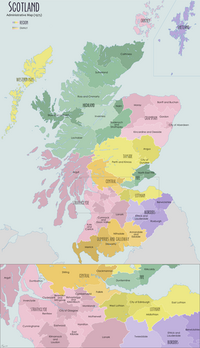
Angus, Scotland
Angus
Aonghas | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Angus within Scotland | |
| Coordinates: 56°40′N 2°55′W / 56.667°N 2.917°WCoordinates: 56°40′N 2°55′W / 56.667°N 2.917°W | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Country | Scotland |
| Lieutenancy area | Angus |
| Admin HQ | Forfar |
| Government | |
| • Body | Angus Council |
| • Control | Ind + Con + LD (council NOC) |
| • MPs |
|
| • MSPs |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 842 sq mi (2,182 km2) |
| Area rank | Ranked 10th |
| Population (mid-2019 est.) | |
| • Total | 116,040 |
| • Rank | Ranked 17th |
| • Density | 140/sq mi (53/km2) |
| ONS code | S12000041 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-ANS |
| Website | www |
Angus (Scots: Angus; Scottish Gaelic: Aonghas) is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland, a registration county and a lieutenancy area. The council area borders Aberdeenshire, Dundee City and Perth and Kinross. Main industries include agriculture and fishing. Global pharmaceuticals company GSK has a significant presence in Montrose in the north of the county.
Angus was historically a county (known officially as Forfarshire from the 18th century until 1928), bordering Kincardineshire to the north-east, Aberdeenshire to the north and Perthshire to the west; southwards it faced Fife across the Firth of Tay; these remain the borders of Angus, minus Dundee which now forms its own small separate council area). Angus remains a registration county and a lieutenancy area. In 1975 some of its administrative functions were transferred to the council district of the Tayside Region, and in 1995 further reform resulted in the establishment of the unitary Angus Council.
History[]
Etymology[]
The name "Angus" indicates the territory of the eighth-century Pictish king of that name.[1]
Prehistory[]
The area that now comprises Angus has been occupied since at least the Neolithic period. Material taken from postholes from an enclosure at Douglasmuir, near Friockheim, about five miles north of Arbroath has been radiocarbon dated to around 3500 BC. The function of the enclosure is unknown, but may have been for agriculture or for ceremonial purposes.[2]
Bronze Age archaeology is to be found in abundance in the area. Examples include the short-cist burials found near West Newbigging, about a mile to the North of the town. These burials included pottery urns, a pair of silver discs and a gold armlet.[3] Iron Age archaeology is also well represented, for example in the souterrain nearby Warddykes cemetery[4] and at West Grange of Conan,[5] as well as the better-known examples at Carlungie and Ardestie.
Medieval history[]
The county is traditionally associated with the Pictish kingdom of Circinn, which is thought to have encompassed Angus and the Mearns. Bordering it were the kingdoms of Ce (Mar and Buchan) to the North, Fotla (Atholl) to the West, and Fib (Fife) to the South.
The most visible remnants of the Pictish age are the numerous sculptured stones that can be found throughout Angus. Of particular note are the collections found at Aberlemno, St Vigeans, Kirriemuir and Monifieth.
Angus is marketed as the birthplace of Scotland. The signing of the Declaration of Arbroath at Arbroath Abbey in 1320 marked Scotland's establishment as an independent nation. It is an area of rich history from Pictish times onwards. Notable historic sites in addition to Arbroath Abbey include Glamis Castle, Arbroath Signal Tower museum and the Bell Rock Light House.
Geography[]

Angus can be split into three geographic areas. To the north and west, the topography is mountainous. This is the area of the Grampian Mountains, Mounth hills and Five Glens of Angus, which is sparsely populated and where the main industry is hill farming. Glas Maol – the highest point in Angus at 1,068 m (3,504 ft) – can be found here, on the tripoint boundary with Perthshire and Aberdeenshire. To the south and east the topography consists of rolling hills (such as the Sidlaws) bordering the sea; this area is well populated, with the larger towns. In between lies Strathmore (the Great Valley), which is a fertile agricultural area noted for the growing of potatoes, soft fruit and the raising of Angus cattle.
