Haldimand County
Haldimand County | |
|---|---|
City (single-tier) | |
| Haldimand County | |
 The Grand River Bridge, which carries Argyle St. over the Grand River in Caledonia. | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 42°56′N 79°53′W / 42.933°N 79.883°WCoordinates: 42°56′N 79°53′W / 42.933°N 79.883°W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Ontario |
| Established | 1800 (County) |
| Restructured | 1974 (Regional Municipality of Haldimand-Norfolk) |
| Amalgamated | 2001 (Single-tier municipality) |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Ken Hewitt |
| • Governing Body | The Council of Corporation of Haldimand County |
| • MPs | Vacant |
| • MPPs | Toby Barrett (Con) |
| Area | |
| • Land | 1,252 km2 (483 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 45,608 |
| • Density | 36.4/km2 (94/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| Postal code span | N0A, N1A, N3W |
| Area code(s) | 519, 226, 905, 289, 365 |
| Website | www.haldimandcounty.on.ca |
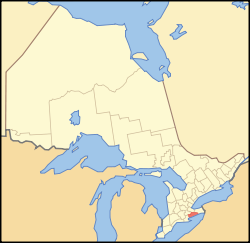
Haldimand County is a rural city-status single-tier municipality on the Niagara Peninsula in Southern Ontario, Canada, on the north shore of Lake Erie, and on the Grand River. Despite its name, it is no longer a county by definition, as all municipal services are handled by a single level of government. Municipal offices are located in Cayuga.
The county is adjacent to Norfolk County, the County of Brant, the City of Hamilton, and the Regional Municipality of Niagara.
History[]
Haldimand's history has been closely associated with that of neighbouring Norfolk County. Upper Canada was created in 1791 by being separated from the old Province of Quebec, Haldimand was created in 1798 as part of the Niagara District.[2] It was named after Sir Frederick Haldimand, the governor of the Province of Quebec from 1778 to 1785. In 1844, the land was surrendered by the Six Nations to the Crown in an agreement that was signed by the vast majority of Chiefs in the Haldimand tract.[citation needed] From 1974 to 2000, Haldimand County and Norfolk County were merged to form the Regional Municipality of Haldimand-Norfolk. See Norfolk County History for the period when Haldimand and Norfolk were governed as a single unit.
Beginning in February 2006, a land dispute by native protesters began near Caledonia over a housing development being built on the outskirts of town, which members of the nearby Mohawk Six Nations people claim is rightfully their land.
Communities[]
The population centres in Haldimand are Caledonia, Dunnville, Hagersville, Jarvis and Cayuga. Part of the Six Nations Reserve is within the geographic area of Haldimand County, but is independent of the county. Most of Haldimand is agricultural land, although some heavy industry, including the former Nanticoke Generating Station, is located here.
Smaller communities within the municipality are Attercliffe Station, Balmoral, Bodri Bay, Brookers Bay, Byng, Canborough, Canfield, Cheapside, Clanbrassil, Crescent Bay, Decewsville, Empire Corners, Featherstone Point, Fisherville, Garnet, Hoover Point, Kohler, Little Buffalo, Lowbanks, Moulton Station, Mount Carmel, Mount Healy, Nanticoke, Nelles Corners, Peacock Point, Port Maitland, Rainham Centre, Selkirk, Sims Lock, South Cayuga, Springvale, Stromness, Sweets Corners, Townsend, Willow Grove, Woodlawn Park and York.
The ghost towns of Cook's Station, Cranston, Dufferin, Erie, Indiana Lambs Corners, Lythmore, Sandusk, Upper, Varency, are also located within Haldimand.
Historic townships[]
Haldimand County's area of 309,300 acres was formed from part of the land grant to the Six Nations in 1783. The County was purchased by treaty and opened for general settlement in 1832. It was first settled by white veterans of Butler's Rangers established there by Joseph Brant. A large number of Germans were among the first settlers.
