Salmas
Salmas
سلماس | |
|---|---|
| Salmas | |
 Revolution Circle | |
| Nickname(s): Shapur (historically) | |
 Salmas | |
| Coordinates: 38°11′41″N 44°45′53″E / 38.19472°N 44.76472°E | |
| Country | Iran |
| Province | West Azerbaijan |
| County | Salmas |
| District | Central |
| Earliest Recognition | 224–242 AD |
| Rebuilt | 1930 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–Council |
| • Body | Salmas |
| • | N/A |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9.26 sq mi (24.0 km2) |
| • Land | 9.26 sq mi (24.0 km2) |
| • Water | 0 sq mi (0 km2) |
| • Metro | 4.75 sq mi (12.3 km2) |
| Elevation | 4,532 ft (1,381 m) |
| Population (2016 Census) | |
| • Total | 92,811 [1] |
| • Rank | TBA, Iran |
| Demonym(s) | Salmasi, Salmassi |
| Time zone | UTC+3:30 (IRST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+4:30 (IRDT) |
| ZIP code | 58811 ≤ 58XXX ≤ 58991 |
| Area code(s) | 44 |
Salmas (Persian: سلماس, Armenian: Սալմաստ, Azerbaijani: سلماس, Kurdish: سهلماس, Syriac: ܣܵܠܵܡܵܣ, romanized: Salamas[2]) is the capital of Salmas County, West Azerbaijan Province in Iran. It is located northwest of Lake Urmia, near Turkey.[3] According to the 2019 census, the city's population is 127,864.[4] The majority of the population is composed of Azerbaijanis and Kurds[5] with some Armenians, Assyrians, Jews.[6]
History[]
Etymology and early history[]

According to Encyclopædia Britannica the earliest historic recognition of Salmas could be found at the time of Ardashir I's reign (224–242 AD) via a petroglyph of him on horseback while receiving surrender of the Parthian personage.[7] In another contribution by Britannica, on an animated political map of Sassanid Empire at the time of Shapur I's reign (240–270 AD), Salmas is markedly acknowledged as one of the renown and apparently important cities of the empire with the same original name as now.[8] There is a speculation that the nickname of the city, Shapur, might be derived from the name of this king (of kings) of Persia.
Salmas was held by the Kurdish Rawadid dynasty and frequented by the Hadhabani tribe in the 10-11th centuries. Al-Maqdisi described it as a Kurdish town who had built a wall around the city.[9][3]
Another Mention of the city was made in 1281, when its Assyrian bishop made the trip to the consecration of the Assyrian Church of the East patriarch Yaballaha in Baghdad.[10]
In the Battle of Salmas on 17–18 September 1429, the Kara Koyunlu were defeated by Shah Rukh who was consolidating Timurid holdings west of Lake Urmia.[11] However, the area was retaken by the Kara Koyunlu in 1447 after the death of Shah Rukh.
Mar Shimun, the Patriarch of the Assyrian Church of the East was murdered by the Kurdish chieftain Simko Shikak in Salmas in March 1918.[12][13][14]
Around the advent of the 1910s, Imperial Russia started to station infantry and Cossacks in Salmas.[15] The Russians retreated at the time of Enver Pasha's offensive in the Iran-Caucasus region, but returned in early 1916, and stayed up to the wake of the Russian Revolution.[15]
Geography[]
Salmas in early atlases[]
The atlases below are some of the earliest maps to have been ever sketched to show the territory and originality of the name of Salmas and are some of the strongest documents providing proofs to some basic facts about the city including its existence and identity.
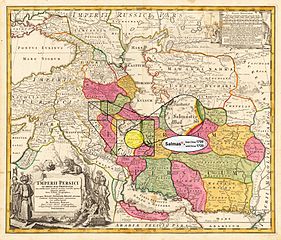
Salmas in 1724[16] Homann Map of "Persian Empire" at the Time of Safavid Dynasty • Modified by Hassan Jahangiri
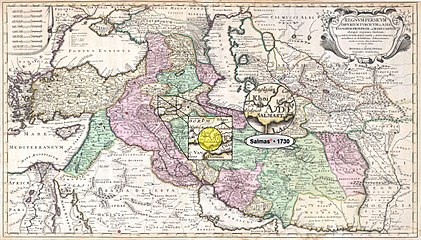
Salmas in 1730 Reiner and Joshua Ottens Map of the "Persian Empire" at the Time of Safavid Dynasty • Modified by Hassan Jahangiri

