Solar eclipse of July 22, 1971
| Solar eclipse of July 22, 1971 | |
|---|---|
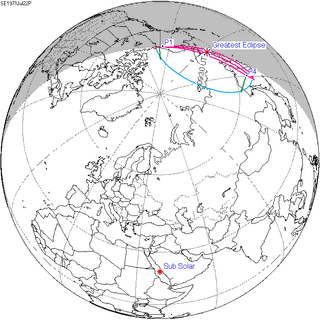 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | 1.513 |
| Magnitude | 0.0689 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 63°30′N 177°00′E / 63.5°N 177°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 9:31:55 |
| References | |
| Saros | 116 (70 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9446 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on July 22, 1971. This was the 70th and final solar eclipse from Solar Saros 116.
Half-Saros cycle[]
Solar Saros 116 and Lunar Saros 109
Solar eclipse of June 19, 1917
Solar eclipse of June 30, 1935
July 1944 lunar eclipse
Solar eclipse of July 11, 1953
Solar eclipse of July 22, 1971
July 1980 lunar eclipse
August 1998 lunar eclipse
August 2016 lunar eclipse
Related eclipses[]
Solar eclipses of 1971–1974[]
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 25, 1971 and August 20, 1971 occur in the next lunar year set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1971–1974 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 116 |  1971 July 22 Partial |
1.51298 | 121 |  1972 January 16 Annular |
-0.93651 | |
| 126 |  1972 July 10 Total |
0.68719 | 131 |  1973 January 4 Annular |
-0.26441 | |
| 136 |  1973 June 30 Total |
-0.07853 | 141 |  1973 December 24 Annular |
0.41710 | |
| 146 |  1974 June 20 Total |
-0.82388 | 151 |  1974 December 13 Partial |
1.07974 | |
Metonic cycle[]
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 events between July 22, 1971 and July 22, 2047 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 21–22 | May 9–11 | February 26–27 | December 14–15 | October 2–3 |
| 106 | 108 | 110 | 112 | 114 |
| July 21, 1952 | May 10, 1956 | February 26, 1960 | December 16, 1963 | October 3, 1967 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 22, 1971 |
 May 11, 1975 |
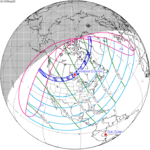 February 26, 1979 |
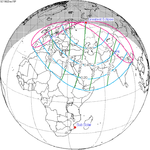 December 15, 1982 |
 October 3, 1986 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
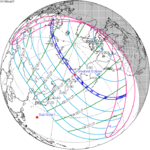 July 22, 1990 |
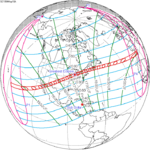 May 10, 1994 |
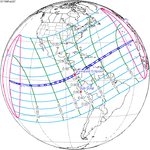 February 26, 1998 |
 December 14, 2001 |
 October 3, 2005 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 22, 2009 |
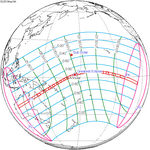 May 10, 2013 |
 February 26, 2017 |
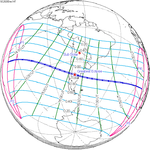 December 14, 2020 |
 October 2, 2024 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 22, 2028 |
 May 9, 2032 |
 February 27, 2036 |
 December 15, 2039 |
 October 3, 2043 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 22, 2047 | ||||
Half-Saros cycle[]
A solar eclipse will be preceded and followed by lunar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This solar eclipse is related to two penumbral lunar eclipses of Lunar Saros 109 on the first and second columns.
From the Earth[]
| 17 July 1962 | 28 July 1980 | 08 August 1998 | 18 August 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|
From the Moon[]
| 17 July 1962 | 28 July 1980 | 08 August 1998 | 18 August 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|
References[]
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links[]
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- 1971 in science
- 20th-century solar eclipses
- July 1971 events
- Solar eclipse stubs



