East Low German
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2019) |
| East Low German | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Germany, Poland, Brazil |
Indo-European
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | nds for Low German |
| ISO 639-3 | nds for Low German |
| Glottolog | nort2627 |
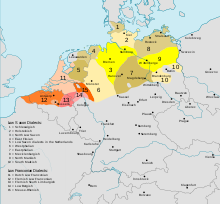 Low German after 1945 and the forced expulsion of German speakers from Eastern and Central Europe. East Low German includes the three dialects in the east, i.e., Mecklenburgish (8), North Markish or North Brandenburgish (9) and Middle Markish or Middle Brandenburgish (10) | |
East Low German (German: ostniederdeutsche Dialekte, ostniederdeutsche Mundarten, Ostniederdeutsch; Low German: Oostplattdütsch) is a group of Low German dialects spoken in north-eastern Germany as well as by minorities in northern Poland. Together with West Low German dialects, it forms a dialect continuum of the Low German language. Before 1945, the dialect was spoken along the entire then-German-settled Baltic Coast from Mecklenburg, through Pomerania, West Prussia into certain villages of the East Prussian Klaipėda Region.[1][2]
East Pomeranian, Central Pomeranian and West Pomeranian should not be confused with the West Slavic Pomeranian language (German: Pomoranisch).
Related languages[]
East Low German belongs to the dialect continuum of the continental West Germanic languages. It developed from the older Middle Low German.
In the West it fades into West Low German. The distinction is usually made referring to the plural endings of the verbs: East Low German endings are based on the old first person ending: -e(n), whereas West Low German endings are based on the old second person ending: -(e)t. The categorization of the Low German dialects into an Eastern and a Western group is not made by all linguists.
In the South, it fades into East Central German. The difference is that the East Low German varieties have not been affected by the High German consonant shift. The areas affected by the High German consonant shift are still expanding today, especially the Berlinerisch dialect that is gaining ground on the Brandenburgisch dialect by which it is surrounded.
Dialects[]
East Low German dialects are:
- In Germany:[3]
- Brandenburgisch (Brandenburgish; in Brandenburg, northern Saxony-Anhalt), incl. Middle Pomeranian
- Mecklenburgisch-Vorpommersch (Mecklenburgish-West Pomeranian; in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern)
- Mecklenburgisch (Mecklenburgish)
- Vorpommersch (West Pomeranian)
- In Poland since 1945 (before that Pomerania, Prussia, Germany):
For some it also includes Plautdietsch (originating from Danzig), which is spoken by Mennonites in North America, Mexico and a few other places in the world. In Berlin a version of Brandenburgisch was spoken in medieval times until the city took up an East Central German dialect that incorporated Brandenburgisch elements and developed into today's Berlin[er]isch.
Baltendeutsch is a High German variety influenced by East Low German formerly spoken by Germans in the Baltic states.

Pomeranian dialects[]
In Pomerania, several dialects of East Low German are, or were, spoken:
- West Pomeranian (German: Vorpommersch), a dialect of Mecklenburgisch-Vorpommersch
- West Central Pomeranian (Westmittelpommersch) and East Central Pomeranian Ostmittelpommersch) – dialects of Brandenburgisch
- East Pomeranian-West Prussian (Hinterpommersch-Westpreußisch, extinct in Europe, living in Brazil)
- Western East Pomeranian (Westhinterpommersch)
- Eastern East Pomeranian (Osthinterpommersch)
- Bublitzisch
- Pommerellisch
The German dialects of Pomerania are compiled and described in the Pommersches Wörterbuch ("Pomeranian Dictionary"), a dictionary of the German dialects spoken within the Province of Pomerania's borders in 1936.
East Pomeranian dialect of East Low German is also spoken in Brazil (see Pomerode, in Santa Catarina, Santa Maria de Jetibá, in Espírito Santo, and Arroio do Padre, Morro Redondo, Turuçu, Canguçu, São Lourenço do Sul and Pelotas, in Rio Grande do Sul).
History[]
By the early Middle Ages, Pomerania was largely populated by Slavic Pomeranians and Liuticians, who spoke the Pomeranian and Polabian languages. During the High Middle Ages, Germans from northern parts of the Holy Roman Empire settled in Pomerania as part of the medieval Ostsiedlung. Most Slavic Pomeranians gradually became Germanized. The new Pomeranian dialects which emerged from the admixture of the Low German dialects of the settlers are classified as East Low German.[4]
After World War II, Germans east of the Oder-Neisse line were expelled to post-war Germany. Most varieties of East Pomeranian dialect have largely died out in the following decades as the expellees were assimilated into their new homes, although West Pomeranian and Central Pomeranian are still spoken in Vorpommern (Western or Hither Pomerania), part of the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.[2]
As a result of German immigration to Brazil, there are still some communities speaking East Pomeranian in Rio Grande do Sul, Santa Catarina and Espírito Santo.[5]
Writers[]
Fritz Reuter and Heinrich Bandlow are among the most famous East Low German writers.
See also[]
| Low German edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
References[]
- ^ Barbour, Stephen; Stevenson, Patrick (1990). Variation in German: A Critical Approach to German Sociolinguistics. Cambridge University Press. pp. 86–. ISBN 978-0-521-35704-3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Russ, Charles V. J., ed. (2013) [originally 1990, reprinted 2000]. The Dialects of Modern German: A Linguistic Survey. Routledge. p. 91. ISBN 978-1-136-08668-7.
- ^ Graefen, Gabriele; Liedke-Göbel, Martina (2020). Germanistische Sprachwissenschaft: Deutsch als Erst-, Zweit- oder Fremdsprache (in German) (3rd ed.). A. Francke. p. 31.
Der niederdeutsche Sprachraum umfasst die niederfränkischen, westniederdeutschen (Westfälisch, Ostfälisch, Nordniedersächsisch) und ostniederdeutschen Dialekte (Mecklenburgisch, Vorpommersch, Brandenburgisch, Märkisch).
- ^ Besch, Werner (1998). Sprachgeschichte: Ein Handbuch zur Geschichte der Deutschen Sprache und ihrer Erforschung (in German) (2nd ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 2699ff. ISBN 3-11-015883-3.
- ^ Dietrich, Renata Pinz (2004-08-31). "180 Anos de Imigração Alemã". Site da Lingua Alemã (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 2004-08-31. Retrieved 2007-08-12.
External links[]
- Low German
- German-Brazilian culture
- German dialects
- Languages of Brazil
- Pomerania