Josep Tarradellas Barcelona–El Prat Airport
Barcelona–El Prat Airport | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | ENAIRE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | Aena | ||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain | ||||||||||||||||||
| Location | El Prat de Llobregat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 14 ft / 4 m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°17′49″N 002°04′42″E / 41.29694°N 2.07833°ECoordinates: 41°17′49″N 002°04′42″E / 41.29694°N 2.07833°E | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | aena.es | ||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||
 BCN Location within Spain | |||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2020) | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Barcelona–El Prat Airport[1][5] (IATA: BCN, ICAO: LEBL) (Catalan: Aeroport Barcelona–El Prat, Spanish: Aeropuerto Barcelona–El Prat), and also known as El Prat Airport, is an international airport located 15 km (9.3 mi) southwest[6][7] of the centre of Barcelona, lying in the municipalities of El Prat de Llobregat, Viladecans, and Sant Boi, in Catalonia, Spain.
It is the second largest and second busiest airport in Spain, and the sixth busiest in Europe. In 2019, Barcelona Airport handled a record 52,686,314 million passengers, up 5.0% from 2018. It is a hub for Level and Vueling, and a focus city for Air Europa, Iberia, EasyJet and Ryanair.
The Barcelona–Madrid air shuttle service, known as "Pont Aeri" (in Catalan) or "Puente Aéreo" (in Spanish), literally "Air Bridge", was the world's busiest route until 2008, with the highest number of flight operations (971 per week) in 2007.[8] The schedule has been reduced since February 2008, when a Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line was opened, covering the distance in 2 hours 30 minutes, and quickly became popular.[9]
History[]
Barcelona's first airfield, located at El Remolar, began operations in 1916. However, it did not have good expansion prospects, so a new airport at El Prat opened in 1918. The first plane was a Latécoère Salmson 300 which arrived from Toulouse with final destination Casablanca. The airport was used as headquarters of the Aeroclub of Catalonia and the base for the Spanish Navy's Zeppelin fleet. Scheduled commercial service began in 1927 with an Iberia service to Madrid Cuatro Vientos Airport. This was Iberia's first route. During the time of the Second Spanish Republic El Prat was one of the bases of LAPE (Líneas Aéreas Postales Españolas).[10]
In 1948, a runway was built (now called runway 07-25); in the same year the first overseas service was operated by Pan American World Airways to New York City, using a Lockheed Constellation. Between 1948 and 1952, a second runway was constructed (runway 16–34), perpendicular to the previous, also taxiways were constructed and a terminal to accommodate passengers. In 1963, the airport reached one million passengers a year. A new control tower was built in 1965. In 1968, a new terminal was opened, which still exists and is in use as what is now Terminal 2B.[11]
On 3 August 1970, Pan American World Airways inaugurated regular service between Barcelona, Lisbon and New York, operated by a Boeing 747.[citation needed] On 4 November of the same year, Iberia began the "Air-shuttle" service between Barcelona and Madrid–Barajas. A few years later, in 1976, a terminal was built specifically for Iberia's air-shuttle service and a terminal exclusively for cargo, an annexed mail service and an aircraft ramp for air cargo. In 1977, the airport handled over 5 million passengers annually.[citation needed]
From the late seventies to the early nineties, the airport was stalled in traffic and investments until the 1992 Summer Olympics held in Barcelona. El Prat underwent a major development consisting of the modernization and expansion of the existing terminal, which became known as Terminal B, and the construction of two further terminals flanking that, known as Terminals A and C respectively.[11] The development included jetways for direct access to the aircraft. This reform was designed by Ricardo Bofill Taller de Arquitectura.[citation needed]
In 1992, a new control tower was inaugurated also designed by Ricardo Bofill, but this was replaced by another much needed control tower in 2006.[citation needed]
The new Terminal 1 was inaugurated on 16 June 2009, covering 545,000 m2 (5,866,331 sq ft). 70% of today's flights operate from Terminal 1. The old Terminals A, B and C are now known as Terminals 2A, 2B and 2C.
