St. Louis–San Francisco Railway
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2011) |
 | |
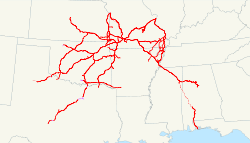 Frisco system as of 1918; the Fort Worth and Rio Grande in central Texas was sold to the Santa Fe Railway in 1937 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Springfield, Missouri[1] |
| Reporting mark | SLSF |
| Locale | Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Kansas, Mississippi, Missouri, Oklahoma, Tennessee, Texas |
| Dates of operation | 1876 –1980 |
| Successor | Burlington Northern |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway (reporting mark SLSF), commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to April 17, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980.[2] Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.
History[]

The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway was incorporated in Missouri on September 7, 1876. It was formed from the Missouri Division and Central Division of the Atlantic and Pacific Railroad. This land grant line was one of two railroads (the other being the M-K-T) authorized to build across Indian Territory. The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railroad, interested in the A&P right of way across the Mojave Desert to California, took the road over until the larger road went bankrupt in 1893; the receivers retained the western right of way but divested the ATSF of the St. Louis–San Francisco mileage on the Great Plains. After bankruptcy, the Frisco emerged as the St. Louis and San Francisco Railroad, incorporated on June 29, 1896,[3][4] which also went bankrupt. On August 24, 1916, the company was reorganized as the St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, though the line never went west of Texas, terminating more than 1,000 miles (1,600 km) from San Francisco.
The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway had two main lines: St. Louis–Tulsa–Oklahoma City-Floydada, Texas and Kansas City–Memphis–Birmingham. The junction of the two lines was in Springfield, Missouri, home to the company's main shop facility and headquarters. Other lines included:
- Springfield–Kansas City (via Clinton, Missouri)
- Monett, Missouri (Pierce City)–Wichita, Kansas
- Monett, Missouri–Hugo, Oklahoma–Paris, Texas
- St. Louis–River Junction, Arkansas (Memphis, Tennessee)
- Tulsa, Oklahoma–Dallas, Texas
- Tulsa, Oklahoma–Avard, Oklahoma
- Lakeside, Oklahoma–Hugo, Oklahoma–Hope, Arkansas
- Amory, Mississippi-Pensacola, Florida
From March 1917 through January 1959, the Frisco, in a joint venture with the Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad, operated the Texas Special. This luxurious train, a streamliner from 1947, ran from St. Louis to Dallas, Texas, Fort Worth, Texas, and San Antonio, Texas.
The Frisco merged into the Burlington Northern Railroad on November 21, 1980.[2]
The city of Frisco, Texas, was named after the railroad and uses the former railroad's logo as its own logo. The logo is modeled after a stretched-out raccoon skin[5][6] (giving rise to Frisco High School's mascot, the Fighting Raccoons).
Passenger trains[]

While the Texas Special may be the most famous passenger train operated by Frisco, it was just one of a fleet of named trains. These included:
- Black Gold (a joint Frisco-Katy operation inaugurated between Tulsa and Houston on January 23, 1938 and continuing until January 18, 1960)[7]
- The Bluebonnet (St. Louis to San Antonio—with through service by M-K-T-- leaving early afternoon, arriving Dallas/Ft. Worth the next morning, and arriving San Antonio late afternoon.)[8][9]
- Firefly (at various times serving St. Louis, Kansas City, Fort Scott, Tulsa, and Oklahoma City.[10] This was Frisco’s first streamliner, and the first streamliner to be built in the southwest, the streamline modifications being done by Frisco itself)[10]
