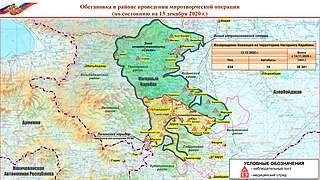
Peacekeeping operations in Nagorno-Karabakh

Peacekeeping mission in Nagorno-Karabakh refers to the ongoing peacekeeping operations, primarily by Russia, in the Nagorno-Karabakh region in the aftermath of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The operation is intended to monitor the ceasefire between the Armenian and Azerbaijani forces. Turkey also participates in observing.
After the war, in accordance to the ceasefire agreement signed on 10 November 2020, Russia sent a peacekeeping contingent of 1,960 servicemen, provided by the 15th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade of the Russian Ground Forces, and led by Lieutenant General Rustam Muradov, to the region. The peacekeeping forces, headquartered near Stepanakert, established observation posts along the contact line in Nagorno-Karabakh and along the Lachin corridor. The Russian peacekeeping forces started to assist the International Committee of the Red Cross on finding and exchanging the bodies of the fallen soldiers from both sides in November, and the Russian peacekeepers later started demining operations in the region.
On 11 November, a memorandum of understanding was signed between Russia and Turkey to create a Russian-Turkish Joint Monitoring Centre (RTJMC) near Marzili in Aghdam, Azerbaijan. In December, Turkey sent 136 sappers to Azerbaijan to assist in the demining of the region, as well as to train mine clearance personnel of Azerbaijan. It also sent 35 of its officers to Azerbaijan. The RTJMC was opened on 30 January 2021, with a total of 60 servicemen from both sides monitoring the ceasefire using unmanned aerial vehicles. The Turkish staff of the RTJMC is headed by Major General Abdullah Katırcı, and the Russian staff is headed by Major General Victor Fedorenko, while the centre itself is guarded by the Azerbaijani servicemen.
The first major breach of the ceasefire that was confirmed by the Russian peacekeeping forces in the region occurred on 11 December, near Hadrut. Chaylaggala (Khtsaberd), Hin Tagher (Kohne Taghlar) villages, as well as the Katarovank monastery had become an Artsakh holdout in the Hadrut Province during the war. Clashes erupted around the Armenian holdout pocket despite the ceasefire agreement, and it has been reported that the Azerbaijani forces seized control of Hin Tagher on 12 December, with some clashes continuing in the area. Later, Artsakh authorities confirmed that six of their servicemen had been injured. Both sides accused each other of reigniting the conflict. The Russian peacekeeping forces requested both sides to respect the ceasefire. On 13 December, the Russian peacekeeping contingent took control of Hin Tagher. However, the next day, the Russian Ministry of Defence released a map showing both villages outside of the borders of the peacekeeping mission, and both came under Azerbaijan's control.
Background[]
On 27 September 2020, clashes broke out in the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region, which is de facto controlled by the self-proclaimed and unrecognized Republic of Artsakh, but de jure part of Azerbaijan.[1] Azerbaijani forces first advanced in Fuzuli and Jabrayil districts, taking their respective administrative centres.[2] From there, they proceeded towards Hadrut.[3] Azerbaijani troops began to advance more intensively after the fall of Hadrut around 15 October, and Armenians began to retreat, with Azerbaijanis then taking control of Zangilan and Qubadli.[4] Launching an offensive for Lachin,[5] they also penetrated into Shusha District through its forests and mountain passes.[6][7]
Following the capture of Shusha, the second-largest settlement in Nagorno-Karabakh, a ceasefire agreement was signed between the President of Azerbaijan, Ilham Aliyev, the Prime Minister of Armenia, Nikol Pashinyan, and the President of Russia, Vladimir Putin, ending all hostilities in the area from 00:00, 10 November 2020 Moscow Time.[8][9][10] Under the agreement, the warring sides kept control of their currently held areas within Nagorno-Karabakh, while Armenia will return the surrounding territories it occupied in 1994 to Azerbaijan. Azerbaijan will also gain land access to its Nakhchivan exclave bordering Turkey and Iran.[11] Approximately 2,000 Russian soldiers was deployed as peacekeeping forces along the Lachin corridor between Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh for a mandate of at least five years.[12]
