League of Nations mandate

- Red: Class A (ex Ottoman)
- Blue: Class B (ex German Central Africa)
- Yellow: Class C (ex German South West Africa and Pacific)
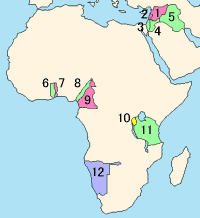
- Syria
- Lebanon
- Palestine
- Transjordan
- Mesopotamia
Class B, Mandates in Africa:
Class C, Mandates in Africa:
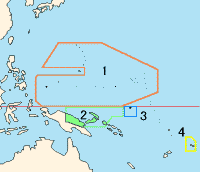
- Japanese Pacific Mandate
- Territory of New Guinea
- Nauru
- Western Samoa
| Paris Peace Conference |
|---|
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League of Nations. These were of the nature of both a treaty and a constitution, which contained minority rights clauses that provided for the rights of petition and adjudication by the Permanent Court of International Justice.[1]
The mandate system was established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, entered into force on 28 June 1919. With the dissolution of the League of Nations after World War II, it was stipulated at the Yalta Conference that the remaining Mandates should be placed under the trusteeship of the United Nations, subject to future discussions and formal agreements. Most of the remaining mandates of the League of Nations (with the exception of South-West Africa) thus eventually became United Nations Trust Territories.
Two governing principles formed the core of the Mandate System, being non-annexation of the territory and its administration as a "sacred trust of civilisation" to develop the territory for the benefit of its native people.[2]
Basis[]
The mandate system was established by Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, drafted by the victors of World War I. The article referred to territories which after the war were no longer ruled by their previous sovereign, but their peoples were not considered "able to stand by themselves under the strenuous conditions of the modern world". The article called for such people's tutelage to be "entrusted to advanced nations who by reason of their resources, their experience or their geographical position can best undertake this responsibility".[3]
Generalities[]
All of the territories subject to League of Nations mandates were previously controlled by states defeated in World War I, principally Imperial Germany and the Ottoman Empire. The mandates were fundamentally different from the protectorates in that the Mandatory power undertook obligations to the inhabitants of the territory and to the League of Nations.
The process of establishing the mandates consisted of two phases:
- The formal removal of sovereignty of the state previously controlling the territory.
- The transfer of mandatory powers to individual states among the Allied Powers.
Treaties[]
The divestiture of Germany's overseas colonies, along with three territories disentangled from its European homeland area (the Free City of Danzig, Memel Territory, and Saar), was accomplished in the Treaty of Versailles (1919), with the territories being allotted among the Allies on 7 May of that year. Ottoman territorial claims were first addressed in the Treaty of Sèvres (1920) and finalised in the Treaty of Lausanne (1923). The Turkish territories were allotted among the Allied Powers at the San Remo conference in 1920.
Types of mandates[]
The League of Nations decided the exact level of control by the Mandatory power over each mandate on an individual basis. However, in every case the Mandatory power was forbidden to construct fortifications or raise an army within the territory of the mandate, and was required to present an annual report on the territory to the Permanent Mandates Commission of the League of Nations.
The mandates were divided into three distinct groups based upon the level of development each population had achieved at that time.
The first group, or Class A mandates, were territories formerly controlled by the Ottoman Empire that were deemed to "... have reached a stage of development where their existence as independent nations can be provisionally recognized subject to the rendering of administrative advice and assistance by a Mandatory until such time as they are able to stand alone. The wishes of these communities must be a principal consideration in the selection of the Mandatory."
The second group of mandates, or Class B mandates, were all former German colonies in West and Central Africa, referred to by Germany as Schutzgebiete (protectorates or territories), which were deemed to require a greater level of control by the mandatory power: "...the Mandatory must be responsible for the administration of the territory under conditions which will guarantee freedom of conscience and religion." The mandatory power was forbidden to construct military or naval bases within the mandates.
