French Togoland
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2016) |
Territory of Togoland Togo français | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1916–1960 | |||||||||
 Flag
 Seal
| |||||||||
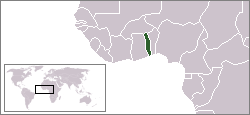 | |||||||||
| Status | Mandate of France | ||||||||
| Capital | Lomé | ||||||||
| Common languages | French (official), Ewe, Kabye, Kotokoli etc | ||||||||
| Commissioner | |||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Occupation | 27 August 1914 | ||||||||
• Togoland partitioned | 27 December 1916 | ||||||||
| 20 July 1922 | |||||||||
• Autonomy | 1955 | ||||||||
• Independence | 27 April 1960 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Togo | ||||||||
French Togoland (French: Togo français) was a French colonial League of Nations mandate from 1916 to 1960 in French West Africa. In 1960 it became the independent Togolese Republic, and the present day nation of Togo.
Transfer from Germany to France and a mandate territory[]

French troops landed at Little Popo on 6 August 1914, meeting little resistance. The French proceeded inland, taking the town of Togo on 8 August.[1] On 26 August 1914, the German protectorate of Togoland was invaded by French and British forces and fell after five days of brief resistance. The colony surrendered "without conditions" with British and French troops landing in Kamina on 27 August 1914. The Germans had offered to surrender to the British on terms, to which the British responded a surrender must be unconditional, promising to respect private property, with little interference in trade or private interests and firms.[2] Period news reports suggest the Germans had used expanding bullets during the campaign and had armed native people not under their control, both violations of the Hague Conventions.[1] Togoland was divided into French and British administrative zones in 1916, and following the war, Togoland formally became a League of Nations mandate divided for administrative purposes between France and the United Kingdom.
German nationalists in the Weimar Republic were reported to have objected to the seizure of the colony by the French via an interpellation in 1920, expressing their view that it violated Article 22 of the Treaty of Versailles. They also exclaimed via a news release that "the German Government naturally leaves nothing undone to prevent an interpretation of the treaty which would justify France's alleged intention."[3] The value of the colony to France was found in the existing railways, permitting a new link to the railway in Dahomey at Atakpamé and the ports of Lome, Segura and Little Popo.[4]
After World War II, the mandate became a UN trust territory, still administered by French commissioners.
By statute in 1955, French Togoland became an autonomous republic within the French Union, although it retained its UN trusteeship status. A legislative assembly elected by universal adult suffrage had considerable power over internal affairs, with an elected executive body headed by a prime minister responsible to the legislature. These changes were embodied in a constitution approved in a 1956 referendum. On 10 September 1956, Nicolas Grunitzky became prime minister of the Autonomous Republic of Togo. However, due to irregularities in the plebiscite, an unsupervised general election was held in 1958 and won by Sylvanus Olympio. On 27 April 1960, in a smooth transition, Togo severed its constitutional ties with France, shed its UN trusteeship status, and became fully independent under a provisional constitution with Olympio as president.[5]
Governors[]
See also[]
- List of colonial heads of French Togoland
- History of Togo
- French West Africa
- French colonisation in Africa
- French colonial Empire
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Colored People's Part in the World War: The Fight in Africa: Many Square Miles Wrenched From Germany: Black Troops Display Great Valor". The Richmond Planet. Richmond, VA. 2 March 1918. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ^ "German Togoland Surrenders Without Conditions to Allies". New York Tribune. New York, NY. 27 August 1914. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Germany Will Oppose French Annexation Plan". New York Tribune. New York, NY. 3 October 1920. Retrieved 13 November 2016.
- ^ "African Tribes Pleased at Overthrow German Masters". The Chattanooga News. Chattanooga, TN. 27 February 1920. Retrieved 13 November 2016.
- ^ Jacques Meyer May (1968). The Ecology of Malnutrition in the French Speaking Countries of West Africa and Madagascar: Senegal, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Togo, Dahomey, Cameroon, Niger, Mali, Upper Volta, and Madagascar. Hafner Publishing Company. p. 133.
Further reading[]
- Kurtas, Susan. "Research Guides: UN Documentation: Trusteeship Council: Togoland under French administration". research.un.org. United Nations. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
Agreement, Petitions, Reports of Administering Power, and Reports of Visiting Missions
- French Togoland
- French West Africa
- History of Togo
- History of West Africa
- Former colonies in Africa
- Former French colonies
- French colonisation in Africa
- French Union
- League of Nations mandates
- United Nations trust territories
- States and territories established in 1916
- States and territories disestablished in 1960
- 1916 establishments in French Togoland
- 1960 disestablishments in Togo
- 1916 establishments in French West Africa
- 1960 disestablishments in the French colonial empire
- Former polities of the Cold War