Russian peacekeeping contingent[]

The Russian peacekeeping forces, provided by the 15th Separate Motor Rifle Brigade of the Russian Ground Forces,[13] consisting of 1,960 servicemen,[14] and led by Lieutenant General Rustam Muradov, were dispatched to the region as part of the ceasefire agreement to monitor compliance by Armenia and Azerbaijan with its terms.[15] The peacekeeping forces, headquartered near Stepanakert, established observation posts along the contact line in Nagorno-Karabakh and along the Lachin corridor.[16] Reuters reported that the peacekeeping forces were accompanied with armoured personnel carriers, tanks and multiple rocket launchers.[17] On 17 November, the Russian peacekeeping forces started to assist the International Committee of the Red Cross on finding and exchanging the bodies of the fallen soldiers from both sides,[18] and on 23 November, started demining operations in the region.[19]
By 22 November, 25,000 displaced Armenians had returned to the region.[20] On 10 December, the Mayor of Stepanakert stated that about 18,000 displaced Armenians had returned to the city.[21] On 11 December, a car belonging to an Armenian civilian collided with a truck of the Russian peacekeeping forces in Stepanakert–Askeran highway.[22]
The contingent is currently led by Major General Mikhail Kosobokov.[23]
Russian-Turkish Joint Monitoring Centre[]

On 11 November, the Russian and Turkish defence ministers signed a memorandum of understanding to create a Russian-Turkish Joint Monitoring Centre (RTJMC) in Azerbaijan,[24] although the Russian officials stated that Turkey's involvement in the peacekeeping operations will not affect Nagorno-Karabakh.[25] On 16 November, the Turkish government submitted a motion to the Grand National Assembly on deploying peacekeepers in Azerbaijan.[26] The Turkish parliament approved the motion following day, giving the Turkish Armed Forces a one-year mandate on sending troops to Azerbaijan.[25][27] On 1 December, the Turkish sappers arrived in Azerbaijan and started demining the Azerbaijani-controlled territories in the region, alongside the Azerbaijani sappers,[28] and the following day, the Ministry of National Defence of Turkey, Hulusi Akar, stated that the Turkish government had agreed with Russia, and that the RTJMC was under construction.[29][30] According to the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Russia, Sergey Lavrov, the RTJMC will operate remotely, using drones and other technical means to monitor possible violations.[31] On 16 December, 136 members of the Turkish Land Forces Special Mine Search Clearance Team were sent to Azerbaijan to assist in the demining of the region, as well as to train mine clearance personnel of Azerbaijan.[32] On 29 December, Turkey sent 35 of its officers to Azerbaijan.[33]
The Turkish officers arrived in Azerbaijan on 30 January 2021,[34] and the RTJMC was opened near Marzili in Aghdam on the same day.[35] The Azerbaijani Minister of Defence, Zakir Hasanov, the Deputy Turkish Minister of National Defence, Yunus Emre Karaosmanoğlu, the Deputy Russian Minister of Defence, Alexander Fomin, represented their countries at the opening. They first cut the red ribbon in front of the RTJMC, followed by the national anthems of Azerbaijan, Turkey, and Russia respectively The opening ceremony ended with a tree planting event by Azerbaijani, Turkish and Russian officials.[36]
The total area of RTJMC is about 4 hectares. There are 65 modular service, administrative and living rooms in the area. In addition, there are separate and general monitoring centres, a briefing room, a canteen for a hundred people, a medical centre, a laundry, a hairdresser, a tailor and a shop for the use of both parties. There is a water station, a transformer, a generator, a parking lot, two outdoor sports camps, as well as two indoor gyms, food and cold storage in the area. The whole area was fenced along the perimeter, four observation towers were installed, and round-the-clock security was organized.[37] Right after the opening ceremony, the Russian and Turkish servicemen started to work on a parity basis. The RTJMC is guarded by Azerbaijani servicemen. Total of 60 servicemen from Turkey and Russia serve at the RTJMC. The RTJMC monitors the ceasefire in Nagorno-Karabakh using unmanned aerial vehicles. When the monitoring center was opened, it was initially announced that a general and 38 servicemen would serve on the Turkish side. The Turkish staff of the RTJMC is headed by Major General Abdullah Katırcı, and the Russian staff is headed by Major General Victor Fedorenko.[38]