The Class C mandates, including South West Africa and certain of the South Pacific Islands, were considered to be "best administered under the laws of the Mandatory as integral portions of its territory"
List of mandates[]
Column header abbreviations: C = Class, sov. = sovereignty
| C | Mandate | Territory | Mandate Power | Prior name | Prior sov. | Comments | Current state | Document |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon | Various Ottoman sanjaks | 29 September 1923 – 24 October 1945. Joined the United Nations on 24 October 1945 as an independent state. | 
| ||||
| Various Ottoman sanjaks | 29 September 1923 – 24 October 1945: This mandate included Hatay Province (a former Ottoman Alexandretta sandjak), which broke away from the mandate on 2 September 1938 to become a separate French protectorate, which lasted until Hatay Province was ceded to the new Republic of Turkey on 29 June 1939. Joined the United Nations on 24 October 1945 as an independent state. | |||||||
| Mandate for Palestine | Ottoman sanjaks of Jerusalem, Nablus and Acre | 29 September 1923 – 15 May 1948.[4][5][6] A United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine for peacefully dividing the remainder of the Mandate failed.[7] The Mandate terminated at midnight between 14 May and 15 May 1948. On the evening of 14 May, the Chairman of the Jewish Agency for Palestine had declared the establishment of the State of Israel.[8] Following the war, 75% of the area was controlled by the new State of Israel.[9] Other parts, until 1967, formed the West Bank of the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and the All-Palestine Government under the Egyptian-controlled Gaza Strip. | 
| |||||
| Ottoman sanjaks of and Ma'an | In April 1921, the Emirate of Transjordan was provisionally added as an autonomous area under the United Kingdom,[10][11] and it became the independent Hashemite Kingdom of Transjordan (later Jordan) on 17 June 1946 upon joint ratification of the Treaty of London of 1946. | |||||||
| Indirect | Various Ottoman sanjaks | The draft British Mandate for Mesopotamia not enacted and was replaced by the Anglo-Iraqi Treaty of October 1922.[12] Britain committed to act the responsibilities of a Mandatory Power in 1924.[13] Iraq attained independence from the United Kingdom on 3 October 1932. | 
| |||||
| B | Belgian Mandate for East Africa | From 20 July 1922 to 13 December 1946. Formerly two separate German protectorates, they were joined as a single mandate on 20 July 1922. From 1 March 1926 to 30 June 1960, Ruanda-Urundi was in administrative union with the neighbouring colony of Belgian Congo. After 13 December 1946, it became a United Nations Trust Territory, remaining under Belgian administration until the separate nations of Rwanda and Burundi gained independence on 1 July 1962. | 
| |||||
| British Mandate for East Africa[14] | From 20 July 1922 to 11 December 1946. It became a United Nations Trust Territory on 11 December 1946, and was granted internal self-rule on 1 May 1961. On 9 December 1961, it became independent while retaining the British monarch as nominal head of state, transforming into a republic on the same day the next year. On 26 April 1964, Tanganyika merged with the neighbouring island of Zanzibar to become the modern nation of Tanzania. | Equivalent document as for Ruanda-Urundi, with all articles substantially the same[15] | ||||||
| British Mandate for the Cameroons | Became part of the United Nations trust territories after World War II on 13 December 1946 | Part of |
Equivalent document as for French Cameroons, with all articles substantially the same[16] | |||||
| French Mandate for the Cameroons | Under a Resident and French Cameroun under a Commissioner until 27 August 1940, then under a governor. Became part of the United Nations trust territories after World War II on 13 December 1946 | 
| ||||||
| British Mandate for Togoland | British Administrator post filled by the colonial Governor of the British Gold Coast (present Ghana) except 30 September 1920 – 11 October 1923 Francis Walter Fillon Jackson). Transformed on 13 December 1946 into United Nations trust territories; on 13 December 1956 it ceased to exist as it became part of Ghana | Volta Region, |
Equivalent document as for French Togoland, with all articles substantially the same[16] | |||||
| French Mandate for Togoland | French Togoland under a Commissioner till 30 August 1956, then under a High Commissioner as Autonomous Republic of Togo | 
| ||||||
| C | Mandate for the German Possessions in the Pacific Ocean situated South of the Equator other than German Samoa and Nauru | Included German New Guinea and "the group of islands in the Pacific Ocean lying south of the equator other than German Samoa and Nauru".[17] From 17 December 1920 under an (at first Military) Administrator; after (wartime) Japanese/U.S. military commands from 8 December 1946 under UN mandate as North East New Guinea (under Australia, as administrative unit), until it became part of present Papua New Guinea at independence in 1975 | Part of |