Due to the strong drop in air traffic after 1999 and the crisis in the aviation sector in 2001 many charter operations from Girona and Reus were diverted to El Prat, which helped the airport to survive the crisis.
On 1 February 2014, Barcelona–El Prat was the first Spanish airport to receive a daily flight with the Airbus A380-800, on the Emirates route to Dubai International Airport. Emirates also offers a second daily flight, also operated by the A380-800.
International Airlines Group (IAG) announced in December 2016 flights from Barcelona to the US, Latin America and Asia for the summer of 2017. IAG, formed by British Airways, Iberia, Vueling and Aer Lingus, created Level, the second airline, after Norwegian, launching low-cost long haul flights from the Catalan city.[12] They announced flights from June 2017 to Los Angeles, Oakland, Punta Cana and Buenos Aires.[relevant?]
In October 2019 it was the first target of protesters after the sentencing of the trial of Catalonia independence leaders. Called upon Democratic Tsunami thousands flocked all the accesses and concourses disrupting normal operations. Catalan Police ordered the closing of all transportation services (bus, Metro and Rail) to avoid further arrivals of demonstrators. The blockade of C-32 highway with people walking between the terminals and city center made Taxi and other services unavailable. Deployment of riot police from Civil Guard, National Police and Mossos d'Esquadra to evict protesters lead to massive confrontations leaving dozens injured. More than a hundred flights were cancelled during the 14th of October and twenty more were announced for the next day by the main operator, Vueling.[13][14][15]
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a serious decrease in passenger, operations and cargo numbers during 2020, with numbers way below 2019's statistics.
Operations[]
Most of the traffic at Barcelona Airport is domestic and European, in which Vueling has an operational base. Intercontinental connections have not generated a significant amount of passenger traffic during the last years. In the early twenty-first century the airport passenger carried numbers and the number of operations increased significantly.
Low-cost airline traffic grew significantly, especially after the creation of operating bases by Vueling and Clickair at the airport. Vueling and Clickair merged in July 2009, operating under the Vueling name. Other low-cost airlines operate from the airport, including Ryanair, EasyJet, Norwegian Air International, EasyJet Switzerland, Wizz Air and Transavia.com. A new base was established at the airport in September 2010.
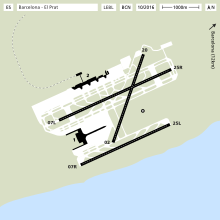
The airport has 3 runways, two parallel, nominated 07L/25R and 07R/25L (the later opened in 2004), and a cross runway 02/20. There are two terminals: T2, which is the sum of the previous Terminals A, B and C, located on the north side of the airport and T1, on the west side, which opened on 16 June 2009. As of 2014 the two terminals had a combined total of 268 check-in counters and 64 boarding gates. Operations at the airport are restricted exclusively to Instrument flight rules (IFR) flights, except for sanitary, emergency and government VFR flights.
A plan for expansion (Plan Barcelona)[16] was completed in 2009, adding a third terminal building (also designed by Ricardo Bofill) and control tower. An additional runway (07R/25L) was also built. The airport became capable of handling 55 million passengers annually (up from 33 million in 2007). The airport expanded in area from 8.45 to 15.33 square kilometres (3.26 to 5.92 sq mi). Further expansion was planned to be finished by 2012, with a new satellite terminal to raise capacity to 70 million passengers annually, this is better explained in Terminal T1 section.
The airport is the subject of a political discussion over management and control between the Generalitat of Catalonia and the Spanish Government, which has involved AENA (airport manager) and various airlines, Iberia and Spanair mainly. Part of the controversy is about the benefits that the airport generates, which are used in maintenance and investments in other airports in the network of AENA and government investments in other economic areas.[by whom?]
