-22.
- ^ The Articles of War
- ^ U.S. Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces: U.S. v. Stirewalt, September 29, 2004 Archived May 25, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, accessed August 16, 2010
- ^ U.S. Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces: U.S. v. Marcum, August 23, 2004 Archived April 7, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, accessed August 16, 2010
- ^ "United States v. Webster M. Smith" (PDF). Uscg.mil. Retrieved 2013-10-21.
- ^ United States v. Bullock, Army 20030534 (United States Army Court of Criminal Appeals 2004).
- ^ Johnson, Chris (December 20, 2013). "Defense bill contains gay-related provisions". Washington Blade. Archived from the original on December 22, 2013. Retrieved December 21, 2013.
- ^ SodomyLaws.org: "United States Sodomy Laws," January 28, 1998 Archived December 16, 2013, at the Wayback Machine, accessed August 17, 2010
- ^ GLAPN - Case Law: "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-10-01. Retrieved 2010-09-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link), accessed September 25, 2010
- ^ "Jegley v. Picado 80 S.W.3d 332". Apa.org. Archived from the original on 2013-11-04. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ "Senate Bill 984" (PDF). Arkansas State Legislature. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 22, 2014. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- ^ "800.02 Unnatural and lascivious act. A person who commits any unnatural and lascivious act with another person commits a misdemeanor of the second degree". Archive.flsenate.gov. Archived from the original on 2013-12-04. Retrieved 2013-12-02.
- ^ "Flsenate Archive: Statutes & Constitution > View Statutes". Archive.flsenate.gov. Archived from the original on 2014-03-11. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ "The History of Sodomy Laws in the United States - Kansas". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2013-02-11. Retrieved 2012-08-05.
- ^ "The History of Sodomy Laws in the United States - Kentucky". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2011-11-08. Retrieved 2012-08-05.
- ^ Google Scholar: Stephen Adam Schochet v. State of Maryland, October 9, 1990, accessed March 11, 2011
- ^ [4]
- ^ Massachusetts Cases: Commonwealth v. Richard L. Balthazar, 366 Mass. 298 Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine, accessed March 11, 2011
- ^ Supreme Judicial Court of Massachusetts: GLAD v. Attorney General, February 21, 2002 Archived February 25, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, accessed August 17, 2010
- ^ Michigan Organization for Human Rights v. Kelley, No. 88–815820 CZ slip op. (Mich. 3rd Cir. Ct. July 9, 1990).
- ^ Gay Times: Michigan Archived 2011-09-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Sodomy laws - Michigan". Gay & Lesbian Archives of the Pacific Northwest. Archived from the original on April 3, 2014. Retrieved August 2, 2013.
- ^ People v. Brashier, 496 NW 2d 385 (Mich. App. December 29, 1992).
- ^ "Doe v Ventura". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2012-11-03. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ "Montana". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2011-10-04. Retrieved 2011-08-31.
- ^ "Montana Kills Sodomy Law". Thetaskforce.org. 1997-07-04. Archived from the original on 2011-08-04. Retrieved 2011-08-31.
- ^ "Montana governor signs bill to strike down obsolete sodomy law – LGBTQ Nation". Lgbtqnation.com. Archived from the original on 2013-10-25. Retrieved 2013-10-21.
- ^ "LAWS Detailed Bill Information Page". Laws.leg.mt.gov. Archived from the original on 2013-10-22. Retrieved 2013-10-21.
- ^ [5] Archived July 10, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ [6] Archived October 20, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The History of Sodomy Laws in the United States - Tennessee". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2013-04-24. Retrieved 2012-08-05.
- ^ "The History of Sodomy Laws in the United States - Texas". Glapn.org. Archived from the original on 2011-10-04. Retrieved 2011-08-31.
- ^ Weiner, Rachel (6 March 2014). "Virginia lawmakers repeal sodomy ban". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 18 May 2014.
Further reading[]
- Ellen Ann Andersen, Out of the Closets and Into the Courts: Legal Opportunity Structure and Gay Rights Litigation (University of Michigan Press, 2006), ISBN 0-472-11397-6, Ch. 4 "Sodomy Reform from Stonewall to Bowers," Ch. 5 "Sodomy Reform from Bowers to Lawrence", available in part online, accessed August 26, 2010
- Carlos A. Ball, From the Closet to the Courtroom: Five LGBT Rights Lawsuits that have Changed our Nation (Beacon Press, 2010), ISBN 0-8070-0078-7
- Patricia A. Cain, Rainbow Rights: The Role of Lawyers and Courts in the Lesbian and Gay Civil Rights Movement (Boulder, CO: Westview Press, 2000), ISBN 0-8133-2618-4, Ch. 4 "Private Rights: 1950-1985", available in part online, accessed August 26, 2010
- William N. Eskridge, Dishonorable Passions: Sodomy Laws in America, 1861-2003 (NY: Viking, 2008), ISBN 0-670-01862-7
- Leslie Moran, The Homosexual(ity) of Law (NY: Routledge, 1996)
- Martha C. Nussbaum, From Disgust to Humanity: Sexual Orientation and Constitutional Law (NY: Oxford University Press, 2010), ISBN 0-19-530531-0
- Jason Pierceson, Courts, Liberalism, and Rights: Gay Law and Politics in the United States and Canada (Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2005), available in part online, accessed August 26, 2010
- Daniel R. Pinello, Gay Rights and American Law (Cambridge University Press, 2003), available in part online, accessed August 26, 2010
- Jerald Sharum "Controlling Conduct: The Emerging Protection of Sodomy in the Military" in Albany Law Review, vol. 69, No. 4, 2006
External links[]
- Legal history of the United States
- History of LGBT civil rights in the United States
- LGBT law in the United States
- LGBT-related lists
- United States repealed legislation