Ceasefire violations[]
2020[]

The villages of Chaylaggala (Khtsaberd) and Hin Tagher (Kohne Taghlar) as well as the Katarovank monastery, became an Artsakh holdout in the Hadrut Province during the war.[39]
In mid-December, Azerbaijani media reported that armed Armenian groups were attacking Azercell employees, who were installing equipment, and on 11 December, that an Azerbaijan soldier was injured as a result of an attack from another group of armed Armenians.[40][41] This was confirmed by the Azerbaijani military authorities later on, who stated that three Azerbaijani servicemen were killed and two were wounded as a result of a "sudden attack by the Armenians" in Sor, Khojavend District on 26 November. Also, according to the ministry, on 8 December, one Azerbaijani serviceman was killed and an Azercell employee was seriously injured during the installation of communication facilities and transmission equipment near Hadrut. Some Azerbaijani sources have claimed that Armenian servicemen have remained in the forests around Hadrut after the battle over the town, and stated that these Armenian pockets were related to the clashes. Retired Azerbaijani colonel Shair Ramaldanov had stated that there could be "provocative" and "guerrilla-type" actions from the Armenian forces in the region. However, according to Ramaldanov, the Azerbaijani military authorities were taking "security measures" against them.[42][43] The following day, the President of Azerbaijan, Ilham Aliyev reiterated the Azerbaijani media reports, calling the incident an "act of terrorism" and[44] threatening to crush Armenian forces with an "iron fist".[45] Later on, the Azerbaijani military authorities accused the Armenian forces of violating the ceasefire and stated that its forces restored the ceasefire.[46]
Artsakh authorities refuted that any Armenian forces had attacked Azerbaijani positions, and stated that Azerbaijani forces had launched military operations in the region, injuring six Armenian servicemen,[47] while the Azerbaijani ministry of foreign affairs reiterated that the "provocative activity" was committed by the remnants of the Armenian forces.[42] Later, Artsakh authorities stated that the Azerbaijani forces had launched a new offensive in Chaylaggala and Hin Tagher, the only settlements in the region that were still controlled by Armenian forces. They noted that the two villages have been fully encircled by the Azerbaijani army, which controls the only road leading to them.[46] The office of the Armenian prime minister urged the Russian peacekeepers to respond.[48] Artsakh authorities confirmed that the Azerbaijani forces had entered the villages, and stated that the Russian peacekeeping forces had arrived to resolve the situation.[49] The Armenian President, Armen Sarksyan stated that Hin Tagher had been captured by Azerbaijani forces on 12 December, continuing their advance towards Chaylaggala.[50][51]
The Russian peacekeeping forces confirmed that the ceasefire was breached,[46] and requested that both sides respect the ceasefire.[52] On 13 December, Hin Tagher came under the control of the Russian peacekeeping contingent.[53] On the same day, the Armenian president Armen Sarkissian called on the National Assembly to convene an extraordinary session regarding the issue.[54] and the Armenian PM Nikol Pashinyan convened an emergency meeting of the Armenian Security Council.[55] However, the next day, the Russian Ministry of Defence released a map showing both villages outside of the borders of the peacekeeping mission,[56] and both came under Azerbaijan's control.[57]
