Solar eclipse of April 29, 2014
| Solar eclipse of April 29, 2014 | |
|---|---|
 Partial from Adelaide, Australia | |
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | -1.00001 |
| Magnitude | 0.9868 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | - |
| Coordinates | 70°36′S 131°18′E / 70.6°S 131.3°E |
| Max. width of band | - km |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 3:52:38 |
| (U1) Total begin | 5:47:50 |
| Greatest eclipse | 6:04:33 |
| (U4) Total end | 6:09:20 |
| (P4) Partial end | 8:14:28 |
| References | |
| Saros | 148 (21 of 75) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9539 |
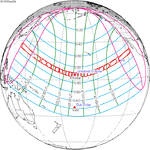
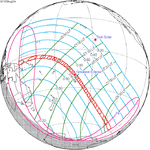
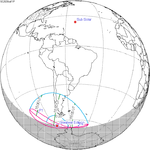
An annular solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, April 29, 2014. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The center of the Moon's shadow missed the Earth's South Pole, but the partial eclipse was visible from parts of Antarctica and Australia, and an annular eclipse was visible from a small part of Antarctica.
This eclipse's gamma value is closer to 1 than any other eclipse from 2000 B.C. to 3000 A.D. This means the center of the moon shadow passes almost exactly at the surface of the Earth, barely missing the Antarctic continent by a few kilometers.
Visibility[]
Animation of eclipse path
Images[]

Simulated annularity from Victoria Land

Partial from Scarborough, Queensland, 7:03 UTC

Partial from Lake Wendouree, Victoria, 7:04 UTC
Related eclipses[]
Eclipses of 2014[]
- A total lunar eclipse on April 15.
- A non-central annular solar eclipse on April 29.
- A total lunar eclipse on October 8.
- A partial solar eclipse on October 23.
Solar eclipses 2011–2014[]
This eclipse is a member of the 2011–2014 solar eclipse semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1][Note 1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2011–2014 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
118 Partial from Tromsø, Norway |
2011 June 01 Partial (north) |
1.2130 | 123 | 2011 November 25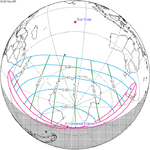 Partial (south) |
-1.0536 | |
128 Middlegate, Nevada |
2012 May 20 Annular |
0.4828 | 133 Cairns, Australia |
2012 November 13 Total |
-0.3719 | |
138 Churchills Head, Australia |
2013 May 10 Annular |
-0.2693 | 143 Partial from Libreville, Gabon |
2013 November 03 Hybrid |
0.3271 | |
148 Partial from Adelaide, Australia |
2014 April 29 Annular (non-central) |
-0.9999 | 153 Partial from Minneapolis |
2014 October 23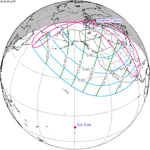 Partial (north) |
1.0908 | |
Note: Total Solar Eclipse on March 20, 2015, and a Partial Solar Eclipse of September 13, 2015 occur during the next lunar year set.
Saros 148[]
Solar saros 148, repeating every about 18 years and 11 days, contains 75 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on September 21, 1653. It has annular eclipses on April 29, 2014, and May 9, 2032, and a hybrid eclipse on May 20, 2050. It has total eclipses from May 31, 2068, to August 3, 2771. The series ends at member 75 as a partial eclipse on December 12, 2987. The longest total eclipse will be on April 26, 2609, at 5 minutes and 23 seconds.[2]
| Series members 15–25 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 16 | 17 |
 February 23, 1906 |
 March 5, 1924 |
 March 16, 1942 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 |
 March 27, 1960 |
 April 7, 1978 |
 April 17, 1996 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
 April 29, 2014 |
 May 9, 2032 |
 May 20, 2050 |
| 24 | 25 | |
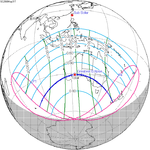 May 31, 2068 |
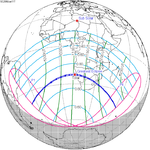 June 11, 2086 | |
Tritos series[]
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
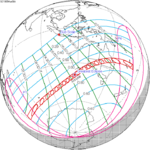 March 6, 1905 (Saros 138) |
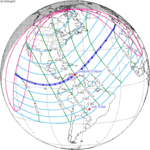 February 3, 1916 (Saros 139) |
 January 3, 1927 (Saros 140) | |
 December 2, 1937 (Saros 141) |
 November 1, 1948 (Saros 142) |
 October 2, 1959 (Saros 143) | |
 August 31, 1970 (Saros 144) |
 July 31, 1981 (Saros 145) |
 June 30, 1992 (Saros 146) | |
 May 31, 2003 (Saros 147) |
 April 29, 2014 (Saros 148) |
 March 29, 2025 (Saros 149) | |
 February 27, 2036 (Saros 150) |
 January 26, 2047 (Saros 151) |
 December 26, 2057 (Saros 152) | |
 November 24, 2068 (Saros 153) |
 October 24, 2079 (Saros 154) |
 September 23, 2090 (Saros 155) |
|
Metonic series[]
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between July 11, 1953 and July 11, 2029 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 10–12 | April 29–30 | February 15–16 | December 4–5 | September 21–23 |
| 96 | 98 | 100 | 102 | 104 |
| July 12, 1915 | April 30, 1919 | February 15, 1923 | December 5, 1926 | September 22, 1930 |
| 106 | 108 | 110 | 112 | 114 |
| July 11, 1934 | April 30, 1938 | February 15, 1942 | December 4, 1945 | September 22, 1949 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 11, 1953 |
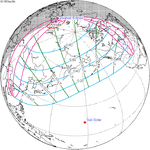 April 30, 1957 |
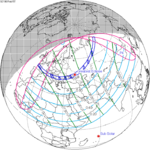 February 15, 1961 |
 December 4, 1964 |
 September 22, 1968 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 10, 1972 |
 April 29, 1976 |
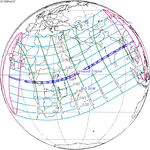 February 16, 1980 |
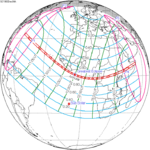 December 4, 1983 |
 September 23, 1987 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 April 29, 1995 |
 February 16, 1999 |
 December 4, 2002 |
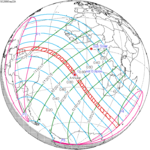 September 22, 2006 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 11, 2010 |
 April 29, 2014 |
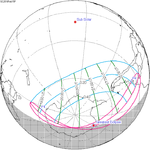 February 15, 2018 |
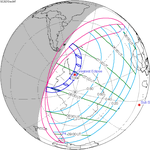 December 4, 2021 |
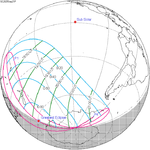 September 21, 2025 |
| 156 | 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 |
 July 11, 2029 |
April 29, 2033 | February 15, 2037 | December 4, 2040 | September 21, 2044 |
Notes[]
- ^ The partial solar eclipses of January 4, 2011 and July 1, 2011 occurred in the previous semester series.
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2014 April 29. |
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- A Partially Eclipsed Setting Sun, APOD 4/30/2014, partial eclipse of Adelaide, South Australia
- Brisbane Sunset Moonset, APOD 5/1/2014, partial eclipse of Brisbane, Queensland
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
- Annular solar eclipses
- 2014 in science
- 21st-century solar eclipses
- April 2014 events
- Solar eclipse stubs