Terminals[]



Terminal 1[]
A new Terminal 1, designed by Ricardo Bofill Taller de Arquitectura was inaugurated on 16 June 2009. The airport terminal has an area of 548,000 m2 (5,900,000 sq ft), an aircraft ramp of 600,000 m2 (6,500,000 sq ft), 13,000 new parking spaces and 45 new gates expandable to 60. This terminal is also capable of handling large aircraft like the Airbus A380-800 or Boeing 747-8I.
The terminal handles both Schengen and non-Schengen flights. It is split into 5 Modules with Module A handling flights to Madrid, Module B handling Schengen flights, Module C handling Air Nostrum flights, Module D handling non-Schengen European flights and Module E handling non-Schengen non-European flights.
Its facilities include:
- 258 check-in counters
- 60 jetways (some are prepared for the A380, with double jetway)
- 15 baggage carousels (one new carousel is equivalent to 4 carousels in the old terminal) and
- 12,000 parking spaces, in addition to the 12,000 already in terminal 2.
The forecast is that the airport will be able to handle 55 million passengers annually —as opposed to the 30 million people before its construction— and will reach 90 operations an hour.
The extension of the airport with a total investment of €5.1 billion in the future[when?] will include a new satellite terminal and refurbishment of existing terminals. The civil engineering phase of the South Terminal had a budget of €1 billion.
It is also planned the construction of a satellite terminal —T1S or Terminal 1 Satèl·lit, in Catalan— considering that the airport is on the verge of overcrowding because terminals cannot handle all passengers because of space shortage. This terminal will be at 1,5 kilometres from the current T1 terminal, behind the 02-20, transversal, runway. With this action, the airport will be able to increase its passenger capacity to 70 million people annually.
There are two lounges located in Terminal 1.
Terminal 2[]
Terminal 2 is divided into three linked sections, known as Terminal 2A, 2B and 2C. Terminal 2B is the oldest part of the complex still in use, dating back to 1968. Terminals 2A and 2C were added in order to expand the airport capacity before the arrival of the 1992 Summer Olympics held in city.[11] This expansion was also designed by Ricardo Bofill.
This terminal is mostly occupied by low-cost airlines, although there are some full-service airlines which also use this terminal.
Following the opening of Terminal 1 in 2009, Terminal 2 became almost empty until the airport authorities lowered landing fees to attract low-cost and regional carriers to fill the terminal. Whilst this has helped, the complex is nowhere near full capacity and Terminal 2A is currently unused for departures. Terminal 2C is used only by EasyJet and EasyJet Switzerland flights, with flights to the UK using module M0, whilst flights to the rest of Europe use module M1. Terminal 2B is mostly used by Ryanair and others, like Transavia. And T2A is adapted for large airplanes, such as B777. The terminal is also split into Modules, where flights to schengen destinations use Module U and flights to non Schengen destinations use Modules W and Y.