On 15 December, the Azerbaijani sources shared footage, apparently showing over 100 Armenian POWs from the Hadrut region. The following day, Artsakh authorities stated that they had started an investigation to identify the people in the videos,[58] and then reported that about 60 Armenian servicemen went missing.[59] Hours later, Artsakh authorities confirmed several dozen of the troops were captured by the Azerbaijani forces.[60] Meanwhile, the Armenian media reported that the Azerbaijani forces allowed about 30 Armenian soldiers who were encircled to leave the region with the help of the Russian peacekeeping forces.[61] Then, the people in Shirak blocked the road leading to the Armenia–Georgia border, demanding the return of the Armenian POWs.[62]
On December 28, 2020, an Azerbaijani soldier was killed and another injured during a shooting attack in Nagorno-Karabakh. Azerbaijan blamed the attack on "an Armenian armed group"; all six attackers were shot dead.[63]
2021[]
On 9 October 2021, an Artsakh civilian, 55-year-old Aram Tepnants, was killed during agricultural work in the Martakert Province as a result of shelling from the Azerbaijani side.[64][65] The Artsakh Foreign Ministry stated that the purpose of the shooting was to not only trigger a “mass emigration” of Karabakh Armenians but also undermine the Russian peacekeeping mission. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Armenia accused Baku of violating the terms of a Russian-brokered ceasefire and demanded a “proper investigation” into Tepnants’s death.[66] The Russian Defense Ministry announced that the command of the Russian peacekeeping contingent is investigating the incident with the involvement of representatives of both sides.[64]
On 13 October 2021, in the area of the Sarsang Reservoir, a convoy of construction equipment of Azerbaijan, which followed the Madagiz-Getavan-Vank route in Artsakh, was fired upon.[67]
In the evening on 14 October 2021, according to the Artsakh's Ombudsperson, Azerbaijani militaries have attacked the positions of the Artsakh Defence Army stationed near the Nor Shen community in the Martuni District as a result of which six Armenian servicemen were wounded.[68]
According to the Artsakh's Investigative Committee, on 8 November at 15:00, a serviceman of the Azerbaijani Armed Forces "made his way from the territory controlled by the Azerbaijani side near the city of Shushi to the Shushi-Berdzor road with the aim of carrying out a terrorist act and fired at a group of workers who were repairing the water pipeline." Martik Yeremyan, a resident of the city of Stepanakert, died on the spot. Gevorg Melkumyan, Gagik Ghazaryan and Armen Sargsyan received gunshot wounds.[69] This is the second case of the death of a civilian in Nagorno-Karabakh as a result of shooting from the Azerbaijani side after the establishment of a ceasefire in 2020.[69] This incident was also confirmed by Russian peacekeepers.[70]
On 13 November, at around 07:00, a man got out of a taxi in front of the joint post near Shusha, where Russian peacekeepers and Azerbaijani servicemen were stationed, and threw a grenade towards the Azerbaijani military. The Azerbaijani sources reported at least three injuries and released footage of the attack. Azerbaijani sources identified the man as a 46-year-old local Armenian Norayr Mirzoyan. He was detained by Russian peacekeepers, while the Azerbaijani government demanded his transfer. The Armenian media reported that the attacker was the brother of an Armenian worker killed in this area on November 8,[71] however, this was later denied.[72]
On 3 December 2021, a resident of Chartar village, Seyran Sargsyan, was killed by the Azerbaijani armed forces.[73][74] The Armenian MFA stated that the recent atrocities are "a continuation of the policy of Armenophobia, annihilation and ethnic cleansing of Armenians of Artsakh by the Azerbaijani authorities, which once again proves that guaranteeing the physical security and the right to life of the Armenians of Artsakh is impossible under the Azerbaijani jurisdiction."[73]
Criticism[]
Allegations of being pro-Armenia[]

In early January 2021, the Azerbaijani authorities accused the Russian peacekeepers of "exhibiting a pro-Armenia attitude, instead of taking the required neutral stance for the implementation of the peace agreement." Araz Aslanli, chairman of the Academy of State Customs Committee, stated that some practices of the Russian peacekeepers "did not contribute to the permanent solution of the Nagorno-Karabakh issue" and had caused "doubts in Azerbaijan and Turkey about Russia's good intentions." Nazim Jafarsoy, the deputy chair of the Caucasus International Relations and Strategic Studies Centre accused the Russian peacekeepers of causing the "continuation of the illegal military forces' presence in the region rather than providing peace between the Armenians and the Azerbaijanis." Rustam Muradov's meeting with senior Artsakh figures, and the presence of the Artsakh flag at Muradov's meetings had resulted in negative reactions from the Azerbaijani authorities, while the usage of the phrase "Nagorno-Karabakh Republic" was removed from the official website of the Russian Ministry of Defence after Azerbaijan's objection.[75] On 7 January, the Azerbaijani president Ilham Aliyev denounced the Armenian minister of foreign affairs, Ara Ayvazyan, for his recent visit to the Nagorno-Karabakh, calling it a "provocative step" and adding that if continued, "Armenia will regret even more." Aliyev also reiterated that that Azerbaijan did not allow visit of any foreign citizen to Nagorno-Karabakh without its permission.[76]
Claims of the violation of Azeri sovereignty[]
On 2 January 2021, the Turkish pro-government[77] newspaper, Yeni Şafak, reported that Russia had violated the terms of the ceasefire agreement, sending over five thousand people to the region "under the name of soldiers, civil servants, technical experts, doctors, nurses and construction workers."[78]
In late April, rehearsal began taking place at Stepanakert Airport for a victory day parade of peacekeepers. Many have seen this as a violation of the agreements signed in November 2020.[79] The press service of the Azerbaijani opposition party Musavat assessed parade as an action that contradict the mandate of the peacekeeping forces and "prove the occupational nature of Russia’s actions in Karabakh".[80] It also described it as "an insult" to the memory of the victims of the Khojaly massacre.[80] The Ministry of Defense of Azerbaijan only acknowledged the planned parade on 8 May, the day before it was scheduled to take place, reiterating that the troops were in the region in accordance with the agreement.[81]
References[]
- ^ "Armenia and Azerbaijan fight over disputed Nagorno-Karabakh". BBC. 27 September 2020. Archived from the original on 27 September 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Kucera, Joshua (29 September 2020). "As fighting rages, what is Azerbaijan's goal?". EurasiaNet. Archived from the original on 4 October 2020. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
The Azerbaijani offensive against Armenian forces is its most ambitious since the war between the two sides formally ended in 1994.
- ^ Avaliani, Dimitri (12 October 2020). "Karabakh: the battle for Hadrut and why it's important". Jam News. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^ Aksenov, Pavel (11 November 2020). "Почему Азербайджан выиграл войну в Карабахе? Отвечают военные эксперты" [Why did Azerbaijan win the war in Karabakh? Military experts answer]. BBC Russian Service (in Russian). Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ Roblin, Sebastien (26 October 2020). "Despite Ceasefire, Fate Of The Nagorno-Karabakh May Turn On The Lachin Corridor". Forbes. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ Hakobyan, Tatul (17 November 2020). "Շուշին. պատերազմի իմ չգրված նոթատետրից" [Shushi. from my unwritten notebook of war]. CivilNet. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2020.
- ^ "Azerbaijan says key Karabakh town captured, Armenia says it didn't happen". France24. 8 November 2020. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ "Путин выступил с заявлением о прекращении огня в Карабахе" (in Russian). RIA Novosti. 9 November 2020. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^ "Пашинян заявил о прекращении боевых действий в Карабахе" (in Russian). RIA Novosti. 9 November 2020. Archived from the original on 9 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh: Russia deploys peacekeeping troops to region". BBC News. 2020-11-10. Archived from the original on 2020-12-03. Retrieved 2020-11-11.