Equivalent document as for Nauru, with all articles substantially the same[17] | ||||
| Mandate for Nauru | British mandate, administered by Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Became part of the United Nations trust territories after liberation from occupation by Japan in World War II | 
| ||||||
| Mandate for the German Possessions in the Pacific Ocean lying North of the Equator[18] | Known as the South Seas Mandate. Became part of the United Nations trust territories administered by the United States after World War II | Equivalent document as for Nauru, with all articles substantially the same[17] | ||||||
| Mandate for German Samoa | From 17 December 1920 a League of Nations mandate, renamed Western Samoa (as opposed to American Samoa), from 25 January 1947 a United Nations trust territory until its 1 January 1962 independence | Equivalent document as for Nauru, with all articles substantially the same[17] | ||||||
| Mandate for German South West Africa | From 1 October 1922, Walvis Bay's administration (still merely having a Magistrate until its 16 March 1931 Municipal status, hence a Mayor) was also assigned to the mandate | Equivalent document as for Nauru, with all articles substantially the same[17] |
Rules of establishment[]
According to the Council of the League of Nations, meeting of August 1920:[20] "draft mandates adopted by the Allied and Associated Powers would not be definitive until they had been considered and approved by the League ... the legal title held by the mandatory Power must be a double one: one conferred by the Principal Powers and the other conferred by the League of Nations,"[21]
Three steps were required to establish a Mandate under international law: (1) The Principal Allied and Associated Powers confer a mandate on one of their number or on a third power; (2) the principal powers officially notify the council of the League of Nations that a certain power has been appointed mandatory for such a certain defined territory; and (3) the council of the League of Nations takes official cognisance of the appointment of the mandatory power and informs the latter that it [the council] considers it as invested with the mandate, and at the same time notifies it of the terms of the mandate, after ascertaining whether they are in conformance with the provisions of the covenant."[21][22]
The U.S. State Department Digest of International Law says that the terms of the Treaty of Lausanne provided for the application of the principles of state succession to the "A" Mandates. The Treaty of Versailles (1920) provisionally recognised the former Ottoman communities as independent nations.[3] It also required Germany to recognise the disposition of the former Ottoman territories and to recognise the new states laid down within their boundaries.[23] The terms of the Treaty of Lausanne (1923) required the newly created states that acquired the territory detached from the Ottoman Empire to pay annuities on the Ottoman public debt and to assume responsibility for the administration of concessions that had been granted by the Ottomans. The treaty also let the States acquire, without payment, all the property and possessions of the Ottoman Empire situated within their territory.[24] The treaty provided that the League of Nations was responsible for establishing an arbitral court to resolve disputes that might arise and stipulated that its decisions were final.[24]
A disagreement regarding the legal status and the portion of the annuities to be paid by the "A" mandates was settled when an Arbitrator ruled that some of the mandates contained more than one State:
The difficulty arises here how one is to regard the Asiatic countries under the British and French mandates. Iraq is a Kingdom in regard to which Great Britain has undertaken responsibilities equivalent to those of a Mandatory Power. Under the British mandate, Palestine and Transjordan have each an entirely separate organization. We are, therefore, in the presence of three States sufficiently separate to be considered as distinct Parties. France has received a single mandate from the Council of the League of Nations, but in the countries subject to that mandate, one can distinguish two distinct States: Syria and the Lebanon, each State possessing its own constitution and a nationality clearly different from the other.[25]
Later history[]
After the United Nations was founded in 1945 and the League of Nations was disbanded, all but one of the mandated territories that remained under the control of the mandatory power became United Nations trust territories, a roughly equivalent status.[7] In each case, the colonial power that held the mandate on each territory became the administering power of the trusteeship, except that Japan, which had been defeated in World War II, lost its mandate over the South Pacific islands, which became a "strategic trust territory" known as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands under United States administration.
