Limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase
| Limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase catalytic domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | LEH | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07858 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0051 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013100 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1nww / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 133 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 2bng | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.3.2.8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In enzymology, a limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- limonene-1,2-epoxide + H2O limonene-1,2-diol
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are and H2O, whereas its product is .
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on ether bonds (ether hydrolases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase. This enzyme is also called limonene oxide hydrolase. This enzyme participates in limonene and pinene degradation.
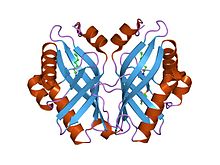
Epoxide hydrolases catalyse the hydrolysis of epoxides to corresponding diols, which is important in detoxification, synthesis of signal molecules, or metabolism. Limonene-1,2- epoxide hydrolase (LEH) differs from many other epoxide hydrolases in its structure and its novel one-step catalytic mechanism. Its main fold consists of a six-stranded mixed beta-sheet, with three N-terminal alpha helices packed to one side to create a pocket that extends into the protein core. A fourth helix lies in such a way that it acts as a rim to this pocket. Although mainly lined by hydrophobic residues, this pocket features a cluster of polar groups that lie at its deepest point and constitute the enzymes active site.[1]
References[]
- ^ Arand M, Hallberg BM, Zou J, Bergfors T, Oesch F, van der Werf MJ, de Bont JA, Jones TA, Mowbray SL (June 2003). "Structure of Rhodococcus erythropolis limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase reveals a novel active site". EMBO J. 22 (11): 2583–92. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg275. PMC 156771. PMID 12773375.
Further reading[]
- van der Werf MJ, Overkamp KM, de Bont JA (1998). "Limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase from Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 belongs to a novel class of epoxide hydrolases". J. Bacteriol. 180 (19): 5052–7. doi:10.1128/JB.180.19.5052-5057.1998. PMC 107539. PMID 9748436.
- Barbirato F, Verdoes JC, de Bont JA, van der Werf MJ (1998). "The Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase gene encodes an enzyme belonging to a novel class of epoxide hydrolases". FEBS Lett. 438 (3): 293–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01322-2. PMID 9827564. S2CID 25639310.
- Protein domains
- EC 3.3.2
- Enzymes of known structure
- Hydrolase stubs