- Canborough, area 21,586 acres (87 km2). Granted in 1794 by Joseph Brant to John Dochstader of Butler's Rangers. Purchased by Benjamin Canby in 1810 for £5,000, he named the village-site "Canborough. Community centre: Canborough, Darling and it touches Dunnville
- Dunn, area 15,122 acres (61 km2). Opened for settlement in 1833. Community centre: Dunnville
- Moulton, area 27,781 acres (112 km2). Landowner Henry John Boulton named the township from the Boulton family seat in England.
- North Cayuga, area 32,825 acres (133 km2).
- Oneida, area 32,598 acres (132 km2). Joseph Brant granted a 999 year lease of part of Oneida and Seneca townships to Henry Nelles, of Butler's Rangers and his sons, Robert, Abraham, William, Warner and John. Community centres were: Caledonia, Dufferin and Hagersville.
- Rainham, area 25,705 acres (104 km2) Community centres: Balmoral, Selkirk, Rainham Centre and Fisherville.
- Seneca, area 41,721 acres (169 km2). Community centres: York and Caledonia
- Sherbrooke, area 5,098 acres (21 km2), the smallest township in Ontario. Opened in 1825 and named from Sir John Coape Sherbrooke, a Governor-General of Canada. The Township was granted by the Indians to William Dickson (a lawyer) as a professional fee. Community centres: Stromness and Port Maitland.
- South Cayuga, area 13,293 acres (54 km2).
- Walpole, area 66,213 acres (268 km2). Community centres were: Hagersville, Jarvis, Selkirk, Cheapside and Nanticoke.
Source: Province of Ontario – A History 1615 to 1927 by Jesse Edgar Middleton & Fred Landon, copyright 1927, Dominion Publishing Company, Toronto
Demographics[]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 42,041 | — |
| 2001 | 43,728 | +4.0% |
| 2006 | 45,212 | +3.4% |
| 2011 | 44,876 | −0.7% |
| 2016 | 45,608 | +1.6% |
| [3][4][1] | ||
| hideCanada census – Haldimand County community profile | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2011 | 2006 | |
| Population: | 45,608 (+1.6% from 2011) | 44,876 (-0.7% from 2006) | 45,212 (3.4% from 2001) |
| Land area: | 1,251.54 km2 (483.22 sq mi) | 1,251.57 km2 (483.23 sq mi) | 1,251.58 km2 (483.24 sq mi) |
| Population density: | 36.4/km2 (94/sq mi) | 35.9/km2 (93/sq mi) | 36.1/km2 (93/sq mi) |
| Median age: | 44.5 (M: 43.7, F: 45.2) | ||
| Total private dwellings: | 19,472 | 19,108 | 18,386 |
| Median household income: | $$76,117 | ||
| References: 2016[5] 2011[6] 2006[7] earlier[8] | |||
Ethnocultural statistics[]
Only ethnic groups that comprise greater than 1% of the population are included. Note that a person can report more than one group.[9]
- English: 37.4%
- "Canadian": 32.7%
- Scottish: 24.9%
- Irish: 20.1%
- German: 18.4%
- Dutch: 13.4%
- French: 8.6%
- Italian: 4.4%
- Aboriginal: 3.3%
- Ukrainian: 2.7%
- Polish: 2.7%
- Hungarian: 2.4%
- Welsh: 2.0%
- British Isles (other): 1.7%
- Portuguese: 1.3%
Local government[]
The city is within the federal electoral riding of Haldimand—Norfolk and within provincial electoral riding of Haldimand—Norfolk.
Current Mayor: Ken Hewitt[10]
Previous Mayors:
- 2004–2010: Marie Trainer
- 2000–2004: Lorraine Bergstrand
Policing[]
Policing in the county is provided by the Haldimand detachment of the Ontario Provincial Police located in Cayuga.
Fire services[]
Fire services in the county is provided by the Haldimand County Fire Department which was created in 2001 following the separation of Haldimand and Norfolk. The department currently consists of 11 stations located strategically throughout the county. With almost 300 firefighters and 40 fire apparatuses, it is one of the largest volunteer fire departments in Ontario. The department consists of;
- Station 1 – Caledonia
- Station 2 – Hagersville
- Station 3 – Jarvis
- Station 4 – Cayuga (Headquarters)
- Station 5 – Canfield
- Station 6 – Canborough
- Station 7 – Lowbanks
- Station 9 – Dunnville
- Station 11 – South Haldimand
- Station 12 – Fisherville
- Station 13 – Selkirk
Transportation[]
The Southern Ontario Railway operates in southwestern Haldimand.