Airlines and destinations[]
Passenger[]
The following airlines operate regular scheduled flights to and from Barcelona:[17]
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aegean Airlines | Athens |
| Aer Lingus | Dublin |
| Aeroflot | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Aeroméxico | Mexico City |
| Air Algérie | Algiers, Oran (suspended) |
| Air Arabia Maroc | Casablanca, Fez, Marrakesh, Nador, Tangier |
| Air Canada | Seasonal: Montréal–Trudeau, Toronto–Pearson |
| Air China | Beijing–Capital, Shanghai–Pudong |
| Air Europa | Madrid, Palma de Mallorca |
| Air France | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Air Transat | Montréal–Trudeau, Toronto–Pearson |
| airBaltic | Riga |
| Alitalia | Rome–Fiumicino |
| American Airlines | Miami, New York–JFK (suspended) Seasonal: Chicago–O'Hare, Philadelphia (both suspended) |
| Arkia | Tel Aviv |
| Asiana Airlines | Seoul–Incheon |
| Atlantic Airways | Seasonal: Vágar |
| Austrian Airlines | Vienna |
| Avianca | Bogotá (suspended)[18] |
| Belavia | Minsk (suspended) |
| Blue Air | Bacău, Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, Iași,(begins 27 March 2022)[19]Milan–Linate |
| British Airways | London–Heathrow |
| Brussels Airlines | Brussels |
| Bulgaria Air | Seasonal: Sofia |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| Croatia Airlines | Zagreb |
| Czech Airlines | Prague |
| Delta Air Lines | New York–JFK Seasonal: Atlanta |
| easyJet | Basel/Mulhouse, Berlin, Bordeaux, Bristol, Geneva, Glasgow, Liverpool, London–Gatwick, London–Luton, Lyon, Manchester, Milan–Malpensa, Naples, Nice, Paris–Charles de Gaulle Seasonal: Amsterdam,[20] Belfast–International, Olbia,[20] Prague,[21] Salzburg,[20] Zürich[20] |
| EgyptAir | Cairo |
| El Al | Tel Aviv |
| Emirates | Dubai–International, Mexico City |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi |
| Eurowings | Cologne/Bonn, Düsseldorf, Hamburg, Prague (begins 31 October 2021),[22] Stuttgart |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Georgian Airways | Seasonal: Yerevan |
| Iberia | Madrid |
| Iberia Regional | Badajoz, Burgos, León |
| Iran Air | Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| Israir Airlines | Seasonal: Tel Aviv |
| Jet2.com | Birmingham, Leeds/Bradford, Manchester |
| KLM | Amsterdam |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| Level | Boston, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, New York–JFK, San Francisco, Santiago de Chile Seasonal: Cancún |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin Seasonal: Katowice, Wrocław |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Luxair | Luxembourg |
| Norwegian Air Shuttle[23] | Copenhagen, Oslo, Stockholm–Arlanda Seasonal: Bergen, Helsinki, Stavanger |
| Pegasus Airlines | Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen |
| PLAY | Seasonal: Reykjavík–Keflavík[24] |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Rossiya | Saint Petersburg |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca, Marrakesh, Nador, Tangier |
| Royal Jordanian | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Ryanair | Athens (resumes 2 November 2021), Beauvais, Bergamo, Berlin, Billund, Birmingham, Bologna, Brindisi (begins 31 October 2021),[25] Bristol (begins 1 November 2021),[26] Brussels, Budapest, Charleroi, Cologne/Bonn, Dublin, Edinburgh, Eindhoven, Fez, Frankfurt, Fuerteventura, Gothenburg, Gran Canaria, Hamburg, Ibiza, Jerez de la Frontera, Krakow, Kyiv–Boryspil, Lanzarote, Lisbon (begins 31 October 2021),[27] Liverpool, London–Luton, London–Stansted, Luxembourg, Málaga, Malta, Manchester, Marrakesh, Menorca, Nador, Naples, Odessa, Oudja (begins 2 November 2021),[28] Palermo (begins 31 October 2021),[29] Palma de Mallorca, Podgorica, Porto, Prague, Rabat (begins 2 November 2021),[30] Riga, Rome–Fiumicino, Santander, Santiago de Compostela, Seville, Stockholm-Arlanda (begins 2 November 2021),[31] Sofia, Tallinn (begins 31 October 2021),[32] Tenerife–North, Tenerife–South, Turin, Valladolid, Venice, Vienna, Vigo (resumes 31 October 2021),[33] Vilnius, Warsaw–Modlin Seasonal: Agadir (begins 1 November 2021),[33] Alghero, Belfast–City (ends 11 September 2021),[34] Cardiff, Corfu, East Midlands, Glasgow–Prestwick, Heraklion, Maastricht, Rhodes,[35] Rome–Ciampino |
