Thracian Sea
This article cites Wikipedia (or sources that take information from Wikipedia), in a circular manner. (September 2021) |
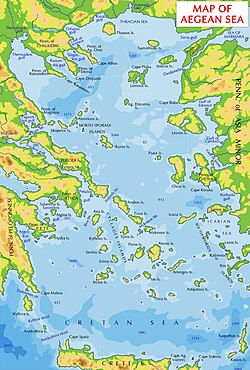
The Thracian Sea (Greek: Θρακικό Πέλαγος, Thrakiko Pelagos; Turkish: Trakya Denizi) is the northernmost part of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded by Macedonia and Thrace as well as northwestern Turkey. The entire area of the sea lies north of the 40th parallel. Its length from east to west is from 23°E to about 25.8°E, or from the Strymonian Gulf east to the northernmost part of the Gallipoli peninsula and the width from north to south is about 40.25°N to 41°N, or from the Dardanelles north to the boundary between the Xanthi and the Rhodope regional units. Islands includes Thasos and Samothrace in Greece and Gökçeada (Imvros in Greek) and Bozcaada (Tenedos in Greek) in Turkey. The bays and gulfs includes the to the southwest, the Strymonian Gulf where the Strymon River empties, the and the Saros Gulf in Turkey. Rivers emptying into this portion of the gulf include the Nestos and the Evros/Meriç. The famous thermal springs are in Kavala.[1][circular reference]
Ports[]
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Aegean Sea - Unionpedia, the concept map". en.unionpedia.org. Retrieved 2021-05-21.
- Thracian Sea
- Marginal seas of the Mediterranean
- Aegean Sea
- Seas of Greece
- Thrace
- Landforms of Xanthi (regional unit)
- Landforms of Rhodope (regional unit)
- Landforms of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace
- Landforms of Thasos
- Landforms of Evros (regional unit)
- Seas of Turkey