Irbesartan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ɜːrbəˈsɑːrtən/ |
| Trade names | Avapro, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698009 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Cardiovascular agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60% to 80% |
| Protein binding | ~90% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C9) |
| Elimination half-life | 11 h to 15 h |
| Excretion | Kidney 20%, feces 65% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.119.966 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H28N6O |
| Molar mass | 428.540 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Irbesartan, sold under the brand name Avapro among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease.[2] It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure.[2] It is taken by mouth.[2] Versions are available as the combination irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide.[2][3]
Common side effects include dizziness, diarrhea, feeling tired, muscle pain, and heartburn.[2][4] Serious side effects may include kidney problems, low blood pressure, and angioedema.[2] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby and use when breastfeeding is not recommended.[5] It is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist and works by blocking the effects of angiotensin II.[2]
Irbesartan was patented in 1990, and approved for medical use in 1997.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[4] In 2019, it was the 181st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions.[7][8]
Structure activity relationship[]
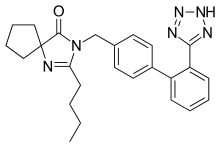
Irbesartan has the common structural features seen within the Angiotensin-II Receptor blockers or ARB medications. The medicine has an extended diphenyl group with a tetrazole at the 2-prime position. At the 4'prime position, the molecule has a diazaspiro04-none, which is on a methyl.
Medical uses[]
Irbesartan is used for the treatment of hypertension. It may also delay progression of diabetic nephropathy and is also indicated for the reduction of renal disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes,[9] hypertension and microalbuminuria (>30 mg/24 h) or proteinuria (>900 mg/24 h).[10]
Combination with diuretic[]
Irbesartan is also available in a fixed-dose combination formulation with hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic, to achieve an additive antihypertensive effect. [11] Irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination preparations are marketed under various brand names.[12]
Society and culture[]
It was developed by Sanofi Research (part of Sanofi-Aventis). It is jointly marketed by Sanofi-Aventis and Bristol-Myers Squibb under the brand names Aprovel, Karvea, and Avapro.[3][1]
References[]
- ^ a b "Irbesartan (Avapro) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 16 August 2018. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Irbesartan Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ a b "Avalide- irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 31 July 2018. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 175. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ "Irbesartan Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 470. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2019". ClinCalc. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ "Irbesartan - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, Ritz E, Atkins RC, Rohde R, Raz I, Collaborative Study Group (2001). "Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes". N Engl J Med. 345 (12): 851–60. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa011303. hdl:2445/122787. PMID 11565517.
- ^ Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006. ISBN 0-9757919-2-3
- ^ "Irbesartan and Hydrochlorothiazide (Professional Patient Advice)". Drugs.com. June 5, 2019. Retrieved March 19, 2020.
- ^ "Irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide Advanced Patient Information". Drugs.com. December 24, 2019. Retrieved March 19, 2020.
External links[]
- "Irbesartan". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Hydrochlorothiazide mixture with irbesartan". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists
- Sanofi
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Tetrazoles
- Biphenyls
- Lactams
- Spiro compounds
- Nitrogen heterocycles