Salmas in 1747 Bowen Map of the "Persian Empire" at the Time of Afsharid Dynasty • Modified by Hassan Jahangiri

Salmas in 1814 Thomson Map of the "Persian Empire" at the Time of Qajar Dynasty • Modified by Hassan Jahangiri

Salmas in 1818 Pinkerton Map of "Turkey in Asia, Iraq, Syria, and Palestine" (Concurred with the Time of Qajar Dynasty) • Modified by Hassan Jahangiri
Climate[]
Under the Köppen climate classification, using the 0 °C (32 °F) isotherm, Salmas features a continental climate (Dsa), and is thus the one of the few cities in the Middle East and one of the 6 in the country with this categorization.
| Climate data for Salmas (Weather Station Located in Khoy Airport) [1987-2017] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 49 (9) |
61 (16) |
73 (23) |
90 (32) |
92 (33) |
99 (37) |
106 (41) |
109 (43) |
102 (39) |
93 (34) |
74 (23) |
67 (19) |
109 (43) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 30.6 (−0.8) |
34.0 (1.1) |
45.3 (7.4) |
58.1 (14.5) |
68.4 (20.2) |
78.4 (25.8) |
86.9 (30.5) |
86.4 (30.2) |
79.0 (26.1) |
64.8 (18.2) |
50.9 (10.5) |
37.0 (2.8) |
60.0 (15.5) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 21.6 (−5.8) |
24.6 (−4.1) |
36.1 (2.3) |
48.0 (8.9) |
56.8 (13.8) |
65.1 (18.4) |
73.0 (22.8) |
72.1 (22.3) |
64.6 (18.1) |
52.7 (11.5) |
40.6 (4.8) |
28.4 (−2.0) |
48.6 (9.2) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 12.7 (−10.7) |
14.9 (−9.5) |
26.6 (−3.0) |
37.4 (3.0) |
44.8 (7.1) |
51.1 (10.6) |
58.6 (14.8) |
57.6 (14.2) |
49.1 (9.5) |
40.3 (4.6) |
30.4 (−0.9) |
20.1 (−6.6) |
37.0 (2.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −18 (−28) |
−21 (−29) |
−17 (−27) |
−8 (−22) |
13 (−11) |
40 (4) |
52 (11) |
47 (8) |
37 (3) |
20 (−7) |
−7 (−22) |
−17 (−27) |
−21 (−29) |
| Average rainfall inches (mm) | 1.22 (31) |
1.45 (37) |
2.07 (53) |
3.54 (90) |
6.47 (164) |
4.84 (123) |
2.44 (62) |
1.71 (43) |
2.13 (54) |
2.2 (56) |
1.54 (39) |
1.22 (31) |
30.83 (783) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 3.45 (8.8) |
2.35 (6.0) |
2.32 (5.9) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1.96 (5.0) |
10.08 (25.7) |
| Average rainy days | 7.9 | 9.1 | 11.8 | 12 | 13.1 | 8.4 | 3.9 | 3.3 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 94.5 |
| Average snowy days | 2.75 | 2.25 | 1.75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.25 | 9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 75.0 | 64.3 | 55.8 | 48.6 | 43.3 | 38.4 | 37.0 | 36.0 | 39.8 | 47.0 | 52.9 | 66.4 | 50.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 147.6 | 202.8 | 239.8 | 311.2 | 352.6 | 343.4 | 356.3 | 355.6 | 276.9 | 202.6 | 150.8 | 153.2 | 3,092.8 |
| Source: "Weather Trends 360".[17] Weatherbase[18] "World Weather Online".[19] | |||||||||||||
| Year | Population | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1930 | ~8000 | — |
| 1934 | ~7000 | — |
| 1956 | 13,161 | — |
| 1966 | 21,703 | +64.9% |
| 1976 | 27,638 | +27.3% |
| 1986 | 50,573 | +83.0% |
| 1996 | 65,416 | +29.3% |
| 2006 | 89,617 | +37.0% |
| 2011 | 97,060 | +8.3% |
| 2016 | 101,441 | +4.5% |
| 2021 | N/A | — |
| Note: The data presented of 1976 and earlier (1956–1976) are from the censuses before Iranian Revolution and the data of 1986 and later (1986–2016) are from the censuses after it. The data for the years 1920 and 1924 are not of any censuses. Sources: "Population and Housing Census". Statistical Center of Iran. (used for censuses of 2006 and later), "An Analysis to the Urban System of West Azerbaijan Province During the Years 1956 till 2006". Urban Ecology Researches. (used for censuses of 1996 and earlier; the amounts are obtained from the data given in "Real Population" columns!), "Location and Geography of the City". Salmas County Municipality.[permanent dead link] (used for data of the years 1920 and 1924) | ||
Notable people[]
- (b. 1966) – Sculptor
- Stepanos V of Salmast (d. 1567) – Catholicos of the Armenian Apostolic Church
- Yohannan Gabriel (1758–1833) – Chaldean Catholic bishop of Salmas
- Nicholas I Zaya (d. 1855) – Patriarch of Babylon of the Chaldeans
- Raffi (1835–1888) – Armenian novelist
- Paul Bedjan (1838–1920) – Chaldean Catholic priest and orientalist
- Abraham Guloyan (1893–1983) – politician
- Murad Kostanyan (1902–1989) – actor
- Ardeshir Ovanessian (c. 1905–1990) – Communist leader
- Timur Lakestani (1915–2011) – aka Father of Iranian Electrical Industry
- Jafar Salmasi (1918–2000) – weightlifter
- Emmanuel Agassi (1930–2021) – boxer and father of Andre Agassi
- Hadi Asghari (b. 1981) – football player
Gallery[]