Montrose in the north east of the county is notable for its tidal basin. Angus's coast is fairly regular, the most prominent features being the headlands of Scurdie Ness and . The main bodies of water in the county are Loch Lee, , , , , Loch of Forfar, Loch Fithie, Rescobie Loch, , , , , , Loch of Kinnordy, Loch of Lintrathen, Backwater Reservoir, Auchintaple Loch, , and .[citation needed]
Demography[]
Population structure[]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 65,068 | — |
| 1811 | 69,376 | +6.6% |
| 1821 | 74,436 | +7.3% |
| 1831 | 84,630 | +13.7% |
| 1841 | 106,890 | +26.3% |
| 1851 | 119,357 | +11.7% |
| 1911 | 118,748 | −0.5% |
| 1921 | 101,767 | −14.3% |
| 1931 | 93,803 | −7.8% |
| 1941 | 95,290 | +1.6% |
| 1951 | 96,777 | +1.6% |
| 1961 | 93,666 | −3.2% |
| 1971 | 90,554 | −3.3% |
| 1981 | 98,685 | +9.0% |
| 1991 | 107,866 | +9.3% |
| 2001 | 108,400 | +0.5% |
| 2011 | 116,000 | +7.0% |
| Source: [6][7] | ||
In the 2001 census the population of Angus was recorded as 108,400. 20.14% were under the age of 16, 63.15% were between 16 and 65 and 18.05% were aged 65 or above.
Of the 16 to 74 age group, 32.84% had no formal qualifications, 27.08% were educated to 'O' Grade/Standard Grade level, 14.38% to Higher level, 7.64% to HND or equivalent level and 18.06% to degree level.
Language in Angus[]
The most recent available census results (2001) show that Gaelic is spoken by 0.45% of the Angus population. This, similar to other lowland areas, is lower than the national average of 1.16%.[8] These figures are self-reported and are not broken down into levels of fluency.
| Category | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| All people | 108,400 | 100 |
| Understands spoken Gaelic but cannot speak, read or write it | 351 | 0.32 |
| Speaks reads and writes Gaelic | 238 | 0.22 |
| Speaks but neither reads nor writes Gaelic | 188 | 0.17 |
| Speaks and reads but cannot write Gaelic | 59 | 0.05 |
| Reads but neither speaks not writes Gaelic | 61 | 0.06 |
| Writes but neither speaks nor reads Gaelic | 13 | 0.01 |
| Reads and writes but does not speak Gaelic | 22 | 0.02 |
| Other combination of skills in Gaelic | 7 | 0.01 |
| No knowledge of Gaelic | 107,461 | 99.13 |
Meanwhile, the 2011 census found that 38.4% of the population in Angus can speak Scots, above the Scottish average of 30.1%. This puts Angus as the council area with the sixth highest proficiency in Scots, behind only Shetland, Orkney, Moray, Aberdeenshire, and East Ayrshire.
Historically, the dominant language in Angus was Pictish until the sixth to seventh centuries AD when the area became progressively gaelicised, with Pictish extinct by the mid-ninth century.[9] Gaelic/Middle Irish began to retreat from lowland areas in the late-eleventh century and was absent from the Eastern lowlands by the fourteenth century. It was replaced there by Middle Scots, the contemporary local dialect of Modern Scots, while Gaelic persisted as a majority language in the highland Glens until the 19th century.[10][11]
Angus Council are planning to raise the status of Gaelic in the county by adopting a series of measures, including bilingual road signage, communications, vehicle livery and staffing.[12]
Government[]

Angus Council Comhairle Aonghais | |
|---|---|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Provost | |
Leader of the Council | |
Chief executive | Margo Williamson[15] |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 28 |
 | |
Political groups |
|
Length of term | Full council elected every 4 years |
| Elections | |
Voting system | Single transferable vote |
Last election | 5 May 2017 |
Next election | 5 May 2022[19] |
| Website | |
| www | |
Local government[]

The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 established a uniform system of county councils in Scotland and realigned the boundaries of many of Scotland's counties. Subsequently, Angus County Council was created in 1890. In May 1975 the county council was abolished and its functions were transferred to Tayside Regional Council: the local area was served by Angus District Council. The county council was based at the County Offices in Market Street in Forfar.[20]
Angus Council is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland after the two-tier local government council was abolished and Angus was established as one of the replacement single-tier Council Areas in 1996. As of May 2017 there are 28 seats on the council. From the May 2017 elections the seats are held as follows – Independent 9, SNP 9, Conservative 8, Liberal Democrat 2.
The council's civic head is the Provost of Angus. There have been six Provosts since its establishment in 1996 – Frances Duncan, Bill Middleton, Ruth Leslie-Melville, Helen Oswald and Alex King. On 16 May 2017 Cllr Ronnie Proctor was appointed Provost from the councillors elected in Angus at the 2017 elections. As Angus is a county area the Lord Lieutenant of Angus is separate role.
