Far East
| Far East | |||
|---|---|---|---|
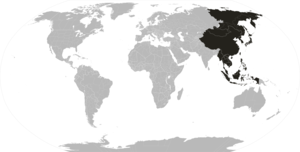 Location of the Far East, geographically defined. | |||
| Chinese name | |||
| Traditional Chinese | 遠東 | ||
| Simplified Chinese | 远东 | ||
| Literal meaning | Far East | ||
| |||
| Burmese name | |||
| Burmese | အရှေ့ဖျား ဒေသ | ||
| IPA | [ʔəʃḛbjá dèθa̰] | ||
| Vietnamese name | |||
| Vietnamese alphabet | Viễn Đông | ||
| Chữ Hán | 遠東 | ||
| Thai name | |||
| Thai | ตะวันออกไกล Tawan-oak klai | ||
| Korean name | |||
| Hangul | 극동 | ||
| Hanja | 極東 | ||
| |||
| Mongolian name | |||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Алс Дорнод Als Dornod | ||
| Japanese name | |||
| Kanji | 極東 | ||
| Katakana | キョクトウ | ||
| |||
| Malay name | |||
| Malay | تيمور جاءوه Timur Jauh | ||
| Indonesian name | |||
| Indonesian | Timur Jauh | ||
| Filipino name | |||
| Tagalog | Silanganan (poetic) Malayong Silangan (literal) | ||
| Tamil name | |||
| Tamil | தூர கிழக்கு Tūra Kiḻakku | ||
| Portuguese name | |||
| Portuguese | Extremo Oriente | ||
| Russian name | |||
| Russian | Дальний Восток IPA: [ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok] | ||
| Romanization | Dál'niy Vostók | ||
| Lao name | |||
| Lao | ຕາເວັນອອກໄກ Taven-oak kai | ||
| Khmer name | |||
| Khmer | ឆ្ងាយខាងកើត Chhngay Khangkaet | ||
| Tetum name | |||
| Tetum | Dok Lorosa'e | ||
The Far East is a geographical region that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East.[1] The term "Far East" came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 12th century[citation needed], denoting the Far East as the "farthest" of the three "easts", beyond the Near East and the Middle East. Likewise, in Qing Dynasty of the 19th and early 20th centuries the term "Tàixī (泰西)" – i.e., anything further west than the Arab world – was used to refer to the Western countries.
Since the 1960s, both East and Southeast Asia[a] respectively has become the most common term for the region in international mass media outlets.[2][3]
Popularization[]
Among Western Europeans, prior to the colonial era, "Far East" referred to anything further east than the Middle East. In the 16th century, King John III of Portugal called India a "rich and interesting country in the Far East[4] (Extremo Oriente)." The term was popularized during the period of the British Empire as a blanket term for lands to the east of British India.
South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.[5]
In pre-World War I European geopolitics, the Near East referred to the relatively nearby lands of the Ottoman Empire, the Middle East denoted northwestern South Asia and Central Asia, and the Far East meant countries along the western Pacific Ocean and eastern Indian Ocean. Many European languages have analogous terms, such as the French (Extrême-Orient), Spanish (Lejano Oriente), Portuguese (Extremo Oriente), German (Ferner Osten), Italian (Estremo Oriente), Polish (Daleki Wschód), Norwegian (Det fjerne Østen) and Dutch (Verre Oosten).
Cultural as well as geographic meaning[]
Significantly, the term evokes cultural as well as geographic separation; the Far East is not just geographically distant, but also culturally exotic. It never refers, for instance, to the culturally Western nations of Australia and New Zealand, which lie even farther to the east of Europe than East Asia itself. This combination of cultural and geographic subjectivity was well illustrated in 1939 by Robert Menzies, a Prime Minister of Australia. Reflecting on his country's geopolitical concerns with the onset of war, Menzies commented that:
The problems of the Pacific are different. What Great Britain calls the Far East is to us the Near North.[6]
Far East in its usual sense is comparable to terms such as the Orient, which means East; the Eastern world; or simply the East. Southeast Asia, the Russian Far East, and occasionally South Asia might be included in the Far East to some extent.