The sole exception to the transformation of the League of Nations mandates into UN trusteeships was that South Africa refused to place South-West Africa under trusteeship. Instead, South Africa proposed that it be allowed to annex South-West Africa, a proposal rejected by the United Nations General Assembly. The International Court of Justice held that South Africa continued to have international obligations under the mandate for South-West Africa. The territory finally attained independence in 1990 as Namibia, after a long guerrilla war of independence against the apartheid regime.
Nearly all the former League of Nations mandates had become sovereign states by 1990, including all of the former United Nations Trust Territories with the exception of a few successor entities of the gradually dismembered Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (formerly Japan's South Pacific Trust Mandate). These exceptions include the Northern Mariana Islands which is a commonwealth in political union with the United States with the status of unincorporated organised territory. The Northern Mariana Islands does elect its own governor to serve as territorial head of government, but it remains a U.S. territory with its head of state being the President of the United States and federal funds to the Commonwealth administered by the Office of Insular Affairs of the United States Department of the Interior.
Remnant Micronesia and the Marshall Islands, the heirs of the last territories of the Trust, attained final independence on 22 December 1990. (The UN Security Council ratified termination of trusteeship, effectively dissolving trusteeship status, on 10 July 1987.) The Republic of Palau, split off from the Federated States of Micronesia, became the last to effectively get its independence, on 1 October 1994.
See also[]
Sources and references[]
- Anghie, Antony "Colonialism and the Birth of International Institutions: Sovereignty, Economy, and the Mandate System of the League of Nations" 34 (3) New York University Journal of International Law and Politics 513 (2002)
- Hall, H. Duncan (1948). Mandates, Dependencies and Trusteeship.
- Nele Matz, Civilization and the Mandate System under the League of Nations as Origin of Trusteeship, in: A. von Bogdandy and R. Wolfrum, (eds.), Max Planck Yearbook of United Nations Law, Volume 9, 2005, p. 47–95.
- Pugh, Jeffrey, "Whose Brother's Keeper? International Trusteeship and the Search for Peace in the Palestinian Territories", International Studies Perspectives 13, no. 4 (November 2012): 321–343.
- Tamburini, Francesco "I mandati della Società delle Nazioni", in Africana, Rivista di Studi Extraeuropei, n.XV – 2009, pp. 99–122.
- Wright, Quincy (1968). Mandates Under the League of Nations. Greenwood Press.
Further reading[]
- Bruce, Scot David, Woodrow Wilson's Colonial Emissary: Edward M. House and the Origins of the Mandate System, 1917–1919 (University of Nebraska Press, 2013).
- Callahan, Michael D. Mandates and empire: the League of Nations and Africa, 1914–1931 (Brighton: Sussex Academic Press, 1999)
- Haas, Ernst B. "The reconciliation of conflicting colonial policy aims: acceptance of the League of Nations mandate system," International Organization (1952) 6#4 pp: 521–536.
- Margalith, Aaron M. The International Mandates (1930) online Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine[ISBN missing]
- Pedersen, Susan. The Guardians: the League of Nations and the Crisis of Empire, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2015)
- Sluglett, Peter. "An improvement on colonialism? The 'A' mandates and their legacy in the Middle East," International Affairs (2014) 90#2 pp. 413–427. On the former Arab provinces of the Ottoman Empire
References[]
- ^ "Legal Consequences for States of the Continued Presence of South Africa in Namibia (South West Africa) notwithstanding Security Council Resolution 276 (1970)" (PDF). International Court of Justice: 28–32. 21 June 1971. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2015. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ Matz, 2005, pp 70-71, "Primarily, two elements formed the core of the Mandate System, the principle of non-annexation of the territory on the one hand and its administration as a 'sacred trust of civilisation' on the other... The principle of administration as a 'sacred trust of civilisation' was designed to prevent a practice of imperial exploitation of the mandated territory in contrast to former colonial habits. Instead, the Mandatory's administration should assist in developing the territory for the well-being of its native people."
- ^ Jump up to: a b See Article 22 of the Peace Treaty of Versailles
- ^ "Papers relating to the foreign relations of the United States, The Paris Peace Conference, 1919 Volume XIII, Annotations to the treaty of peace between the Allied and Associated Powers and Germany, signed at Versailles, June 28, 1919". Foreign Relations of the United States. United States State Department. June 28, 1919. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory" (PDF). Advisory Opinions. The International Court of Justice (ICJ). 2004. p. 165. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 July 2010. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
70. Palestine was part of the Ottoman Empire. At the end of the First World War, a class "A" Mandate for Palestine was entrusted to Great Britain by the League of Nations, pursuant to paragraph 4 of Article 22 of the Covenant
- ^ "Italy Holds up Class A Mandates". The New York Times. July 20, 1922. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
LONDON, July 19. – The A mandates, which govern the British occupation of Palestine and the French occupation of Syria, came today before the Council of the League of Nations.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Pugh, Jeffrey D. (2012-11-01). "Whose Brother's Keeper? International Trusteeship and the Search for Peace in the Palestinian Territories". International Studies Perspectives. 13 (4): 321–343. doi:10.1111/j.1528-3585.2012.00483.x. ISSN 1528-3577.
- ^ Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs: The Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel. May 14, 1948: Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- ^ Edmund Jan Osmańczyk; Anthony Mango (2003). Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: G to M. Taylor & Francis. p. 1178. ISBN 978-0-415-93922-5. Retrieved 17 November 2011.
- ^ The Making of Jordan: Tribes, Colonialism and the Modern State, By Yoav Alon, Published by I.B.Tauris, 2007, ISBN 1-84511-138-9, p. 21
- ^ Determining Boundaries in a Conflicted World: The Role of Uti Possidetis, By Suzanne Lalonde, Published by McGill-Queen's Press (MQUP), 2002, ISBN 0-7735-2424-X, pp. 89–100
- ^ Wright 1968, p. 595.
- ^ Wright 1968, p. 593.
- ^ Hall 1948, p. 303.
- ^ Wright 1968, p. 611.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Wright 1968, p. 616.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Wright 1968, p. 618.
- ^ Hall 1948, p. 307.
- ^ Treaty of Peace and South West Africa Mandate Bill of 1919
- ^ (pp. 109–110)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Quincy Wright, Mandates under the League of Nations, Univ.Chicago Press, 1930.
- ^ See also: Temperley, History of the Paris Peace Conference, Vol VI, pp. 505–506; League of Nations, The Mandates System (official publication of 1945); Hill, Mandates, Dependencies and Trusteeship, pp. 133ff.
- ^ See Article 434 of the Peace Treaty of Versailles
- ^ Jump up to: a b Article 47, 60, and Protocol XII, Article 9 of the Treaty of Lausanne
- ^ See Marjorie M. Whiteman, Digest of International Law, vol. 1 (Washington, DC: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1963) pp. 650–652, 21 Apr. 2010
- League of Nations mandates
- 1946 disestablishments
- 20th century in Japan
- Decolonization
- French colonial empire
- Governance of the British Empire