| S7 Airlines | Moscow–Domodedovo |
| Scandinavian Airlines | Seasonal: Oslo |
| Singapore Airlines | Singapore |
| SkyUp | Kyiv–Boryspil Seasonal: Kharkiv, Lviv, Odessa, Zaporizhzhia |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Geneva, Zürich |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon |
| TAROM | Bucharest |
| Transavia | Amsterdam, Eindhoven, Paris–Orly, Rotterdam/The Hague |
| Tunisair | Tunis |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul |
| Ukraine International Airlines | Kyiv–Boryspil |
| United Airlines | Newark Seasonal: Washington–Dulles (resumes 6 May 2022) |
| Ural Airlines | Seasonal: Moscow–Domodedovo |
| Volotea | Nantes, Strasbourg Seasonal: Verona (begins 8 April 2022)[36] |
| Vueling[37] | Aalborg, A Coruña, Algiers, Alicante, Almería, Amsterdam, Asturias, Athens, Banjul, Bari, Basel/Mulhouse, Beirut, Berlin, Bilbao, Birmingham, Bologna, Bordeaux, Brussels, Cagliari, Catania, Copenhagen, Dakar–Diass, Dublin, Dubrovnik, Düsseldorf, Florence, Fuerteventura, Geneva, Granada, Gran Canaria, Hamburg, Hannover, Ibiza, Jerez de la Frontera, Lanzarote, La Palma, Lisbon, London–Gatwick, Lyon, Madrid, Málaga, Malta, Manchester, Marrakesh, Marseille, Menorca, Milan–Malpensa, Munich, Nantes, Naples, Nice, Nuremberg, Oran, Oslo, Palermo, Palma de Mallorca, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Paris–Orly, Pisa, Porto, Prague, Rennes, Rome–Fiumicino, San Sebastián, Santander, Santiago de Compostela, Seville, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Tangier, Tel Aviv, Tenerife–North, Tenerife–South, Turin, Valencia, Valladolid, Venice, Vienna, Vigo, Zürich Seasonal: Ancona, Belfast–City, Belgrade, Bergen, Billund, Corfu, Edinburgh, Faro, Genoa, Gothenburg, Helsinki, Heraklion, Kyiv–Zhuliany, Larnaca, Murcia, Mykonos, Nador, Newcastle upon Tyne, Reykjavík–Keflavík, Santorini, Split, Stavanger, Tunis, Zagreb |
| WestJet | Seasonal: Toronto–Pearson |
| Wizz Air | Belgrade (begins 18 December 2021),[38] Bucharest, Budapest, Chișinău, Cluj-Napoca, Iași, Katowice, Kraków, Skopje, Sofia, Timişoara, Tirana,[39] Varna, Vienna, Warsaw–Chopin Seasonal: Gdańsk |
Cargo[]
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Emirates SkyCargo[40] | Dubai–Al-Maktoum |
| FedEx Express[41] | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| MNG Airlines[42] | Istanbul–Atatürk |
| Swiftair[43] | Palma de Mallorca |
| UPS Airlines[44] | Cologne/Bonn |
Statistics[]
Largest airlines[]
| Rank | Airline | Passengers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vueling | 20,381,235 |
| 2 | Ryanair | 7,828,218 |
| 3 | Iberia | 1,761,680 |
| 4 | EasyJet Europe | 1,724,336 |
| 5 | EasyJet UK | 1,607,272 |
| 6 | Lufthansa | 1,492,483 |
| 7 | Air Europa | 1,095,636 |
| 8 | Norwegian Air International | 1,058,699 |
| 9 | Wizz Air | 1,041,784 |
| 10 | British Airways | 784,889 |
Busiest routes[]
| Rank | Airport | Passengers | Airlines |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Madrid-Barajas | 2,569,295 | Air Europa, Vueling, Iberia |
| 2 | Palma de Mallorca Airport | 2,172,796 | Air Europa, Ryanair, Vueling |
| 3 | London-Gatwick | 1,587,255 | EasyJet, Norwegian Air International, Vueling |
| 4 | Rome Fiumicino | 1,402,095 | Alitalia, Ryanair, Vueling |
| 5 | Amsterdam Schiphol | 1,384,598 | KLM, LEVEL, Transavia, Vueling |
| 6 | Paris Charles De Gaulle | 1,372,239 | Air France, EasyJet, Vueling |
| 7 | Ibiza Airport | 1,206,563 | Ryanair, Vueling |
| 8 | Paris-Orly | 1,148,503 | Transavia France, Vueling |
| 9 | Seville Airport | 1,041,850 | Ryanair, Vueling |
| 10 | Frankfurt Airport | 1,036,557 | Lufthansa, Ryanair |
Passenger numbers[]
See source Wikidata query and sources.
