Solomon Islands rain forests
| Solomon Islands rain forests | |
|---|---|
 Makira Island | |
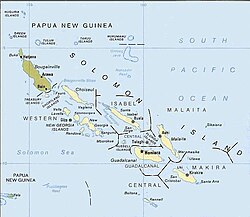 The Solomon Islands archipelago, with the nation Solomon Islands in beige and Bougainville (a part of Papua New Guinea) in dun. | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Australasia |
| Biome | Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests |
| Geography | |
| Area | 42,976 km2 (16,593 sq mi) |
| Countries | Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands |
| Autonomous region of Papua New Guinea | Bougainville |
| Elevation | 0 - 2635 meters |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | vulnerable |
| Global 200 | Solomons-Vanuatu-Bismarck moist forests |
| Protected | 662 km² (2%)[1] |
The Solomon Islands rain forests are a terrestrial ecoregion covering most of the Solomon Islands archipelago. [2] [3] [4]
Geography[]
Included are the islands of Bougainville and Buka, which are part of Papua New Guinea and most of the islands within the nation of Solomon Islands. Excluded are the eastern islands of the nation of Solomon Islands, the Santa Cruz Islands, which lie in the Vanuatu rain forests ecoregion together with the neighbouring archipelago of Vanuatu. Both ecoregions are part of the Australasian realm, which also includes the neighbouring Bismarck Archipelago and New Guinea, as well as New Caledonia, Australia and New Zealand.
The Solomon Islands rain forests are a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion, also known as a tropical rainforest.
Flora[]
The natural vegetation of the Solomon archipelago consists of lowland and montane tropical forests. The major plant communities include coastal strand, mangrove forests, freshwater swamp forests, lowland rain forests, and montane rain forest. Seasonally-dry forests and grasslands are found on the northern (leeward) slopes of Guadalcanal.[5]
Fauna[]
The islands are home to 47 native mammal species, including bats, murid rodents, and possums, gliders, and cuscuses. 26 species are endemic or near-endemic – 17 species of bats, and nine species of murid rodent.
199 bird species are native to the Solomon archipelago, of which 69 species are endemic.[6] The ecoregion corresponds to the Solomon group endemic bird area. [7]
Conservation and threats[]
The rainforests of this region are under threat as the governments of both Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands rely on logging for revenue, plan to expand farm land and to develop roads.
External links[]
- "Solomon Islands rain forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- Solomon group endemic bird area (BirdLife International)
References[]
- ^ Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545; Supplemental material 2 table S1b. [1]
- ^ "Map of Ecoregions 2017". Resolve. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ "Solomon Islands rain forests". Digital Observatory for Protected Areas. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ "Solomon Islands rain forests". The Encyclopedia of Earth. Retrieved August 20, 2021.
- ^ Wikramanayake, Eric; Eric Dinerstein; Colby J. Loucks; et al. (2002). Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment. Washington, DC: Island Press
- ^ Wikramanayake, Eric; Eric Dinerstein; Colby J. Loucks; et al. (2002). Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment. Washington, DC: Island Press
- ^ BirdLife International (2020) Endemic Bird Areas factsheet: Solomon group. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 02/06/2020.
- Australasian ecoregions
- Ecoregions of Papua New Guinea
- Ecoregions of the Solomon Islands
- Environment of the Solomon Islands
- Flora of Melanesia
- Flora of Papua New Guinea
- Flora of the Solomon Islands (archipelago)
- Geography of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville
- Geography of the Solomon Islands
- Natural history of Papua New Guinea
- Solomon Islands (archipelago)
- Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests