Pantetheine
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
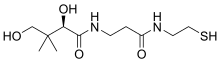
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-N-{3-oxo-3-[(2-sulfanylethyl)amino]propyl}butanamide | |
| Other names
Pantetheine
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1714196 R | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.114 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Pantetheine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H22N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 278.37 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Pantethine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Pantetheine is the cysteamine amide analog of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). The dimer of this compound, pantethine is more commonly known, and is considered to be the most potent form of vitamin B5. Pantetheine is an intermediate in the production of coenzyme A by the body.[1][2][3]
References[]
- ^ MB Hoagland, GD Novelli (1954). "Biosynthesis of coenzyme A from phosphopantetheine and of pantetheine from pantothenate". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 207 (2): 767–773. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)65696-0. PMID 13163064.
- ^ Cronan, John E. (2014). "The Chain-Flipping Mechanism of ACP (Acyl Carrier Protein)-Dependent enzymes Appears Universal". Biochemical Journal. 460 (2): 157–163. doi:10.1042/BJ20140239. PMID 24825445.
- ^ Nitto, Takeaki; Onodera, Kenji (2013). "The Linkage Between Coenzyme a Metabolism and Inflammation: Roles of Pantetheinase". Journal of Pharmacological Sciences. 123 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1254/jphs.13R01CP. PMID 23978960.
Categories:
- Carboxamides
- Thiols
- Vitamins
- Diols
- Alcohol stubs