Source: Airport of Barcelona, AENA. |
|
|
Ground transportation[]
Rail[]
Train Terminal 2 has its own Rodalies Barcelona commuter train station on the line R2, which runs from the Maçanet-Massanes station every 30 minutes, with major stops at Barcelona Sants railway station and the fairly central Passeig de Gràcia railway station to provide transfer to the Barcelona Metro system, also in Clot station. Passengers for T1 must take a connecting bus from Terminal 2B to Terminal 1. As part of the major expansion above, a new shuttle train is going to be built from Terminal 1 to Barcelona Sants (connected with the high speed train, the AVE) and Passeig de Gràcia Stations is expected by the end of 2020.
Metro Also this airport is linked to Barcelona by underground (metro) since 12 February 2016[46][47] by Line 9 of the Barcelona Metro with a station in each terminal, the Aeroport T1 station situated directly underneath the airport terminal T1 and the Aeroport T2 station close to the Aeroport rail station at the terminal T2. The line connects with several Barcelona Metro lines to the city center.
Road[]
The C-32B highway connects the airport to a main traffic interchange between Barcelona's Ronda de Dalt beltway and major motorways. There is provision for parking cars at the airport, with about 24,000 parking spaces.
Bus[]
The Transports Metropolitans de Barcelona (TMB) public bus line 46 runs from Paral·lel Avenue. The Aerobús offers direct transfers from T1 and T2 to the city center at Plaça Catalunya. Another company offers transfers from Barcelona Airport to nearest airports like Reus Airport or Girona–Costa Brava, provincial and national capitals and links with France or Andorra.
Incidents and accidents[]
- On 21 October 1994, a Falcon 20 cargo aircraft made an emergency landing at the airport after suffering a malfunction in its landing gear; none of the three crewmembers were injured.
- On 19 February 1998, two people, the commander and the pilot died in an Ibertrans general aviation plane crash in the borough of Gavà shortly after taking off from El Prat.
- On 28 July 1998, a general aviation cargo plane carrying press from Mallorca crashed next to one of the fences surrounding the airport, killing two crew members and co-pilot.
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "BOE.es - Documento BOE-A-2019-2943". www.boe.es (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 April 2019.
Modificar la denominación oficial del aeropuerto de Barcelona-El Prat, que en adelante pasa a denominarse «Aeropuerto Josep Tarradellas Barcelona-El Prat».
- ^ "Tráfico de pasajeros, operaciones y carga en los aeropuertos españoles" (PDF) (in Spanish). AENA. 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ "Spanish AIP (AENA)". Archived from the original on 7 March 2012.
- ^ "Presentación - Aeropuerto de Barcelona-El Prat - Aena.es". aena.es.
- ^ "Barcelona-El Prat Airport - Official website - Aena.es". www.aena.es. Retrieved 8 March 2019.
- ^ Aena (ed.). "Aeropuerto de Barcelona-El Prat". Archived from the original on 21 November 2014. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ^ EUROCONTROL basic. Eurocontrol.int. Retrieved on 4 October 2011.
- ^ "Air passenger transport in Europe in 2007". eurostat.eu. Retrieved 14 September 2015.
- ^ "Why the train in Spain is more popular than the plane". elpais.com. Retrieved 14 April 2014.