Concerning the term, John K. Fairbank and Edwin O. Reischauer, professors of East Asian Studies at Harvard University, wrote (in East Asia: The Great Tradition):
When Europeans traveled far to the east to reach Cathay, Japan and the Indies, they naturally gave those distant regions the general name 'Far East.' Americans who reached China, Japan and Southeast Asia by sail and steam across the Pacific could, with equal logic, have called that area the 'Far West.' For the people who live in that part of the world, however, it is neither 'East' nor 'West' and certainly not 'Far.' A more generally acceptable term for the area is 'East Asia,' which is geographically more precise and does not imply the outdated notion that Europe is the center of the civilized world.[3]
Today, the term remains in the names of some longstanding institutions, including the Far Eastern Federal University in Vladivostok, Far Eastern University in Manila, the Far East University in South Korea, and Far East, the periodical magazine of the Missionary Society of St. Columban. Furthermore, the United States and United Kingdom have historically used Far East for several military units and commands in the region; the Royal Navy's Far East Fleet, for instance.
Territories and regions conventionally included under the term Far East[]
| Name of region[7] and territory, with flag |
Area (km2) |
Population |
Population density (per km2) |
Capital | Forms of government | Currency | Official languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Asia | |||||||
| 6,952,600 | 8,371,257 | 1.2 | Moscow[10] | Federal semi-presidential republic | Ruble | Russian and 27 other co-official languages | |
| Southeast Asia | |||||||
| 5,765 | 417,200 | 72.11 | Bandar Seri Begawan | Absolute Islamic Sultanate | Brunei dollar | Malay and English | |
| 181,035 | 16,245,729 | 81.8 | Phnom Penh | Constitutional monarchy | Riel | Khmer | |
| 135 | 1,843 | 10.39 | Flying Fish Cove | External territory of Australia | Australian dollar | English[12] | |
| 14 | 544 | 43.0 | West Island | External territory of Australia | Australian dollar | None[14] | |
| 1,904,569 | 261,115,456 | 138.0 | Jakarta | Presidential republic | Rupiah | Indonesian | |
| 237,955 | 6,758,353 | 26.7 | Vientiane | Socialist Republic | Kip | Lao | |
| 330,803 | 32,049,700 | 92.0 | Kuala Lumpur | Federal constitutional monarchy, Parliamentary democracy |
Ringgit | Malay | |
| 676,578 | 53,582,855 | 76.0 | Naypyidaw | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
Kyat | Burmese | |
| 300,000 | 100,981,437 | 336.0 | Manila | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
Philippine peso (Piso) | Filipino and English | |
| 722.5 | 5,638,700 | 7,804.0 | Singapore | Parliamentary republic | Singapore dollar | Malay, English, Chinese (Mandarin), and Tamil | |
| 513,120 | 68,863,514 | 132.1 | Bangkok | Constitutional monarchy, Parliamentary democracy |
Baht | Thai | |
| 15,410 | 1,167,242 | 78.0 | Dili | Parliamentary republic | U.S. dollar / Centavo coins | Tetum and Portuguese | |
| 331,212 | 94,569,072 | 276.03 | Hanoi | One-party led state, Socialist Republic |
đồng | Vietnamese | |
| East Asia | |||||||
| 9,598,094[16] |
1,371,821,094[17] | 145.0 | Beijing | One-party socialist republic | Yuan (Renminbi) | Chinese (Mandarin)[18] | |
| 1,108 | 7,448,900 | 6,777.0 | Hong Kong | Special administrative region of the People's Republic of China. |
Hong Kong dollar | Chinese,[20] English | |
| 377,973 | 126,440,000 | 334.0 | Tokyo | Parliamentary democracy, Constitutional monarchy |
Yen | None[21] | |
| 115.3 | 653,100 | 21,340.0 | Macau | Special administrative region of the People's Republic of China |
Pataca | Chinese,[23] Portuguese | |
| 1,566,000 | 3,081,677 | 1.97 | Ulaanbaatar | Parliamentary republic | Tögrög | Mongolian | |
| 120,540 | 25,368,620 | 212.0 | Pyongyang | Juche unitarian dictatorship Socialist Republic |
North Korean won | Korean | |
| 100,363 | 51,446,201 | 507.0 | Seoul | Presidential republic | South Korean won | Korean | |
| 36,197 | 23,577,271 | 650.0 | Taipei | Semi-presidential system | New Taiwan dollar | Chinese (Mandarin) | |
Cities[]
See also[]
| Look up far east in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Asia-Pacific
- East Asia
- East Asian cultural sphere
- East–West dichotomy
- Far West, a term for Europe
- Four Asian Tigers
- Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere, Japanese idea from the 1930s-1940s
- Inner Asia
- List of Mongol states
- List of Turkic dynasties and countries
- North Asia
- Russian Far East
- Siberia
- Orient
- South Asia
- Southeast Asia
- Tropical Asia
- Turkic migration
- Turkic peoples
Wars[]
- List of conflicts in Asia#East Asia
- List of Chinese wars and battles
- List of wars involving the People's Republic of China
- Indochina Wars
- Korean War
- Pacific War, part of World War II
- Russo-Japanese War
Notes[]
- ^ Other terms such as Northeast Asia or ASEAN have also been used.