The council has had four Chief Executives since its formation – Sandy Watson 1996–2006, David Sawers 2006–2011, Richard Stiff 2011–2017 and Margo Williamson 2017 to date. Margo Williamson is the first female Chief Executive since the council was formed. The council's main offices are located at Angus House at Orchardbank in Forfar and at Bruce House in Arbroath while council meetings are held in the Town and County Hall in central Forfar. The council's offices include the historic County Buildings in Forfar adjacent to the Sheriff Court.
The boundaries of the present council area are the same as those of the historic county minus the City of Dundee.
The council area borders Aberdeenshire, Dundee City and Perth and Kinross.
As of 2018 Angus is divided into 25 community council areas and all apart from Friockheim district have an active council.[21] The areas are: Aberlemno; Auchterhouse; Carnoustie; ; ; ; Glamis; ; Inverarity; ; Kirriemuir; ; ; ; ; Monifieth; ; Montrose; Muirhead, ; ; ; Royal Burgh of Arbroath; ; Strathmartine; and Tealing.
Parliamentary representation[]
UK Parliament[]
Angus is represented by three MPs for the UK Parliament.
- Angus — covers most of the council area, is represented by of the Scottish National Party.
- Dundee East — mainly covers Dundee, however a small portion of eastern Sidlaw and Carnoustie areas are part of the constituency, is represented by Stewart Hosie of the Scottish National Party.
- Dundee West — mainly covers Dundee, however a small portion of western Sidlaw area is part of the constituency, is represented by Chris Law of the Scottish National Party.
Scottish Parliament[]
Angus is represented by two constituency MSPs for the Scottish Parliament.
- Angus North and Mearns — covers the north of Angus and a southern portion of Aberdeenshire, is represented by Mairi Gougeon of the Scottish National Party.
- Angus South — covers the south of Angus, is represented by Graeme Dey of the Scottish National Party.
In addition to the two constituency MSPs, Angus is also represented by MSPs from the North East Scotland Region
Transport[]
The Edinburgh-Aberdeen railway line runs along the coast, through Dundee and the towns of Monifieth, Carnoustie, Arbroath and Montrose.
There is a small airport at Dundee, which at present operates flights to London and Belfast.[22]
Towns and villages[]


Towns[]
- Arbroath, the largest town in the modern county
- Brechin
- Carnoustie
- Forfar, the county town and administrative centre
- Kirriemuir
- Monifieth
- Montrose
Villages[]
- Aberlemno
- Airlie
- Arbirlot
- Ardovie
- Auchinleish
- Auchmithie
- Auchnacree
- Auchterhouse
- Balintore
- Balkeerie
- Balmirmer
- Barry
- Birkhill
- Boddin
- Bowriefauld
- Boysack
- Brechin
- Brewlands Bridge
- Bridge of Craigisla
- Bridgefoot
- Bridgend of Lintrathen
- Bucklerheads
- Burnside of Duntrune
- Caldhame
- Camuston
- Careston
- Carlogie
- Carmyllie
- Castleton
- Charleston
- Clayholes
- Clova
- Colliston
- Cortachy
- Craichie
- Craigo
- Craigton
- Douglastown
- Dun
- Dunnichen
- Eassie
- Elliot
- East Haven
- Edzell
- Farnell
- Ferryden
- Folda
- Friockheim
- Finavon
- Gallowfauld
- Gateside
- Glamis
- Greystone
- Guthrie
- Hillside
- Inveraldie
- Inverkeilor
- Inverarity
- Kellas
- Kincaldrum
- Kingennie
- Kingsmuir
- Kirkbuddo
- Kirkinch
- Kirkton of Glenisla
- Kirkton of Kingoldrum
- Letham
- Liff
- Little Brechin
- Little Forter
- Lucknow
- Lunan
- Lundie
- Marywell
- Memus
- Menmuir
- Milden
- Milton of Finavon
- Milton of Ogilvie
- Monikie
- Muirdrum
- Muirhead
- Murroes
- Newbigging
- Newtyle
- Noranside
- Oathlaw
- Old Balkello
- Panbride
- Redford
- Ruthven
- St Vigeans
- Salmond's Muir
- Stracathro
- Strathmartine
- Tannadice
- Tarfside
- Tealing
- Templeton
- Trinity
- Unthank
- Upper Victoria
- Wellbank
- Wester Denoon
- Whigstreet
- Woodhill
Places of interest[]
- Aberlemno (Pictish symbols)
- Angus Folk Museum, Glamis
- Arbroath Abbey, place of signing of the Declaration of Arbroath[24]
- Barry Mill
- Brechin Cathedral
- Brechin Castle
- Caledonian Railway (Brechin)
- Cairngorms National Park
- Corrie Fee National Nature Reserve
- Eassie Stone[25]
- Edzell Castle
- Glamis Castle[26]
- Glenesk Folk Museum
- House of Dun
- Meffan Institute, museum and art gallery in Forfar
- Monboddo House
- Montrose Air Station Heritage Centre, site of the first operational military airfield in Britain RAF Montrose
- Montrose Basin Nature Reserve
- Montrose Museum
Sister areas[]
 – Yantai, Shandong, China.[27]
– Yantai, Shandong, China.[27]
Surnames[]
Most common surnames in Angus (Forfarshire) at the time of the United Kingdom Census of 1881:[28]
- 1. Smith
- 2. Robertson
- 3. Anderson
- 4. Stewart
- 5. Scott
- 6. Mitchell
- 7. Brown
- 8. Duncan
- 9. Milne
- 10. Thomson
See also[]
- Earl of Angus
- High schools in Angus
- List of counties of Scotland 1890–1975
- Medieval Diocese of Angus
- Primary schools in Angus
References[]
- ^ Field, John (1980). Place-names of Great Britain and Ireland. Newton Abbot, Devon: David & Charles. p. 24. ISBN 0389201545. OCLC 6964610.