- ^ Kramer, Andrew E. (November 10, 2020). "Facing Military Debacle, Armenia Accepts a Deal in Nagorno-Karabakh War". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 10, 2020. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
- ^ "Deal Struck to End Nagorno-Karabakh War". The Moscow Times. 10 November 2020. Archived from the original on 10 November 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ "Azerbaijani troops enter Lachin district in Nagorno-Karabakh". TASS. 2020-11-30. Archived from the original on 2020-12-01. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "1,960 Here's what Russia has pledged (and risked) with peacekeepers in Nagorno-Karabakh". Meduza.io. 2020-11-11. Archived from the original on 2020-11-10. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Turkey widens footprint, sends 'peacekeepers' to Azerbaijan". The Arab Weekly. 2020-11-17. Archived from the original on 2020-11-17. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Россия направила в Нагорный Карабах почти 2 тыс. миротворцев". TASS (in Russian). 2020-11-10. Archived from the original on 2020-11-09. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Russia moves rocket launchers towards Nagorno-Karabakh after peace deal". Reuters (in Russian). 2020-11-16. Archived from the original on 2020-11-16. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Armenia, Azerbaijan exchange troops' bodies after ceasefire". Al Jazeera. 2020-11-17. Archived from the original on 2020-11-29. Retrieved 2020-11-29.
- ^ "Russia Starts Mine Clearance In Karabakh". Azatutyun. 2020-11-23. Archived from the original on 2020-11-30. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh: Thousands displaced by war return home". Deutsche Welle. 2020-12-22. Retrieved 2020-11-12.
- ^ "Мэр Степанакерта сообщил, что в город вернулись до 18 тысяч человек". RIA Novosti (in Russian). 2020-12-10. Archived from the original on 2020-12-10. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Крупное ДТП в Карабахе с участием машины российских миротворцев: погибли два человека". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-11. Archived from the original on 2021-01-19. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ https://asbarez.com/armenias-defense-minister-welcomes-new-commander-of-russian-peacekeepers/
- ^ "Turkey, Russia to set up joint center to watch Nagorno-Karabakh peace". Hurriyet Daily News. 2020-11-11. Archived from the original on 2020-12-24. Retrieved 2021-01-30.
- ^ a b Fraser, Suzan (2020-11-18). "Turkish parliament approves peacekeepers for Azerbaijan". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 2020-11-17. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Turkey seeks approval to deploy peacekeepers in Azerbaijan". Al Jazeera. 2020-11-16. Archived from the original on 2020-11-23. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Turkey Approves Sending Troops To Joint Russian Monitoring Center In Azerbaijan". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 2020-11-17. Archived from the original on 2020-11-17. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Turkish Sappers Arrived in Azerbaijan". Turan Information Agency. 2020-12-01. Archived from the original on 2021-01-19. Retrieved 2020-12-13.
- ^ "Karabakh: Russian and Turkish peacekeepers, Azerbaijani and Armenian military – who's where". JAMNews. 2020-11-21. Archived from the original on 2020-11-22. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Military personnel from Turkey, Russia to work together to make truce lasting in Nagorno-Karabakh: Turkish defense minister". Anadolu Agency. 2020-12-02. Archived from the original on 2020-12-02. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh: Turkey to send peacekeepers to Azerbaijan to monitor truce". France24. 2020-12-02. Archived from the original on 2020-11-17. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Bu günün xəbərləri: 136 Türkiyə minaaxtaranı Azərbaycanda, Suqovuşan və Talış kəndlərinə gedən yollar asfaltlanır". BBC Azerbaijani Service (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-16. Archived from the original on 2020-12-16. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Hulusi Akar: "35 zabit Azərbaycana gedib", Lavrov Çavuşoğlu ilə Qarabağa "xarici muzdlu əsgərlərin daxil olmaması"nı müzakirə edib". BBC Azerbaijani Service (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-29. Archived from the original on 2020-12-29. Retrieved 2021-01-01.