Highways that travel through Haldimand include Ontario Highway 3 and Ontario Highway 6.
Protected areas[]
- Haldimand Conservation Area
- Selkirk Provincial Park
- Taquanyah Conservation Area
- Hedley Forest Conservation Area
- Canborough Conservation Area
- Ruigrok Tract Conservation Area
- Oswego Conservation Area
- Byng Island Conservation Area
- Rock Point Provincial Park
Attractions[]
- Port Maitland Outer Range Lighthouse and Pier
- Canadian Heritage Grand River
- Grand Valley Trail
- Toronto Motorsports Park (Dragway Park)
- Indiana Ghost Town
- Ruthven Park National Historic Site Mansion and Park
- Haldimand County Museum & Archives (Cayuga)
- Jukasa Motor Speedway
- Grand River Dinner Cruises
- Edinburgh Square Heritage Centre (Caledonia)
- Killman Zoo
- Cottonwood Mansion
- Caledonia Grand Trunk Station
- The Wilson Pugsley MacDonald Museum (c. 1872) is a National Historic Site of Canada on the Canadian Register of Historic Places.[11] The Museum was named in honour of Wilson MacDonald
- No. 6 RCAF Dunnville Museum
- Canadian Drilling Rig Museum
- Caledonia Old Mill
- Byng Island Conservation Area and Pool
- Mohawk Island Lighthouse (abandoned)
- Townsend Planned Community (1970)
- Nanticoke Generating Station
Notable people[]
- Birthplace of Canadian Olympic high jump medalist Ethel Catherwood.
- Birthplace of Canadian Women's Hockey Gold Medalist Becky Kellar-Duke
- Birthplace of Spud Johnson Major League Baseball player
- Boston Bruins' Nathan Horton, who won the Stanley Cup in 2011
- San Jose Sharks Head Coach Peter DeBoer
- Edmonton Oilers goaltender Cam Talbot
- Chicago Blackhawks goaltender Ray Emery, who won Stanley Cup in 2013
- Marty McSorley, retired NHL player
- Peter Robertson, inventor of the Robertson screw
See also[]
- List of townships in Ontario
- List of secondary schools in Ontario#Haldimand County
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Census Profile, 2016 Census: Haldimand County, City [Census subdivision], Ontario". Statistics Canada. Retrieved November 20, 2019.
- ^ An act for the better division of this province, SUC 1798 (38 Geo. III), c. 5, s. 31, s. 32. Reprinted in The Statutes of Upper Canada to the Time of Union, Revised and Published by Authority, Vol. I - Public Acts (Toronto: Robert Stanton, Queen's Printer, 1843).
- ^ Statistics Canada: 1996, 2001, 2006 census
- ^ "Haldimand County census profile". 2011 Census of Population. Statistics Canada. 2012-02-08. Retrieved 2012-03-27.
- ^ "2016 Community Profiles". 2016 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. February 21, 2017.
- ^ "2011 Community Profiles". 2011 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. July 5, 2013.
- ^ "2006 Community Profiles". 2006 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. March 30, 2011. Retrieved 2009-02-24.
- ^ "2001 Community Profiles". 2001 Canadian Census. Statistics Canada. February 17, 2012.
- ^ "Haldimand County community profile". 2006 Census data. Statistics Canada. 2007-03-13. Retrieved 2011-02-03.
- ^ "Ken Hewitt: Mayor". Haldimand County. Retrieved October 15, 2019.
- ^ "HistoricPlaces.ca – Recherche". Historicplaces.ca. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Haldimand County, Ontario. |
- Haldimand County
- Former counties in Ontario
- Single-tier municipalities in Ontario
- Populated places disestablished in 1974
- Southwestern Ontario