- ^ Kendrick, Jill (1995). contributions by Barclay, Gordon J.; Cowie, Trevor G.; Saville, Alan; illustrations by Townshend, Angela; Braby, Alan. "Excavation of a Neolithic enclosure and an Iron Age settlement at Douglasmuir, Angus" (PDF). Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland. 125: 29–67. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2007.
- ^ Jervise, Andrew (1863). "Notice of stone cists and an urn, found near Arbroath, Forfarshire" (PDF). Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland. 5: 100–102. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 June 2007.
- ^ Watkins, Trevor (1978). contributions by Barclay, G. "Excavation of a settlement and souterrain at Newmill, near Bankfoot, Perthshire" (PDF). Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland. 110: 165–208. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 June 2007.
- ^ Jervise, Andrew (1863). "An account of the excavation of the round or "bee-hive" shaped house, and other underground chambers, at West Grange of Conan, Forfarshire". Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland. 4: 429–499. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 June 2007.
- ^ "Angus District through time | Population Statistics | Total Population". www.visionofbritain.org.uk.
- ^ "Vision of Britain; 1911 Census: County Report". www.visionofbritain.org.uk.
- ^ "Scotlands Census Results Online (SCROL)", Comparative Population Profile: Angus Council Area Scotland, retrieved 26 June 2013
- ^ Forsyth, 1997; Forsyth, 2006[full citation needed]
- ^ Smout, T.C. (2001). A history of the Scottish people: 1650–1830. Fontana Press. ISBN 978-0-00-686027-3.[page needed]
- ^ Withers, Charles W. J. (1984). Gaelic in Scotland, 1698-1981: The Geographical History of a Language. Edinburgh: John Donald Publishers. ISBN 978-0-85976-097-3.[page needed]
- ^ Gaelic Language Plan 2014-2019 (PDF) (Report). Angus Council. 17 September 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ^ "The Provost of Angus". Angus Council. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Political make up of the council". Angus Council. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Chief Executive". Angus Council. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Councillor Ronnie Proctor". Angus Council. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Councillor David Fairweather". Angus Council.
- ^ "Political make up of the council". Angus Council. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Upcoming elections". Angus Council. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ Historic Environment Scotland. "County Offices, Market Street, Forfar (LB31610)". Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ "Find your community council". Angus Council. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- ^ Morkis, Stefan. "Dundee Airport to introduce new routes to London City and Belfast".
- ^ Wilson, John Marius, Rev. (1854). Imperial Gazetteer of Scotland. Vol. I. A. Fullarton & Co. p. colour image preceding page 671.
|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ "Angus Council: Arbroath Abbey". Archived from the original on 20 February 2014.
- ^ "Eassie Stone". The Megalithic Portal.
- ^ "Welcome to Glamis Castle". Glamis-Castle.co.uk.
- ^ A Review of Angus Council's "Angus in China" Initiative and "Sister Area" Agreement with Yantai (PDF) (Report). Angus Council. 15 November 2001.
- ^ "Most Common Surnames in Angus". Forebearers.co.uk. 1881.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Angus. |
- Angus, Scotland
- Council areas of Scotland
- Counties of Scotland
- Lieutenancy areas of Scotland
- Counties of the United Kingdom (1801–1922)