- General Wood (Originally between St. Louis and Springfield, Missouri from May 1941; truncated in June 1942 to service between St. Louis and Newburg, Missouri; and, discontinued entirely in the fall of 1946.)[11]
- Governor (Joplin-Tulsa-Oklahoma City)[12]
- Kansas City–Florida Special (Kansas City–Jacksonville)
- Kansas Limited (St. Louis-Wichita-Ellsworth)[12]
- Kansas Mail (St. Louis-Wichita)[12]
- Memphian (St. Louis–Memphis)
- Memphis Passenger (St. Louis–Memphis)[12]
- Meteor (St. Louis–Tulsa-Oklahoma City by night with connecting train Monett-Fort Smith-Paris, TX)
- Oil Fields Special (Kansas City-Tulsa-Dallas-Ft. Worth, with through service to Houston)[12]
- Oklahoman (Once connected Kansas City–Tulsa but was later rerouted (between St. Louis–Oklahoma City)
- Southland (Kansas City–Birmingham) (truncated successor to the Kansas City–Florida Special)
- Southwest Limited (St. Louis-Tulsa-Oklahoma City-Lawton)[12]
- St. Louis-Memphis Limited (St. Louis-Memphis-Birmingham)[12]
- Sunnyland (Kansas City/St. Louis–Atlanta/Pensacola/New Orleans)
- Tulsa Texan (a joint Frisco-Katy operation inaugurated between Tulsa and Houston in 1937, and phased out between March and July 1940)[7]
- Texas Flash (Tulsa-Sherman-Dallas by day)
- Texokla Limited (St. Louis-Springfield-Dallas)[12]
- Texas Limited (St. Louis-Springfield-Dallas, with through service to Houston-Galveston)[12]
- Texas Special (St. Louis-Springfield-Dallas-Ft. Worth, with through service to Austin-San Antonio)[12]
- Will Rogers (St. Louis–Oklahoma City/Wichita by day, 1936-1965; with through service northbound out of St. Louis to Chicago via the Alton Railroad or Wabash Railroad)[9]
- Chadwick Flyer (Branch line from Springfield to Chadwick, Missouri; discontinued by March 1933)[13]
Former Frisco lines today[]

The core of the former Frisco system continues to be operated by BNSF Railway as high-density mainlines. Other secondary and branchlines have been sold to shortline operators or have been abandoned altogether.
- Kansas City – Springfield – Memphis – Birmingham: Operated by BNSF
- St. Louis – Springfield – Tulsa – Dallas: Operated by BNSF
- Fort Scott, Kansas to Afton, Oklahoma: Operated by BNSF
- St. Louis to Memphis, Tennessee: Operated by BNSF
- Tulsa, Oklahoma to Avard, Oklahoma: Operated by BNSF
- Fredonia, Kansas to Cherryvale, Kansas to Columbus, Kansas: Operated by South Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad
- Cherokee, Kansas to Pittsburg, Kansas: Operated by South Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad
- Fredonia, Kansas to Ellsworth, Kansas: Abandoned
- Cherokee, Kansas to Cherryvale, Kansas: Abandoned
- Monett, Missouri to Fort Smith, Arkansas: Operated by Arkansas and Missouri Railroad
- Lakeside, Oklahoma to Hope, Arkansas: Operated by Kiamichi Railroad (Genesee & Wyoming Inc.)
- Tulsa, Oklahoma (Sapulpa) to Oklahoma City, Oklahoma: Operated by Stillwater Central Railroad
- Oklahoma City to Snyder, Oklahoma: Operated by Stillwater Central Railroad
- Snyder, Oklahoma (Long Siding) to Quanah, Texas: Operated by BNSF
- Enid, Oklahoma to Frederick, Oklahoma: Operated by Grainbelt/Farmrail
- Amory, Mississippi to Pensacola, Florida: Operated by Alabama and Gulf Coast Railway (RailAmerica)
- Springfield to Kansas City (via Clinton)(two routes): Abandoned
- Monett (Pierce City) to Carthage, Missouri: Out of service
- Carthage, Missouri to Wichita, Kansas: Mostly abandoned
- Chaffee, Missouri to Poplar Bluff, Missouri to Hoxie, Arkansas (Hoxie Sub): Abandoned
Surviving equipment[]
Steam locomotives[]
- Frisco 19, a 2-8-0 Consolidation-type built in 1910 and on static display in Frisco, Texas located adjacent to the Frisco Depot replica and the BNSF tracks that run through the city.[14] (Note: This locomotive is lettered Frisco, but it did not actually operate on the SLSF. It is the former Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad 19. It was purchased by the City of Frisco, Texas, as a static display, and is representative of a typical Frisco locomotive. Frisco operated a number of Consolidations as Frisco-series 1306 engines.[15] Specifically Nos. 1306 through 1345 were built by ALCO (the Schenectady Locomotive Works plant) for the Frisco in 1912; all were originally coal-burners, but 22 were later converted to oil-burners.)[16]
