Crista galli
| Crista galli | |
|---|---|
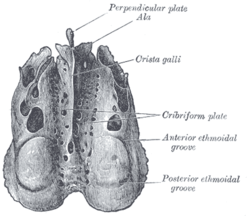 Ethmoid bone from above. | |
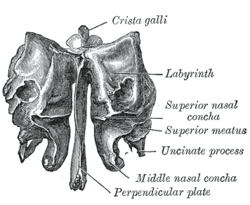 Ethmoid bone from behind. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone |
| System | skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Crista galli |
| TA98 | A02.1.07.004 |
| TA2 | 724 |
| FMA | 57442 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The crista galli (Latin: "crest of the rooster") is the upper part of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone of the skull. It rises above the cribriform plate. The falx cerebri (a fold of the dura mater surrounding the brain) attaches to the crista galli.
Structure[]
The crista galli is the upper part of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone of the skull.[1] It rises above the cribriform plate.[2] The falx cerebri (a fold of the dura mater surrounding the brain) attaches to the crista galli. The olfactory bulbs of the olfactory nerve lie on either side of the crista galli on top of the cribriform plate.
Variation[]
The crista galli varies in height.[2] In most people, it extends slightly below the cribriform plate.[2] In around 28%, it is completely above the cribriform plate, whilst in around 8%, it is over 50% below the top of the cribriform plate.[2]
History[]
The term "crista galli" is Latin for "crest of the rooster".
References[]
- ^ "Ethmoid bone". www.anatomynext.com. Retrieved 2018-03-01.
- ^ a b c d Hajiioannou, Jiannis; Owens, David; Whittet, Heikki B. (2010). "Evaluation of anatomical variation of the crista galli using computed tomography". Clinical Anatomy. 23 (4): 370–373. doi:10.1002/ca.20957. ISSN 1098-2353.
External links[]
- MedEd at Loyola Radio/curriculum/ENT/jay84a.jpg
- Floor of the cranial cavity (close-up)[dead link] - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Cross section image: skull/x-front—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
- Bones of the head and neck
- Musculoskeletal system stubs