Naphazoline
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Clear Eyes, Cleari, Naphcon-A, Rohto |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Ophthalmic drug administration, nasal administration |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.492 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
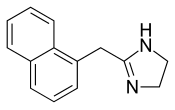
| Formula | C14H14N2 |
| Molar mass | 210.274 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Naphazoline is a medicine used as a decongestant, and a vasoconstrictor added to eye drops to relieve red eye. It has a rapid action in reducing swelling when applied to mucous membrane. It is a sympathomimetic agent with marked alpha adrenergic activity that acts on alpha-receptors in the arterioles of the conjunctiva to produce constriction, resulting in decreased congestion.
It was patented in 1934 and came into medical use in 1942.[1]
Medical uses[]

Nasal administration[]
Nasal decongestant.[2]
Ophthalmic drug administration[]
Eye drops (brand names Clear Eyes, and Cleari) narrowing swollen blood vessels (ophthalmic arteries, and ophthalmic veins) to relieve red eye.[2]
Temporary red eye can safely be treated when the cause of the redness is established (eg cannabis induces corneal vasodilation[3]). However, long-term use is not recommended without knowing the underlying condition.
Side effects[]
A few warnings and contraindications that apply to all naphazoline-containing substances intended for medicinal use are:
- Hypersensitivity to naphazoline
- Use in infants and children can result in central nervous system depression, leading to coma and marked reduction in body temperature
- Should be used with caution in patients with severe cardiovascular disease including cardiac arrhythmia and in patients with diabetes, especially those with a tendency toward diabetic ketoacidosis
- A possible association with stroke has been suggested.[4]
Nasal administration[]
- Extended use may cause rhinitis medicamentosa, a condition of rebound nasal congestion.
Ophthalmic drug administration[]
- Stinging
- Discomfort
- Irritation
- Increased red eyes
- Blurred vision
- Mydriasis
- Punctate keratitis
- Lacrimation (tears)
- Increased intraocular pressure
Contraindications[]
- Patients taking MAO inhibitors can experience a severe hypertensive crisis if given a sympathomimetic drug such as naphazoline HCl
- Drug interactions can occur with anaesthetics that sensitize the myocardium to sympathomimetics (e.g. cyclopropane or halothane cautiously)
- Exercise caution when applying prior to use of phenylephrine.
Pharmacology[]
Pharmacodynamics[]
Naphazoline is a mixed α1- and α2-adrenergic receptor agonist.[2]
Chemistry[]
The non-hydrochloride form of Naphazoline has the molecular formula C14H14N2 and a molar mass of 210.28 g/mol. The HCl salt form has a molar mass of 246.73 g/mol.
Society and culture[]
Brand names[]
It is an active ingredient in several over-the-counter eye drop formulations including Clear Eyes, Rohto, Eucool, and Naphcon-A.[7]
References[]
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 552. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ a b c Hosten LO, Snyder C (2020). "Over-the-Counter Ocular Decongestants in the United States - Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Utility for Management of Ocular Redness". Clinical Optometry. 12: 95–105. doi:10.2147/OPTO.S259398. PMC 7399465. PMID 32801982.
- ^ Yazulla, S (September 2008). "Endocannabinoids in the retina: from marijuana to neuroprotection". Progress in retinal and eye research. 27 (5): 501–26. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.07.002. PMC 2584875. PMID 18725316.
- ^ Zavala JA, Pereira ER, Zétola VH, Teive HA, Nóvak EM, Werneck LC (September 2004). "Hemorrhagic stroke after naphazoline exposition: case report". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria. 62 (3B): 889–91. doi:10.1590/S0004-282X2004000500030. PMID 15476091.
- ^ "Naphazoline - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses". Drugs.com.
- ^ "naphazoline ophthalmic (eye): Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing - WebMD". www.webmd.com.
- ^ Green SM (2008). "Ophthalmology: Naphazoline". Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2009. Jones and Bartlett. ISBN 978-0-7637-6572-9.
- Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonists
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists
- Decongestants
- Imidazolines
- Naphthalenes
- Vasoconstrictors
- Ophthalmology drugs