- Frisco 73, a 2-6-0 “Mogul” built by Baldwin in 1916.[17] It has 19" cylinders and 49-1/2" driving wheels.[17] Numbered as 34 when Frisco acquired its owner, the Jonesboro, Lake City and Eastern Railroad in 1925, the locomotive was renumbered to 73 and kept by the Frisco until sold on September 19, 1945 to the Delta Valley and Southern Railway, a short line operator in northeast Arkansas.[17] It is preserved on the Lee Wesson Plantation in Victoria, Arkansas[18] under the Delta Valley & Southern Locomotive No. 73 name with no visible numbers on the cab or tender,[19] but with the original Frisco raccoon-skin-shaped number board and “73” on its nose.[17]
- Frisco 76 and Frisco 77, 2-8-0 Consolidation-type engines built as Numbers 40 and 41 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in December, 1920 for the Jonesboro, Lake City and Eastern Railroad.[20] When that line became part of the Frisco, the locomotives were re-numbered as 76 and 77.[20] After performing freight service for years, both engines were sold in 1947 to the Mississippian Railway where they retained the Frisco numbers.[20] Following several further changes in ownership for each engine,[20][21] #76 is now owned by the Oakland B&O Museum in Oakland, Maryland where it has been renumbered and relettered as the Baltimore & Ohio 476,[22] and #77 is now with Alberta Prairie Railway in Stettler, Alberta where it pulls excursion trains and has been renumbered back to 41.[21]
- Frisco 1351, built in 1912 as a 2-8-0 Consolidation (Frisco 1313), and converted by Frisco to a 2-8-2 Mikado in November 1943.[15] Now on static display in Collierville, Tennessee.[23]
- Frisco 1352, built by ALCO in 1912 as a 2-8-0 Consolidation (Frisco 1321), and converted by Frisco in June 1944 to a 2-8-2 Mikado.[24] Disassembled in Taylorville, Illinois; awaiting restoration to operating condition.[25]
- Frisco 1355, built by ALCO in 1912 as a 2-8-0 Consolidation (Frisco 1318), and converted in October 1945[24] to a 2-8-2 Mikado in Frisco's main shops in Springfield.[26] Given that the 1350-1356 series were both the last steam locomotives rebuilt by Frisco and the last Mikados built anywhere in the United States, No. 1355 is the last surviving.[24] Following refurbishment by Frisco, it was donated to the City of Pensacola and moved to a location on Garden Street in that city in March 1957,[27] near the site of the SLSF passenger depot demolished in 1967.[28] Additional refurbishment was done by the Naval Brig Staff of the Pensacola Naval Air Station in late 1991/early 1992.[27]
- Frisco 1501, one of thirty 4-8-2 Mountain type locomotives purchased from Baldwin for freight and passenger service.[29] The 1500 series, all oil-burners, arrived in three batches, being Nos. 1500-1514 in the spring of 1923, Nos. 1515-1519 in 1925, and Nos. 1520-1529 in the summer of 1926.[30] No. 1501 has been on static display in Schuman Park, Rolla, MO since 1955. Several parts from Frisco 1501 were donated to Frisco 1522 to make/keep 1522 operational. Video
- Frisco 1519, a Baldwin 4-8-2 Mountain-type delivered in 1925,[29] now at the Railroad Museum of Oklahoma in Enid, Oklahoma.[31][32][33]
- Frisco 1522, a Baldwin 4-8-2 Mountain-type delivered in 1926.[29] It was at the Museum of Transportation in St. Louis, Missouri until 1988, when it began pulling excursions. In 2002, it was returned to the Museum of Transportation.[34]
- Frisco 1526, a Baldwin 4-8-2 Mountain-type delivered in 1926,[29] located at the Museum of the Great Plains in Lawton, Oklahoma.[35][33]
- Frisco 1527, a Baldwin 4-8-2 Mountain-type delivered in 1926.[29] On static display in Langan Park in Mobile, Alabama[36] since 1964.