- ^ "Polkovnik Vaqif Dərgahlı: Türkiyə-Rusiya Birgə Monitorinq Mərkəzində yer alacaq türkiyəli heyət artıq Azərbaycandadır VİDEO". Azerbaijan State News Agency (in Azerbaijani). 30 January 2021. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Российско-турецкий центр по Карабаху приступит к работе 30 января" [Russian-Turkish Center for Karabakh to start working on January 30]. TASS (in Russian). 29 January 2021. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Ağdamda Türkiyə-Rusiya Monitorinq Mərkəzinin açılışı olub". (in Azerbaijani). 30 January 2021. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Türkiyə-Rusiya Birgə Monitorinq Mərkəzində şəxsi heyətə rəhbərlik edəcək şəxslərin adları açıqlanıb". (in Azerbaijani). 30 January 2021. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Türkiyə-Rusiya Birgə Monitorinq Mərkəzinin mühafizəsini Azərbaycan Ordusu həyata keçirəcək". (in Azerbaijani). 30 January 2021. Archived from the original on 30 January 2021. Retrieved 30 January 2021.
- ^ "Renewed Fighting Reported in Southern Karabakh". CivilNet. 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-14. Retrieved 2021-01-25.
- ^ "Armenians commit terror act in Nagorno-Karabakh region". Trend News Agency (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-11. Archived from the original on 2020-12-11. Retrieved 2020-12-11.
- ^ "Armenians carry out armed provocation in Nagorno-Karabakh region". AzVision (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-11. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-11.
- ^ a b "Azərbaycan MN: "4 hərbi qulluqçumuz öldürülüb"". BBC Azerbaijani Service (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-12. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Azerbaijan Says 4 Soldiers Killed Amid Cease-Fire Violations in Nagorno-Karabakh". Voice of America. 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2020-12-13. Retrieved 2020-12-13.
- ^ "Azərbaycan Prezidenti son terror aktı ilə bağlı Ermənistana və erməni yaraqlılarına xəbərdarlıq edib". (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-12. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh: Russian army reports ceasefire breach". Deutsche Welle. 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-12. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ a b c "Nagorno-Karabakh: both sides blame each other over ceasefire violations". The Guardian. 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-12. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire breached with fighting under way". Al Jazeera. 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2020-12-13. Retrieved 2020-12-13.
- ^ "Пресс-секретарь премьер-министра Армении призвала российских миротворцев отреагировать на атаку азербайджанцев". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Айк Ханумян: "Азербайджанцы вошли в села Хцаберд и Ин Тахер, но ведутся переговоры"". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-26. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Russian Peacekeepers Take Control of Captured Artsakh Village". Asbarez. 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2021-01-25. Retrieved 2021-01-23.
- ^ "Dozens Of Armenian Soldiers 'Captured' In Nagorno-Karabakh Raid". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty. 2020-12-16. Archived from the original on 2021-01-23. Retrieved 2021-01-23.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh ceasefire that ended conflict in Azerbaijan and Armenia in November breached, says Russian army". South China Morning Post. 2020-12-12. Archived from the original on 2020-12-12. Retrieved 2020-12-12.
- ^ "Арцахское село Хин тахер, за которое шли ожесточенные бои, перешло под контроль российских миротворцев". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2020-12-26. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Президент Армении потребовал от МО и МИД разъяснений по Гадруту и призвал НС созвать внеочередное заседание". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Пашинян созвал экстренное заседание Совбеза Армении". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Инфографика". Ministry of Defence of Russia (in Russian). 2020-12-14. Archived from the original on 2020-12-14. Retrieved 2020-12-14.
- ^ "Hadrutun iki kəndi yenidən Azərbaycanın nəzarətindədir". BBC Azerbaijani Service (in Azerbaijani). 2020-12-13. Archived from the original on 2020-12-13. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Минобороны Армении ждет разъяснений от Армии обороны Арцаха о видеозаписях пленения азербайджанцами армянских военных". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-15. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh: Dozens of Armenian soldiers 'captured in raid'". BBC News. 2020-12-16. Archived from the original on 2020-12-16. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ Reuters Staff (2020-12-16). "Nagorno-Karabakh accuses Azeri forces of capturing troops despite ceasefire". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2020-12-16. Retrieved 2021-01-30 – via www.reuters.com.
- ^ "Более 30 оказавшихся в азербайджанском окружении армянских военных смогли выбраться". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-16. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Возмущенные тем, что правительство не интересуется пропавшими солдатами, жители Ширака перекрыли дорогу". Armenian Report (in Russian). 2020-12-16. Archived from the original on 2021-01-20. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- ^ "Nagorno-Karabakh: Azerbaijan says one dead in Armenian attack". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 2020-12-28. Retrieved 2021-01-30.
