Curie (Martian crater)
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (October 2013) |
 Viking Orbiter 1 image | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 29°06′N 4°48′W / 29.1°N 4.8°WCoordinates: 29°06′N 4°48′W / 29.1°N 4.8°W |
| Quadrangle | Oxia Palus |
| Diameter | 114.1 km (70.9 mi) |
| Eponym | Pierre Curie, a French physicist-chemist (1859-1906) |
Curie is an impact crater in the Oxia Palus quadrangle of Mars. It was named after Pierre Curie, a French physicist-chemist (1859-1906).[1]
Impact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them, in contrast volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits. As craters get larger (greater than 10 km in diameter) they usually have a central peak.[2] The peak is caused by a rebound of the crater floor following the impact.[3]

Central Curie crater, as seen by HiRISE.
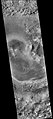
Curie crater, as seen by CTX camera on MRO

Channels in Curie crater, as seen by CTX camera. Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image.
Close-up of layers in central mound of Curie crater, as seen by HiRISE.

A topographic map created using Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. This map shows the elevation of the central peak and rim of Curie crater relative to Martian areoid.
See also[]
- Impact crater
- Impact event
- List of craters on Mars
- Ore resources on Mars
- Planetary nomenclature
- Water on Mars
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Curie (Martian crater). |
- ^ "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature | Curie". usgs.gov. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ "Stones, Wind, and Ice: A Guide to Martian Impact Craters".
- ^ Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- Oxia Palus quadrangle
- Impact craters on Mars
- Mars stubs
- Astrogeology stubs