- Frisco 1529, a Baldwin 4-8-2 Mountain-type, delivered in 1926.[29] The locomotive pulled a train carrying President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1934, and was eventually the last steam engine to make a passenger run for Frisco. Now on static display in Frisco Park in Amory, Mississippi.[33]
- Frisco 1615 and the other locomotives in Frisco-series 1600 were 2-10-0 Russian locomotive class Ye (Russian Decapods) with a 5’ gauge built for the Tsarist government in Russia.[29] When that government was overthrown before delivery, the units were rebuilt as standard-gauge locomotives (by fitting extra-wide tires on the wheels)[37] and sold through the United States Railroad Administration to American railways.[29] Frisco acquired 20 of the units (17 directly from the government, 3 from other companies), which became Nos. 1613 to 1632.[38] Of these, Nos. 1615, 1621, 1625, 1630 and 1632, all coal-burning, were later sold in the 1951 timeframe to Eagle-Picher and used to haul lead and zinc from the Picher Field to the E-P mill in Miami, Oklahoma.[38][39] All these units were placed in storage by 1957 when that operation was closed.[38] By 1964, homes were being sought for all of these engines.[38] Frisco 1615, built in 1917 as part of Frisco’s first batch of engines (Nos. 1613-1623) which were constructed by ALCO’s Richmond Locomotive Works in the fall of 1917 and spring of 1918, was acquired by the City of Altus, Oklahoma on October 22, 1967, and remains on static display there.[38][39]
- Frisco 1621 is another 2-10-0 Russian Decapod, built in 1918. On static display at the Museum of Transportation in St. Louis, Missouri.[40]
- Frisco 1625 is another 2-10-0 Russian Decapod, built in 1918 at ALCO's Schenectady Locomotive Works.[38] Now on static display at the Museum of the American Railroad in Frisco, Texas.[41]
- Frisco 1630 is another 2-10-0 Russian Decapod, part of Frisco's batch (Nos. 1626-1632) which were all constructed by Baldwin in 1918.[38] It has been in excursion service at the Illinois Railway Museum in Union, Illinois since 1967, and is considered by the museum as their most famous locomotive.[42]
- Frisco 1632 is another 1918 Baldwin 2-10-0 Russian Decapod. It was donated to the Smoky Hill Railway and Historical Society in Ottawa, Kansas in 1964, and was moved in 1991 to the Belton, Grandview and Kansas City Railroad in Belton, Missouri where it is on static display.[38][43]
- Frisco 3695 is a Frisco-series 3600 locomotive, which were 0-6-0 switch engines built between August, 1883, and July, 1906.[44] Ninety-five in number, the only survivor is No. 3695, built in July, 1906 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works and serving Frisco thirty-one years before being sold to the Scullin Steel Company and renumbered No. 95.[44][45] The engine was donated in 1956 and is on display at the National Museum of Transportation in St. Louis.[45]
- Frisco 3749 is a Frisco-series 3700 locomotive, which was a class of forty-six 0-6-0 switch engines built between 1906 and 1910.[46] However, another source says No. 3749 in particular was built in 1913, by the Baldwin Locomotive Works.[47] Retired from Frisco service in 1952, the engine was leased to the Atmore Prison Farm in Atmore, Alabama before being used in 1956 as a prop in an MGM movie, The Wings of Eagles, starring John Wayne.[46] After later sitting idle for a number of years and being sold for scrap, the engine was moved to the Church Street Station in Orlando, Florida as a static display.[46] In 2012 it was acquired and put on display by the Florida Railroad Museum.[47]
- Frisco 4003, a coal-burning 2-8-2 Mikado built in 1919 by Lima and on static display at the Fort Smith Trolley Museum in Fort Smith, Arkansas. See Frisco 4003
- Frisco 4018, a coal-burning 2-8-2 Mikado built in 1919 by Lima which is on static display at Sloss Furnaces in Birmingham, Alabama.[48] This locomotive has the distinction of being the last Frisco steam locomotive in regular service, completing its final run (a five-mile trek from Bessemer to Birmingham, Alabama) on February 29, 1952.[49]
- Frisco 4500, a 4-8-4 oil-fired Northern-type built in 1942,[50] on static display in Tulsa, Oklahoma, being a locomotive which pulled the Frisco's crack Meteor train.[51]
- Frisco 4501, an oil-fired 4-8-4[50] on static display at the Museum of the American Railroad in Frisco, Texas,[41] also a former Meteor locomotive.