- ^ a b "Информационный бюллетень Министерства обороны Российской Федерации о деятельности российского миротворческого контингента в зоне нагорно-карабахского конфликта (на 10 октября 2021 г.)". mil.ru (in Russian). Ministry of Defence (Russia). Retrieved 13 October 2021.
On October 9, during agricultural work in the Mardakert region, near the line of contact, a civilian from the village of Madagiz was mortally wounded as a result of shelling from the Azerbaijani side
- ^ "Russian side investigating murder of Karabakh civilian by Azeris". PanARMENIAN.Net. 11 October 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Karabakh Civilian Killed In Truce Violation". azatutyun.am. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 11 October 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Информационный бюллетень Министерства обороны Российской Федерации о деятельности российского миротворческого контингента в зоне нагорно-карабахского конфликта (на 14 октября 2021 г.)". mil.ru (in Russian). Ministry of Defence (Russia). 13 October 2021. Retrieved 15 October 2021.
- ^ "Six Karabakh militaries wounded near Nor Shen village". kavkaz-uzel.eu. Caucasian Knot. 15 October 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Инцидент под Шуши: СК Нагорного Карабаха представил подробности". eadaily.com. 9 November 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Информационный бюллетень Министерства обороны Российской Федерации о деятельности российского миротворческого контингента в зоне нагорно-карабахского конфликта (на 9 ноября 2021 г.)" (in Russian). Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation. 9 November 2021. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ^ "Khankendi road reopens after grenade incident". JAMnews. 13 November 2021. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ "Ադրբեջանական հենակետի վրա նռնակ նետած Նորայրը Մարտիկի եղբայրը չէ, նրան մեր իրավապահներին պետք է հանձնեն. պատգամավոր". news.am (in Armenian). 13 November 2021. Retrieved 14 November 2021.
- ^ a b "Armenia Condemns Killing of Artsakh Villager by Azerbaijani Troops". hetq.am. 4 December 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ "Artsakh Prosecutor's Office: Chartar village resident killed by long-range shot by Azerbaijan (VIDEO)". news.am. 25 December 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ "Azerbaijan dissatisfied with Russian peacekeepers' pro-Armenia attitude". Daily Sabah. 2021-01-07. Archived from the original on 2021-01-11. Retrieved 2021-01-11.
- ^ Aliyev, Jeyhun (2021-01-07). "Azerbaijani leader warns Armenia over visit to Karabakh". Anadolu Agency. Archived from the original on 2021-01-11. Retrieved 2021-01-11.
- ^ Usluata, Ayseli; Rosenbaum, John (2005). Shaping the future of communication research in Europe. İstanbul: Yeditepe University Publications. p. 140. ISBN 978-9753070126.
- ^ Eroğlu, Aybike (2021-01-02). "Rusya anlaşmayı ihlal etti" [Russia violated the agreement]. Yeni Şafak. Archived from the original on 2021-01-11. Retrieved 2021-01-11.
- ^ "Военный парад на территории Ходжалинского аэропорта - Что хочет сказать этим Москва? -". m.zerkalo.az. 2021-04-23. Retrieved 2021-05-08.
- ^ a b "Russian peacekeepers prepare for Victory Day parade in Karabakh, official Baku is silent". English Jamnews. 2021-04-21. Retrieved 2021-05-08.
- ^ "Press release of the Ministry of Defense on the occasion of the 76th anniversary of the Victory over fascism". MINISTRY OF DEFENCE OF THE REPUBLIC OF AZERBAIJAN. Retrieved 2021-05-08.
- Aftermath of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war
- Peacekeeping operations
- Armenia–Azerbaijan relations
- Armenia–Russia relations
- Armenia–Turkey relations
- Azerbaijan–Russia relations
- Azerbaijan–Turkey relations
- Russia–Turkey military relations