References[]
- ^ "Oxford Dictionaries - Dictionary, Thesaurus, & Grammar". askoxford.com.
- ^ "A menagerie of monikers". The Economist. 7 January 2010. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Reischauer, Edwin and John K Fairbank, East Asia: The Great Tradition, 1960.
- ^ Robert Sewell (1901). A Forgotten Empire: Vijayanagar; A Contribution to the History of India.
- ^ The 'Far Eastern Economic Review' for example covers news from India and Sri Lanka.
- ^ "Historical documents". Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade.
- ^ Continental regions as per UN categorisations (map), except 12. Depending on definitions, various territories cited below (notes 6, 11-13, 15, 17-19, 21-23) may be in one or both of Asia and Europe, Africa, or Oceania.
- ^ Russia is a transcontinental country located in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia, but is considered European historically, culturally, and ethnically, and the vast majority of its population (78%) lives within its European part.
- ^ Only the Russian Far East.
- ^ Moscow is located in Europe.
- ^ Christmas Island is an External Territory of Australia.
- ^ English does not have de jure status in Christmas Island and in Australia, but it is the de facto language of communication in government.
- ^ The Cocos (Keeling) Islands are an External Territory of Australia.
- ^ English does not have de jure status in the Cocos (Keeling) Islands and in Australia, but it is the de facto language of communication in government.
- ^ The state is commonly known as simply "China", which is subsumed by the eponymous entity and civilisation (China). Figures given are for Mainland China only, and do not include Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan.
- ^ Includes PRC-administered area (Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract, both territories claimed by India).
- ^ Information listed is for Mainland China only. The Special administrative region (i.e. Hong Kong and Macau), the island territories under the control of the Republic of China (which includes the islands of Taiwan, Quemoy, and Matsu) are excluded.
- ^ "Law of the People's Republic of China on the Standard Spoken and Written Chinese Language (Order of the President No.37)". Chinese Government. 31 October 2000. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
For purposes of this Law, the standard spoken and written Chinese language means Putonghua (a common speech with pronunciation based on the Beijing dialect) and the standardized Chinese characters.
- ^ Hong Kong is a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China
- ^ No specific variety of Chinese is official in the territory. Residents predominantly speak Cantonese, the de facto regional standard.
- ^ Japan's National Diet have not officially enacted a law stating that the official language is Japanese.
- ^ Macau is a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China.
- ^ No specific variety of Chinese is official in the territory. Residents predominantly speak Cantonese, the de facto regional standard.
- ^ Figures are for the area under the de facto control of the Republic of China (ROC) government, commonly referred to as Taiwan. Claimed in whole by the PRC; see political status of Taiwan.
Further reading[]
- Clyde, Paul Hibbert, and Burton F. Beers. The Far East: A History of Western Impacts and Eastern Responses, 1830-1975 (1975). online
- Crofts, Alfred. A history of the Far East (1958) online free to borrow
- Fairbank, John K., Edwin Reischauer, and Albert M. Craig. East Asia: The great tradition and East Asia: The modern transformation (1960) [2 vol 1960] online free to borrow, famous textbook.
- Green, Michael. By More Than Providence: Grand Strategy and American Power in the Asia Pacific Since 1783 (2019) excerpt
- Iriye, Akira. After Imperialism; The Search for a New Order in the Far East 1921-1931. (1965).
- Keay, John. Empire's End: A History of the Far East from High Colonialism to Hong Kong (Scribner, 1997). online free to borrow
- Macnair, Harley F. & Donald Lach. Modern Far Eastern International Relations. (2nd ed 1955) 1950 edition online free, 780pp; focus on 1900–1950.
- Norman, Henry. The Peoples and Politics of the Far East: Travels and studies in the British, French, Spanish and Portuguese colonies, Siberia, China, Japan, Korea, Siam and Malaya (1904) online
- Paine, S. C. M. The Wars for Asia, 1911-1949 (2014) excerpt
- Ring, George C. Religions of the Far East: Their History to the Present Day (Kessinger Publishing, 2006).
- Vinacke, Harold M. A History of the Far East in Modern Times (1964) online free
- Vogel, Ezra. China and Japan: Facing History (2019) excerpt
- Woodcock, George. The British in the Far East (1969) online.
- Regions of Asia
- Regions of Eurasia
- Geographical regions
- North Asia
- Southeast Asia
- East Asia
- Eurocentrism