- Frisco 4516, 4-8-4 Northern-type coal-fired locomotive[50] on static display at Missouri State Fairgrounds, Sedalia, Missouri, also known as "Old Smokie."[52]
- Frisco 4524, another wartime 4500-series 4-8-4 coal-fired Northern-type,[50] donated to Springfield, Missouri in November 1954,[53] now on static display at the Railroad Historical Museum inside Grant Beach Park in Springfield, and wearing the "Frisco Faster Freight" paint scheme.[54][55] Being the last engine of the last group of steam locomotives that Frisco purchased, this engine has the distinction of being the last steam locomotive built for the Frisco.[50]
Diesel locomotives[]
- Frisco 814, an operational General Motors EMD F9A, located at the Oklahoma Railway Museum in Oklahoma City.[56] (Note: While the locomotive has been lettered by the museum as Frisco, this was not a Frisco unit. It was originally purchased in 1954 by the Northern Pacific Railway, Road Number 7003-D, and became the Burlington Northern Railroad 814 due to a merger.[56] The Frisco's only operation of F9A units occurred when two of the line's EMD F3A units were converted into F9A units.[57])
Buildings and structures[]
Multiple surviving buildings and structures associated with the Frisco are on the National Register of Historic Places, including the St. Louis and San Francisco Railroad Building in Joplin, Missouri, the St. Louis-San Francisco Railroad Depot in Poplar Bluff, Missouri, the St. Louis and San Francisco Railway Depot in Comanche, Texas, the Beaumont St. Louis and San Francisco Railroad Retention Pond, and the Beaumont St. Louis and San Francisco Railroad Water Tank. The Frisco Building, being the former Frisco headquarters in Springfield built in 1910 and now known as the Landmark Building, is an official City of Springfield counsel-approved landmark.[58][59] The Frisco Bridge at Memphis was the first bridge over the Mississippi River south of St. Louis, and the third longest bridge in the world at the time of its dedication on May 12, 1892;[60] it is now listed as an Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.
4-4-0s[]
Locomotives with 4-4-0 wheel arrangements, known as the "American" type because they were considered for many years to be the standard in American locomotives, originally served Frisco in great numbers.[61] In July, 1903, the Frisco had 159 4-4-0's in service, built by twenty-five different companies.[61] Frisco renumbered its units in that year, assigning the 4-4-0's either numbers between 1-299 (140 units), or 2200-series numbers (19 units).[61] The oldest Frisco 4-4-0 locomotive was No. 47, built in 1869 by Hinkley Locomotive Works.[61] The last serving 4-4-0's were retired in July, 1935.[61]
4-6-0s[]
Even more numerous on the Frisco were 4-6-0 “Ten-wheelers.”[62] The first such engines entered the Frisco system in 1870.[62] By 1903, Frisco had a fleet of 430 such locomotives, which were renumbered that year into seven class series, using 400, 500, 600, 700, 1100, 1400, and 2600-series numbers.[62] The last 4-6-0's on the Frisco roster were the 1400 series, with the last engine to be retired from service being #1409, dismantled and sold for scrap in November, 1951.[62]
Doodlebugs[]
Frisco-series 2100 equipment consisted of self-propelled rail motor-cars, mostly gas-electric models,[63] with a few gas-mechanical models given 3000-series numbers.[64][65][66] These railway vehicles were commonly known as “Doodlebugs” for their insect-like appearance and the slow speeds at which they would doddle or "doodle" down the tracks.[63] These were used to service various low-volume branch lines in the Frisco organization.[63][67] An initial order for ten was placed in 1910, with seven more arriving by 1913, putting Frisco in the forefront of gas-electric operation at that time.[63] The initial batch, numbered 2100 to 2109, included nine baggage-coach combinations, as well as one baggage-mail-coach unit.[63] Frisco's peak year for motor-car mileage was 1931, and its fleet at that time included twenty-three gas-electrics, five gas-mechanical cars, four trailer coaches, and six mail-baggage units.[63] The final Frisco run of a Doodlebug was on November 8, 1953, when No. 2128 traveled from Ardmore, Oklahoma for the four hour trip to Hugo, Oklahoma.[63]
Frisco Series 4300 and 4400[]