- ^ aomd88 (14 April 2011). "Airline memorabilia: Alas de la República: CLASSA, LAPE (1934)". Retrieved 1 June 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "History – Barcelona–El Prat Airport". aena. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ^ "IAG operará vuelos 'low cost' de largo radio desde El Prat a partir de junio". La Vanguardia. 22 December 2016.
- ^ "Continúan las cancelaciones en el Prat: estos son los aviones que se quedan en tierra hoy". El Confidencial (in Spanish). 15 October 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- ^ "Las protestas independentistas colapsan los accesos al aeropuerto de El Prat". Canarias7 (in Spanish). Barcelona. EFE. 15 October 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- ^ "Protests in Spain leave at least 37 injured, dozens of flights canceled in Barcelona". CBS News. 14 October 2019. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- ^ Barcelona / Plan Barcelona Archived 5 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine. Aena.es. Retrieved on 4 October 2011.
- ^ aena.es - Destinos retrieved 16 February 2017
- ^ https://www.avianca.com/co/en/experience/covid-19/
- ^ "Blue Air lansează ruta directa Iași – Dublin începând din decembrie 2021". 5 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d https://www.easyjet.com/en/
- ^ "easyJet bude létat z Prahy do Barcelony". flyondrej.eu. 21 June 2021. Retrieved 21 June 2021.
- ^ "Eurowings flight schedule". eurowings.com. Retrieved 21 June 2021.
- ^ "Route map". norwegian.com.
- ^ "Route Map". flyplay.com.
- ^ "Ryanair".
- ^ https://www.ryanair.com/gb/en
- ^ "Ryanair Anuncia 22 Novas Rotas e Mais 3 Aviões Em Lisboa | Ryanair's Corporate Website".
- ^ https://www.ryanair.com/gb/en
- ^ https://www.ryanair.com/gb/en
- ^ https://www.ryanair.com/gb/en
- ^ https://www.ryanair.com/gb/en
- ^ https://www.ryanair.com/gb/en
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Ryanair".
- ^ https://www.belfasttelegraph.co.uk/business/northern-ireland/ryanair-pullingout-of-northern-ireland-asflights-from-belfast-airports-to-end-40782457.html
- ^ "Ryanair Opens Three New Bases In Greece For Summer '21 | Ryanair's Corporate Website". corporate.ryanair.com.
- ^ "Booking Engine". Volotea. Retrieved 10 July 2021.
- ^ vueling.com - Where we fly retrieved 18 October 2020
- ^ https://www.exyuaviation.com/2021/08/wizz-air-unveils-belgrade-expansion.html
- ^ "Wizz Air allocates fifth plane to TIA base: Direct flights to Barcelona and Cologne to begin". Tirana International Airport.
- ^ skycargo.com - Air retrieved 18 July 2020
- ^ airlineroutemaps.com - FedEx retrieved 18 July 2020
- ^ "MNG schedule". Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ^ swiftair.com - Cargo retrieved 18 July 2020
- ^ airlineroutemaps.com - UPS United Parcel Service retrieved 18 July 2020
- ^ "Aena.es". portal.aena.es.
- ^ "Cuenta atrás para la inauguración del metro al aeropuerto de El Prat" [Countdown to the opening the metro to the airport of El Prat]. La Vanguardia (Press release) (in Spanish). La Vanguardia. 14 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ^ "El metro hacia El Prat comenzará a funcionar el día 12 de febrero" [The metro to el Prat gonna starts on 12 February]. La Vanguardia (Press release) (in Spanish). La Vanguardia. 20 January 2016. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
External links[]
![]() Media related to Barcelona Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Barcelona Airport at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Barcelona El Prat Airport travel guide from Wikivoyage
Barcelona El Prat Airport travel guide from Wikivoyage
- Airports in Catalonia
- Ricardo Bofill buildings
- Buildings and structures in Baix Llobregat
- Transport in Barcelona
- Transport in El Prat de Llobregat
- Airports established in 1918
