Minnesota Territory
| Territory of Minnesota | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organized incorporated territory of the United States | |||||||||||||
| 1849[1]–1858 | |||||||||||||
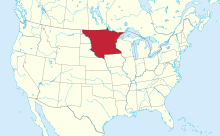 Location of Minnesota Territory within the U.S. including U.S. state boundaries | |||||||||||||
| Capital | St. Paul | ||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||
| • Type | Organized incorporated territory | ||||||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||||||
• 1849–1853 | Alexander Ramsey | ||||||||||||
• 1853–1857 | Willis A. Gorman | ||||||||||||
• 1857–1858 | Samuel Medary | ||||||||||||
| Legislature | Minnesota Territorial Legislature | ||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
| March 3 1849[1] | |||||||||||||
• Statehood | May 11 1858 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Territory of Minnesota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1849, until May 11, 1858, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Minnesota.
History[]

The Minnesota Territory was formed on March 3, 1849.[2] At the time of formation there were 5000 settlers living in the Territory. There were no roads from adjoining Wisconsin or Iowa. The easiest access to the region was via waterway of which the Mississippi River was primary. The primary mode of transport was the riverboat. Minnesota Territory had three significant pioneer settlements: St. Paul, St. Anthony/Minneapolis, and Stillwater plus two military reservations: Fort Snelling and Fort Ripley. All of these were located on a waterway. A reservation for the Winnebago had been created at Long Prairie in 1848. The Chippewa Agency, at Crow wing, was founded in 1852. The Upper and Lower Sioux Agencies were created in 1853. All of these were located adjacent a waterway also. The primary territorial institutions were in the three main settlements, St. Paul was made the capital; Minneapolis was selected as the site of the University of Minnesota; and Stillwater was chosen for the Territorial Prison.[3] The Military Reservations were Federal land of which the Fort Snelling Unorganized Territory still exists. Fort Ripley is now the Minnesota National Guard's Camp Ripley. The first school in the Territory was located at Fort Snelling as was the first Post Office.[4] [5] The first justice of the peace was at Mendota as was the first Church in Minnesota. St. Peter's Catholic Church at Mendota was built in 1840.
Governor Ramsey requested that Congress approve funds for five military roads in the Territory: Mendota/Fort Snelling to the Big Sioux confluence with the Missouri River, Point Douglas to Fort Ripley, Fort Ripley Road/Swan River to Long Prairie Indian Agency, Point Douglas to Superior.[6] Money was approved in 1850 for four with the Point Douglas Fort Ripley Military Road being the first. Money was approved later for a survey of the route to the Big Sioux/Missouri, the Fort Ridgely and South Pass Wagon Road and the Wagon Road from Fort Ripley to Fort Abercrombie. Private trails were being cut too. The most well known of these was Dodd Road from 1853. It was named after Capt. Dodd, and significant portions of it still exist.[6]
When the region was Wisconsin Territory the Red River Trails were further developed by Joe Rolette.[6] There were three main trails now identified as the : West Plains Trail, East Plains Trail, and the Woods Trails.[6] They connected Fort Gerry and the Selkirk Settlement with Fort Snelling and the American Fur Trading Company at Mendota.[6] Later, the Oxcarts became synonymous with St. Paul's Kellogg St. and the riverboat landing. Fort Ripley lay along the East Plains Trail.
In 1850, 10 years after the end of the Second Great Awakening (1790–1840), of the 3 churches with regular services in the Minnesota Territory, 1 was Catholic, 1 was Methodist, and 1 was Presbyterian.[7] In the 1850 United States census, 9 counties in the Minnesota Territory reported the following population counts:[8]
| Rank | County | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ramsey | 2,227 |
| 2 | Kittson | 1,134 |
| 3 | Washington | 1,056 |
| 4 | Dakota | 584 |
| 5 | Benton | 418 |
| 6 | Wabasha | 243 |
| 7 | Wahnata | 160 |
| 8 | Mahkahta | 158 |
| 9 | Itasca | 97 |
| Minnesota Territory | 6,077 |
Territorial Governors[]
| # | Governor | Took office | Left office | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alexander Ramsey | 
|
June 1, 1849 | May 15, 1853 | Whig |
| 2 | Willis Arnold Gorman | 
|
May 15, 1853 | April 23, 1857 | Democratic |
| 3 | Samuel Medary | 
|
April 23, 1857 | May 24, 1858 | Democratic |
Territorial Secretaries[]
- Charles K. Smith, 1849–1851
- Alexander Wilkin, 1851–1853
- Joseph Rosser, 1853–1857
- Charles L. Chase, 1857–1858
Territorial Attorneys General[]
- Lorenzo A. Babcock, 1849–1853
- Lafayette Emmett, 1853–1858
Congressional Delegates[]
- Henry Hastings Sibley, 31st Congress, 32nd Congress, 1849–1853
- Henry Mower Rice, 33rd Congress, 34th Congress, 1853–1857
- William W. Kingsbury, 35th Congress, 1857–1858
See also[]
- John Catlin
- Historic regions of the United States
- History of Minnesota
- Interior Plains
- Territorial era of Minnesota
- Territorial evolution of the United States
- Territory of Dakota, 1861–1889
References[]
- ^ 9 Stat. 403
- ^ See The Student Page of the Minnesota Secretary of State Archived July 1, 2007, at the Wayback Machine for an overview of how Minnesota's state boundaries were determined.
- ^ "History of the Minnesota Territory". Minnesota Territorial Pioneers. Archived from the original on July 24, 2016. Retrieved August 25, 2019.
- ^ Colbruno, Michael "Lives of the Dead: Mountain View Cemetery in Oakland." December 12, 2009. Retrieved March 5, 2015.
- ^ The Post Office in Early Minnesota, Minnesota History Vol. 40 No.2, Summer 1966, J. W. Patterson, p.78, MHS website [1]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e A History of Minnesota's Highways Part One, Streets MN webpage, Monte Castleman, February 9, 2018 [2]
- ^ Selcer, Richard F. (2006). Balkin, Richard (ed.). Civil War America: 1850 to 1875. New York: Facts on File. p. 143. ISBN 978-0816038671.
- ^ Forstall, Richard L. (ed.). Population of the States and Counties of the United States: 1790–1990 (PDF) (Report). United States Census Bureau. pp. 85–87. Retrieved May 18, 2020.
External links[]
![]() Media related to Minnesota Territory at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Minnesota Territory at Wikimedia Commons
- States and territories disestablished in 1858
- Minnesota Territory
- 1849 establishments in Minnesota Territory
- 1858 disestablishments in the United States
- Former organized territories of the United States