Two series of Frisco locomotives not surviving were Frisco 4300s and 4400s. These were all 4-8-2 units assembled by Frisco itself in the late 1930s to the early 1940s from other locomotives. Eleven, being units 4300 through 4310, were built in 1936 and 1937 from used 2-10-2 parts. They had 27 x 30 cylinders, 70″ drivers, a boiler pressure of 250 psi, and a tractive effort of 66,400 lbs, weighing 431,110 pounds. Another twenty-three 4-8-2s were built using the boilers from 2-10-2s between 1939 and 1942. Units 4400 through 4412 were oil-burning, while units 4413 through 4422 burned coal. These locomotives had 29 x 32 cylinders, 70″ drivers, a boiler pressure of 210 psi, and a tractive effort of 68,600 lbs. Weighing in at 449,760 pounds, they were the heaviest Mountain-type locomotives ever built.[33]
Dieselization[]
Frisco’s first acquisition of diesel locomotives came in November 1941, when the line received five Baldwin VO-1000 thousand-horsepower switchers.[68][69] Frisco started a serious dieselization program in 1947, which took about five years.[70] When the period of steam power ended for Frisco in February, 1952 with the last run of steam engine 4018, the Frisco’s diesel fleet included seventeen 2,250-HP passenger, six 2,000-HP passenger, twelve 1,500-HP combination freight and passenger, one hundred and twenty-three 1,500-HP freight, one hundred and thirty-three 1,500-HP general purpose, eleven 1,000-HP general purpose, and one hundred and five yard-switcher units, for a total of 407 diesel locomotives.[71] At that time, the Frisco became the largest Class I railroad in the U.S. to be operating strictly with diesel power.[70]
The Frisco gave names to its 2000-series diesel passenger locomotives, EMD E7 and (mostly) EMD E8 units,[72] using the theme of famous horses.[73] These included racehorses such as Gallant Fox (#2011), Sea Biscuit (#2013), and Citation (#2016).[73] However, other horses also made the list: for instance, when #2022 was rebuilt after a wreck, it was given the name of Champion, after ex-Frisco-employee Gene Autry’s trusty steed in the movies.[73]
Frisco Silver Dollar Line[]
The amusement park Silver Dollar City in Branson, Missouri runs multiple diesel-fired or heating oil-fired steam trains around the park on its 2-foot-gauge rail line, known as the Frisco Silver Dollar Line. The Frisco operated in that part of the country, and supplied construction help to the Park, along with the rails and ties, back when this line was being built in 1962. Perhaps for these reasons, the trains sport the Frisco name and logo. However, this was never an actual Frisco rail line, and the steam locomotives started life as industrial engines on German intraplant railroads, not as actual rolling stock on the Frisco.[74]
Predecessors[]
The following companies were predecessors of the Frisco:
- Pacific Railroad, charter granted by Missouri on March 3, 1849
- Southwest Pacific Railroad, John C. Frémont reorganized in August 1866
- Atlantic and Pacific Railroad, incorporated on July 27, 1866
- Arkansas and Choctaw Railway; 1895[75]
Acquisitions[]

The following railroads were acquired or merged into the Frisco:
This list is incomplete; you can help by . (August 2008) |
- : 1879
- : 1882
- : 1885
- : 1886
- : 1887
- : 1887
- : 1900
- Arkansas and Oklahoma Railroad: 1901
- : 1901
- Kansas City, Fort Scott and Memphis Railway: 1901
- Arkansas Valley and Western Railway: 1907
- Blackwell, Enid and Southwestern Railway: 1903
- : 1904
- : December 19, 1904
- : May 20, 1905
- : 1907 – December 19, 1910
- : 1917
- : 1922
- Jonesboro, Lake City and Eastern Railroad:1924
- (Pittsburg, Kansas): 1925–1926
- : May 11, 1926
- Kansas City and Memphis Railway and Bridge Company: 1928
- : July 21, 1928
- Kansas City, Clinton and Springfield Railway: September 1, 1928
- Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad: December 28, 1948
- Central of Georgia Railway: 1956. The Interstate Commerce Commission did not approve the purchase, so the Frisco sold it to Southern Railway in 1961.
- : December 27, 1963 (Division dissolved February 27, 1967; Roads involved include: NEO RR, , and )
Asset absorptions[]
The following is a list of partial or full asset absorptions, many times through bankruptcy courts or creditors. In some cases the Frisco was a creditor. Assets can include mineral rights, property, track and right of way, trains, bonds, mortgages, etc.