Overall View of Imam St. and Shahrdari Sq.

Islamic Republic Blvd., Near Panahi Technical School
Khan Takhti-Rd near Salmas

The Haftvan Church

Chaldean Catholic Church in Salmas


Salmas

An angled front view of Salmas Imam Khomeini Prayer House, 2017

A view of Nation Park in a Winter night, 2016
See also[]
- 1930 Salmas earthquake
- Nor Shirakan
- Battle of Dilman
- Assyrian homeland
- Khoy Khanate
References[]
- ^ "Statistical Center of Iran > Home".
- ^ "List of all entries". Assyrian Languages. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ a b Bosworth, C. E. (2012). "Salmās". Encyclopedia of Islam. doi:10.1163/1573-3912_islam_SIM_6560.
- ^ "2016 Population and Housing Census". Statistical Center of Iran. Retrieved 20 May 2017.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 26 December 2014. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ http://thegraduatesocietyla.org/images/author-padia-others.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ "Ancient Iran - the Sāsānian period".
- ^ https://www.britannica.com/media/full/851961/2031[dead link]
- ^ Potts, D.T. Nomadism in Iran: From Antiquity to the Modern Era. New York: Oxford University Press, 2014.
- ^ Houtsma, M. Th. et al. (1993 reprint) "Salmas" E. J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913–1936 Volume 4, E.J. Brill, New York, page 118, ISBN 90-04-09796-1
- ^ Houtsma, M. Th. et al. (1993 reprint) "Tabrīz" E. J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913–1936 Volume 4, E.J. Brill, New York, page 588, ISBN 90-04-09796-1
- ^ Houtsma, M. Th. et al. (1993 reprint) "Shakāk" E. J. Brill's First Encyclopaedia of Islam, 1913–1936 Volume 4, E.J. Brill, New York, page 290, ISBN 90-04-09796-1
- ^ O'Shea, Maria T. (2004) "Trapped Between the Map and Reality: Geography and Perceptions of Kurdistan Routledge, New York, page 100, ISBN 0-415-94766-9
- ^ Nisan, Mordechai (2002) Minorities in the Middle East: A History of Struggle and Self-Expression (2nd edition) McFarland, Jefferson, North Carolina, page 187, ISBN 0-7864-1375-1
- ^ a b Atabaki 2006, p. 70.
- ^ "Imperii Persici in omnes suas provincias nova tabula geographica". Library of Congress.
- ^ "Weather Trends 360". Weather Trends International, Inc. Retrieved 26 February 2017.
- ^ "Salmas, Iran". Weatherbase. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ "World Weather Online". Data provided by WorldWeatherOnline.com. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
Sources[]
- Atabaki, Touraj (2006). Iran and the First World War: Battleground of the Great Powers. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1860649646.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Salmas. |
- Populated places in Salmas County
- Cities in West Azerbaijan Province
- Mass murder in 1915
- Kurdish settlements in West Azerbaijan Province