- St. Louis, Wichita and Western Railway: 1882
- : 1898
- : October 23, 1900
- : 1900–1903
- : 1907
- : 1907
- : 1907
- : 1907
- : 1910
- Fort Worth and Rio Grande Railway: 1919–1937
- : 1926
- : 1926
- Kansas City, Memphis and Birmingham Railroad: September 1, 1928
- : 1928–1947
- : 1950
- : 1950
- St. Louis, San Francisco and Texas Railway: 1963–1964
- : 1967 (liquidation of BB RR and distribution of assets)
See also[]
- Frisco, Texas
- Gulf Coast Lines
- Benjamin Franklin Yoakum
- Fort Worth and Rio Grande Railway
- Frisco 1522
References[]
- ^ Patrick Hiatte, Springfield, Missouri: The Heart of the Frisco, 1955, Trains magazine, December 2003
- ^ Jump up to: a b "About the Frisco Railroad". Frisco.org. October 6, 2013. Retrieved March 6, 2020.
- ^ "History of the Frisco". TheLibrary.org. Springfield, Missouri: Springfield-Greene County Library District.
- ^ "Corporate History: St. Louis – San Francisco Railway Company". The Truman Area Community Network. Henry County Library. June 2, 2008. Archived from the original on July 22, 2012.
- ^ "FRISCO INTERNATIONAL WIDE VISION CABOOSE #239". Canadian Model Trains Inc. March 12, 2009. Retrieved March 18, 2012.
- ^ "100 Years of Service". Frisco Veterans' Reunion via Springfield-Greene County Library. Retrieved March 18, 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Frisco, Texas" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, April, 1989 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- ^ "To Texas (copy of advertisement)" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, May, 1990 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 19, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Will Rogers" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, Aug-Sept 1990 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 19, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Pride of the Firefly" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, June 1989 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ "Building the Railroad to Fort Leonard Wood" (PDF). Old Settlers Gazette. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j "Official Guide of the Railways and Steam Navigation Lines of the United States, Porto Rico, Canada, Mexico and Cuba, January 1923, pp.621-636". 1923. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ "Pokin Around: Plans call for part of Chadwick Flyer spur line to become recreational trail". Steve Pokin, Springfield News-Leader, April 4, 2020.
- ^ "1910 Steam Locomotive". Frisco Heritage Association. September 2, 2010. Retrieved February 26, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b http://www.steamlocomotive.com/mikado/?page=slsf Archived 2017-06-11 at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved 6-11-15.
- ^ "The Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, December, 1987 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "New Frisco Survivor" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, January, 1990 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 23, 2020.
- ^ "Surviving Steam Locomotives in Arkansas". SteamLocomotive.com. Retrieved October 23, 2020.
- ^ "Historic Trains of Arkansas—Locomotives and Railcars". Julie Kohl, Only in Arkansas, February 5, 2019. February 5, 2019. Retrieved October 23, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "The Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, November, 1987 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Mississippian #77". HawkinsRails. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ "Homepage". Oakland B&O Museum. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ "Collierville's Resident Steam Engine Gets Its Own Special Day". Town of Collierville. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "The Whyte System" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, July, 1989 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 20, 2020.
- ^ Frisco 1352
- ^ "SLSF 1350 #1355". rgusrail.com. Retrieved February 26, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Pride of Pensacola" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, October–November 1992 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Frisco Railroad". Pensapedia.com. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "1501". rgusrail.com. Retrieved February 26, 2020.
- ^ "The Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, January, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Railroad Museum of Oklahoma, On Track for Railroad History!". Railroad Museum of Oklahoma. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "Railroad Museum of Oklahoma". TravelOK.com. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "The Frisco Park Steam Engine". City of Amory, Mississippi. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "1926 St. Louis-San Francisco Railway #1522 Locomotive (Frisco)". The National Museum of Transportation. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "Frisco 1526 (photo)". Museum of the Great Plains. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "A Walk in the Park- Langan Park, aka Municipal Park, Mobile, AL". ExperienceFineLiving.com. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "Alabama, Tennessee & Northern 2-10-0 #401 -- A Locomotive Blessed with the Luck of Lindy". John B. Corns, Age of Steam Roundhouse Museum. Retrieved January 27, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "The Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, March, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "SLSF #1615". rgusrail.com. Retrieved March 4, 2020.
- ^ "Eagle-Picher St. Louis-San Francisco Railway #1621". The National Museum of Transportation. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Railroad, Museum of the American. "Steam Locomotives". www.museumoftheamericanrailroad.org.
- ^ "Frisco 1630's 100th birthday Celebration September 15th". Illinois Railway Museum. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "Locomotives". Belton, Grandview & Kansas City Railroad. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, May, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 10, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "St. Louis & San Francisco 95/3695 "Frisco"". The National Museum of Transportation. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, July, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Non-active Steam Locomotives". Florida Railroad Museum. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ "St Louis-San Francisco RR No. 4018". SteamLocomotive.info. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ "Frisco Survivors" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, September, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "St. Louis - San Francisco Railway Company ("Frisco") 4501". Museum of the American Railroad. Retrieved February 9, 2020.
- ^ "Route 66 Historical Village". TravelOK.com. Retrieved January 16, 2019.
- ^ "Old Smokie, Frisco Engine 4516, Sedalia, Missouri". Waymarking.com. Retrieved September 29, 2019.
- ^ "Getting it Correct" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, December, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Railroad Historical Museum". Springfield-Greene County Park Board. Retrieved September 29, 2019.
- ^ "The Whyte System" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, January, 1990 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "OKRX 814 – EMD F9A". Oklahoma Railway Museum. Retrieved February 28, 2020.
- ^ "St Louis - San Francisco (Frisco) All-Time Diesel Roster". The Diesel Shop. Retrieved February 28, 2020.
- ^ "Historical Postcards of Springfield, Missouri—Frisco Office Building". TheLibrary.org. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ "Local Historic Sites / Landmarks". City of Springfield. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ "The Great Frisco Bridge" (PDF). Michael Finger, All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, January–February, 1993 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 31, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "The Whyte System" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, January, 1989 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "The Whyte System" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, February, 1989 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 17, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g "Doodlebugging on the Frisco, Part II" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, April, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 10, 2020.
- ^ "Doodlebugging on the Frisco" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, October–November, 1991 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Doodlebugging on the Frisco" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, August–September, 1991 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Doodlebugging on the Frisco" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, December 1991-January 1992 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 20, 2021.
- ^ "Doodlebugging on the Frisco, Part III" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, May, 1988 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved October 10, 2020.
- ^ "VO-1000 Switcher" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, January, 1989 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 31, 2021.
- ^ "Yard Power Part Five, Three Pairs" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, March–April 1993 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 31, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Era of Steam Power Ends on Frisco" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, August 1987 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ "Frisco First Generation Diesels" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, September 1987 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ "The Frisco Lines, Diesel Locomotives-Racehorse Series". TheLibrary.org. Retrieved January 25, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "The Frisco Stable" (PDF). All Aboard, The Frisco Railroad Museum, June 1987 (accessed on CondrenRails.com). Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ "All Aboard--Silver Dollar City Boasts Historic Steam Locomotives, Romantic Ride on the Rails". Laurinda Joenks, Northwest Arkansas Democrat Gazette, July 30, 2014. Retrieved July 9, 2020.
- ^ "Railroad Era Resources Of Southwest Arkansas, 1870-1945". Arkansas Historic Preservation Program (a National Park Service “National Register of Historic Places Multiple Property Documentation Form” filing), 1996, p.19. Retrieved July 15, 2020.
External links[]
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to St. Louis-San Francisco Railway. |
- "100 Years of Service". 1960. Retrieved April 20, 2006.
- Frisco.org – Official Preservation Site
- Frisco Archive – Photos and documents relating to the Frisco Railroad
- The Frisco: A Look Back at the St. Louis–San Francisco Railway (historical information at the Springfield-Greene County Library District)
- Mike Condren's Frisco Railroad Homepage
- The Frisco Railroad in Kansas
- Western Historical Manuscript Collection—Rolla—University of Missouri-Rolla "Guide to the Historical Records of the St. Louis–San Francisco Railway Company" Retrieved September 16, 2005
- "The Frisco in photographs," Classic Trains magazine, January 18, 2001, accessed 13 February 2020. Includes photos and system map.
- "Frisco System," Handbook of Texas Online, accessed 5 April 2011.
- Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory
- St. Louis–San Francisco Railway
- Predecessors of the Burlington Northern Railroad
- Former Class I railroads in the United States
- Companies based in St. Louis
- Companies based in Springfield, Missouri
- Defunct Alabama railroads
- Defunct Arkansas railroads
- Defunct Florida railroads
- Defunct Kansas railroads
- Defunct Mississippi railroads
- Defunct Missouri railroads
- Defunct Oklahoma railroads
- Defunct Tennessee railroads
- Defunct Texas railroads
- Railway companies established in 1916
- Railway companies disestablished in 1980
